According to Art. 487 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, an advance payment is a full or partial payment for goods/services before the actual shipment by the seller. Prepayment is accounted for in special accounting subaccounts and is not the income of the supplier using the accrual method until the organization fulfills its obligations. Let's consider the nuances of reflecting an advance payment as a business transaction, and provide the main entries for advances issued and received.
Note! The legal status of the advance payment is fixed in the terms of the contract, the regulatory regulation of counter-fulfillment of obligations is carried out in accordance with Art. 328 Civil Code.
Advances received – postings
Accounting for advances received from buyers as payment for goods before their shipment is kept on the account. 62.2 “Advances received.” Prepayments for products are also reflected here if the seller, for various reasons, violates the sales deadlines. Regular settlements are carried out in subaccount 62.1.
Example
Let’s assume that the supplier company “Spectrum” and the buyer “Titul” entered into an agreement for the shipment of electrical equipment for a total amount of 708,000 rubles, including VAT 18% - 108,000 rubles. According to the terms of the transaction, payment is made with 100% prepayment, which was received into the Spectrum account on December 5, and the shipment was completed on December 8. The Spectra accountant will reflect the transactions as follows:
- 5.12 – advance payment received from the buyer, posting D 51 K 62.2 for 708,000.
- 5.12 – VAT charged D 76.AV K 68.2 on 108,000.
- 8.12 – equipment D 62.1 K 90.1 was delivered for 708,000.
- 8.12 – VAT allocated D 90.3 K 68.2 for 108,000.
- 8.12 - advance payment credited, posting D 62.2 K 62.1 for 708,000.
- 8.12 – VAT restored D 68.2 K 76.AB for 108,000.
Conclusion - when receiving advances, transactions regarding the calculation of VAT for payment are carried out 2 times: at the time the money is received in the current account and directly upon sale. Then, after shipment, the advance payment is counted and the amount of VAT from it is restored through reverse posting.
Advance VAT posting
An advance payment is an advance payment to the supplier against future deliveries, work performed or services performed.
Transferring an advance payment to a supplier does not mean receiving economic benefits, since the supplier may, for various reasons, fail to fulfill its obligations under the contract: fail to ship goods, fail to provide a service.
In this case, the advance payment is returned to the buyer’s account if it was transferred through a bank, or to the cashier if received in cash.
In general, there is no obligation to return the deposit from the supplier.
To account for VAT on advances in the chart of accounts, there is a subaccount on account 76, most often its code is 76.AB.
The buyer can accept VAT as a deduction only if the following conditions are met:
- Presence of an advance payment clause in the contract;
- Documents confirming the transfer of prepayment;
- The supply of goods (services, etc.) is intended for use in activities subject to VAT;
- Availability of a supplier's SF with a dedicated tax.
The buyer does not have the right to accept VAT as a deduction if all of the above conditions are not met. Acceptance of VAT deduction is not an obligation, but a right of the purchasing organization.
If an organization decides to use VAT deduction from an advance issued, then after the provision of the service and the closing of this advance, it will be obliged to restore this VAT to the budget.
Advances issued - postings
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 60.2 | 51 | Transfer of advance payment | 23 600 | Payment order ref. |
| 19 | 60.2 | VAT on advance | 3 600 | Advance invoice (received) |
| 68 | 76(advances) | VAT deduction from advance payment | 3 600 | Book of purchases |
| 10 | 60.1 | The received goods are registered | 20 000 | Invoice |
| 19 | 60.1 | Incoming VAT reflected | 3 600 | SF supplier |
| 60.1 | 60.2 | Advance offset | 23 600 | Accounting information |
| 60.2 | 68 | Recovered VAT from advance payment | 3 600 | Sales book |
Advances received
When an organization sells goods, works or services, the buyer can make an advance payment before the moment of sale.
According to the requirements of the Tax Code, the seller is obliged to charge VAT on the advance received. VAT is calculated using the formula:
VAT on the advance received = Sales amount *18/100
Let's consider the previous example from the point of view of the selling organization, that is. VAT is charged on the advance payment at the time of its receipt; the amount of such VAT is reimbursed to the budget at the end of the tax period - quarter.
VAT on sales is accrued at the time of shipment, that is, at the time the sales transaction is created Dt 62 - Kt 90.1.
Advances received - postings
When receiving an advance from a buyer, the accountant makes the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 51 | 62.2 | Advance received from buyer (including VAT) | 23 600 | Payment order in. |
| 76(advances) | 68 | VAT accrual on advance payment | 3 600 | Invoice issued, accounting certificate |
| 62.1 | 90.1 | Sales revenue accrued | 23 600 | Sales certificate, invoice |
| 90(VAT) | 68 | VAT on sales | 3 600 | SF issued, accounting certificate |
| 68 | 76(advances) | Accepted for deduction of VAT on advances (after sale) | 3 600 | Book of purchases |
VAT on advances issued
An organization that has paid an advance to a supplier has the right to claim for deduction the VAT paid. Necessary conditions for obtaining a VAT deduction from an advance payment:
- the condition for advance payment must be clearly stated in the contract with the supplier;
- the advance payment must be presented to the SF (no later than 5 days after payment).
VAT deduction is provided in the tax period when the advance was transferred. When the final payment for the delivery occurs, that is, the goods are received from the supplier under the acceptance certificate, the organization is obliged to restore the amount of VAT previously claimed for deduction.
In addition to the receipt of goods, the obligation to restore the deduction arises for the organization in the following cases:
- changes in the terms of the contract;
- termination of the contract and return of the advance.
VAT is restored in the same amount in which it was previously accepted for offset. If the terms of the contract determine that the delivery of goods occurs after receiving 100% advance payment, the buyer can transfer the advance in installments. In this case, the amount of VAT reflected in the SF for the supply is restored. In any case, this value coincides with the amount of VAT on all advance tax payments for this supply.
VAT on advances received
When selling products (goods, services) to the buyer, a mandatory condition may be specified in the contract - advance payment in the amount of up to 100%.
On the received advance, the organization issues a tax return and charges VAT at a rate of 18/118%. The amount of this advance is included in the sales book as accrued VAT, that is, a tax that the organization is obliged to pay to the budget.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h5OOL0dUlDk
In practice, after issuing a SF for the advance received, 3 situations are possible:
- during the advance period the sale occurred;
- no sales occurred during the advance period;
- refund of the advance payment to the buyer (termination of contract, change of conditions, etc.).
In the first case, after the shipment has been made, the selling organization has the right to present previously paid VAT on the advance received for deduction. That is, the advance SF is closed with a purchase ledger entry.
In the second case, the amount of the advance and the VAT accrued on it is reflected in the VAT return for the current period in line 070 of Section 3.
In the case of an advance refund, it is also possible to claim the VAT paid for deduction, that is, an entry is created in the purchase book. You can take advantage of the deduction within a year after termination of the contract.
In the event of liquidation of the purchasing organization before full fulfillment of the delivery conditions, if it is impossible to return the advance payment, VAT accrued upon receipt of the advance payment is not subject to deduction.
Example of an operation for advances received
Harmony LLC, under an agreement with the buyer Amalgama LLC, must supply a consignment of goods in the amount of 212,400 rubles, incl. VAT — 32,400 rub. 07/10/2017 "Amalgam" transfers an advance payment of 50% of the contract amount: 106,200 rubles. VAT on advance: 106,200 * 18/118 = 16,200 rub.
We reflect in the postings VAT on advances received from the buyer:
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 51 | 62.2 | Reflection of the advance received | 106 200 | Bank statement |
| 76.AB | 68 (VAT) | VAT charged on advance | 16 200 | SF issued |
In August, Harmony ships a consignment of goods to Amalgam. Sales transactions and deduction of VAT from advances received:
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 62.1 | 90.1 | Sales of goods reflected | 212 400 | Act |
| 90.3 | 68 | VAT charged on sales | 32 400 | SF |
| 62.2 | 62.1 | The offset of the buyer's advance is reflected | 106 200 | Accounting information |
| 68 | 76.AB | VAT on advance payment is deductible | 16 200 | Book of purchases |
Transactions on advances issued
Let's consider the same operation from the buyer's side. The accountant of Amalgama LLC will reflect VAT on advances issued by postings:
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description | Amount, rub | Document |
| 60.2 | 51 | Advance paid to supplier | 106 200 | Payment order ref. |
| 68(VAT) | 76.VA | VAT on advance payment is deductible | 16 200 | Invoice, purchase book |
| 41 | 60.1 | Goods receipt reflected 0) | 180 000 | Invoice |
| 19 | 60.1 | Incoming VAT reflected | 32 400 | SF |
| 60.1 | 60.2 | The offset of the advance is reflected | 106 200 | Accounting information |
| 76.VA | 68(VAT) | Recovered VAT from advance payment | 16 200 | Sales book |
After receiving the goods, VAT is deducted from the delivery:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 68 | 19 | VAT deduction upon receipt of goods | 32 400 | Book of purchases |
Sales book sheet form with explanations:
>Instructions: what transactions to reflect advance payments
Postings for state employees
Advance reports (accounting entries) are also compiled depending on the direction of movement of these funds. BU are compiled in form 0504053 in accordance with the provisions of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 123n dated September 23, 2005.
Typical accounting entries for account 206 00 000:
Dt 206 00 000 Kt 201 01 610, 304 05 000 - advance payment to the supplier (posting), advance payments to financial authorities;
Dt 302 00 000 Kt 206 00 000 - receipt of goods and materials or consumption of services against the previously listed prepayment.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n7vq_Z5fbHs
The crediting of received proceeds for advance payment to buyers (customers) will be reflected in account 0 205 00 000 “Calculations for income”.
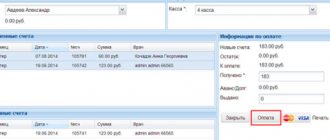
An advance payment has been received from the buyer, the wiring for the control unit will be as follows:
Dt 2,201 11,510 Kt 2,205 31,660 (account “Advances received”).
In commercial and non-profit organizations, to reflect mutual settlements on prepayments, account 61 “Settlements on advances issued” is used (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 94n dated October 31, 2000).
Analytical accounting is carried out on the basis of the turnover sheet and balance at the beginning and end of the reporting period. On the debit of the account.
61 reflects the listed advance, the loan reflects the return of previously issued amounts and the offset of money upon actual receipt of goods, work or services.
Typical accounting entries for accounts. 61:
Dt 61 Kt 50, 51 - an advance was issued to the supplier, posting (basis - cash settlement, payment, etc.);
Dt 60 Kt 61 - offset of a previously issued prepayment (basis - invoice, act, etc.).
- When is VAT paid to organizations that combine UTII and STSC? In the event that a company combines UTII and the general taxation regime, income,...
- Including VAT February 17, 2017 How to calculate VAT including March 27, 2021 The employee provided services unofficially:…
Source: https://prioritetspb.ru/2021/03/avans-nds-provodki/
Advances issued – postings
Advances transferred to the company's supplier counterparties are taken into account in the account. 60.2 “advances issued”, normal operations are carried out on subaccount 60.1. In situations where the amounts of prepayments turn out to be greater than the sales amounts, the difference remains with the supplier as payment for planned deliveries or is returned at the request of the buyer to the specified details.
Example
Let’s assume that Dorstroy LLC purchases materials for production from RPK LLC. On November 25, Dorstroy transferred an advance payment in the amount of 354,000 rubles, and the goods and materials were received at the warehouse in full on December 2. The Dorstroy accountant should reflect these transactions in the following order:
- 25.11. – advance payment is transferred to the supplier – posting D 60.2 K 51 for 354,000.
- 25.11 – VAT is accepted for reimbursement in the presence of an advance invoice from “RPK” D 68.2 K 76.AB for 54,000.
- 2.12 – materials received D 10.1 K 60.1 for 300,000.
- 2.12 – VAT allocated D 19.3 K 60.1 for 54,000.
- 2.12 – the advance was offset, posting D 60.1 K 60.2 for 354,000.
- 2.12 – previously refunded VAT D 76.AV K 68.2 was accrued for 54,000.
- 2.12 – VAT offset was completed upon completion of the transaction D 68.2 K 19.3 for 54,000.
When accounting for VAT on prepayments issued, you should keep in mind that the tax can be reimbursed without waiting for the goods to be shipped. The justificatory grounds are listed in Art. 172 clause 9. These are the following documents:
- Advance invoice submitted by the supplier.
- A document confirming payment of the advance payment.
- An agreement specifying the terms of the advance payment.
Attention! When an advance is issued to the supplier (the posting is given above), the invoice is issued for the amount of the advance payment, and upon shipment - for the sales amount. At the same time, it is legally possible to restore VAT even in the event of complete termination of a transaction for which an advance payment with VAT was previously transferred.
Advance payment transferred to supplier
Let's look at the features of reflecting in 1C the transfer of an advance to a supplier.
You will learn:
- how the actual debiting of funds from the organization’s bank account is reflected;
- what transactions are automatically generated by the program if an advance is transferred.
Step-by-step instruction
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
Transfer of advance payment to the supplier
The actual payment to the supplier, which was made according to the bank statement, is reflected in the program by the document Write-off from the current account transaction type Payment to the supplier .
The document states:
- from – date of payment to the supplier, according to the bank statement;
- The recipient —the supplier to whom the payment was made—is selected from the Counterparties directory;
- Agreement - a document according to which settlements with the supplier are carried out. Type of agreement - With the supplier .
In our example, settlements under the agreement are carried out in rubles, therefore, as a result of selecting such an agreement, the following subaccounts for settlements with the supplier are automatically established Write-off from the current account
- Settlement account – 60.01 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”;
- Advances account – 60.02 “Settlements for advances issued.”
- Amount – payment amount in rubles, according to the bank statement;
- VAT rate – the VAT rate corresponding to the future supply;
- VAT amount – the amount of VAT corresponding to the future supply. Calculated automatically from Amount and the selected VAT Rate ;
- DDS item is a cash flow item. In our example, fixed assets are acquired, therefore the DDS Article is indicated with the Type of movement - Acquisition, creation, modernization and reconstruction of non-current assets .
- In. Number and In. Date – number and date of the payment order. Filled in automatically with data from the Number field from the Payment order document . If the document Write-off from a current account is not filled out on the basis of a Payment order , then the number and date of the payment order must be entered manually.
- Bank account - the bank account of the organization from which the payment was made, selected from the Bank Accounts directory ;
- Debt repayment – Automatically . With this method, the program automatically determines the payment status: advance or repayment of debt for settlements with the specified Recipient in the context of the concluded Agreement .
If the accountant does not want the program to automatically determine the payment status, then you can choose other methods of debt repayment . Find out more about them .
Postings according to the document
Due to the fact that there was no debt to the supplier Avtopark LLC under supply agreement No. 418 dated March 12, 2021, the transferred amount will be classified by the program as an advance:
- Dt 60.02 Kt 51 – advance payment issued to the supplier.
Checking mutual settlements with the supplier
You can check settlements with the supplier in terms of contracts using the analysis of mutual settlements in the report Analysis of subcontos in the context of Counterparties and Contracts.
If the supplier has issued an advance invoice, the Organization may exercise the right to deduct VAT on advances issued to suppliers. See the continuation of the publication.
Accounting for settlements on advances issued
Institutions and organizations make payments for purchased products, work performed and services provided on the basis of concluded contracts. At the same time, in accordance with Art. Art. 487, 711 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, full or partial advance payment (advance payment) of goods to the supplier is allowed before transferring it to the buyer.
General provisions
Why are advances made? Payment of an advance payment can serve as the funds necessary for the seller to purchase products, works, and services. In addition, it ensures that the buyer is interested in the purchase.
In relation to budgetary institutions, advance payments are provided for in Art.
250 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation, according to which recipients of budget funds, within the established limits of budget obligations, have the right to accept monetary obligations to be fulfilled at the expense of the federal budget.
The acceptance of monetary obligations is carried out by concluding agreements (contracts) by the recipient of budget funds and the supplier of products (works, services) in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
When determining the amount of advance payments to pay for contracts for the purchase of products, performance of work, provision of services at the expense of the federal budget, budget funds of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipalities, one should be guided by clause 9 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 02.03.
2005 N 107 “On measures to implement the Federal Law “On the Federal Budget for 2005” (hereinafter referred to as Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation N 107), according to which the recipient of federal budget funds when concluding agreements (contracts) for the purchase of products (works, services) subject to payment from the federal budget, has the right to provide for advance payments:
- in the amount of 100% of the amount of the agreement (contract) - under agreements (contracts) on the provision of communication services, on subscription to printed publications and on their purchase, on training in advanced training courses, on the purchase of air and railway tickets, tickets for city and suburban transport, as well as vouchers for sanatorium and resort treatment;
- for other agreements (contracts) - in the amount of 30% of the contract amount, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Please note: the federal budget for 2006 was approved by Law of the Russian Federation N 189-FZ, however, the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation on measures to implement this Law, which determines the amount of advance payments for 2006, has not been published.
In this regard, before the relevant resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation is issued, we recommend that when concluding contracts for the purchase of products (works, services), advance payments are provided in the amounts established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 107. Federal Law of December 26.
2005 N 189-FZ “On the federal budget for 2006”.
The contract should indicate the conditions for advance payment for the purchase of goods, works, and services.
For example , when a budgetary institution purchases inventory from a commercial company, the contract must reflect that an advance payment in the amount of 30% of the contract price must be transferred to the company within a certain period of time (10 days from the date of conclusion of the contract).
Reflection of advances issued in accounting
To account for settlements on advances issued in budgetary institutions, Instruction No. 70n provides for account 0 206 00 000 “Settlements on advances issued”. Please note that this account only takes into account advances transferred to institutions for purchased goods (work, services). Issuance of advances to accountable persons is recorded in account 0 208 00 000 “Settlements with accountable persons”.
Instructions for budget accounting, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 26, 2005 N 70n.
Source: https://obd2bluetooth.ru/perechislen-avans-postavshhiku-provodka/
Advance reports - accounting entries
In addition to settlements with counterparties - buyers and suppliers, the company regularly issues funds to its employees. How to correctly make accounting entries for expense reports? And is it true that the amount from the advance report is deducted from profit? Let's look at a specific example.
Example of settlements with accountable persons regarding advances issued:
The Pit Stop enterprise reported to employee E.I. Kovalev. for a business trip 8,000 rubles. Kovalev spent 5,400 rubles, and unused funds amounted to 2,600 rubles. returned to the cashier. The accountant will need to do the following:
- An advance was issued for travel expenses - posting D 71 K 50 for 8000.
- The balance of unspent money was returned - posting D 50 K 71 for 2600.
The accountable person is obliged to report on the expenditure of funds within 3 days after the end of the issuance period, and in the case of being on a business trip - after the employee returns. Specific deadlines are set by the head of the organization. If an employee, without good reason, has spent more than the allocated funds and is unable to account for them, the excess is withheld from his income. Buh. The entries for expense reports in this situation look like this:
- The amount not returned on time is reflected - D 94 K 71.
- The shortfall from the employee’s earnings is withheld - D 70 K 94, but not more than 20% monthly.
Advance transferred from current account posting
In accounting, an advance is considered to be full or partial prepayment of a concluded transaction. How advances are reflected in accounting, what entries are generated when receiving an advance from a buyer, as well as entries for advances issued, we will consider further.
An advance is often confused with a deposit. Both the advance and the deposit have one function - advance payment for a product or service, partial or full. There is no clear definition in the legislation to separate these concepts, but according to established practice, an advance payment is considered to be the amount of prepayment for the transfer of which a separate agreement to the contract has not been drawn up:
An advance was transferred from the current account to the supplier transaction
- 1 Postings for an advance received from a buyer 1.1 Example of a reflection of an advance received for goods (services, work)
- 2.1 Reflection of the prepayment transferred to the seller for raw materials and materials
2 How to reflect an advance to an employee for business needs
Each enterprise keeps records of settlements with suppliers and contractors. Payments to suppliers include not only the supply of goods, but also the provision of various types of services and work.
The peculiarities of interaction between an organization and a supplier are discussed in this article. Tables with postings are provided. -lesson. “Accounting for account 60: subaccounts, postings” The video lesson explains in detail how to conduct accounting for account 60 “Settlements with suppliers”, subaccounts are considered, examples of drawing up basic postings and operations.
⇓ Download the presentation for the video “Accounting for account 60: subaccounts, postings, examples” in .pdf format Accounting for settlements with suppliers.
Posting the transfer of debt to suppliers
In its structure, account No. 60 is active-passive : its debit records the amounts of obligations fulfilled to suppliers (taking into account advances and prepayments), its credit records the cost of completed work (services rendered) accepted for accounting in correspondence with the corresponding accounts for their accounting.
Any mutual settlements with counterparty enterprises take place in the enterprise’s accounting department under account No. 60, which has a similar name: “Settlements with suppliers and contractors.”
Information on it for each counterparty is shown separately. According to the purposes of management accounting, various sub-accounts can be opened for it.
In this article we will examine in detail the accounting features of transferring debt to suppliers.
Settlements with suppliers (account 60)
The debit of account 60 corresponds with the credit of cash accounting accounts (accounts 50, 51, 52,55), the credit of account 60 corresponds with the debit of accounts for goods, materials, fixed assets, intangible assets and other asset accounts (account 41 , 10, 08, 43, 44, 20, 23, etc.).
Suppliers are organizations that supply inventory and other assets, as well as provide various types of services and perform certain work. To account for settlements with suppliers, accounting account 60 is used.
September 24, 2016Reconciled entries for salary advances and vacation pay
– Is it possible to withhold personal income tax from an advance, as they say, on your own initiative?
– I don’t recommend doing this. According to the Federal Tax Service of Russia, personal income tax cannot be transferred to the budget before the employer has withheld it from the employee’s income.
For the simple reason that personal income tax in this case is not a tax. After all, the last day of the month has not yet arrived (letter dated September 29, 2014 No. BS-4-11/19716). It is also impossible to transfer taxes to the budget late.
Thus, the salary tax must be transferred, firstly, along with the final payment for the month. And secondly, strictly in the amount in which you withheld it from the income of employees.
So it turns out that if you transfer your salary to cards, you must pay personal income tax on the same day. This is the only way you will avoid trouble (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 12, 2013 No. 03-02-07/1/12347).
Interesting: Filling out a registration card for issuing personal protective equipment
There are no clear rules on how exactly to determine the amount of the reserve in PBU 8/2010. Paragraph 15 only says that such an amount should be enough to pay off creditors immediately and in full.
Simply put, the amount of the reserve for vacation pay in accounting at the end of each month or quarter should cover the amount of debt that would arise if all employees went on vacation at once.
Moreover, here it is necessary to take into account not only net payments to employees, but also personal income tax with insurance contributions.
Calculation of VAT on advances received from the buyer
In January 2021, Snezhinka LLC entered into an agreement with the buyer Ldinka LLC for the supply of refrigerators. The amount under the contract is 118,000 rubles. (including VAT 18,000 rubles). On January 15, 2021, Snezhinka LLC received an advance payment in the amount of 59,000 rubles from the buyer. (transfer of advance payment is provided for in the supply agreement).
So, we have analyzed the general procedure, now let’s see what VAT entries are made from the advance received, and what happens in the future with this VAT. The organization not only maintains tax accounting, but also accounting. And the accounts in the situation we are analyzing are very specific, many accountants get confused about them.
Transferred from the current account prepayment to the supplier debit credit
Let's consider which transactions reflect the accounting of settlements with suppliers in both of these cases. Payment upon receipt of goods and materials In this case, we first receive assets, work, services from the supplier, and debit them to the corresponding account. After this, we pay for the delivery, repaying the debt.
The wiring looks like this: Postings to account 60: Debit Credit Name of transaction 08, 10, 15, 20, 23, 25, 26, 41, 43, 44 60 The organization’s debt for acquired assets, work performed, services provided is reflected 19 60 VAT is allocated from the amount 68.
VAT 19 VAT is deductible 60 50, 51, 52, 55 Payment has been made for assets supplied, work performed, services provided Accounting for settlements on advances issued The organization first transfers a certain amount of money - an advance, after which the supplier makes a delivery against this advance.
Accounting in this case will become a little more complicated.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=043gmLHUn1A
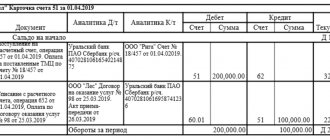
After receiving the delivery for which the advance was issued, it is offset by the following entry: D60 K60 (subaccount “Advance issued”). Let's give an example: organization “One” transferred an advance payment to its supplier organization “Two” in the amount of 100,000 rubles. A week later, goods from organization “Two” arrived at organization “One” for the full cost of the advance payment.
At the time of transferring the advance, “Odin” makes the following entry: D 60/2 K 50 (51.52) 100,000 rubles (based on a payment order or bank statement). A week later, we receive the goods received: D 10 (41) K 60/1 84,446 rubles (based on the delivery note, invoice).
We immediately note the VAT: D 19 K 60/1 15,254 rubles (100,000 * 18: 118) (based on the invoice).
- Free video tutorial on 1C Accounting 8.3 and 8.2;
- Tutorial on the new version of 1C ZUP 3.0;
- Good course on 1C Trade Management 11.
- Presence of an advance payment clause in the contract;
- Documents confirming the transfer of prepayment;
- The supply of goods (services, etc.) is intended for use in activities subject to VAT;
- Availability of a supplier's SF with a dedicated tax.
This means that accounts receivable for advances issued and accounts payable for settlements with suppliers should be shown separately in the balance sheet: in assets and liabilities, respectively. To achieve these goals, a subaccount “Advances issued” is usually opened to account 60.
Therefore, for advances issued, the posting will look like this: Debit account 60, subaccount “Advances issued” - Credit accounts 50, 51, 52, etc. And if an advance was received from the buyer, the posting will be similar to the entry for the buyer repaying his debt.
However, similar to account 60, to differentiate between the debit and credit balances of account 62, subaccounts are added to it. So, for advances received, the posting will be as follows: Debit of accounts 50, 51, 52, etc.
– Account credit 62, subaccount “Advances received” It is clear that the accounting entry “Debit 51 - Credit 62” means that the seller received funds from the buyer to the current account.