Account 44 in accounting: postings, subaccounts and examples for dummies
Account 44 in accounting is the active “Sales Expenses” account, designed to reflect data on expenses incurred by the organization when selling goods, products or services. Using standard postings and examples for dummies, we will study the specifics of using account 44 and the features of reflecting transactions for accounting for sales expenses.
Account 44 in accounting
This is an active account, that is, the receipt of expenses is reflected in the Dt of the account, the disposal - in the Kt. An account can be simultaneously classified as an expense account if the expenses on the account are direct, and collective and distribution expenses if they are indirect.
What is included in selling costs?
In trade organizations, account 44 reflects the following expenses:
- for the transportation of goods;
- for payment;
- for renting premises;
- for the maintenance of retail equipment and retail premises;
- for advertising;
- for entertainment expenses, etc.
The Selling Expenses account can also be used by non-trading organizations. In this case, the following expenses are reflected on the account:
- for loading and delivery of products;
- by contents in warehouses;
- on packaging and packaging;
- for advertising;
- on commissions (fees), etc.
In the Chart of Accounts approved by the Ministry of Finance, account 44 refers to section 4 “Finished products and goods”. The synthetic account of sales expenses includes two subaccounts: 44.1 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities” and 44.2 “Business expenses in organizations engaged in production and other industrial activities.”
The organization uses one of these subaccounts: 44.01 - in trading, 44.02 - in production. If it is necessary to clarify the analytics, subaccounts are created for them.
Scheme of movements on count 44:
Typical postings for account 44
As can be seen from the previous diagram, account 44 corresponds on the credit side with material, cost and settlement accounts with counterparties and “accountables”, and on the debit side - with the expense account.
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
The main transactions are shown in the table:
In organizations engaged exclusively in trading activities, all management costs can be classified as selling expenses. The general expenses account will be used only if another type of activity arises.
Closing 44 accounts
At the end of the period, account 44 is closed to account 90, sales expenses subaccount:
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| 90.7 | 44 | Closing an account |
The account is closed monthly. In conditions of incomplete sales (for trade organizations), account closure may be partial. Then transportation costs for write-off are distributed in proportion to the volume of goods sold. The amount corresponding to the balance of unsold products is not closed, but transferred to the next period.
For manufacturing enterprises, the distribution of packaging and transportation costs is made by type of product shipped.
The methodology for accounting and writing off costs is chosen by the organization independently and is prescribed in the accounting policy.
Accounting for goods and materials on account 44
The occurrence of transport and procurement costs for the buyer is due to the fact that upon delivery the counterparty allocates transport costs separately. The purchasing organization, depending on the accounting methodology used, can include the amounts of TRP in the cost of the goods, or allocate them.
Expenses for the delivery of goods by third-party organizations are allocated to account 44, if the accounting policy does not provide for their inclusion in the cost of goods, that is, capitalization to account 41 “Goods”.
Example of using account 44 “Sales expenses”
Antik LLC, engaged in trading, reflected the following transactions for October 2021:
- wages - 209,000 rubles;
- insurance premiums - 62,700 rubles;
- expenses for stationery - 11,000 rubles;
- depreciation of fixed assets - 19,000 rubles;
- services of third-party organizations - 38,000 rubles;
- costs for transporting products - 42,000 rubles;
- sales revenue - RUB 849,600, incl. VAT RUB 129,600;
- cost of goods sold - 415,000 rubles;
- balance of goods in the warehouse - 113,000 rubles.
These transactions will be reflected by postings:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 44 | 70 | Reflection of labor costs | 209 000 | Accounting information |
| 44 | 69 | Insurance premiums reflected | 62 700 | Accounting information |
| 44 | 10 | Reflection of expenses for stationery | 11 000 | Accounting certificate, invoice |
| 44 | 02 | Depreciation calculation | 19 000 | Accounting information |
| 44 | 60 (76) | Cost of third party delivery services | 38 000 | Invoice, act |
| 62 | 90.1 | Reflection of revenue | 849 600 | SF, acts, invoices |
| 90.2 | 41 | Reflection of cost write-off | 415 000 | Invoices |
| 90.3 | 68 | Reflection of accrued VAT | 129 600 | Sales book |
| 44 | 60(76) | Transportation costs reflected | 42 000 | Invoice, act |
Let's do the calculations:
- The balance of goods in the warehouse amounted to 113,000 rubles.
- The total amount of goods sold and unsold was 113,000 + 415,000 = 528,000 rubles.
- Let's calculate the share of goods sold: 415,000 / 528,000 * 100 = 78%.
- Amount of expenses on invoice 44 for October: 209,000 + 62,700 + 11,000 + 19,000 + 38,000 = 339,700 rubles.
- Therefore, the amount of write-off of transportation costs to account 90 will be: 42,000 * 78% = 32,760 rubles.
The closure of account 44 will be reflected using the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 90.7 | 44 | Sales expenses written off | 339 700 | Accounting information |
| 90.7 | 44 | Transportation costs are written off in proportion to sales | 32 760 | Accounting information |
Amount 9,240 rub. (42,000 - 32,760) will remain not written off and will be transferred to the next period.
Source: https://BuhSpravka46.ru/buhgalterskiy-plan-schetov/schet-44-v-buhgalterskom-uchete-provodki-subscheta-i-primeryi-dlya-chaynikov.html
What is 60 count?
Suppliers are organizations that deliver material values, assets, and provide services. Account 60 is used to account for settlements with them. This is an active-passive account, i.e. the movement of funds is carried out by debit and credit. It displays cost data:
- inventory items, work performed, services provided, including provided electricity, gas, water, etc.;
- identified surplus inventory items;
- transportation, communication services received, etc.;
- advances issued for shipment of goods and materials or work performed.
Account 60 “Settlements with suppliers” displays the movement of funds between the company and all counterparties, regardless of the basis on which the payment was made.
Account 44 in accounting
Organizing sales of finished products, services or goods requires certain investments from the company. In this article we will look at what expenses can be included in sales costs and how to correctly reflect them in accounting.
ConsultantPlus FREE for 3 days
Get access
The costs of selling goods, works and services are individual depending on the main type of activity. Let's look at typical types of expenses for some areas:
| Kind of activity | What applies |
| Industry and manufacturing |
|
| Trade |
|
| Agriculture |
|
Please note that the above list of sales costs, which is taken into account in account 44, is not exhaustive. The composition of these expenses is determined individually for each company; such a list should be fixed in the company’s accounting policies.
In other words, accounting account 44 for dummies should include company costs that are aimed at selling goods, services or work, as well as increasing sales volumes.
Accounting Features
Accounting account 44 is active, therefore, the debit reflects the increase in costs, and the credit reflects their write-off. In accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n, the working plan of accounting accounts provides for special sub-accounts for account 44:
- account 44-01 is used to reflect transactions in companies whose main activity is trade;
- 44-02 is applicable in industrial and manufacturing enterprises.
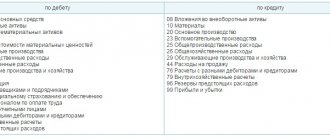
Typical wiring:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Expenses included in sales costs | 44 | |
| Depreciation | 02 | |
| Wage | 70 | |
| Insurance premiums | 69 | |
| Purchase of inventories | 10 | |
| Finished products for presentation | 41 | |
| Settlements through accountable persons | 71 | |
| General expenses | 26 |
Wiring Dt 44 and Kt 44 (nuances)
Dt 44 Kt 44 reflect the costs of the organization, the accounting of which has a number of features. We will consider the nuances of using accounting 44, as well as typical transactions with it, in our material.
What is count 44 used for?
Features of writing off account 44
What typical wiring includes Dt 44 and Kt 44
Results
What is count 44 used for?
Dt 44 Kt 44 “Sales expenses” collects all kinds of expenses incurred by the company in connection with the sale of products. The main costs attributed by organizations to this account are:
- packaging costs;
- delivery costs;
- advertising expenses;
- entertainment expenses;
- other costs associated with the sale of products in accordance with the instructions to the Chart of Accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On approval of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities...” dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n (hereinafter referred to as the Instructions).
Please note that the list of expenses may vary depending on the type of activity of the organization:
- for trade organizations, this account includes, in addition to the above, expenses for rent, labor, storage of goods and others in accordance with the Instructions;
- for agricultural organizations, such expenses include the maintenance of animals and maintenance of premises in which the procurement and acceptance of agricultural products is carried out.
Features of writing off account 44
Expenses reflected in account 44 can relate to both fixed and variable costs and are written off to account 90 “Sales”.
For information on accounting for direct and variable costs, see the article “How to calculate variable costs (examples, formula).”
Write-offs can be made in two ways:
In this case, phased write-off is carried out:
- by production organizations in the form of a monthly distribution of transport services and packaging costs between specific types of shipped products, taking into account their physical characteristics or other indicators;
- for trade organizations and intermediaries - distribution of transport costs taking into account products sold and their balance at the end of the month;
- for agricultural producers - distribution according to accounts 15 (“Procurement and acquisition of material assets”) and 11 (“Animals for growing and fattening”) of expenses for the procurement of agricultural raw materials.
Other expenses (not mentioned above) recorded on account 44 are written off monthly.
What typical wiring includes Dt 44 and Kt 44
Dt 44 Kt 44 is most often contained in the following postings:
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – debt to the supplier for services rendered;
- Dt 44 Kt 10 – the cost of materials is taken into account in expenses;
- Dt 44 Kt 02 – depreciation;
- Dt 44 Kt 70 – wage costs;
- Dt 44 Kt 69 – expenses for contributions to extra-budgetary funds;
- Dt 44 Kt 71 – expenses for accountable persons;
- Dt 44 Kt 94 – expenses for shortages.
Kt 44 is used when writing off to account 90.
Let's look at a few examples using Dt 44 Kt 44 .
Example 1
An organization engaged in trading activities recorded in March:
- salaries for consultants and sales floor cashiers in the amount of 500,000 rubles;
- expenses for renting a sales area in the amount of 150,000 rubles;
- accrued depreciation on equipment in the hall - 200,000 rubles;
- advertising expenses – 450,000 rubles. (non-standardized for the purpose of calculating income tax).
For information on advertising expenses in tax accounting, see the publication “Art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2015): questions and answers.”
In the accounting for March, these transactions were reflected by the following entries:
- Dt 44 Kt 70 – salary 500,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – rental services RUB 150,000;
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – advertising expenses 450,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 02 – depreciation 200,000 rub.
On March 31, the posting was made: Dt 90.2 Kt 44 – RUB 1,300,000. (writing off account 44).
Example 2
The trading organization reflected in its accounting for April on account 44 transportation expenses in the amount of 300,000 rubles. wiring Dt 44 Kt 60.
The balance on the account as of March 31 is 44 - 75,000 rubles.
The cost of goods sold for March is RUB 1,780,000.
The cost of the remaining goods as of March 31 is 360,000 rubles.
It is necessary to distribute transport costs.
To do this, we determine the average percentage of transport costs attributable to the balance of the goods:
(300 000 + 75 000) : (1 780 000 + 360 000) × 100% = 17,52%
The amount of transportation costs for the remaining goods is 360,000 × 17.52% = 63,072 rubles.
The amount of transportation expenses to be written off in April is 300,000 + 75,000 – 63,072 = 311,928 rubles.
On April 30, an entry will be made: Dt 90.2 Kt 44 – RUB 311,928.
For information on tax accounting registers, see the material “Maintaining analytical tax accounting registers (forms).”
Results
Postings using Dt 44 Kt 44 reflect information about the organization’s expenses associated with the sale of goods, work, and services. Monthly write-off of Dt 44 Kt 44 must be done taking into account the specifics of the organization’s activities and the type of expenses reflected in this account.
Subscribe to our accounting channel Yandex.Zen
Subscribe
Source: https://nalog-nalog.ru/buhgalterskij_uchet/vedenie_buhgalterskogo_ucheta/provodka_dt_44_i_kt_44_nyuansy/
Account 44 – postings
The collection and distribution account 44 in accounting is intended for the formation of sales expenses in trading and manufacturing enterprises. The information is summarized by type of cost for the sale of goods or services. Let's look at examples of how to close account 44 - you will find the postings in this article.
Accounting account 44 is...
Selling expenses account 44 is otherwise called “Selling Expenses”. The use of this account, in accordance with the requirements of Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000, is possible not only by trading companies, but also by manufacturing enterprises. The latter, in particular, on the account. 44 reflects the following types of costs:
- For packaging and packaging of GP (finished products) in warehouses.
- For transportation of products to customers, including loading operations.
- For commission payments for intermediary services.
- For advertising and marketing services.
- For the maintenance of reception points, general procurement costs and for maintaining livestock and poultry - for agricultural producers.
In trading companies, accounting account 44 is a general account for the costs of transportation and packaging of goods, depreciation of fixed assets, personnel salaries, product advertising, and repair of work equipment.
Thus, the characteristics of account 44 differ depending on the industry of the organization. In trading, closing account 44 ( postings below) allows you to obtain final data on the main and additional sales costs of the business.
And in production/industry it is used to collect information not on the cost of production, but in terms of the costs of its implementation.
Account correspondence 44
Active account 44: entries are made with an increase in debit and a decrease in credit, subject to closure at the end of the reporting period through a routine operation by allocating costs to the base indicator. Before we figure out how to close account 44, let’s list the main subaccounts:
- Account 44.01 - is intended to formulate the value of distribution costs in trading companies.
- Account 44.02 - is used to collect data on commercial expenses for sales in manufacturing/industrial enterprises.
By debit account 44 reflects the organization’s expenses for the reporting period in correspondence with accounts - 02, 04, 05, 10, 23, 29, 16, 19, 60, 68.71, 69, 70, 76, 94, 97, 96, etc. For the loan sch. 44, full or partial closure of account 44 is performed with postings to the enterprise’s income accounts - 90, 99.
How to close account 44 - postings
Monthly closure of 44 accounts (entries can be generated manually or through a routine operation) differs depending on the type of activity of the organization. In this case, the zeroing of cost costs occurs for all types of expenses, with the exception of some, distributed as follows:
- In trade and intermediary firms, transport costs are distributed among inventory balances according to the total sales volume and warehouse balances at the end of the period.
- In production and industry, transport costs and packaging costs are subject to distribution between individual product types of sold products, taking into account weight, volume, cost and other factors.
- Agricultural producers use accounts 15 and/or 11 to distribute procurement costs.
***
Companies that are engaged in sales (products, products, goods, works, services) use account 44 “Sales expenses” in accounting. The debit of the account reflects the costs of transportation, procurement, storage, pre-sale preparation, advertising and other expenses necessary for trading; The loan is written off monthly, in full or in part.
The debit balance at the end of the period on account 44 is reflected on line 1210 “Inventories” as work in progress, and the credit turnover for the period is reflected on line 2210 “Business expenses” of the financial results report.
Analysis of account 44 helps to understand the composition and structure of commercial costs and, if necessary, optimize distribution costs.