Accounting account 76 is a special account that is used by organizations to carry out settlements with other counterparties, as well as to reflect transactions that are not subject to accounting on accounts 60-75. What types of transactions are taken into account on account 76 and what transactions they are reflected in - our article will tell you about this.
general characteristics
Depending on the type of settlements, the corresponding subaccounts 76 of the accounting account for a separate type of operation are opened. Each of them is intended for grouping and further analysis of the economic processes of the enterprise in monetary terms. Among the accounts for certain types of obligations and settlements with debtors, you can find categories for accounting for unpaid wages for various reasons, insurance of property of the organization and employees, receivables from employees for the use of housing and communal services and other transactions not mentioned in accounts 60-75.
Characteristics of account 90 “Sales”
To systematize information about the level of profitability and the size of the cost part when carrying out ordinary activities, the enterprise uses account 90 in the accounting department. It is classified as a matching type of account and is characterized by the absence of a closing balance. In relation to the sections of the balance sheet, account 90 is active or passive, depending on the turnover of a specific subaccount; in the Chart of Accounts it is listed as active-passive.
Account 90 “Sales” reflects the total amount of revenue with the formed cost of:
- all types of finished products;
- work with services for various purposes;
- purchased products to form a complete set of manufactured products;
- account 90 in accounting is also necessary to reflect work related to construction and installation;
- product groups;
- transportation services;
- loading and unloading operations;
- sch. 90 is used in cases of leasing one’s property;
- transfer of rights to patented inventions on a paid basis.
The debit of account 90 “Sales” reflects the formed set of expenses for the production of a specific product in the form of cost. When reflecting this loan transaction, accounts 41, , , 20 may be involved in correspondence. Account credit 90 shows the total amount of revenue received during the reporting period. Debit turnovers pass through account 62.
For enterprises specializing in the production of agricultural products, the cost price is reflected according to planned values. The difference between the planned indicators and the calculated actual data based on the results of the annual calculation is recorded as a separate debit amount. 90 account is not reflected in the balance sheet, since it is subject to reset upon closing at the end of the reporting period.
The 90 counting scheme looks like this:
| Debit 90 | Credit 90 |
| Expenses in the form of product costs including VAT, including sales costs | Income part in the form of proceeds from sales, including VAT |
| Total expenses | Total income |
| The balance indicates a loss | The balance shows profit |
Main subaccounts of account 76
The accounting policy regulates the use of the following subaccounts of type 76.00:
- 76.01 - for accounting for settlements based on court documents;
- 76.02 - for accounting for amounts not received by employees for labor;
- 76.03 - for accounting for settlements with debtors for housing and communal services;
- 76.04 - for accounting for trade union dues and payments;
- 76.05 and 76.06 - for accounting for settlements with subsidiaries and dependent organizations, respectively;
- 76.07 - for calculations for payment of income;
- 76.08 - for settlements with individuals who do not work in the organization;
- 76.09 - for settlements on received and submitted claims;
- 76.10 - for settlements on insurance matters;
- 76.11 - to account for targeted fees for housing and communal services;
- 76.12 - for accounting for undetected amounts;
- 76.13 - for settlements with the state. organs;
- 76.80 - for other settlements with debtors and creditors.
Additionally, accounting account 76 is opened “VAT on advances and prepayments” and accounting account 76 “VAT on advances and prepayments issued”, which correspond to account 68. The use of VAT accounts is mandatory and important for all tax payer companies.
What sub-accounts are opened on account 76
In practice, accounting account 76 is used - if not most often, then regularly - with the use of subaccounts:
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
- 76-1 (“Insurance”);
- 76-2 (“Claims”);
- 76-3 (“Dividends”);
- 76-4 (“Depositing wages”).
The above names of subaccounts are conditional (partially correspond to those recommended for account 76 according to the chart of accounts, which was approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). The names of sub-accounts, their composition, and the depth of analytics can, in principle, be anything - the law does not impose restrictions. At the same time, one should not forget about the main rule: analytical accounting data must correspond to the turnover and balances of synthetic accounts.
Let's get acquainted with the features of using postings to the listed subaccounts.
Subaccount 76.01
In settlements based on enforcement documents, it is implied the withholding of funds from the amounts of remuneration for the labor of employees for the account of individuals and legal entities, based on court decisions and documents.
Let's consider possible types of correspondence of subaccount 76.01 with other accounts: Typical transactions using account 76.01
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of an accounting transaction |
| 70.01 | 76.01 | amount due due to court order withheld |
| 76.01 | 51 | the amount was paid according to the court decision from the current account |
| 76.01 | 50 | the amount of the court order was paid from the cash register |
| 50 or 51 | 76.01 | the previously transferred amount was returned to the cash register/account according to a court decision |
| 76.01 | 91.01 | writing off debts under court documents for enterprise income |
Subaccount 76.01 is debited with accounts 50 or 51 when the company makes the payment of the amounts required by executive documents. After the expiration of the limitation period for the documents, the debt amount is written off to the income of the enterprise and debited from 91.01 “Other income and expenses.”
The first entry in accounting for such a situation will be the correspondence of accounts 70 and 76.01, which reflects the process of withholding the amount payable. Subaccount 76.01 is credited with accounts 50, 51, 55 in the event that the organization returns amounts under executive documents.
Property insurance accounting
Accrual of insurance payments is written off to the cost of production, goods by posting D20 (44) K76/1 .
The transfer of insurance payments from the current account is formalized by posting D76/1 K51.
When an insured event occurs, the received amount of insurance compensation is reflected by posting D51 K76/1 .
The residual value of property lost as a result of an insured event is written off by posting D76/1 K01 (10, 41, 43) .
If the damaged property can be repaired, then the associated costs are also charged to the insurance compensation using posting D76/1 K20 (23, 25, 26) .
If, under the terms of the insurance contract, any losses are not subject to compensation, then they are considered extraordinary expenses and are written off by posting D99 K76/1 .
If the amount of insurance compensation exceeds losses from property damage, this excess amount is considered emergency income and is reflected by posting D76/1 K99 .
Example of property insurance
The company is insured for 100,000 rubles. property. As a result of the fire, property worth 80,000 rubles burned down; according to the property insurance contract, the amount of 90,000 rubles was reimbursed. What entries for account 76 need to be reflected in accounting?
Postings:
| Sum | Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| 100000 | 76/1 | 51 | Insurance payment transferred |
| 100000 | 20 | 76/1 | The insurance payment is written off against the cost of production |
| 80000 | 76/1 | 01 | The value of the burned property was written off |
| 90000 | 51 | 76/1 | The amount of insurance compensation has been transferred |
| 10000 | 76/1 | 99 | The amount of excess of insurance compensation over the value of the burnt property is reflected in income |
Subaccount 76.02
Account 76.02 in accounting is used for deposited wages that were not received on time by the company's employees for various reasons.
Typical transactions using account 76.02
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of an accounting transaction |
| 70.04 | 76.02 | the amount of the deposited salary is transferred |
| 51 | 76.02 | unpaid funds are transferred to a bank account |
| 76.02 | 50 | deposited salary was paid from the organization's cash desk |
| 76.02 | 91.01 | debt on deposited wages is written off to the organization’s income |
The amount not received for wages is debited from account 70.04 and reflected in credit 76.02. Funds can be issued to the employee, which is described by posting Dt 76.02/Kt 50. If the statute of limitations expires, the amount of the deposited salary is written off to the income of the enterprise.
Typical accounting entries for account 76
The table below shows the most commonly used accounting entries involving account 76.
| Account debit | Account credit | Business transaction |
| On account credit 76 | ||
| 20 "Main production" 23 “Auxiliary production” 25 “General production expenses” 26 “General business expenses” 44 “Sales expenses” | 76 | Reflection of property insurance costs |
| 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” | 76 | Reflection of deposited salary |
| 91 “Other income and expenses” | 76 | Write-off of losses from insured events not compensated by insurance compensation |
| 91 “Other income and expenses” | 76 | Reflection of penalties payable by the buyer for non-compliance with contractual terms |
| On the debit of account 76 | ||
| 76 | 10 "Materials" | Write-off of material losses due to an insured event |
| 76 | 28 "Defects in production" | Recognition by the supplier of a fine for manufacturing defects |
| 76 | 50 "Cashier" | Issuance of deposited wages from the cash register |
| 76 | 51 “Current accounts” | Reflection of a claim against the bank for erroneous debiting of funds from an account |
| 76 | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | Reflection of a claim against a supplier |
| 76 | 90 “Sales” 91 “Other income and expenses” | Accrual of income from participation in the activities of other organizations |
| 76 | 91 “Other income and expenses” | Court awarding a fine to a supplier for non-compliance with contractual terms |
For more entries, see the article “Account entries 76 (nuances).”
Subaccount 76.03
Account “Settlements with residents for housing and utility sales” (sub-account “Revenue”).
Typical transactions using account 76.03
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of an accounting transaction |
| 76.03 | 90.01 | amount due for utility bills |
| 86.01 | 76.03 | the amount of compensation from the budget for housing and communal services was transferred |
| 70.01 | 76.03 | money from tenants transferred |
| 76.03 | 73.80 | the amount payable due to the subsidy has been repaid |
Citizens who are entitled to government benefits may be transferred amounts of compensation for payment of housing and communal services. Budget funds are accounted for in account 86.01. Receipt of payment for the use of housing and communal services of the organization from employees is reflected in the credit of account 76.03 and in the debit of account 70. In the case when payment for housing is made through subsidies provided by the organization, subaccount 73.80 is used.
Account 76: subaccounts 3 and 4
Clause 76.3 controls dividends and other types of income due to the company that do not contradict the partnership agreement. D76 K91 – profit to be received (distributed). D51 K76 – funds received by the organization from debtors.
The fourth subaccount is intended to take into account amounts accrued to employees of the enterprise, but not paid within a certain period due to the non-appearance of recipients. In such cases, the following wiring is performed: D70 K76. When a worker receives money, an entry is made to the debit of account 76.
Settlements with trade unions
Accounting for contributions by members of the trade union organization and the use of accumulated funds is carried out in account 76.04 “Settlements with trade union organizations”. Contributions are withheld from the amounts of remuneration for the labor of the enterprise's employees at the established rate and are displayed in the debit of account 70.01, then transferred to the organization's bank account. The process of transferring funds can be described by posting Dt 76.04/Kt 51.
Payment of amounts received from trade union organizations is made using accounts 50, 51, 55 and settlements with employees. The accounting entries for such an operation look like this: Dt 76.04 / Kt 70.01 or Dt 76.04 / Kt 50. When paying for vouchers to an employee of an organization from trade union contributions, account 76.04 corresponds with account 73.
Account 76 in the balance sheet
Based on the entries in account 76, information is entered into the balance sheet. In this case, account 76 in the balance sheet can be shown in both the active part of the balance sheet and the passive part. To do this, analyze its expanded balance.
Each balance is used in its own way to fill out the balance sheet: debit - for its active part (line 1230), credit - for the passive part (line 1520). At the same time, the debit balance in terms of VAT amounts calculated from advances and reflected in account 76 affects the indicator on line 1260 of the balance sheet.
Dividend calculation
To record settlements with individuals and legal entities regarding income, accounting account 76 is used. This is subaccount 76.07 “Calculations for due dividends and other income.” The funds that need to be paid are reflected in the debit of subaccount 76.07 and in the credit 91.01.
Intangible assets transferred to the organization as income are listed in the debit of asset accounting accounts and credit 76.07. Patents, copyrights, brands, and licenses for the production of a certain type of product can be transferred as intangible assets.
Applicable subaccounts
Position 76 has the following subaccounts:
1) 76.1 – implementation of mutual settlements for personal and property insurance;
2) 76.2 – making payments on legal claims;
3) 76.3 – mutual settlements for dividends;
4) 76.4 – making payments on deposited funds, etc.
Within the first subaccount, the company shows amounts for settlements for property and personal insurance, where the organization plays the role of a person insuring its valuables or the interests of employees.
Analytics for subaccount 76.1 is carried out in the context of insurers and individual insurance contracts.
When keeping records 76.2, the amounts of claims that were presented to counterparties are reflected, as well as the amounts of fines, penalties and penalties imposed and recognized.
In this situation, analytical accounting is carried out in the context of each debtor and each claim.
Under subposition 76.3, companies keep records of dividends and other income due to them, including profits and losses, as well as results obtained under simple partnership agreements.
Payments to individuals
Subaccount 76.08 is intended for conducting transactions between the organization and former employees. For example, to issue a voucher to a pensioner, the following entries are made: Dt 76.08/ Kt 60-01, Dt 76.08/ Kt 90.01, Dt 76.08/ Kt 91.01. If part of the funds allocated to pay for the trip is transferred to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, then account 69.01 is used. The amount transferred by the fund is shown in debit 69.01. In cases where the organization takes on part of the payment for the trip, the following correspondence is generated: Dt 91.02 / Kt 76.08.
Subaccount 76.08 is also used to calculate income tax for an individual who is not a current employee of the organization. The operation is carried out if the value of the gift due exceeds the established value. Account 76.08 corresponds with 68.02.
Subaccount 76-2: why is it needed and how is it used
This subaccount is used to account for transactions related to the company’s participation in legal relations that are caused by the emergence of various claims on its part against suppliers. For example, this could be a legal relationship in which lawsuits are filed against suppliers.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Yandex.Zen VKontakte Telegram
The following entries are possible here:
- Reflecting the accrual of the amount of claims against the counterparty.
Examples of such postings:
- Dt 76-2 Kt 60 (if there are claims regarding delivery, as an option, if the product is of poor quality);
- Dt 76-2 Kt 91-1 (if a fine or penalty is collected from the supplier as provided for in the contract).
In both cases, a special asset is formed on account 76-2 in the form of a property right for the amount of the claim.
- Reflecting the write-off of the amount of claims against the counterparty.
Possible postings (for the two above scenarios respectively):
- Dt 60 Kt 76-2;
- Dt 91-2 Kt 76-2.
That is, the asset initially shown in the subaccount decreases. Such entries can be drawn up if, for example, the court has determined that the company made a claim unlawfully (or if the debtor does not have property from which the company could collect penalties).
Claims and insurance settlements
76.09 an accounting account was created to reflect settlements of claims made against suppliers and contractors and fines awarded. Cash requirements are reflected in the debit of account 76.09. Only those claims that are made on the basis of a concluded agreement between the companies are considered justified.
In this case, the following accounts are credited: 60, 20, 50, 51, 55 and a group of accounts payable for loans. Bills not paid on time lead to the accrual of interest, which is charged to account 91.01. Posting Dt 79.02 / Kt 76.09 or Dt 51 / Kt 76.09 describes the process of receiving funds in favor of the enterprise.
Subaccount 76.10 reflects transactions for the calculation of insurance of property and employees of the organization.
This does not include Social Security and Medicare payments. Typical transactions using subaccount 76.10
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of an accounting transaction |
| 20 44 | 76.10 76.10 | amount of insurance payments accrued |
| 70.01 | 76.10 | the insurance premium is deducted from the employee’s salary |
| 76.10 | 51 or 79.02 | the amount of insurance payments is transferred to the insurance organization |
| 76.10 | 99.03 | insurance compensation accrued |
| 51 | 76.10 | insurance payment received in case of emergency |
Subaccount 76-1: purpose and postings
The considered subaccount of account 76 is used to register business transactions within the framework of the company’s participation in those legal relations that are related to the insurance of employees through specialized insurance companies (that is, when policies are purchased).
The following postings can be used:
- When assigning the amount for insurance policies to the expenses of the main production (let's agree that the insured employees work there): Dt 20 Kt 76-1.
The loan creates a liability - in the form of the company’s obligation to pay for policies (that is, actually make expenses).
- When paying for insurance policies: Dt 76-1 Kt 51.
By debit, the liability decreases due to the repayment of the specified obligation.
- Upon receipt of payment from an insurance company for insured events: Dt 51 Kt 76-1.
The loan again reflects an obligation - this time to transfer payments to the employee.
- When transferring payments to an employee: Dt 76-1 Kt 73.
The debit reflects the repayment of the specified obligation.
Characteristics of subaccounts 76.11, 76.12, 76.13, 76.5
Account 76.11 “Calculations for target fees for housing and communal services” is used to calculate payments for the use of utility services.
Account 76.12 “Settlements for unclear amounts” is used to carry out operations in cases where it is not possible to find documents for transferring amounts to the appropriate accounts. If the recipients of funds for debts are not identified, the amounts are written off from account 76.12 in favor of the organization.
Account 76.13 “Settlements with government agencies” is used to carry out operations to pay fines and debts to the state administration.
In the course of a company's activities in the production and sale of products or services, account 76 is widely used in accounting.
Postings using subaccounts 76.11, 76.12 and 76.13
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of an accounting transaction |
| 76.03 | 76.11 | accrued amount of payments for utilities |
| 76.11 | 51 or 55 | funds were transferred to utility service providers |
| 51 or 55 | 76.12 | Unidentified amounts were credited to the current account/special bank account |
| 76.12 | 91.01 | writing off outstanding debts to the organization's income |
| 91.02 | 76.13 | a fine was imposed on the company |
| 76.13 | 51, 50 or 79.02 | the amount of the fine is transferred to the relevant government agency |
| 97.03 | 76.13 | expenses for issuing a license are reflected |
| 76.13 | 51 | the debt for the issued license has been repaid from the bank account |
Account 76.5 in accounting is used for settlements with other suppliers and contractors. Do not forget that the main account for settlements with suppliers is 60, a subaccount 76.5 exists to pay for additional services not included in it. Here the amounts of the cost of packaging, the work of transport companies, and VAT for importing products can be recorded.
Application of subaccount 76/3 in practice
There are accounts receivable in the amount of RUB 1,350,000. on account 62 “Settlements with customers and buyers”. For certain reasons, before the payment deadline, she transferred for 750,000 rubles. its rights to the company Iceberg LLC, which was able to recover 900,000 rubles against the debt due. In such a situation, several questions arise:
- Are accounts receivable a purchase of property or a financial investment in assets?
- The buyer's asset is RUB 1,350,000. or 750,000 rubles?
- In this case, is the debt of debtors considered income, and 750,000 rubles. - expense of the enterprise Iceberg LLC?
In such a situation, Oasis LLC must make, from a legal point of view, the following transactions:
Debit 91.2 Credit 62 1,350,000 rub. — writing off the right of claim from buyers.
Debit 51 Credit 91.1 RUB 750,000 - compensation received.
Such operations make it possible to record in the “Other income and expenses” accounts the loss of the Oasis enterprise that arose from the assignment of the right of claim. Accountants must make a debit entry to account 76.3 to record the debt from counterparties. The difference between the rights received and the costs for them is shown in the credit of accounts 98/1, 83 or 90/1.
Even partial collection of payment leads to mutual agreement of both parties and full repayment of debts. The unpaid portion is reflected in the debit of account 51, and the written-off portion is reflected in account 98.1. In the example under consideration it turns out:
Debit RUB 51,900,000.
Debit 98.1 765,000 rub.
Account credit 76 1,350,000 rub.
spent 750,000 rubles. for the acquisition of rights and returned 900,000 rubles, that is, the profit is 150,000 rubles. The wiring is like this:
Debit 98.1 Credit 91.1 RUB 150,000
The actual amount of profit from the operation is reflected in account 98/1, intended for recording income for future periods.
Deduction of VAT on advances received
Accounting account 76 is not only settlements with debtors and creditors, but also payment of VAT for advance payments. Advance is the amount received by the supplier before the goods are shipped. Upon receipt of an advance payment, the taxpayer is obliged to transfer the amount of VAT to the budget.
76-av accounting account is used to calculate VAT on advances received. Within 5 days, the supplier issues an invoice, one copy of which is sent to the buyer. VAT can be paid only after the sale of goods, then a 76-account is opened. The entries for calculating VAT on the advance received are as follows: Dt 51/ Kt 62, Dt 76-av/ Kt 68. When terminating the contract and returning the advance to the buyer, the manufacturer may require a deduction of the VAT amount. In this case, the reverse operation occurs: Dt 68/ Kt 76-av.
Account 90 in accounting: postings
Subaccounts 90.3-90.5 are not used in practice by all enterprises. Their presence is determined by the taxation system of the organization and the specifics of the chosen area of economic activity. Typical transactions for account 90 are presented in two blocks - debiting and crediting the sales account.
Postings to account 90 when reflecting revenue:
- D76 – K90.1 from organizations considered other debtors and creditors;
- D50 (55, 51, 52) – K90.1 upon receipt of proceeds from the sale transaction into the accounts of the selling company;
- D79 - K90.1 - in this case, correspondence from account 90 shows the amount of income from subsidiaries and branch divisions;
- D98 - K90.1 when attributing part of the proceeds to deferred income in the case of making advance payments.
Additional postings to account 90 “Sales”:
- D90.2 – K43, 41, 40 when writing off goods or categories of finished products at discount prices;
- account 90 in accounting, when reflecting trade margins, forms a posting between D90.2 and K42;
- D90.3 – K68 at the time of issuing VAT on products sold.
VAT on listed advances
Accounting account 76 is used to calculate VAT on the listed advances. After receiving the goods, the organization debits account 76 with account 68, after which the invoice is reflected in the purchase book.
If the company paying the advance to the manufacturer is a VAT payer, it can deduct VAT. The buyer has such a right only after receiving an invoice for products sold and meeting the following conditions:
- the supplier has issued a VAT invoice;
- the advance was paid for the upcoming supply or provision of services;
- there is documentary evidence of payment;
- an invoice has been issued for the advance payment;
- an agreement on the use of the advance was signed.
Compliance with all points guarantees the buyer the opportunity to deduct VAT and reduce the total amount of tax payable to the budget.
Subaccount 76.AV “Value added tax on advances and payments”
Account 76.AB allows you to summarize information on calculations for paying VAT from preliminary payments. Accounting is maintained with those customers and buyers from whom money has been received in advance for the planned shipment of goods or for the provision of various types of services.
Business transactions may be different. For example: D68.02 K76.AV - accounting for value added tax on payment received from the client in advance. D 76.AV K68.02 - VAT accrual on funds received in advance from customers. Account 76. AB has the following sub-accounts (analytical characteristics): “Counterparties”, “Invoices”.
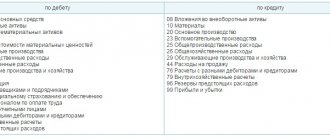
Loan correspondence
Account 76 can interact with the following categories of the chart of accounts: “Investments in non-current assets”, “Fixed assets”, “Intangible assets”, “Equipment for installation”, “Income investments in MC”. In the “Production Inventories” section, correspondence is carried out with the accounts “Materials”, “Procurement and acquisition of medical supplies”, “Animals for growing and fattening”, “VAT on purchased values”.
Account 76 can also interact on credit with all settlement accounts (except 68, 69, 75, 77) and the “Production Costs” category. From the section “Finished products and goods” - with accounts 52, 50, 51, 44.55, 41, 57, 45, and 58. In addition, correspondence is carried out with most current accounts and, of course, with those that reflect monetary transactions (91, 97, 94, 96, 99).