Using account 57
Conducting activities without using the 57 account may not always reliably reflect the financial situation of the enterprise. The money may not be used for its intended purpose and may be returned to the company's cash desk. Or lost or stolen after delivery to the responsible person or collector.
That is why accounting using account 57 is methodologically more correct.
Account 57 “Transfers in transit” is an active balance sheet account; receipts are reflected in Dt, and debits are reflected in Ct.
The account is used as a transit account in the following cases:
- transferring money at the end of the day from the cash register or to collectors;
- movement of funds between foreign currency accounts of one organization or foreign currency and current accounts;
- corporate plastic card of one bank with an account in another bank, etc.
Example of typical postings
Galaxy LLC is engaged in retail trade. The daily proceeds in the amount of 45,000 rubles were issued to the collectors for transfer to the bank. While sorting the cash, the collector discovered a counterfeit 1,000 ruble bill. Therefore, the next day the amount of 44,000 was credited to the store’s account.
Postings
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 57 | 50 | The funds were transferred to the collector | 45000 | Transmittal sheet, RKO |
| 57 | DS transferred by the collector to a bank account | 44000 | Bank statement | |
| 57 | The amount of the shortfall is recorded | 1000 | Accounting information |
Typical transactions for account 57 “Transfers in transit”
The main entries for account 57 “Transfers in transit” are presented in the table below:
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 57.01 | 50 | Depositing proceeds into a bank account at the end of the month | Bank receipt, bank account statement |
| 50/51,52 | 57 | Cash “in transit” arrived at the cash desk/bank | Bank statement |
| 57.02 | 50 | Transfer of proceeds to the bank through the collection service | KO-2, receipt for bag, accompanying statement (copy) |
| 51 | 57.02 | Funds are credited to the account (collection) | Bank account statement |
| 57.03/ 57.04 | 51/52 | Transferred funds for the purchase/sale of foreign currency | Payment order/Bank statement |
| 57 | 62/76 | A money transfer for repayment of debt from a buyer/debtor that has not yet been credited. Receipt – return posting. | Payment order/Bank statement |
Acquiring operations
Acquiring is payment by bank card through an electronic payment terminal.
Postings for electronic payment
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 57 | 90 | Sales revenue received | 25000 |
Postings if necessary, specifying the buyer
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 57 | 62 | Receiving payment from the buyer | 1500 | Cash receipt |
| 57 | Receipt of proceeds to the current account | 1500 | Bank statement | |
| 91 | The commission of the acquiring bank is written off | 9 | Bank statement |
Account 57 in accounting. Transfers within the organization
To reflect cash flow, revenue for goods sold, and money transfers, account 57 is used in organizations for the following purposes:
- Topping up your current account. Funds are transferred to the organization's employees or collection services for crediting to the bank through the organization's cash desk.
- Cash withdrawal. Based on the issued bank receipt, funds can be credited to account 57 before the cash is posted to the cash desk.
- To transfer funds to the enterprise’s corporate card from current bank accounts.
- For acquiring operations.
Currently, the possibility of paying for goods by individuals using payment terminals is widespread. This form of payment is relevant not only for regular stores, but also for making purchases online.
Organizations using such methods, in addition to having specialized equipment, enter into agreements with banks for servicing payment terminals - acquiring. An authorized bank, an intermediary (acquirer), installs its own payment terminals in the institution, through which the population makes payments for purchased goods.
In such cases, funds are not immediately credited directly to the organization. The 57 count should also be used here.
Debit 57 - Credit 90 (36,000 rubles) - revenue from customer cards is reflected.
Debit 90 - Credit 68 (5491.53 rubles) - accrual for VAT sales.
Debit 51 – Credit 57 (35,460 rubles) – receipt of funds to the institution’s current account.
Debit 91 - Credit 57 (540 rubles) - bank expenses under the acquiring agreement.
If an organization is a VAT payer, tax must be charged on the full amount of revenue.
Read more about the accounts used in transactions in the articles: account 68 (accounting for calculations of taxes and fees), account 90 (accounting for the sale of finished products), account 91 (accounting for other income and expenses).
Using account 57 in foreign exchange transactions
If the operations of debiting rubles from an account, selling currency and crediting proceeds take more than one day, account 57 must be used.
Example of transactions when purchasing currency
Master LLC submitted an application to the bank to purchase currency and for these purposes transferred 600,000 rubles to it. The bank purchased currency on the stock exchange at a price of 60 rubles per dollar. The Central Bank exchange rate on this date was 58 rubles per dollar.
Postings
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 57 | DS for currency purchases are listed | 600000 | Bank statement | |
| 57 | The purchased currency is credited to the account (10,000 USD * 58 rubles per USD) | 580000 | Bank statement | |
| 91 | 57 | The difference between the Central Bank rate and the acquisition rate is reflected ((60 rubles per USD -58 rubles per USD)*10000) | 20000 | Bank statement |
Example of an operation when selling currency
On October 1, Master LLC submitted an order to the bank to sell $1,000 on October 2. The Central Bank dollar exchange rate as of October 2 is 60 rubles/USD. On October 2, the bank sold the currency at the rate of 61 rubles/USD.
Postings:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 57 | The currency to be sold has been written off (at the Central Bank rate) | 60000 | Bank statement | |
| 57 | The sales amount is credited at the bank rate (1000 * 61 rubles/USD) | 61000 | Bank statement | |
| 57 | 91 | Other income reflected (exchange difference) | 1000 | Bank statement |
Account 57. Transfers between organizational accounts
Account 57 is also used when transferring funds between an organization’s accounts, filling the time gap between the write-off of assets and their receipt to another current account. The following transactions are created:
Debit 57 - Credit 51-1 (20,000 rubles) - funds were withdrawn from the current account of bank A for subsequent crediting to the account of bank B.
Debit 51-2 - Debit 57 (20,000 rubles) replenishment of the amount in the account of bank B by transfer from bank A.
In such situations, there will be no temporary lack of funds when assets have already been written off from one account, but not yet credited to another.
Retail wiring
In accounting, goods sold at retail and paid for by card are reflected in account 57. A separate sub-account 57.3 is opened for it.
It refers to active accounts: then the debit indicates the actual amounts of purchases, including settlements with clients (correspondence with account 62). And for a loan – the actual amount credited to the company’s account.
How to carry out acquiring in retail trade in accounting:
- Dt 57 Kt 90.01: sales revenue;
- Dt 90.03 Kt 68.2: accrual of VAT on the sales amount;
- Dt 51 Kt 57: crediting of funds made via non-cash payment;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 51: indicate the amount of interest withheld by the bank for the acquiring service, let’s say 2.7%.
Each bank sets its own percentage, depending on the monthly turnover of the company.
Typical correspondence and postings
There is a certain time period between several final moments of receiving and transferring funds. However, the transfer of funds may take more than one day. The simplest example is when cash was withdrawn from the cash register at the end of the working day, and transferred to the account only the next day.
Example: at the end of the working day on February 1 of this year, the company recorded revenue of 67,000 rubles. 20,000 was left in the cash register for current business expenses. The remaining funds had to be redirected to a bank account so that the limit of 30,000 rubles was not violated. The whole process can be reflected with the following entries.
01.02.2017
- Debit 50 Credit 62 - receipt of revenue from the sale of goods in the amount of 67 thousand rubles.
- Debit 71 Credit 50 - funds were given to the accountable person in the amount of 20,000 rubles.
- Debit 57 Credit 50 - money was transferred to collectors in order to replenish the current account.
02.02.2017
- Debit 51 Credit 57 - the organization’s revenue was transferred to the current account.
The fact of using account 57 in this case allows you to comply with the established cash order by depositing funds into the account upon receipt
In addition, it is important to understand that the simplest posting Debit 50 Credit 54 is not always able to fully reflect the current financial situation in the organization. After all, in the end, some circumstances arise that will certainly lead to the fact that the money may not be spent as planned.
For example, they can be returned to the enterprise in the form of cash due to technical work at the bank. In addition, you should not exclude the possibility of various force majeure cases, for example, theft or loss of funds by collectors. In these cases, the transfer operation was not completed, which means it could not be reflected in this account.
Within the organization
Account 57 in a company when reflecting the movement of cash can be used for the following purposes:
- Topping up an existing current account. An employee or collectors take them from the company's cash register.
- Cash withdrawal. Based on the receipt issued by the banking institution, funds can be posted to the 57 account before being posted to the enterprise's cash desk.
- The account can be used when transferring money to a company’s corporate card from a bank account.
- When acquiring. Today, payment for individuals is quite common. persons of various goods or services using electronic payment systems, such as terminals. This is true both for regular stores and for those that provide their services online.
An enterprise that uses such payment methods in its work, in addition to special equipment, must also enter into an additional agreement with the bank for the possibility of servicing terminals - acquiring. The bank (acquirer), which in this case is an intermediary, must install its own terminals in the organization to make payments.
With this system of operation of the enterprise, funds are not immediately credited to the organization’s account. The score 57 should also be used here.
- Debit 57 Credit 90 - revenue received from customer cards;
- Debit 90 Credit 68 - VAT, which is charged on sales;
- Debit 51 Credit 57 - transfer of finances to the official account of the enterprise;
- Debit 91 Credit 57 - tank expenses under the acquiring agreement.
If the company is a VAT payer, then this tax is required to be charged on the entire amount of revenue.
Between organizations
Account 57 acts as a conductor of money between the accounts of several organizations. In fact, count 57 in this case is the time between sending money. There may be the following entries:
- Debit 57 Credit 51.1 - funds were withdrawn from settlement bank No. 1 in order to subsequently credit them to the account of bank No. 2;
- Debit2 Credit 57 - replenishment of account No. 2 due to the initial financial transfer from bank No. 1.
In such cases, there is no temporary lack of assets when finances have left the first account but have not yet arrived in the other.
Characteristics and Application
Transfers in transit are financial funds that have been deposited at the cash desks of credit institutions or post offices for crediting to a current account, but have not yet been credited at the moment.
In most cases, we are talking about the revenue that the company should receive from the sale of services or goods. Summarization of all information about “transfers in transit” both in foreign and national currency occurs in account 57.
The debit of this account records funds (for example, in the process of depositing proceeds received from the sale) on the basis of a mail receipt, a credit institution, or a copy of the accompanying documentation for the deposit of funds by collectors.
This account can also be used in the process of paying for services or goods using bank cards (this is called acquiring), or when purchasing foreign currency.
All movement of funds in this account must be described separately for each individual currency. In simple terms, this is a way of describing the process of transferring money to a bank account.
Almost any trading enterprise transfers funds received from revenue to a current account. This is where the use of account 57 of accounting begins, since it is possible to keep records as accurately and continuously as possible.
In addition to transfers from the enterprise itself, this account 57 can include funds transferred by customers as payment for services rendered or goods purchased, but which did not have time to be finally transferred to the account before the end of the reporting period.
Using account 57 is appropriate in cases where the transfer of funds takes more than a day from the start of the transfer. The following services can be used for this:
- banking institutions;
- savings banks;
- postal service branches.
When transferring, it is necessary to have basic documents proving the fact of transfer of funds. It can be:
- receipts from executive organizations;
- accompanying collection statements;
- other accounting documents.
The movement of funds in foreign currency must occur separately from other transfers.
How to close
There are quite a lot of options for how account 57 can be closed. It all depends on which accounts it corresponds with, for example:
- Debit 51,52,55 Credit 57 - in cases of crediting funds;
- Debit 70 Credit 57 - transfer of funds to an employee;
- Debit Credit 57 - issuing loans to employees using received funds.
For example, in the case of selling funds through an online store:
- Debit 51 Credit 57 - transfer of money from the acquiring bank;
- Debit 57 Credit 52 - preparation of a report on non-cash retail trade.
Or this example. The balance of unspent funds in rubles when purchasing currency was transferred to the organization’s current account. The following entries are relevant here:
- Debit 57.02 Credit 51 - debiting money from the client’s account in the process of purchasing money in foreign currency;
- Debit 52 Credit 57.02 - crediting the currency itself during a transaction involving its purchase.
These postings will be sufficient to reflect the transaction. Although it is also acceptable to use account 76 to emphasize that currency is being purchased from the bank.
Correspondence of account 57 with other accounts
In accounting, there are active, passive (passive determines the movement within the enterprise) and active-passive accounts. SCH-57 is an asset account, which means recording any income in debit, and expenses in credit. At the end of the accounting month, either a debit balance is formed, or the register is closed if money successfully arrives at the bank. Based on this, it is possible to determine the interaction of “Transfers in transit” for debit and credit.
Account 57 corresponds (debits) with the following registers:
- 50, 51, 52, describing intra-economic needs;
- 62, 64, 67, describing settlements with clients;
- 78 as calculation of dependent companies;
- 45 and 46, describing goods sold;
- 99 how to profit and loss when buying currencies.
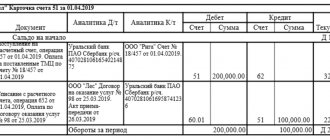
Type of postings according to SCh-57 in the 1C environment
When closing the Account. 57 interacts with accounts 50, 51, 52, 64, 73. When money is credited to the required account, a posting is made confirming this.