Account 45 “Goods shipped” is intended for accounting for goods sold, the revenue for which is recognized later than the moment of shipment. Such situations are possible during export operations, under commission agreements or during transfer without registration of ownership.
Account 45 is active. The cost of goods recorded on the account consists of the actual cost and shipping costs. Accounting on this account is carried out in the context of location (storage) and objects.
Fragment of the approved Chart of Accounts, Section 4, Finished products and goods
Characteristics of account 45 “Goods shipped”
45 account – this account is called “Goods shipped”. The debit of this account takes into account the cost of shipped goods, finished products at actual cost (before the ownership is transferred to the buyer, for example, before payment) sales expenses can also be taken into account. For the loan, write-off of the actual cost (dt 90 Kt 45). The account is active with a debit balance at the beginning and a balance at the end. The formula for calculating the closing balance of an account is 45 = Debit balance + Debit turnover - Credit turnover. On the balance sheet, account 45 is reflected in the item “RESTORES” in the balance sheet asset. 76/VAT is reflected in the balance sheet in the line other current assets.
An agreement in which ownership does not transfer during shipment is called an agreement with a special procedure for transferring ownership (this may be the moment of payment).
In what operations is it used:
- When selling, when ownership of the goods transfers after payment (below is an example)
- When selling goods through an intermediary.
- For barter transactions (example below)
- When transferring ownership of goods or products upon receipt from a transport organization.
Basics of accounting in trade
Watch the lecture on: INTUIT | youtube.com
If you have problems with the video, click the youtube link above.
The presentation for this lecture can be downloaded here.
Purpose of the lesson:
consider the basic provisions of accounting for goods and accounting in trade organizations.
General provisions
If an organization purchases a computer in order to use it for production purposes, we will consider this computer as a fixed asset. And if the same computer is purchased for the purpose of resale, we will deal with the goods. Organizations that sell various goods are trading organizations. Everything we will talk about here applies primarily to them. However, organizations for which trade is not their main activity can also purchase something for resale.
The procedure for accounting for goods in organizations whose main profile is not the sale of purchased goods is regulated by Section 5 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n “On approval of guidelines for accounting of inventories.”
In particular, in accordance with paragraph 217 of the Order, organizations that carry out trading activities along with other types of activities are called “non-trading organizations”. In accordance with paragraph 218 of the Order, non-trading organizations can sell goods purchased by the organization specifically for sale.
In accordance with paragraph 229 of the Order, revenue from the sale of goods in non-trading organizations is taken into account in the same way as the rules established for finished products.
Features of accounting for goods are regulated by PBU 5/01 “Accounting for inventories”.
The following accounts are used to record goods and related transactions:
- 41 "Products"
- 42 “Trade margin”
- 44 “Sales expenses”
- 45 “Goods shipped”
Accounting for goods can be formalized both by primary documents developed by the organization independently, and by primary accounting documentation in accordance with Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 1998 No. 132 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for accounting of trade operations.” In particular, the following general forms of accounting documentation used in trade have been approved:
- TORG-1 “Act of acceptance of goods”
- TORG-2 “Act on the established discrepancy in quantity and quality when accepting inventory items”
- TORG-3 “Act on established discrepancies in quantity and quality when accepting imported goods”
- TORG-4 “Act of acceptance of goods received without a supplier’s invoice”
- TORG-5 “Act on the receipt of packaging not specified in the supplier’s invoice”
- TORG-6 “Act on container curtain”
- TORG-7 “Logbook of registration of inventory items that require a curtain of containers”
- TORG-8 “Order - selection list”
- TORG-9 “Packaging label”
- TORG-10 “Specification”
- TORG-11 “Product label”
- TORG-12 “Consignment note”
- TORG-13 “Invoice for internal movement, transfer of goods, containers”
- TORG-14 “Invoice and invoice (for small retail trade)”
- TORG-15 “Act on damage, damage, scrap of inventory items”
- TORG-16 “Act on write-off of goods”
- TORG-17 “Incoming group plumb line”
- TORG-18 “Logbook for the movement of goods in a warehouse”
- TORG-19 “Consumption plumb line (specification)”
- TORG-20 “Act on part-time work, sub-sorting, repacking of goods”
- TORG-21 “Act on sorting (sorting) of fruits and vegetables”
- TORG-22 “Act on control (selective) inspection of eggs”
- TORG-23 “Commodity magazine of a small retail trade worker”
- TORG-24 “Act on re-measuring fabrics”
- TORG-25 “Act on markdown of flaps”
- TORG-26 “Order”
- TORG-27 “Logbook of fulfillment of customer orders”
- TORG-28 “Card of quantitative and cost accounting”
- TORG-29 “Commodity report”
- TORG-30 “Report on containers”
- TORG-31 “Accompanying register of documents delivery”
There are other forms of documents used when selling goods on credit (their codes begin with the name KR), when accounting for transactions in commission trade (their codes begin with KOMI), when accounting for transactions in public catering (their codes begin with OP).
Receipt of goods
When goods arrive at a trade organization, its acceptance is handled by a financially responsible person or a special commission, depending on the size of the organization and the scope of work. The receiving party checks the compliance of the delivered goods with the accompanying documents. If these data coincide, the goods are included in the following accounting entry:
D41 K60
— goods have arrived from the supplier
If the trading organization is a VAT payer and VAT on goods received is highlighted in the invoice, the following entry is made:
D19 K60
— the amount of input VAT on accepted goods. As you already know, input VAT recorded on account 19 can be deducted.
Payment of the supplier's invoice is reflected in accounting as follows:
| D60 K51 - supplier’s invoice paid by bank transfer |
| D60 K50 - supplier’s invoice paid in cash |
Goods in trade organizations can be accounted for at purchase prices - this procedure is used in wholesale and retail trade organizations, and at sales prices - this procedure can be used for retail organizations that sell goods at a premium. The method of valuing goods is determined in the accounting policy of the organization.
If goods are accounted for at sales prices, upon receipt of goods, together with the previous ones, the following entry is made:
D41 K42
- the amount of the trade margin. The size of the trade margin is determined by the internal documents of the organization.
It should be noted that account 42, in which information about the trade margin is stored, is a contractual account to account 41. That is, the trade margin is not reflected in the organization’s balance sheet, it only reduces the indicator of account 41. Therefore, the balance sheet indicators of the balance of goods for account 41 in the organization’s balance sheet contain information about goods at purchase prices. On account 42, in addition to markups, discounts on the cost of goods can also be taken into account.
Accounting with the seller (transfer of ownership upon payment)
Postings to account 45:
- Debit 45 Credit 43 or 41 - Finished products or goods shipped to the buyer.
- Debit 45/VAT or 76/VAT credit 68/VAT - VAT has been accrued for shipped products. (VAT is accrued since VAT must be accrued to the buyer on shipments). (In 1c, to account for VAT on shipped goods, an account is provided 76/OT)( 76/VAT is reflected in the balance sheet in the line other current assets.)
- Debit 51 Credit 62-Payment received from buyer.
- Debit 62 Credit 90-1-Accrued revenue from sales.
- Debit 90-2 Credit 45-Write off the cost of finished products or goods.
- Debit 90-3 Credit 76/VAT or 45/VAT - VAT reflected.
Example:
01/01/2019-Shipped goods to the buyer in the amount of 100,000 rubles at cost. The sale price is 150,000 rubles. Wh VAT
01/15/2019-The buyer paid the invoice.
Transfer of ownership of the goods after payment.
Solution:
01,01,2019:
1) Debit 45 Credit 41-100,000 rubles - The cost of shipped goods has been written off.
2) Debit 76/VAT Credit 68/VAT-25,000 rubles (150,000/120*20) - VAT is charged on goods shipped.
15,01,2019:
3) Debit 51 Credit 62-150,000 rubles - Payment received from the buyer including VAT.
4) Debit 62 Credit 90-1-150000 -Proceeds from the sale are reflected.
5) Debit 90-2 Credit 45-100,000 rubles - Cost of goods sold is written off.
6) Debit 90/VAT credit 76/VAT-25000 VAT is reflected.
Examples of transactions and postings on account 45
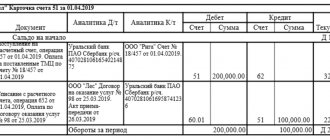
Example. Accounting for goods accepted for commission under account 45
Let’s say that LLC “Leto” and LLC “Vesna” entered into a commission agreement for the sale of goods with a cost of 30,000 rubles. According to the terms of the agreement, the selling price of goods is 59,000 rubles, incl. VAT – 9,000 rubles, and commission – 10%.
In the accounting of Leto LLC, the following entries are made to account 45 for accounting for consignment goods:
| Dt | CT | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 45 | 41 | 30 000 | Goods shipped | TTN, Invoice |
| 76 | 68 VAT | 9 000 | VAT calculation | TORG-12, Invoice |
| 76 | 90.01 | 59 000 | Reflection of sales proceeds | Commissioner's report + primary documentation |
| 90.02 | 45 | 30 000 | Write-off of cost of goods sold | Bank account statement, Accounting certificate |
| 76 | 68 VAT | 9 000 | VAT (reversal) | Invoice |
| 90.03 | 68 VAT | 9 000 | VAT accrual on revenue | |
| 51 | 76 | 59 000 | Receipt of funds from Vesna LLC | Bank statement |
| 44 | 60 | 5 000 | Calculation of remuneration for Vesna LLC | Certificate of completion of work, Invoice |
| 19 | 60 | 900 | VAT on remuneration is taken into account | |
| 68 VAT | 19 | 900 | Tax deduction | Invoice, Accounting statement, Purchase book |
| 60 | 51 | 5 900 | Remuneration has been paid | Payment order |
| 90.02 | 44 | 5 000 | Write-off of the remuneration amount | Certificate of completion |
| 90.09 | 99 | 15 000 | Reflection of the financial result from the sale of goods (profit) | Accounting information |
Add a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Find out how your comment data is processed.
Accounting for the buyer during the transfer of ownership upon payment.
Postings:
Debit 002 Credit NO - Goods accepted, ownership of the goods has not been transferred to the buyer
Debit 60 Credit 51-Payment to supplier.
After payment:
Credit 002-Goods written off from off-balance account after payment
Debit 41 Credit 60/01 - Ownership of the goods has passed to the buyer.
Example: The cost of purchased goods is 120,000 rubles (including VAT). Transfer of ownership after payment.
- Debit 002 (inventory accepted for safekeeping) - 120,000 rubles - The goods arrived, the ownership of the goods was not transferred to the buyer
- Debit 60 Credit 51-120,000 rubles - Payment to supplier
- Credit 002-120000 rubles - Goods written off from account 002
- Debit 41 Credit 60-100,000 rubles (120,000/120*100) - Ownership of the goods transferred to the buyer
- Debit 19 Credit 60-20,000 rubles (120,000/120*20) - VAT on purchase.
Barter using account 45
Usually in barter transactions (barter is the mutual exchange of goods and services without the use of cash payments). Until you receive goods (MPS) in exchange for your products transferred to the supplier, the products will be listed on account 45.
Postings:
- Debit 45 Credit 41 (43) - Goods were transferred by barter (goods were not received in return).
- Debit 76/VAT Credit 68/VAT – VAT on shipment is reflected
- Debit 41 (or 10) Credit 60-Goods received
- Debit 19 Credit 60-VAT from purchase.
- Debit 62 Credit 90 - Revenue reflected
- Debit 90 Credit 45 - Cost of goods transferred is written off.
- Debit 90 Credit 76/VAT – VAT on sales
- Debit 60 Credit 62-Offset has been made.
Example:
Condition:
The cost of goods received is 120,000 rubles (including VAT 20%), the cost of goods transferred is 50,000 rubles. Barter
Solution:
On the date of shipment:
- debit 45 Credit 41-50,000 rubles.
- Debit 76/VAT credit 68/VAT-20,000 rubles (120,000/120*20). Date of receipt of goods:
- Debit 62 Credit 90-1-120000 rubles - Sales of goods are reflected.
- Debit 90-2 Credit 45-50,000 rubles - The cost of goods has been written off.
- Debit 90/VAT credit 76/VAT-20,000 rubles-VAT
- Debit 41 Credit 60-100,000 rubles (120,000*120*100)
- Debit 19 Credit 60-20,000 rubles (120,000/120*20) - VAT on goods received.
- Debit 60 Credit 62-120,000 rubles OFF mutual claims.
Account 45 in accounting
Account 45 in the chart of accounts is active, therefore, the shipment and transfer of goods or finished products to commission is reflected as a debit, and their cost as a credit:
Goods are accounted for at cost, which includes:
- actual production cost;
- expenses for shipping products or goods, partial write-off.
Analytical accounting for account 45 is carried out according to:
- types of products or goods shipped;
- their location.
WIRES:
- Debit 45 Credit 10-Materials shipped to customers. (with special condition of transfer of ownership)
- Debit 45 Credit 20 - The cost of work for which sales revenue for which temporarily cannot be determined has been written off.
- Debit 45 Credit 21- Semi-finished products are shipped, upon payment the moment of transfer of ownership.
- Debit 45 Credit 41-Goods shipped to the buyer, the moment of transfer of ownership after payment.
- Debit 45 Credit 43 - Products are shipped to the buyer, the product is ready, the moment of transfer of ownership after payment.
- Debit 45 Credit 44 - Expenses associated with the sale of goods and finished products are written off.
- Debit 45 Credit 71-Reflected expenses associated with the sale of products. (Advance report document)
- Debit 90-2 Credit 45-Write off the cost of shipped products or goods after the transfer of ownership.
- Debit 94 Credit 45-Reflected shortage of goods shipped.
- Debit 99 Credit 45 - The cost of finished goods is written off after emergency circumstances.
- Debit 76 Credit 45-Write off at the expense of the insurance company, goods shipped
Postings on account 45
Account 45 “Goods shipped” is intended for accounting for goods sold, the revenue for which is recognized later than the moment of shipment. Such situations are possible during export operations, under commission agreements or during transfer without registration of ownership.
Account 45 is active. The cost of goods recorded on the account consists of the actual cost and shipping costs. Accounting on this account is carried out in the context of location (storage) and objects.
Fragment of the approved Chart of Accounts, Section 4, Finished products and goods