Author: Ivan Ivanov
Legislation officially adopted in the modern civilized world requires that the workplace of every employed citizen meets standards that monitor safety, as well as protect life and health. The Russian regulatory framework in this aspect is represented by the Labor Code, regulations adopted by the Ministries of Labor and Education, as well as a number of sectoral legal acts.
How often should labor safety instructions be reviewed?
In general, the frequency of revision of labor protection instructions is at least once every 5 years. For electric power enterprises, the standard period is once every 3 years, which can be explained by the increased risk of electric shock to workers.
The validity period of IOT labor safety instructions is valid as long as the employee has a need for it. This means that the life cycle is not limited to any specific period of time.
There are no mandatory requirements establishing a planned period for checking labor safety instructions. This means you can do it more often, but you can’t do it less often. If there are instructions for working with a hammer, then the requirements for the worker may be revised, but the process of working with this impact hand-held plumbing and assembly tool remains the same as a hundred years ago. The requirements for the employee must be specified in this document, therefore, if changes in legislation occur, a corresponding change must be made. If years later it will be possible to work with a hammer only for persons over 21 years of age, then such a requirement is indicated in the IOT no later than the day it comes into force.
Example. Let’s say that from July 1, 2031, changes will occur in the legislation on labor protection when working with a hammer - only persons under 50 years of age will be able to work with it. If the Rules come into force on July 1, 2031, then the employer is obliged no later than July 1 to familiarize the employee with these changes by conducting an unscheduled briefing on the already updated IOT. If the employee is notified of this change not on July 1, but, say, on July 12, and during this period of time an accident occurs with an employee over 50 years old, the employer will bear administrative liability under Part 1 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Requirements before starting activities
The instructions section “Labor safety requirements before starting work” outline the following procedure:
- Preparation of the workplace along with personal protective equipment.
- Checking the serviceability of equipment, and in addition, all kinds of devices and tools, fencing, alarms, blocking and other devices, protective grounding, ventilation, local lighting, etc.
- Performing inspection of source material (blanks, semi-finished products).
- Reception and transfer of shifts in the case of a continuous technological process and work on equipment.
The section entitled “Requirements during operation” recommends the following:
- Methods with techniques for safely performing activities along with the use of equipment, vehicles, lifting mechanisms, tools and devices.
- Requirement for safe handling of source materials (raw materials, blanks, semi-finished products).
- Instructions for the safe maintenance of workplaces.
- Actions that are aimed at preventing certain emergency situations.
- Requirements for the use of personal protective equipment for employees.
Early revision of labor safety instructions
The guiding document is the Methodological Recommendations of the Russian Ministry of Labor for the development of IOT dated May 13, 2004. They determine how often labor safety instructions are revised: the employer is obliged to do this ahead of schedule if there are changes in the rules on occupational safety and in standard IOT, taken as the basis for local ones. Also, paragraph 7 of these methodological recommendations states that if the working conditions of workers change, the instructions should also be amended.
This does not mean that if the UT class has changed from 3.2 to 3.3, it is necessary to cancel or change the current document. This means that if a worker, instead of semi-automatic welding, now works on a manual machine, then he needs to be familiarized with IOT for manual welding. When introducing new equipment and technology, the instructions must change accordingly. If the old equipment is dismantled, then it is necessary to remove the old one from use and issue a new IOT. The new one must be accepted and given to the employee for review before the employee starts working on the new equipment.
The State Traffic Safety Inspector may order a review after an accident. The employer has the right to make such a decision independently, after analyzing the investigation materials, if it turns out that the IOT material is presented formally and does not have a significant impact on ensuring the safety of workers.
Its purpose and basics
Many instructions on labor protection have been issued for representatives of any profession, in addition, for a certain type of each work. It’s no secret that the same profession involves a variety of operations (an example from the field of welding - it can be electric arc, electron beam welding, etc.).
The basis for their development is interindustry rules, standard instructions, requirements given in the technical documentation for equipment supplied by the manufacturer. The conditions of each specific production must be taken into account.
Before their development, the employer, by order, draws up a list of jobs and professions for which they are written. In this case, the staff schedule must be taken into account.
Revision of occupational safety instructions
Employers underestimate the importance of developing occupational safety instructions. Often this is carried out by the labor protection service, and department heads simply sign them at the request of specialists.
If an accident occurs to an employee, the inspector will check how the employee was instructed on labor protection when performing a specific type of high-risk work. If the IOT does not set out the rules for safe work or makes reference to outdated safety standards, the inspector will consider the employee’s training to be formal. This will seriously worsen the employer's position. Therefore, pay close attention to both the development of the IOT and its periodic checking for relevance during the period of validity.
What does it say?
The content of the instructions must consist of specific requirements for the normal operation of the equipment, each of the technological processes, as well as general conditions for safe operation. It regulates the optimal labor techniques and methods in this regard, as well as the order of their implementation.
An instruction is drawn up with the participation of the management of each of the structural divisions and approved with the obligatory approval of persons representing trade unions or other competent bodies.
It is put into effect (i.e. declared mandatory for each employee) from the date of signing.
Review procedure
Attention! Responsibility for compliance of local acts with legal requirements lies with the labor protection service. Responsibility for compliance of the labor protection instructions with the requirements of the operating manual lies with the developer of the instructions - a technical specialist or manager.
An order approving changes to the IOT must be drawn up before the change in legislation comes into force. The employee must be promptly informed of the changed safety requirements. Local acts are amended in the order of their adoption. If the IOT was introduced by order, then it must also be amended or canceled by order.
When changing an occupational safety specialist, is it necessary to review and re-approve the occupational safety instructions? What is the procedure for agreeing on old instructions with a new specialist? There is no need for revision in this case, but a new specialist, having found significant violations in existing instructions, must revise them. This is the decision of the specialist himself.
Is it necessary to replace the instructions on labor protection (planned revision of the instructions in 2021) when changing the name of the organization? What legal act should be followed in this situation? Despite the name change, the organization remained the same, so orders and other administrative documents can be replaced with new ones gradually - when changes need to be made to them.
The legislative procedure for making changes to local regulations in connection with changing the name of an organization is not prescribed. In this case, during the transition period, it is advisable to issue an organizational and administrative document (order) stating that, for example, labor protection instructions (list them) continue to be valid until they are revised.
What should you pay attention to when developing instructions?
When compiling this document, it is recommended to adhere to the structure established by the recommendations; in particular, it is necessary to include a section called “General Requirements”. This reflects the instructions on the need to comply with internal regulations, as well as the following:
- Requirement to implement a rest and work regime.
- List of dangerous and harmful factors that can affect employees during work.
- A list of special clothing, shoes and other personal protective equipment that are issued to employees in accordance with established standards and rules.
- The procedure for notifying the administration regarding cases of injury to employees and malfunction of devices, equipment and tools.
- Rules of personal hygiene that a citizen should know about while performing work.
Next, we will look at additional sections of the instructions.
Extension of the validity period of labor protection instructions
Earlier in this article, we determined that there are no regulatory deadlines for revising IOT, there are only Methodological Recommendations. But there is also a requirement in Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes the obligation for the employer to inform the employee about the conditions and labor protection in the workplace.
Inspections of labor safety instructions are carried out at least once every five years, and for professions and work with increased danger - at least once every three years.
If during the specified period the working conditions in the workplace and the requirements of regulatory legal acts, technical regulatory legal acts used in drawing up the instructions have not changed, then the validity of the instructions can be extended for a new period.
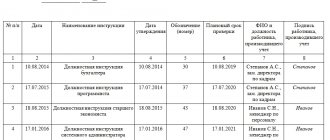
In this case, by order of the organization, the validity of the IOT is extended for the next period, about which a note is made: “Validity period extended. Order dated __ N __" on the first page of the instructions. You can do this twice after revision.
Contents of the instructions
Contains the procedure for the employee before starting work.
The material reflects the conditions for accident-free and safe organization of the technological process, including the use of tools that comply with safety regulations, the use of personal protective equipment by the employee, and every detail must be taken into account.
To do this, before issuing instructions, it is necessary to carefully study the route of the technological process. This is necessary for the manager; if an employee violates safety requirements, then it is possible to find a link to what he did incorrectly.
The contents of the instructions cover:
- general provisions. Here is a list of regulatory documents adopted at the state level, as well as existing standards at the enterprise. The list of the latter is necessary so that there is no information contrary to current standards.
It is also necessary to indicate training, internship and rules for admission to the employee’s workplace. It is equally important to know in what cases an employee should not be allowed to perform production tasks;
- The following is a statement of requirements before starting work. This describes what the employee must do before starting work.
How to compose a document
The order is drawn up by the employee responsible for labor protection in the organization. There is no legally approved form for the document, so a free one is used. But a certain structure must be followed. The order must indicate the following information:
- the name of the company or enterprise (the document is printed on the company’s letterhead, so it is assumed that the details will also be there);
- title of the document, its essence;
- date and place of creation;
- the basis for extending the validity period of the instructions;
- positions for which instructions are being extended;
- who is responsible for monitoring the execution of the order;
- signatures of the manager and responsible employee.
For your information! In large organizations, instead of the manager, an authorized employee, for example, his deputy, can sign.