Safety precautions: basic concepts
Occupational safety instructions for technicians, road workers and other workers are an internal document that defines the specific responsibilities of workers and prescribed safety requirements.
Basic safety rules
In 2021, several types of guidelines have been established, including:
- by specialization and position. For example, specially developed internal instructions for the security department or for the cook;
- with the rules of conduct of personnel in the event of an emergency, this is relevant if any test is being carried out;
- setting up new mechanisms and other production equipment, repairs in explosive areas, or for employees to prevent terrorist acts, emergency workers (in the event of a fire or other emergency) performing specific work at height, for office specialists (any office must have appropriate instructions that meets the requirements of GOST).
Compliance with developed and approved regulations is a mandatory condition for everyone, and ignoring them entails a violation of labor discipline.
Conducting briefing
Important! The document may include rules for conducting training if necessary.
Where to start
Before you begin to draw up labor safety instructions, you need to understand an important point: this document is not a summary of the equipment operating manual or a list of employee responsibilities.
It should describe how to perform the work without risking health and sometimes life.
If an employee, after reading the instructions, has a complete understanding of the safety requirements that apply specifically to him, then the document is drawn up correctly.
There is no point in rewriting standard instructions because they only contain general safety requirements. The specifics of a particular enterprise are not reflected in them.
To create useful instructions that take into account the requirements of current legislation, you need to do some preparatory work.
At the preparatory stage you:
- find the standard instructions you need in the NPD databases (and not just on the Internet) and study it: it will serve as your basis;
- find out from the head of the department what equipment and materials the employee has to work with and what tasks to perform;
- Please pick up the instruction manuals for the equipment you are using and carefully read the “Safety Requirements” section. You shouldn't be concerned with how to operate the equipment: your job is to figure out how to do the job safely;
- study the rules for handling hazardous substances, if any are used during the work process;
- analyze the results of workplace certification (based on working conditions), if it was carried out at your enterprise;
- identify harmful or dangerous factors that are typical for this type of work (or profession) in normal and emergency modes of operation. What means of protection can be used against them? What measures can be taken to prevent them?
- Find out whether there have been accidents at this workplace before. Bring up the correspondence, orders and orders, resolutions of regulatory authorities issued in this regard;
- select personal protective equipment. Capable of protecting the employee in emergency situations and normal operation.
Having thus thoroughly prepared, you can begin writing instructions.
Who develops standard instructions and their purpose?
Workplace safety briefing
The responsibility for drawing up the document rests with the immediate superiors of the company’s structural divisions, since they are the bearers of all the necessary information regarding the working conditions of each individual worker.
The developed instructions are subject to further approval by the company management. It is approved by the relevant order after preliminary agreement with the trade union.
There is an opinion that the development of rules is carried out by the labor protection service or their specialist. However, it is not. Their main responsibilities are:
- control;
- verification;
- approval of the drawn up instructions.
An example of safety rules in a computer science classroom
In addition, they can provide methodological assistance to the compiler in order to comply with GOST requirements and federal legislation.
Types of briefings
Instruction happens:
- introductory (conduct with newly hired employees, trainees seconded to the organization and other persons who are accepted for permanent or temporary work);
- primary (carry out before starting independent work);
- repeated (carry out at least once every six months according to programs developed for initial instruction in the workplace);
- unscheduled (carry out in case of any changes, for example, if new legislation on labor protection appears or technological processes change, etc.);
- targeted (conduct with employees in cases where they need to perform one-time work, eliminate an accident, natural disaster or their consequences, etc.).
These types of instructions are established in paragraph 2.1 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1, Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
The introductory briefing must be conducted by a labor protection specialist or an employee who has been assigned these responsibilities by order of the head of the organization.
Primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted briefings must be carried out by the employee’s immediate supervisor (foreman, foreman, teacher, etc.), who has undergone special training in labor safety.
Situation: how to properly conduct induction training for employees?
To begin, the occupational safety officer (or other employee assigned these responsibilities) must:
- develop and approve an induction training program with the head of the organization;
- compile manuals for employees on labor protection rules in the workplace;
- prepare handouts.
Then, according to the established program, the specialist gives a lecture to employees. The induction program usually includes the following questions:
- familiarity with local regulations and instructions on labor protection;
- actions in case of dangerous situations;
- rules for using personal protective equipment;
- methods of application and location of fire extinguishing means;
- providing first aid to victims;
- causes of accidents, fires, accidents and measures to prevent them.
At the end of the instruction, conduct an oral test of knowledge and skills of safe work practices.
Approve the induction program in a separate document. There are no requirements for what kind of document this is in the current legislation. Therefore, you can draw up, for example, instructions for conducting induction training.
Situation: is it possible not to conduct initial training on labor protection if employees work exclusively in the office?
No you can not.
Instruct all employees on labor protection, even those who work in the office (Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1.1 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 of January 13, 2003, Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation No. 29). Injuries in the workplace can result from careless handling of electrical appliances and computers.
Explain the following occupational safety rules to office employees.
First, the rules for using electrical appliances:
- how to properly turn on and off computers, printers, copiers;
- what not to do to prevent the wiring from burning out and the devices from malfunctioning.
Secondly, rules of conduct in the workplace:
- do not appear at the workplace in a state of intoxication;
- do not eat food at work places - special premises should be designated for this;
- maintain order in the workplace - clutter can lead to injury;
- do not smoke in workplaces.
Thirdly, the rules for providing first aid to victims.
However, some employees may be exempt from initial on-the-job training. These are employees whose activities are not related to the operation, maintenance, testing, adjustment and repair of equipment, the use of electrified or other tools, the storage and use of raw materials. The list of professions and positions of employees exempt from undergoing initial training at the workplace should be approved at the local level. Such rules are established in paragraph 2.1.4 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1, Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
Basic filling requirements
Safety Engineer: Responsibilities
The corresponding instructions (for example, instructions on labor protection for an electrician or electrician, etc.) must be developed according to a clearly defined sequence of actions:
- Issuance of an order indicating the position held and the type of job duties for which appropriate instruction is required. This list is subject to further approval.
- Heads of workshops, sections or foremen are engaged in the responsibilities assigned to them in developing instructions.
- The created project is coordinated with the trade union for compliance with the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation.
- After preliminary approval, the layout is subject to approval by the management of the enterprise. On the title page it is necessary to indicate: the full name of the company, the date of preparation, information about the responsible person who approved the instructions.
- Hired staff, under personal signature, must be familiar with all documentation on labor protection, including: during initial employment, transfer to another position, changes to the initially developed instructions.
- At the next stage, data regarding the rules must be entered into the appropriate logbook for labor protection, for example, at school, and safety in accordance with the norms of the Letter of the Ministry of Labor and other norms of federal legislation.
A typical example of instructions for a mover on duty
Note! The rules are contained in the operating and repair manuals of equipment manufacturers, including technological documentation of a particular enterprise. In addition, specific production conditions are taken into account.
When developing, it is imperative to refer to materials about accidents that occurred at the enterprise. It is necessary to focus on two facts: to exclude repetitions and administrative liability with all the ensuing consequences.
Why do you need occupational safety documentation?
The key objective of a set of local labor protection documents is to create healthy and safe working conditions in the workplace. Safe working conditions are the key to protecting the health and lives of employees. Of course, minimizing or completely preventing accidents during work is not an easy task. Simply downloading documents from the Internet with appropriate titles and standard content before the inspector arrives will not help here. This requires competent and qualified compilation of the required labor protection package in proportion to the types of activities performed. Local regulations and legal acts must not only be kept in the organization, but their content must be constantly guided during work.
The next task that can be solved if you have up-to-date and workable safety documentation is optimizing the organization’s expenses on labor protection. It can be done:
- by establishing a minimum (but sufficient) level of free provision of personal protective equipment to personnel;
- by determining an economical (but adequate) volume of periodic medical examinations of personnel;
- by minimizing or completely eliminating the impact of harmful factors in the working environment on employees (when conducting a special assessment, it will allow us to establish an acceptable class of working conditions and will exempt us from paying additional insurance premiums, as well as from the need to establish additional guarantees and compensation for employees);
- having fulfilled all current legal requirements (which guarantees the absence of administrative fines after inspections by the state labor inspectorate).
It should be noted that the presence in the organization of a set of labor protection documents that meets all current legal requirements is a primary aid for successfully passing inspections. The fact is that the absence or imperfection of safety documentation is the most common basis for imposing administrative fines on employers. This is primarily due to the vastness and versatility of the existing legislative framework, the accounting and correct application of which requires the knowledge and experience of qualified specialists. In accordance with this, even the State Inspectorate began to place more emphasis on documentary inspections, significantly reducing the number of on-site inspections. Inspectors only need to request from the employers being inspected an appropriate package of documents, which, as a rule, reveals a number of shortcomings. Identified inconsistencies serve as sufficient grounds for the imposition of a substantial administrative fine without the need for an inspector to travel directly to the territory of the organization being inspected.
Why is the absence or inadequacy of occupational safety documentation the most common violation?
The regulatory legal framework is very extensive. There is no single set of legal requirements that could apply to each specific employer. This is, of course, due to the heterogeneity of the types of activities carried out by employers, the services provided, the technological processes and equipment used.
In order to determine the list of applicable requirements for each specific organization, it is necessary to refer to the huge variety of existing rules, orders and regulations of various ministries, federal services and departments. Not every occupational safety specialist can do this. And there is no need to talk about the heads of companies, burdened with much more important and urgent management and strategic tasks, provoking a constant shortage of free time.
But still, due to the need to save wages, many company owners make the following decisions:
- Work independently (including documentation development). But due to a chronic lack of time, they cannot pay due attention to this issue.
- Assign responsibility to one of the regular employees (who do not have the relevant experience and qualifications in this area). Naturally, the quality of performance of this function by this employee leaves much to be desired.
- Hire a specialist who would be satisfied with (to put it mildly) a not very high salary level. As practice shows, such specialists (without justified salary ambitions) either do not have enough experience or do not plan to put the necessary effort into their work.
Each of the above situations in the vast majority of cases leads to poor performance of labor protection duties (including the preparation of documents), which provokes the imposition of administrative penalties.
Why is it beneficial to seek help from specialized companies?
Firstly, it is more economical. Even having found a sufficiently experienced and “inexpensive” specialist to join its staff, the employer will ultimately spend significantly more on his maintenance. To develop all the necessary documentation (provided it is up to date and operational), a full-time occupational safety specialist will need several months, during which he must be paid a salary.
Secondly, hiring a reputable specialized company means guaranteed quality of the final result. Contractors who value their reputation will make every effort to satisfy the Customer’s requests. Moreover, you can always apply for further (ongoing) labor protection support, which guarantees your organization the qualified and timely completion of all work not only on safety precautions, but also on civil and emergency situations, ecology and industrial safety.
What is the mandatory minimum for labor protection in every organization?
The entire set of mandatory local labor protection documents can be systematized into three groups:
- Orders and plans.
- Regulations, lists, programs and lists.
- Instructions and magazines.
| Document's name | Base |
| Group 1 | |
| Event plan | Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated March 1, 2012 No. 181n |
| Order on assignment (distribution) of responsibilities | Article 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Order on the organization of training and on the formation of a commission to test the knowledge of workers | Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Ministry of Education of Russia dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29 |
| Order on the appointment of persons responsible for instructing employees | GOST 12.0.004-2015 |
| Order on the appointment of responsible persons for the safe operation of equipment, buildings, structures, etc. | Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Order on the appointment of persons responsible for fire safety | Rules of the Russian Federation PPR dated April 25, 2012 No. 390 |
| Order on the establishment of a certification commission for electrical safety | PTEEP dated January 13, 2003 No. 6 |
| Group 2 | |
| Regulations on the occupational safety and health management system (OSMS), which includes the following sections: — regulations on medical examinations; — provisions on providing workers with PPE; — regulations on the organization of training. | Article 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation; Order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation dated August 19, 2016 No. 438n. |
| Induction program | Resolution No. 1/29 |
| Initial Instruction Program | Resolution No. 1/29 |
| Training program for specialists and blue-collar workers | Resolution No. 1/29 |
| Program for assigning Group I in electrical safety | PTEEP |
| List of PPE required for employees; List of professions for which the issuance of PPE is provided | Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated 01.06.2009 N 290n; Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. |
| List of high-risk works | POT RO 14000-005-98 |
| List of flushing and neutralizing agents required by employees | Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated December 17, 2010 No. 1122n |
| List of professions that require electrical safety group I; List of professions that need to have electrical safety group II and higher | PTEEP |
| List of contingents of employees subject to mandatory medical examinations | Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 12, 2011 No. 302n |
| Name list of employees subject to PMO | Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 12, 2011 No. 302n |
| Group 3 | |
| Safety instructions for all available worker professions and types of work | Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Instructions on the fire safety regime in the organization and on the prescribed actions of workers during a fire | Rules of the Russian Federation PPR dated April 25, 2012 No. 390 |
| Logs: — results of induction training; — initial and repeated instructions in the workplace; — fire safety instructions; — registration of injury cases; — accounting for the assignment of group I for electrical safety | GOST 12.0.004-2015; NPB 645-2007; PTEEP |
What administrative penalties are provided for the lack of local labor protection documentation?
The absence of labor protection documents deprives the employer of the opportunity to confirm the implementation of mandatory measures in accordance with Article 5.27.1. The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation may entail the imposition of the following penalties:
- For failure to comply with established standards:
- for individual entrepreneurs and responsible persons - from 2000 to 5000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 50,000 to 80,000 rubles.
- For allowing uncertified workers to work, or without undergoing a medical examination:
- for individual entrepreneurs and responsible persons - from 15,000 to 25,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 110,000 to 130,000 rubles;
- For failure to provide employees with PPE:
- for individual entrepreneurs and officials - 20,000 to 30,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 130,000 to 150,000 rubles.
What sections should be in the TB instructions?
Health and Safety Inspector
Instructions for occupational safety in preschool institutions or drivers while a vehicle is moving, sanitary workers and other workers should include the following typical sections:
- general explanations;
- occupational safety requirements directly during the execution of work, for example, maintenance of energy systems (rules for working in the contact group of high-voltage networks);
- primary actions in case of an accident and other emergencies;
- occupational safety requirements upon completion of work for a particular category of workers, for example, a specialist in the manufacture of workpieces or a group.
Important! The company's management reserves the full right to supplement the typical instructions if necessary, if this does not contradict the rules of federal law.
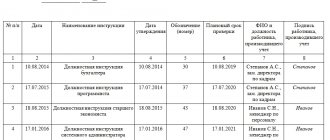
Procedure for keeping a TB journal and sample filling
According to federal legislation, each individual enterprise must maintain a specialized safety journal.
The registration procedure is standard, but you need to know some features. Among them it is customary to highlight:
- the registration log of briefings is a stationery book in A4 format, which was developed in accordance with the requirements of GOST and is in the public domain;
- all sheets, without exception, must be numbered and certified by the signature of the enterprise management, if present with a seal;
- The title page must include the following important data: full name of the organization, name of the instructed structural unit, start and end dates of maintenance.
For convenient systematization, it is strongly recommended to create a registration log separately for each specific type of instruction. At a minimum, this will greatly simplify the work.
For your information! Instructing and filling out a specially designed log is assigned to the immediate supervisor or safety engineer. The authorized responsible person must have a certificate confirming his authority. Training for this takes place every five years.
The sample and form of keeping a TB journal are established by federal legislation.