Definition of the designated category and its classification
In trade relations, goods are the key subject of purchase and sale. The very concept of the designated term has many aspects and includes:
- functional purpose;
- aesthetics, both of the item of purchase and sale, and of its packaging;
- harmlessness and safety in use.
Thus, this item of trade is the result of an activity, including the situation when it comes to performing work or providing services, which is an item of sale or exchange.
Within the framework of market relations, everything that can represent the object of a transaction concluded between sellers and buyers is perceived as the designated subject of a transaction.
If we talk about this category in a broader sense, then it refers to tangible and intangible property sold on the market.
As an object of commercial activity, a product for subsequent sale has the following specific features:
- quality characteristics;
- quantitative;
- valuation;
- range.
The key elements of the designated item of purchase and sale are:
- its physical and consumer characteristics;
- related products;
- brand;
- appropriate packaging;
- related types of services;
- guarantee period.
In practice, all products are divided into the following groups:
- material - a material group, which includes property that has a physical embodiment;
- a group of intangible goods that can include various services and consultations.
Reflection of revenue and accounting for markups in 1C
After completing all the previous steps, the “Products” account and its quotes will open. To reflect revenue from retail trade, you need to open the “Bank and cash desk” sub-item “Cash documents” in the main menu of the program and create a new receipt order as follows:
- Designate the type of transaction: “retail revenue”.
- Fill in the fields: date, payment amount (select “excluding VAT”).
- Post the document.
After viewing the transactions made on the account, you need to go to the “Operations” item, sub-item “Month closure”. In the menu that opens, select the closing month and the item “Calculation of trade margins on goods sold.” Account entries will show that the markup has been written off. Returning to the “Month Closing” menu, select the “Write off trade margin on goods sold” item, after which the trade margin report on goods sold for the selected month will open.
An example of total accounting of goods was considered using the 1C: Accounting 8.3 (rev. 3.0) program.
Organization of warehouse accounting
All products for subsequent sale, as a rule, are combined into a certain accounting group, which is assigned a certain general name, for example, inventory items.
The specified category of products is already in finished form and intended for further sale and is, in fact, a product.
Accounting for objects of sale and purchase in a warehouse occurs at their actual cost. To reflect products in the warehouse in accounting, 41 accounts and its subaccounts are used. If an organization carries out retail trading activities, then the need arises to use 42 accounts.
Accounting in trade
The exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of shipment (June 2, 2006) was 26.29 rubles, and on the day of payment - 26.47 rubles. (as of June 11, 2006 ᴦ.). The following entries will be made:
June 2, 2006 ᴦ.: DT41 KT60 2760.45 rub. (200 pcs. * (0.62-0.095) * 26.29) – the cost of the goods is reflected based on the exchange rate of a conventional unit valid on the date of shipment and DT19 KT60 499.55 rubles. (200 pcs.*0.095*26.29) – VAT is allocated on the received goods.
June 11, 2006 ᴦ.: DT60 KT51 3282.32 rub. (200 pcs.*0.62*26.47) – paid for the supply of peas, DT91 KT60 18.92 (200 pcs.*(0.62-0.095)*(26.29-26.47) – negative amount difference reflected and DT19 KT60 3.4 rubles - VAT allocated on the negative amount difference.
Account 44 “Sales expenses” reflects the organization’s expenses associated with the sale of products, goods, works and services.
For organizations engaged in production activities, account 44 reflects non-operating expenses associated with packaging products, delivery of finished products to the place of departure, loading, commission fees, costs associated with storage, remuneration of sellers, advertising, entertainment expenses, marketing expenses, etc. .
Selling expenses in trade organizations include the following items:
- Transportation costs, including transportation, storage, unloading;
- Labor costs;
- Unified social tax;
- Expenses for rent, maintenance of buildings and structures;
- Depreciation of fixed assets;
- Expenses for repairs of basic facilities;
- Expenses for fuel, gas, electricity, for production needs;
- Expenses for storage, part-time work, packaging, sub-sorting;
- Advertising expenses;
- Expenses for paying interest on loans received;
- Loss of goods and process waste;
- Costs for packaging;
- Other expenses.
The above expenses, in addition to transportation costs, are written off to the cost of products sold, and transportation costs are distributed between the goods sold and the balance of goods at the end of the month at an average percentage.
Example: The amount of transportation expenses for the month was 1000 rubles. (without VAT). Other sales expenses amounted to RUB 2,000. Goods worth 60 thousand rubles were purchased for resale. (without VAT). Products sold for 20 thousand rubles. Determine the amount of sales expenses written off in the reporting period.
The share of transportation costs in sales costs is: 1000*100%/(20000+40000)=1.67%.
Transport costs for the balance of goods: 40,000*1.67/100=668 rubles.
Transport costs for goods sold: 1000-668=332 rubles.
Selling expenses written off in the reporting period: 2000+332=2332 rubles.
Goods that do not belong to the organization and are in custody, the commission is taken into account in accounts 002 and 004.
Account 45 “Goods shipped” takes into account information about the availability and movement of shipped products (goods).
If revenue from the sale of shipped goods and finished products cannot be recognized in accounting for a certain time (when exporting goods), then until the revenue is recognized (before the transfer of ownership rights) the goods are recorded in account 45. In this case, an entry is made Dt 45 Kt 43 , 41. At the time of revenue recognition, an entry is made
Dt 90.2 Kt 45.
Basic accounting entries
In accounting, typical entries for this position are as follows:
1) Dt 41
Kt 15 – acceptance of products on the balance sheet at the discount price;
2) Dt 41
Kt 60 – invoices payable to suppliers for products for resale;
3) Dt 41
Kt 68 – inclusion of accrued VAT in the cost of products;
4) Dt 41
Kt 71 - accounting for products purchased by an accountable person for resale;
5) Dt 41
Kt 73 - accounting for goods that were reimbursed by individuals, etc.
D 41 to 60 primary document
When an organization engaged in retail trade records goods at sales prices, simultaneously with this entry, an entry is made to the debit of account 41 “Goods” and the credit of account 42 “Trade margin” for the difference between the acquisition cost and the cost at sales prices (discounts, markups). Transport (for delivery) and other costs for the procurement and delivery of goods are charged from the credit of account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” to the debit of account 44 “Sales expenses”. The receipt of goods and containers can be reflected using account 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets” or without using it in a manner similar to the procedure for accounting for corresponding transactions with materials. When recognizing revenue from the sale of goods in accounting, their value is written off from account 41 “Goods” to the debit of account 90 “Sales”.
VAT accrued on sales; The following entries were made in tax accounting: D90.02 K41.02 2000 rub. — the book value of goods is written off; in tax accounting this is the purchase price. DPV K90.01.2 2500 rub. — income received from sales is reflected. The document also formed movements in the following registers:
- VAT accrued;
- VAT on inventory lots;
- VAT accounting of distributed payments from buyers;
Please note that the document forms movements on account 50 - that is, it reflects the receipt of revenue at the cash desk.
Based on the Retail Sales Report document, you can enter a Cash receipt order with the transaction type Reception of retail revenue.
It should be noted that this PKO, when carried out, does not generate movements in registers - cash book entries are generated on its basis, so we must generate it.
Account 41 - goods
Before the document was carried out, this type of price for one package of wallpaper glue, which we bring to the warehouse, was set at 590 rubles. That is, 10 packages of glue will cost 5,900 rubles.
And we capitalized 10 packages at an actual cost of 4,000 rubles. 5900 - 4000 = 1900. It is for this amount that the posting D41.11 K42.01 was made. The following entry was generated in tax accounting: D41.
02 KPV 4000 rub.
- VAT presented;
- VAT settlements with suppliers;
- VAT on stock lots.
After the goods have been received, we can continue our example - we will sell them at retail.
On February 17, 2009, 5 packs of wallpaper paste were sold at retail at a price of 590 rubles. per package.
Lesson 12.6
Attention
Subaccount 41-1 “Goods in warehouses” takes into account the presence and movement of inventory located at wholesale and distribution bases, warehouses, storerooms of organizations providing catering services, vegetable storehouses, refrigerators, etc.
Subaccount 41-2 “Goods in retail trade” takes into account the availability and movement of goods located in organizations engaged in retail trade (in shops, tents, stalls, kiosks, etc.) and in buffets of organizations engaged in public catering.
The same sub-account takes into account the presence and movement of glassware (bottles, cans, etc.) in organizations engaged in retail trade and in buffets of organizations providing catering services.
Inventories, goods, finished goods
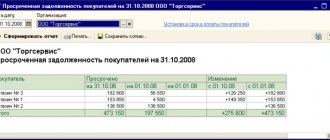
Data on retail sales of goods is entered upon the fact of sale using the document Retail Sales Report (Sales Retail Sales Report). Let us remind you that the goods sold were stored in the warehouse Warehouse in the store, which has the Retail type.
Sales of goods stored in such a warehouse are carried out using cash register equipment. Therefore, when creating the Retail Sales Report document, we select the document type as cash register.
This document can be created by selecting one of two types of operation:
- KKM - to reflect sales made using cash registers;
- NTT - to reflect sales made at a manual point of sale.
In the figure below you can see the completed document form. Let's consider the features of filling it out: Organization: Furniture maker; Cash account: 50.01; Report to tax.
D41.goods in retail trade k41.goods in warehouses
RETURN OF GOODS FROM CUSTOMERS Posting: Account D. 90 “Sales” — Account Account 41 “Goods” We arrive at the cost of goods Amount Reversal: (-1)* calculated amount (depends on the method of calculating the amount of write-off of goods, see below) Posting date: date in the invoice from the client for the sale of goods.
Note: this is one of the entries that is reflected at the time of sale of goods, its essence is to reflect the cost of products that are sold. Documents that accompany invoice 41 “Goods”: 1. Agreement of material liability with the employee.2.
An act of acceptance of goods (form N TORG-1) is drawn up in cases where there are no documents in form Torg-12 from the supplier (example: the goods were delivered from abroad or if it was brought by a transport company and only gives you a piece of luggage).3.
Act on the established discrepancy in quantity and quality when accepting inventory items (Form N TORG-2).
D 60 to 51
Amount: calculated amount (depends on the method of calculating the amount of write-off of goods, see below) Posting date: date in the invoice for the transfer of goods to the promotion Note: WE WILL write off goods transferred to departments for our own needs Posting: D.account 26 “General business expenses” - TO.
accounts 41 “Goods” If you sell household chemicals, then for example you can use soap for your own needs.
Amount: calculated amount (depends on the method of calculating the amount of write-off of goods, see below) Posting date: date in the invoice for the transfer of goods for our own needs Note: WRITTEN OFF the cost of goods upon sale Posting: Account D. 90 “Sales” (Cost) - K .
account 41 “Goods” We write off the cost of goods that were sold to the buyer Amount: calculated amount (depends on the method of calculating the amount of write-off of goods, see below) Posting date: date in the invoice for the sale of goods.
41 “goods” account
In accordance with the instructions for the chart of accounts given in the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia “On approval of the chart of accounts for accounting financial and economic activities” dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n (hereinafter referred to as the chart of accounts), Dt 41 Kt 41 is used by organizations operating in the field of:
- catering;
- trade;
- production.
Depending on the type of activity in the chart of accounts, the following recommendations are given for the use of subaccounts to account 41:
- 41.01 - to reflect information about inventory items in a warehouse or catering storerooms;
- 41.02 - for goods and materials in retail trade and public catering;
- 41.03 - for information on containers for catering and trade;
- 41.04 - for inventory items in production.
At the same time, the organization can approve its own sub-accounts that are unique to it, the use of which may differ from those recommended. Above, we looked at the scheme of entries in accounting accounts for the sale of goods at retail. You may notice that the Retail Sales Report document does not generate a reversal entry of the type D90.02 K42.
Important
This posting can be made by the document Closing the Month (Operations Regular Operations Closing the Month). As a rule, trade margins are written off at the end of the month for all goods sold.
As you can see, the document item Calculation of trade margins on goods sold is responsible for generating records for writing off trade margins. After execution, the document generated the following accounting entry: D90.02.1 K42.01 - 950 rubles. In 1C:Accounting, the reversal entry is made with a negative amount.
D41 K66) 67 Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings (D41 K67) 68 Settlements for taxes and fees (D41 K68) 71 Settlements with accountable persons (D41 K71) 73 Settlements with personnel for other transactions (D41 K73) 75 Settlements with founders (D41 K75) 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors (D41 K76) 79 On-farm settlements (D41 K79) 80 Authorized capital (D41 K80) 86 Targeted financing (D41 K86) 91 Other income and expenses (D41 K91) On the loan 10 Materials (D10 K41 ) 20 Main production (D20 K41) 41 Goods (D41 K41) 44 Selling expenses (D44 K41) 45 Goods shipped (D45 K41) 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors (D76 K41) 79 On-farm settlements (D79 K41) 80 Authorized capital (D80 K41) 90 Sales (D90 K41) 94 Shortages and losses from damage to valuables (D94 K41) 97 Deferred expenses (D97 K41) 99 Profits and losses (D99 K41) Chart of accounts Section I. Dt 41 Kt 41 may have type: Dt 41.05 Kt 41.01 (account 41.01 “Inventory in warehouse”, 41.05 “Inventory in processing”). What type of postings does account 41 involve? In order to understand the meaning of entries using posting Dt 41 Kt 41, let's look at a few examples.
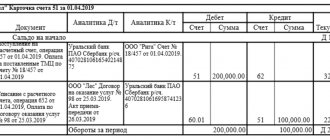
Example 1 On March 10, 2016, Luna LLC purchased goods from Zvezda LLC worth RUB 283,200. (including VAT RUB 43,200). On March 14, Luna LLC transferred the payment.
Luna LLC is engaged in retail trade. Zvezda LLC sells goods wholesale. Let's consider how the implementation of Zvezda LLC will reflect:
- Dt 62 Kt 90 - revenue from the sale of goods in the amount of 283,200 rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 68 - VAT is charged on revenue of 43,200 rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 41 - the cost of goods sold is taken into account: 200,000 rubles.
- Dt 51 Kt 62 - payment received for goods in the amount of 283,200 rubles.
Let's look at the accounting of Luna LLC.
Source: https://advokat-na-donu.ru/d-41-k-60-pervichnyj-dokument/