Account 19 in accounting is intended to reflect generalized information about the amounts of VAT paid by the purchasing organization when purchasing goods from the supplier. The article describes the basic rules for using account 19, and also discusses transactions and examples of typical operations in the form of tables.
Postings and operations
Business transactions and activities related to this issue are recorded in accounting account 19 with such entries as:
- Purchase of goods and materials
Dt 01,02,10 Kt 60 - reflects the cost of the purchased propertyDt 19 Kt 60 - indicates the tax on the purchased property
D 68 Kt 19 - indicates the tax that will be used as a deduction
- When selling products or goods
Dt 90 K 68 - sales tax is charged
| Score 19 | ||
| Debit | Credit | |
| Cor. check | Description | Cor. |
VAT accounting for the buyer of teapots at the retail store "ACTIV" LLC:
- Debit 41 Credit 60,100,000 rubles. -Kettle goods received in the amount of 100,000 rubles. VAT is not included in the price, since the VAT must be returned to us by the budget. On the debit account 41 - on the debit of this account there is an increase in goods, on the credit account 60 - on the credit of this account the occurrence of accounts payable is reflected, i.e. we owe the supplier 100,000 rubles for teapots.
- Debit 19 credit 60 18,000 rubles. -VAT has been allocated on the delivery of goods and we immediately post it so that there is no balance on the 19th VAT account. We reason like this: the debit reflected VAT on the purchase, and the credit 60, i.e. an increase in accounts payable, i.e. we must pay VAT to the supplier.
- Debit 68/VAT credit 19 in the amount of 18,000 rubles. VAT in the amount of 18,000 rubles is accepted for deduction. We write off the purchase VAT to account 68/VAT in debit - debit, since accounts receivable - the budget owes us the VAT that we paid to the supplier.
- Debit 51 credit 68/VAT in the amount of 18,000 rubles. The budget returned 18,000 rubles to our bank account. On debit 51 there is an increase in money. On credit - repayment of receivables, i.e. reduction of budget debt to us. VAT from the 3rd entry is reimbursed to us by the budget. In practice, actual VAT refund to the current account is possible only upon a written application from the organization to the tax authority with the provision of a certain package of documents and after a tax audit. In fact, by the amount of VAT that the budget must return to us, we can reduce the amount of VAT that we ourselves must pay on the sale of purchased goods.
VAT on purchased assets, accounting account 19
check
Description Kt 60 Indicates VAT on purchased property Dt 68 Indicates VAT to be deductedMoreover, if VAT is also established during the sale, then it is necessary to consider the formation of the result on account 68. Typical wiring can be presented as follows:
Dt 68 Kt 19 - 30,000 rub. (VAT to be deducted is displayed)
Dt 90 Kt 68 - 50,000 rub. (VAT required to be paid is displayed)
Result = 50,000 rub. — 30,000 rub. = 20,000 rub. according to Kt 68
The result means that this exact amount of value added tax must be transferred to the budget. When transferring, a posting is made Dt 68 Kt 51 - the purpose of payment indicates the standard wording “1/3 of VAT accrued for the 3rd quarter of 2021”
It should be noted that the amount of VAT on intangible assets or fixed assets can be deducted only if the acquired property is taken into account in full.
Victor Stepanov, 2016-12-06
Questions and answers on the topic
No questions have been asked about the material yet, you have the opportunity to be the first to do so
Save the article to social networks:
Account 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets” is used to collect and process information about the tax paid or required to be transferred to the state budget. These amounts are included in the cost of the purchased property or material assets, as well as the services provided and work performed. The debit shows the amounts attributable to the purchase of property, and the credit shows the amounts accepted for deduction in correspondence with Dt 68.
The created products, works performed or services provided are sold to the buyer not at cost, but at the final price, which, in addition to cost, also includes added value. This premium represents the profit of the organization, which is used to expand the business or implement strategic decisions. The added value is subject to value added tax, which is displayed on account 19 “VAT on acquired values.”
It is active, and the following amounts are taken into account:
- the debit indicates the amounts collected for the purchase of tangible and intangible property;
- the loan takes into account the accumulated amounts, which will then be presented as a deduction.
With this approach, only the amount of tax is collected on the account, and the cost of the purchased property is indicated on accounts that are intended specifically for this.
| Subaccount | Name | Description of the subaccount |
| VAT on the purchase of fixed assets | Used when purchasing or constructing fixed assets, for example, buildings, structures, equipment or vehicles, as well as land | |
| VAT on the purchase of intangible assets | Used when purchasing intangible assets, for example, software, patents, copyrights, databases, trademarks | |
| VAT on the purchase of inventories | Used when purchasing various material and production resources, including semi-finished products, components, goods, raw materials and materials |
It should be noted that taxation arises both when purchasing property and selling one’s own products, and therefore there is a certain connection between these two operations. Account 19 is intended to display the tax on purchased material assets, and it can be used as a deduction.
VAT
This tax is considered indirect. VAT is a form of withdrawal to the state budget of part of the price of a product, service or work. It is created at all stages of the production process and is paid as it is sold. When applying VAT, the final buyer pays the seller tax on the entire price of the purchased good.
But it starts coming into the budget earlier. This is due to the fact that the amount from its part of the price added to the cost of purchased raw materials, services/work required for production is paid to the state by each participant in production at different stages. The VAT rate in the Russian Federation is 18%. It is used by default if the transaction is not classified as taxable at 10% or 0%. In the Russian Federation, VAT was introduced on January 1, 1992. The rules for its calculation and payment were first determined by the relevant Federal Law “On Value Added Tax”. Since 2001, the procedure has been regulated by Ch. 21 NK. For certain categories of payers and transactions, VAT is not established. For example, enterprises may not pay tax if the amount of their revenue for the previous three consecutive months did not exceed a certain limit (2 million rubles according to paragraph 1 of Article 145 of the Tax Code).
Postings and operations
Business transactions and activities related to this issue are recorded in accounting account 19 with such entries as:
- Purchase of goods and materials
Dt 01,02,10 Kt 60 - reflects the cost of the purchased propertyDt 19 Kt 60 - indicates the tax on the purchased property
D 68 Kt 19 - indicates the tax that will be used as a deduction
- When selling products or goods
Dt 90 K 68 - sales tax is charged
| Score 19 | |||
| Debit | Credit | ||
| Cor. check | Description | Cor. check | Description |
| Kt 60 | VAT on purchased property is indicated | Dt 68 | The VAT to be deducted is indicated |
Moreover, if VAT is also established during the sale, then it is necessary to consider the formation of the result on account 68. Typical wiring can be presented as follows:
Dt 68 Kt 19 - 30,000 rub. (VAT to be deducted is displayed)
Dt 90 Kt 68 - 50,000 rub. (VAT required to be paid is displayed)
Result = 50,000 rub. — 30,000 rub. = 20,000 rub. according to Kt 68
The result means that this exact amount of value added tax must be transferred to the budget. When transferring, a posting is made Dt 68 Kt 51 - the purpose of payment indicates the standard wording “1/3 of VAT accrued for the 3rd quarter of 2021”
It should be noted that the amount of VAT on intangible assets or fixed assets can be deducted only if the acquired property is taken into account in full.
Victor Stepanov, 2016-12-06
Questions and answers on the topic
No questions have been asked about the material yet, you have the opportunity to be the first to do so
Save the article to social networks:
Account 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets” is used to collect and process information about the tax paid or required to be transferred to the state budget. These amounts are included in the cost of the purchased property or material assets, as well as the services provided and work performed.
Accounting entries for calculating and writing off VAT on purchased assets
The VAT amounts paid or intended to be paid are reflected in the debit of account 19 in correspondence with the accounts for accounting for settlements. The loan is used to write off the accumulated amounts, usually in conjunction with an account. 68-2 (intended for calculations with the budget). The following entries are made:
- Dt 19 - Kt 60 - reflection of amounts of received VAT in settlements with suppliers and contractors;
- Dt 19 - Kt 76 - with different creditors and debtors.
- Dt “accounts for material assets, services” - Kt 60, 76 - the cost of received materials and services.
Next, incoming amounts are written off to account 68. The entry entry looks like this: Dt 68-2 - Kt 19. At the end of the tax period, the amount of VAT to be transferred to the budget will be reduced by the amount accumulated on the account. 19, taking into account the fact of payment and receipt of services and material assets. It is worth noting here that the submission of a value added tax return from January 1, 2014 is carried out only in electronic form. All companies will have to report via the Internet on the basis of Law No. 134-FZ of June 28, 2013.
Account 19 in accounting
The debit shows the amounts attributable to the purchase of property, and the credit shows the amounts accepted for deduction in correspondence with Dt 68.
The created products, works performed or services provided are sold to the buyer not at cost, but at the final price, which, in addition to cost, also includes added value. This premium represents the profit of the organization, which is used to expand the business or implement strategic decisions. The added value is subject to value added tax, which is displayed on account 19 “VAT on acquired values.”
It is active, and the following amounts are taken into account:
- the debit indicates the amounts collected for the purchase of tangible and intangible property;
- the loan takes into account the accumulated amounts, which will then be presented as a deduction.
With this approach, only the amount of tax is collected on the account, and the cost of the purchased property is indicated on accounts that are intended specifically for this.
| Subaccount | Name | Description of the subaccount |
| VAT on the purchase of fixed assets | Used when purchasing or constructing fixed assets, for example, buildings, structures, equipment or vehicles, as well as land | |
| VAT on the purchase of intangible assets | Used when purchasing intangible assets, for example, software, patents, copyrights, databases, trademarks | |
| VAT on the purchase of inventories | Used when purchasing various material and production resources, including semi-finished products, components, goods, raw materials and materials |
It should be noted that taxation arises both when purchasing property and selling one’s own products, and therefore there is a certain connection between these two operations. Account 19 is intended to display the tax on purchased material assets, and it can be used as a deduction. It corresponds according to Dt with property accounting accounts. The transfer of collected amounts (Kt 19) corresponds with Dt 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, where at the same time the tax on goods or products sold is collected.
Conditions for closing account 19 in accounting
Closing account 19 in accounting with posting Dt 68 Kt 19 is called VAT deduction.
In order for the right to deduction to arise, several conditions must be met (Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- purchased ITRU are registered;
- ITRU data will be used in activities subject to VAT;
- Correctly executed documents with the VAT amount highlighted as a separate line have been received from the supplier;
- When importing imported goods, tax is paid at customs.
The exact date for the deduction of VAT amounts recorded on account 19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has not been established. An organization has the right to deduct the VAT reflected on account 19 within 3 years from the date of acceptance of ITRU for accounting.
The dates for registration of purchased ITRUs vary and depend on the terms of the contract: the goods can become the property of the organization before its arrival at the warehouse, before or after receipt of accompanying documents (if it arrives before, it is taken into account as an uninvoiced delivery).
In some cases, the debit balance on account 19 remains for a long time:
- Contractors carry out long-term capital construction, repair or liquidation of fixed assets.
- The tax payment was made by the tax agent.
- Entertainment or travel expenses have been paid.
- The tax amount is taken into account during export operations.
- Purchased ITRU are intended for non-taxable transactions.
- In other similar situations.
For non-taxable transactions, separate accounting of VAT is carried out, the tax amounts are listed according to Dt 19 until the end of the reporting period (sometimes longer), as a result, the tax amount / part of it is included in the initial cost of the property or attributed to expenses.
Separate VAT accounting is the topic of our other article.
Postings and operations
Business transactions and activities related to this issue are recorded in accounting account 19 with such entries as:
- Purchase of goods and materials
Dt 01,02,10 Kt 60 - reflects the cost of the purchased propertyDt 19 Kt 60 - indicates the tax on the purchased property
D 68 Kt 19 - indicates the tax that will be used as a deduction
- When selling products or goods
Dt 90 K 68 - sales tax is charged
| Score 19 | |||
| Debit | Credit | ||
| Cor. check | Description | Cor. check | Description |
| Kt 60 | VAT on purchased property is indicated | Dt 68 | The VAT to be deducted is indicated |
Moreover, if VAT is also established during the sale, then it is necessary to consider the formation of the result on account 68. Typical wiring can be presented as follows:
Dt 68 Kt 19 - 30,000 rub. (VAT to be deducted is displayed)
Dt 90 Kt 68 - 50,000 rub. (VAT required to be paid is displayed)
Result = 50,000 rub. — 30,000 rub. = 20,000 rub. according to Kt 68
The result means that this exact amount of value added tax must be transferred to the budget. When transferring, a posting is made Dt 68 Kt 51 - the purpose of payment indicates the standard wording “1/3 of VAT accrued for the 3rd quarter of 2021”
It should be noted that the amount of VAT on intangible assets or fixed assets can be deducted only if the acquired property is taken into account in full.
Victor Stepanov, 2016-12-06
Accounting: account 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets”
4 Kt 91.1
4. For the residual value of fixed assets and intangible assets transferred on account of the deposit under a simple partnership agreement:
Dt 91.2 Kt 01.9, 04
5. For the excess of the monetary value of the contribution over the value of the property (residual) transferred on account of the contribution under a simple partnership agreement:
Dt 91.9 Kt 99
6. Excess of the residual value of the property over the valuation of the contribution:
Dt 99 Kt 91.9
7. The participants reflect the amounts of profit (income) due to receive under the simple partnership agreement as follows:
Dt 76.3 Kt 91.1 —
Profit from the activities of a simple partnership to be received by a participant.
8. Receipt of profit amount:
Dt 51 Kt 76.3
9. Monthly reflection of the amount of profit as part of the overall positive financial result:
Dt 91.9 Kt 99
10. Amounts of losses due to be repaid by the partner:
Dt 91.2 Kt 76
11. Repayment of the amount of loss:
Dt 76 Kt 51
12. Monthly reflection of losses as part of the overall negative financial result:
Dt 99 Kt 91.9
If the simple partnership agreement is terminated, the organization will receive the property back. In this case, the following accounting entries are made:
1) Dt 01, 04, 10, 41, 43 Kt 58.4
Return of property. The value of the property returned to the partner upon his withdrawal from the contract, within the limits of the amounts listed in account 58.
2) Dt 01, 04, 10, 41, 43 Kt 91.9
The cost of property returned in excess of the amounts recorded in account 58.
⇐ Previous123
Accounting entries
Typical postings for 76 special accounts will be:
- Dt 01 Kt 76 Write-off of acquired fixed assets to accounts payable;
- Dt 51 Kt 76 Receipt of money from suppliers to current accounts;
- Dt 10 Kt 76 Write-off of consumables in accounts payable;
- Dt 76 Kt 20 Reducing the number of unfinished fixed assets at the expense of debtors;
- Dt 76 Kt 50 Making cash payments to creditors through the organization's cash desk.
Important! Postings on the 76th accounting account are divided into various types, including insurance of property and valuables, insurance of persons and employees, reflection of settlements of claims, accounting of dividends received, etc. This helps to structure the data even better.
Analysis of balance sheet special account 76 can be carried out using its card or using SALT
Thus, account 76 in accounting is a register that displays generalized data on settlement transactions with debtors and creditors that do not belong to groups in special accounts 60-75. Account 76AB is used to receive claims and insurance amounts for debit/credit debts. Its analytics are carried out similarly to other accounting accounts based on SALT and special analytical account cards.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bI7Tr1pceZ0
Invoice 19 VAT on purchased assets
We confirmed the 0% rate on three documents. At the end of the quarter the account balance is now 19.07. Tell me, is this correct? Shouldn't the account be closed? There is also an additional question. Documents have been submitted for additional receipt. services, for services that can be attributed to foreign economic activity. All additional documents are included in the purchase book. services - and for goods for which the 0% rate is confirmed and for which it is not confirmed. Is this section of accounting not implemented in the BP or are we doing something wrong? Thanks in advance for your answers :-)
Try the new free service for quick code analysis of typical configurations 1c-api.com
ATTENTION!
If you have lost the message input window, press
Ctrl-F5
or
Ctrl-R
or the Refresh button in your browser.
The topic has not been updated for a long time and has been marked as archived. Adding messages is not possible.
But you can create a new thread and they will definitely answer you!
Every hour there are more than 2000
people on the Magic Forum.
| Nasya | |
| Naumov | there should be no remainder. |
| Naumov | There is an article on implementing VAT accounting on ITS. read it. |
| Nasya | I read an article on ITS... The article and many other places describe a situation where VAT is first accepted for deduction at a rate of 18%, then in the next quarter it is sold, VAT is restored, and so on according to the scheme. And in the first quarter we bought goods for sale, and in the same quarter we sold them for export (by the way, we have a sales agreement in rubles and there is no way to check the “sale for export” checkbox). So, in the same first quarter, we confirmed the 0% rate on three out of five documents. We did everything using the VAT Accounting Assistant. And we received the account balance on July 19... |
| Sandy_S | (0) look at what balances are on what invoice balances, and the distribution of VAT on services for export is made into a document on the distribution of indirect VAT, although so that it relates purely to exports, I picked this document apart. |
| Nasya | (4) You rewrote the document Distribution of VAT on indirect expenses so that it could distribute VAT on certain services only to activities with 0% VAT, did I understand correctly? |
| Sandy_S | Yes, and also under a specific contract (agreement) and was not distributed to the domestic market. |
| Nasya | (6) and you are using the document Additional Receipt. expenses? |
| Sandy_S | (7) no we come to vocational school services |
| Sandy_S | if additional the services are no longer indirect, they fall on a certain party, although I won’t lie, I didn’t experiment |
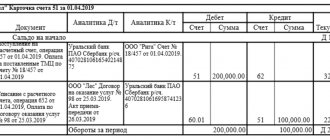
Account balance 19
Due to the fact that the fact of payment is not important now for VAT to be deducted, it would seem that there should be no balance on account 19. However, it is not. There are cases when at the end of the reporting period a VAT balance is formed. Let's consider these situations in order.
Supplement to the weekly “Economy and Life” - “Accounting Supplement”, N 34, 2006 Elena Bukach, expert “EZh”
VAT and Accounting
On January 1, 2006, amendments introduced by Law dated July 22, 2005 N 119-FZ “On amendments to Chapter 21 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and on the recognition as invalid of certain provisions of acts of legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees” came into force. One of these changes is that now, in order to deduct input VAT, the fact of payment is generally not required. To make a deduction, three conditions must be met:
- goods (work, services), property rights acquired for transactions subject to VAT;
- goods (work, services) or property rights are accepted for accounting;
- Invoices have been received from the supplier in which the VAT amount is highlighted as a separate line.
So, the organization has the right to write off the amount of VAT reflected in account 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets” directly to account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees.” Due to the fact that the fact of payment is not important, there should be no balance on account 19 at the end of the reporting period (month, quarter).
However, in practice there are cases when account 19 is not closed.
Let's imagine this situation: a supplier of goods (works, services) issued an invoice to the buyer with errors. The organization will not be able to deduct VAT until the invoice is corrected. According to clause 29 of the Rules for maintaining logs of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books when calculating value added tax, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000 N 914, invoices are not registered in the purchase book and sales book, having erasures and blots. Corrections made to invoices must be certified by the signature of the manager and the seal of the seller, indicating the date the correction was made.
The Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 13, 2006 N 03-04-09/06 states that invoices issued without indicating the numbers of payment and settlement documents by suppliers of goods (works, services) for which advances were transferred cannot serve as a basis for acceptance of VAT for deduction. The updated information included in invoices must be reflected both in the copies remaining with the seller and in the copies issued to the buyer.
The buyer has the right to deduct the amount of VAT paid to suppliers on invoices to which corrections have been made, no earlier than the date the corrections were made to the invoice data. This was reported by the tax authorities in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated February 15, 2005 N 09-11n/9222. An analysis of arbitration practice has shown that there are cases in which arbitrators make similar decisions. An example of this is the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Far Eastern District dated 06/01/2006 N F03-A04/06-2/1434. The court justified its decision by the fact that the invoice is a tax accounting document and the fact that it is absent in the tax period in a properly executed form deprives the taxpayer of the right to receive a VAT deduction. There are also positive solutions. The Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated 06/07/2006 N F09-4719/06-C2 states that the organization claimed VAT for deduction after the actual receipt, posting and payment of the goods (during the period of consideration of the dispute, the fact of payment was required for deduction). The execution of the additionally submitted corrected invoices complied with the requirements established by Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as a result of which the noted invoices were classified by the court as documents that confirm the right to deduction. At the same time, the corrections made did not affect the dates of issue of the considered invoices by suppliers, that is, the tax periods to which the considered invoices related did not change after the corrections were made.
There can be many mistakes when filling out an invoice. Let's give one more. It may be considered a violation if the invoice does not include the surnames, first names and patronymics of the persons who signed this document. Such an invoice cannot serve as a basis for deducting VAT - this is the position of the tax authorities. However, the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated 06/08/2006 N KA-A40/4806-06 states that the court declared such a refusal illegal. The arbitrators noted that there is no requirement to decipher a signature in tax legislation. Accordingly, the absence of such transcripts does not in any way affect the possibility of obtaining a deduction for this document.
Similar decisions are set out in the resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated June 15, 2006 N F04-3482/2006(23428-A27-25), the Moscow District dated May 30, 2006 N KA-A41/4659-06, the Volga District dated April 20, 2006 N A55-15666/2005-31, Northwestern District dated 03/30/2006 N A56-17711/2005 and Central District dated 03/17/2006 N A08-3494/05-16.
There is also the opposite practice - resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus District dated 02/13/2006 N F08-6517/2005-93A, dated 03/09/2006 N F08-646/2006-299A, dated 11/16/2005 N F08-5457/2005-2150A . It is in this case that a balance is formed on account 19.
A balance on account 19 may result due to the fact that the supplier did not receive an invoice on time, that is, the goods were received without this document. In this situation, the organization will not be able to deduct VAT until it has this document. Indeed, in accordance with the norms of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the use of VAT deductions is possible only if three conditions are met simultaneously in one reporting tax period. Thus, if one of the conditions is met in subsequent tax periods, then the organization does not have the right to take advantage of the deduction in the period when the other two conditions were met.
It follows that if the buyer has not received invoices from suppliers for operations that he carried out in the expired tax period before submitting the declaration, then he does not have the right to indicate VAT for deduction when filling out the declaration.
The next situation is when an asset is purchased. After all, as a rule, first its value is formed on account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” and is recorded by posting Debit 08 Credit 60.
Following this operation, the accountant reflects VAT by posting Debit 19
Credit 60. An organization will be able to deduct tax only when the property is accounted for in account 01 “Fixed Assets”. Therefore, until this moment, a balance is formed on account 19.
The balance may also be formed due to the fact that there was no VAT taxable item in the tax period. The Ministry of Finance of Russia in its Letter dated 02/08/2005 N 03-04-11/23 explained that if a taxpayer does not calculate the tax base for value added tax during the tax period, then there is no reason to deduct VAT amounts paid to suppliers of goods (works, services). In this regard, these tax deductions are made no earlier than the reporting period in which the tax base for value added tax arises. In this regard, until VAT is calculated on sales, that is, until credit turnover appears on account 68, VAT should not be deducted. However, this is not certain. After all, it does not follow from Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation that the right to deduction depends on whether VAT was calculated on the sale of goods, works, and services (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated June 2, 2006 N KA-A40/4875-06).
Now let's look at VAT on standardized expenses. Let us remind you that according to clause 7 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT amounts paid on business trip expenses and entertainment expenses, which are taken into account when calculating income tax, are subject to deductions. If expenses in tax accounting are accepted according to the standards, then VAT on these expenses is subject to deduction in an amount that corresponds to the specified standards. A similar position is set out in Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 11, 2004 N 03-04-11/201. Value added tax related to excess expenses that are not taken into account in the reporting period when calculating income tax is not deductible.
When making, for example, advertising expenses, the organization has the right to deduct “input” VAT. And she must do this at the time she accepts the invoice from the supplier. Let us assume that the revenue from which the standard is calculated is unknown, since the reporting period for income tax has not yet ended. The reporting period for income tax is a quarter, and for VAT - a month. In this case, we suggest the following order. When accounting for advertising expenses, immediately deduct the entire amount of VAT on them. If, based on the results of the quarter, it turns out that advertising expenses did not meet the norms, restore VAT on excess expenses.
There is another way. It consists in the fact that the VAT charged by the supplier on advertising expenses is taken into account on account 19. Then the VAT amounts are fully or partially debited to account 68, as the expenses are accepted in tax accounting within the limits of the norms. It is in this case that a balance may arise on account 19.
Let us also consider the case when payment for goods, work, and services is made by a third party’s bill of exchange.
Here you should be guided by clause 2 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
“When a taxpayer uses his own property (including bills of exchange of a third party) in payments for goods (work, services) purchased by him, the tax amounts actually paid by the taxpayer are subject to deductions, which are calculated based on the book value of the specified property (taking into account its revaluations and depreciation, which are carried out in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation), transferred as payment for them.”
The book value refers to the actual costs of purchasing the bill. This conclusion was reached by the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation in Decision No. 10575/03 dated November 4, 2003. Consequently, if an organization received goods in one month, and payment was made by bill of exchange in the next, then the organization can deduct VAT only in the next tax period.
Document Formation of purchase ledger entries. When posted - account balance 19.3
Ø
TurboConf 5 - expanding the capabilities of the 1C Configurator
ATTENTION!
If you have lost the message input window, press
Ctrl-F5
or
Ctrl-R
or the Refresh button in your browser.
The thread has been archived. Adding messages is not possible.
But you can create a new thread and they will definitely answer you!
Every hour there are more than 2000
people on the Magic Forum.
| I | |
| Nemoj | Document Formation of purchase ledger entries. When posted, account balance 19.3 is less than the VAT amount. What to do? I press fill and it fills. I press to spend - the balance is less than VAT. I'm waiting for advice. PS Already two clients have this garbage. |
| Viking | HA... two... |