Home / Labor Law / Employment / Part-time and part-time work
Back
Published: 08/05/2016
Reading time: 7 min
0
2888
Finding additional sources of income besides their main job worries many working citizens. Such a combination of two or more jobs is not prohibited by law, provided that the additional work will be performed during free time from the main job duties. The question of part-time work may also arise for women on maternity leave.
Although this category of workers is paid a benefit, it may not cover the costs of preparing for the birth of a baby or buying things for him after the birth. If the mother feels well and is able to work, she may well get a part-time job. After all, this type of employment implies part-time work, which gives the opportunity to relax and take care of the newborn.
- What does the law say?
- Part-time work for pregnant women
- Work before and after childbirth, wages
- Some features and design
What the law says about part-time mothers
Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 282 regulates issues of external part-time work. This is additional employment in free time from the main one, that is, the same employment, only for shorter working hours.
IMPORTANT! Do not confuse part-time work with combination work: in the first case, the employee confirms employment with different employment contracts.
An employee (in our case, an employee) can work part-time at different enterprises, or at the same one, but simultaneously in several positions. The legislation does not limit the number of part-time positions held; the limit is only on additional work time - no more than 4 hours per working day.
Thus, from the point of view of the law, part-time work is a full-fledged workplace with the same responsibilities of the employer, which also applies to the provision of maternity leave. All requirements of the Labor Code in relation to a woman on maternity leave (saving a job, impossibility of dismissal, due payments, vacation periods) also apply to an additional employer.
NOTE! A woman who “works part-time” without concluding an employment contract cannot count on legal protection of her rights.
Going on a reduced work schedule
Labor legislation does not indicate what exactly can be considered a shortened working day.
According to Rostrud’s explanations, part-time work means one in which an employee works less than the specified standard. The standard working day means 8 hours a day (according to Article 94 of the Labor Code) or 40 hours a week (according to Part 2 of Article 91 of the Labor Code). Thus, working 7 hours a day or 4 days a week instead of 5 is considered a shortened work schedule.
Registration of a woman on maternity leave for part-time work has certain features. The employee should submit an application to the manager on the basis of Part 3 of Art. 256 Labor Code.
Changes in working conditions must be recorded in an additional agreement to the employment contract under Art. 72 of the Labor Code. The start of work for a maternity leaver is prescribed through the issuance of a corresponding order.
An employee has the right at any time to decide to go on vacation and interrupt work . To do this, he submits an application to the employer and signs an additional agreement stating that he stops working in the specified mode.
As you know, the employer has the right to hire only a temporary employee for the position of maternity leave . If an employee decides to return to work after maternity leave on a part-time basis, the employer will terminate the employment contract with the temporary employee on the basis of Part 3 of Art. 79 of the Labor Code.
Read more: How to obtain Greek citizenship for a Russian citizen
For example, to receive 50% of the rate, you need to work 4 hours a day or 20 hours a week (in the latter case, it is assumed that the daily work time can be divided disproportionately). To arrange a special work schedule on a part-time basis, the employer must sign an additional agreement with the employee under Art. 72 of the Labor Code.
When an employee works part-time, the employer’s tasks must include recording working hours in a special time sheet in the T-12 form (13). It indicates the amount of time worked opposite the employee’s full name.
Leave or stay
A part-time woman is employed in an additional position for a relatively short time compared to the main one. Therefore, in the prospect of adding to her family, she needs to decide an important question: whether to leave an additional job or continue her “part-time job” without spending a lot of time on it. Many people decide to do this if they have someone to leave the baby with. This solution has a number of advantages:
- the woman receives additional funds;
- the mother has the opportunity not to get bogged down in the maternity routine and continue to improve as a specialist;
- working skills are not lost;
- psychological relief.
In this case, maternity leave needs to be taken out only at the main workplace, and at the additional one only to go on sick leave relating to childbirth.
Timing of maternity leave
If a woman leaves her job, the terms must be the same at all places of her employment. The law provides her with two types of maternity leave:
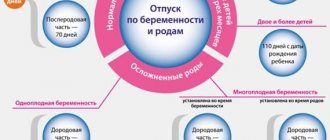
- for pregnancy and childbirth - 140 days in the case of a normal pregnancy and 194 in complicated cases (half before childbirth, half after);
- to care for the baby until he turns 1.5 years old (or 3, but the further period is paid only by compensation from the employer in the amount of 50 rubles per month).
You can submit documents to receive benefits within six months after receiving a certificate of temporary incapacity for work - this is a common practice for sick leave. If a woman quits her job and a month or less has passed since that moment, she can bring the piece of paper to her former employer.
How to go to work before a child is 1.5 years old?
Since the employer appoints (or hires) a temporary employee when an employee goes on maternity leave, early termination of maternity leave entails his transfer or dismissal.
A temporary employee fills out an application for employment during the maternity leave of a permanent employee. Her unplanned exit requires time to design and organize this moment.
If a woman decides to interrupt her maternity leave before the baby reaches the age of 1.5 years, then she must:
- Notify the employer of your decision.
- Write an application for interruption of maternity leave in the form “I ask you.”
- Wait for the employer's decision. If the answer is positive, wait for the order to interrupt the maternity leave.
- Start work from the date indicated in the order.
Thus, you can go to work while on maternity leave for up to 1.5 years, but the mother will no longer be entitled to benefits from the state.
Procedure for future maternity leave
What is the right thing for a pregnant woman to do so that she can easily obtain maternity leave and the entitlements:
- Register for pregnancy at the antenatal clinic. It is recommended to do this before the 12th week of pregnancy.
- At the 30th week of pregnancy, obtain a sick leave certificate from her leading doctor with the start and end dates of temporary disability due to pregnancy and childbirth. Make a copy of it and have it notarized. The original is needed for the main place of work, a copy - for the additional one. You can ask for the required number of original sick leave documents to be issued at once.
- Apply these documents to each of your employers by writing a corresponding application in the prescribed form. They write two separate statements - these are the grounds for calculating future payments.
- If an employee has been working in a given company for less than two years, she will also need a certificate of previous two years of income. If there were none, the minimum wage will be taken as the basis for calculating the accruals due to it.
- You can bring data from other places of work to your chosen manager and arrange to receive payments in one place, or you can contact each employer individually.
After writing an application with a certificate of temporary disability attached to it, the employer must take the necessary actions within 10 days. The only reason for refusal of payment is the provision of a fake sick leave certificate.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! If a woman has been officially employed in several jobs for more than two years, she can count on insurance payments from each employer.
Do they pay maternity leave if they work part-time?
Maternity leave in Russia refers to a period of incapacity for work at the end of pregnancy and after the birth of a child. The exact period of a woman’s incapacity for work is determined by the doctor, who indicates it on the sick leave certificate.
Typically, maternity leave is 140 days - half before childbirth and half after. But if the pregnancy proceeded with complications, twins, triplets were born, or due to a number of other factors, the doctor can extend the vacation up to 194 days.
It is worth noting that parental leave is not included in maternity leave, but is a separate period.
Every employee has the right to maternity leave, no matter how many employers she works for - she has the right to receive leave and insurance payments for each position.
Maternity leave is legally the same case of employee incapacity as a broken leg or a cold. The woman receives a sick leave certificate from the doctor and goes with it to her employer. But what if there are several employers?
To determine which employer will pay the expectant mother maternity benefits, it is necessary to clarify who paid insurance premiums for her in the past two years.
Namely, the situations may be as follows:
- The woman has more than two years of work experience in several jobs at once. Part-time maternity leave will be calculated at each workplace. In other words, a woman receives maternity benefits separately for each place of work. Employers independently of each other (as if the employee works only for them) calculate and accrue payments for the expectant mother. Child care benefits are calculated and paid only from one employer, at the woman’s choice.
- The expectant mother works in two or more places part-time, but over the past two years she has changed several employers under similar conditions - she can choose one of the last employers to whom all maternity payments will be accrued.
- At the time of going on maternity leave, the woman works in different places; in the past two years she was employed, among other things, by other employers. Payments can be made from one place of work, based on the average earnings from all salaries - the employer must first submit certificates of income from other jobs and that benefits were not issued there. Or from all current employers, as in the first situation, each with their average earnings.
You can apply for maternity insurance benefits within six months from the date of receipt of your sick leave. Moreover, a woman has the right to present a certificate even to her former employer if no more than a month has passed since the date of dismissal.
In any situation, payment of benefits is subject to general rules:
- Calculation of maternity benefits is made within 10 days from the receipt by the accounting department of a certificate of incapacity for work;
- Payment is made on the next payday after the end of settlements;
- The full amount is issued at a time, taxes are not withheld from the benefit.
During maternity leave, young mothers receive child care benefits. Often, the amounts of money that are paid to women are not sufficient to cover the costs of a child.
In this regard, there is a need to get a new job, but at the same time keep the previous one.
This can be done by concluding an additional employment agreement with the condition of part-time work.
In accordance with current labor legislation, pregnant women have a number of benefits when performing labor functions.
The most important ones include the following:
- transfer to “light” labor (Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- absence of a probationary period when hiring (Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- a ban on involving a pregnant woman in overtime work and performing labor functions at night, weekends and holidays;
- inability to terminate the employment contract at the initiative of the employer, except for cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- provision of maternity leave, as well as child care leave.
Thus, the legislator seeks to create favorable conditions for the work of a pregnant woman.
In this regard, the question arises: is the performance of part-time work while on maternity leave regulated in a special way?
A special type of rest time is maternity leave.
It is provided to the employee on the basis of a personal statement, as well as a certificate of incapacity for work.
Sample application for maternity leave
In accordance with Art. 255 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, its duration as a general rule is 70 days before childbirth and the same amount after the birth of the child.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation
In some cases, this period may be extended, for example, if there is a multiple pregnancy, or there was a complicated birth.
For the entire time the employee is on vacation, she is paid benefits.
Child care leave is provided in accordance with Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For this period, the employee retains her place of work.
At my main job
The employer's obligations discussed above are fully fulfilled at the main place of work.
The employer’s obligation to ensure full compliance with the requirements of labor legislation is not affected by the fact that the employee has an external job.
At the same time
At an additional place of work, the employee retains all the same benefits that are provided for by current labor legislation.
Of particular interest is the calculation of maternity benefits.
We invite you to read: Obtaining disability for a child: documents, procedure, pension amount
Several situations are possible here:
- A woman works for two or more employers. For the previous two calendar years, she carried out her labor functions with them. In this case, the employee can claim maternity benefits for all places of work. Cash is calculated from earnings for each of them.
- The employee performs a labor function for two or more employers, but has not worked for them in the previous two calendar years. In this situation, she can only claim benefits from one employer. The choice is hers. The amount of the benefit is calculated in total based on the level of income for the 2 previous calendar years.
- The employee entered into employment agreements with two or more employers, but over the previous 2 calendar years she performed labor functions both for them and in other organizations. In this case, the choice remains with the woman herself. Either she will receive benefits for each place of work, or for the total amount of income that she received over 2 years, but for one place of performance of her labor function.
With external part-time work, different options for calculating maternity benefits are possible.
In turn, each employer provides such an employee with special leave.
She attaches a sick leave certificate to it; it can be an original or a copy.
If benefits are accrued at an additional place of work, the original will be required from the employee.
In the case where, in accordance with current legislation, she can only apply for leave at the place of external part-time work, it is enough to attach a copy of the sick leave certificate to the application.
It should be noted that child care benefits are paid exclusively at the main place of work.
When working part-time, there is no need to receive two or more sick leaves.
The benefit will be calculated based on average monthly earnings for the two previous calendar years.
Let's look at the three most typical situations.
Marina works as a lawyer in the construction industry, and also as an external part-time lawyer for IP Petrov A.P. At 30 weeks of pregnancy, she was given a certificate of temporary incapacity for work. However, Marina does not want to go on maternity leave. It's her right.
She will not be able to receive benefits. These funds are paid as insurance compensation. If a woman continues to work at her main or additional place of employment, then the insured event is not considered to have occurred.
Accountant Victoria works internally at Ivolga OJSC. During maternity leave, she decides to go to work part-time.
Teacher Oksana decided to get a part-time job at Municipal Educational Institution Secondary School No. 51 in Yekaterinburg. She is on maternity leave and has her main place of work. Oksana entered into an employment agreement without an entry in the work book.
She has the right to receive funds as part-time benefits and wages.
The legislator does not prohibit pregnant women and young mothers from going to work or continuing their work activities.
In contrast, labor laws provide only rights. Only the workers themselves can resolve this issue.
There are no special rules in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation devoted to part-time work for this category of persons.
Compliance with these rules is mandatory for the employer.
Restrictions
The main restrictions are related to the length of the working day.
A woman on maternity leave does not perform any activity at her main place of work.
However, this does not mean that she can work full time.
The legislator limits the standard working time (0.5 monthly standard). So, if for the main place of work the norm is 40 hours, then for part-time work the duration should not exceed 20 hours.
The work and rest schedule is determined in accordance with the employment contract concluded between the employee and the employer.
What payments are due to a part-time worker?
The law provides several options for assistance to a mother working several jobs, which she can receive from each employer or one of her own choosing:
- payment of sick leave at the rate of 100% of average earnings for the previous two years or from the minimum wage - at each enterprise;
- one-time payment for early registration at the antenatal clinic (up to the 12th week of pregnancy), a fixed amount of 613 rubles 14 kopecks - at any place of work, but only one at a time;
- at the birth of a baby - a one-time amount of 16,350 rubles and 33 kopecks;
- child care payments once a month, 40% of the average salary - from one of the employers (not necessarily the main one, it is chosen by the woman).
How to work on maternity leave and maintain benefits?
Being at home with a child is a woman’s legal right, but not her responsibility . There are several opportunities to start working earlier.
However, in 2021, you can maintain benefits and receive wages at the same time from your main employer only in one case - if you start working part-time.
Art. 13 of the law on benefits allows you to receive state child care benefits if the caregiver (not always the mother) goes to work for a reduced time.
Part-time work is a working day of less than 8 hours or a week of less than 40 working hours. The exception is professions with “shortened” days (for example, teachers).
For them, part-time work is calculated taking into account the working time standards prescribed for this type of activity.
Going part-time does not interrupt maternity leave. This way you can maintain child care benefits for up to 1.5 years and receive a salary. An employer does not have the right to refuse an employee (Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
To register for a part-time job, a woman must:
- submit an application to the HR officer addressed to the employer with a request to leave;
- sign an additional agreement on working part-time (Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), which is drawn up to the existing employment contract.
In practice, it is better to agree in advance on your exit and a suitable work schedule . This can be either a schedule with a shorter working day or a schedule with a full day, but fewer days off per week.
Wages are calculated based on the actual products produced (if payment is piecework) or in proportion to the time worked.
Rules for calculating part-time benefits
In the main, they do not differ from ordinary cases when the following indicators are taken into account:
- billing period – two years;
- average daily earnings;
- duration of vacation.
From 730 or 731 days (if it is a leap year), it is necessary to exclude the periods provided for by law (clause 3.1, article 14 of Federal Law No. 255):
- disability (illness);
- release from work;
- other maternity leaves.
Then you need to add bonuses, vacation pay, indexation, allowances and other payments to your salary during this time, and divide the amount by the number of days worked over 2 years. This will calculate the amount of average daily earnings - the basis for calculating sick leave payments. The number of days indicated in it should be multiplied by it. The fact of deductions to social insurance funds during the specified periods is of key importance.
FOR EXAMPLE. A woman working part-time received a sick leave certificate at the antenatal clinic, gave birth and returned to an additional place of work shortly after giving birth, using not the 140 days indicated on the certificate, but only 90. In this case, the average daily earnings for the previous two years will be multiplied by 90 – this is the amount she will receive in her hands. Taxes and insurance contributions are not deducted from it.
Benefit limits and part-time work
The state has established restrictions on the amount of payments to women on maternity leave: the limit is 266,191 rubles and 80 kopecks for normal childbirth, 296,207 rubles 93 kopecks for a caesarean section or the occurrence of postpartum complications, 368,361 rubles 15 kopecks for the birth of twins or triplets. For part-time workers, this limit will be taken into account for each place of work separately. Thus, it is completely legal for a woman to have the right to receive an amount that actually exceeds the limit.
The smallest amount guaranteed for a woman going on maternity leave is calculated according to the minimum wage and currently amounts to 34,520 rubles 55 kopecks for the usual case of uncomplicated childbirth with 140 days of sick leave.