What is an occupational disease
According to Federal Law No. 125 of June 24, 1998, an occupational disease is a health disorder caused by systematic exposure to harmful factors in unfavorable working conditions. This manifests itself in the dysfunction of one or another organ or vital system. The consequence of an occupational disease at work is temporary or permanent loss of ability to work (Article 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Registration of an occupational disease
What are acute occupational diseases
As previously noted, an acute occupational disease is a pathology that occurs after a single exposure to a harmful substance on the body. That is, the action occurred during one work shift.
Other occupational diseases of a similar nature may be as follows:
- CO gas poisoning
- Poisoning with methemoglobin formers
- Cyanide toxicity
- When exposed to arsenic hydrogen
- Intoxication with organophosphorus substances
- Mercury vapor poisoning
Acute occupational diseases can only arise as a result of poisoning, and if in production the use of hazardous substances was a priority, then the employee who received the pathology needs to register payments and benefits.
What leads to the development of occupational diseases
Working conditions in the workplace: what is it?
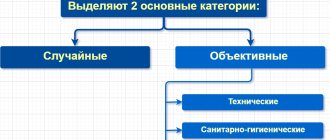
Working conditions that increase the risk of occupational diseases at work include:
- insufficient organization of production processes;
- technical backwardness;
- neglect of sanitary and hygienic standards;
- climatic features.
To reduce the likelihood of getting the disease, the impact of each negative condition can be reduced.
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the concept of hazardous production factors leading to injury is also distinguished. They can be moving mechanisms on equipment, electric current, etc. Both terms are interrelated and important for conducting examinations. Thus, if there is excessive humidity in the room, conductive dust (harmful factors) can cause electric shock (a dangerous factor) to a person. Studying this relationship helps to establish what caused the body’s dysfunction and identify the presence of an occupational disease.
Working in conditions of harmful chemical factors in production
According to GOST 12.0.003-74, harmful factors are divided into four categories: physical, chemical, biological, psychophysiological origin.
The regulation of the maximum permissible level of their impact on the body is fixed within the framework of the relevant labor safety standards and sanitary and hygienic rules.
Procedure for investigating an acute occupational disease
Under the influence of harmful factors, occupational diseases can be diagnosed once.
The investigation is carried out in stages:
- In a medical institution, a diagnosis of pathological change is established in advance
- An immediate message about a case of occupational pathology is sent from the clinic to Rospotrebnadzor
- The Rospotrebnadzor organization, located territorially, clarifies and establishes the reasons for the occurrence of this case. After which a sanitary characteristic for working conditions is drawn up
- The last document is sent to the direct employer or to the place where the employee lives
- The diagnosis is established in a medical institution, and a conclusion is prepared
Classification of occupational diseases
The level and period of exposure to harmful factors gives grounds to classify occupational diseases into such types as acute and chronic. The former means those that are provoked by a loading dose of a substance hazardous to health during its one-time impact on the body.
Safe working conditions: what is it, definition
Chronic disease involves the duration of exposure to harmful factors when performing professional duties. Its course is protracted. In some cases, the consequences may be long-term (for example, carbon monoxide intoxication manifests itself in persistent organic changes in the central nervous system).
Note! In the acute form, the influence of harmful production factors becomes obvious, and therefore the connection with the disease is easier to prove.
Professions at risk of contracting occupational diseases include, first of all, workers of large production enterprises with aggressive nature of harmful factors; teachers suffering from systematic nervous stress; health workers servicing X-ray equipment; persons who are constantly in contact with food. This category also includes drivers, miners, welders, divers, and steeplejacks (Order No. 302n of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation).
X-ray room employee
Types of occupational diseases
The list of occupational diseases was previously established by convection in 1964, and in 1980 this List was updated. In 2012, the Ministry of Health issued an administrative document outlining the List. Occupational pathologists use this order if it is necessary to establish a diagnosis.
Common types of diseases include:
- Intoxication. When working with chemicals, organs of the nervous system, blood, kidneys, respiration and much more are affected.
- Types of pathologies associated with contact with industrial aerosols
- Pathological abnormalities associated with physical factors
- Diseases arising from nervous overload
- Pathological changes in the body associated with biological factors
- Various types of allergic manifestations
- Malignant formations
The duration of passage and level of exposure to hazardous factors are distinguished by:
- Acute character . These are forms of pathologies that appear suddenly after a single exposure to harmful substances on the body.
- Chronic . If the body is exposed to hazardous substances and other production factors for a long time. This includes persistent and long-term diseases associated with poisoning of the body, for example, lung cancer is associated with working in dusty rooms.
List of occupational diseases
The full list of occupational diseases can be found in Order No. 417n of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 12, 2011. According to the document, the professional nature of the dysfunction was established in connection with the corresponding production factor.
What are personal and collective protective equipment for workers?
The list of occupational diseases in the Appendix is compiled depending on the categories of harmful effects.
The disease designation in the document includes:
- Name;
- coding in accordance with the standards of the international classification of occupational diseases;
- factor that caused dysfunction of the body;
- code code for the cause of the disease according to the international classifier.
Note! The list of PPs attached to Order 417n is not exhaustive, but reflects only the most common cases.
What are the payments and benefits for occupational illness in 2018-2019?
The organization makes payments for occupational illness on the basis of sick leave, according to which work duties are correlated with the final diagnosis.
The calculation of benefits is carried out similarly to standard disability compensation, taking into account some features:
- the amount of accruals is 100% regardless of length of service;
- according to the indexation of benefits and benefits for occupational diseases for 2019, from February 1, the maximum payment threshold was increased to RUB 77,283.86* monthly (while from February 1, 2018, the limit was RUB 74,097.66);
- Benefits are calculated using FSS funds.
Note! All payments assigned before February 1, 2019 must be indexed.
Calculations are based on the amount of wages accrued before the onset of illness or disability.
How to register an occupational disease: where to start
To register an occupational disease, you should start with a visit to a medical institution, after which the mechanism for establishing the fact that has taken place is launched:
- The therapist issues a referral for examination by specialized specialists.
- Based on the findings of the medical examination, a preliminary diagnosis is determined.
- Documents from the medical institution are submitted to Rospotrebnadzor, the body that initiates an examination of the place of work.
- The labor safety inspector prepares the result in the form of an extract.
- The enterprise commission draws up an act.
The documents are provided to the experts of the Center for Occupational Pathology, an institution that, based on checking the preliminary diagnosis, gives a final conclusion and establishes the occupational disease.
The procedure for registering an occupational disease using the example of determining the degree of hearing loss in a pilot
Important! The examination should be complete with a range of tests and additional studies, if necessary.
A special assessment of working conditions is... (according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Is it mandatory?
A special assessment of working conditions is a series of activities aimed at establishing the harmfulness and danger of working conditions. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation mentions a special assessment of working conditions in several articles (21, 22, 212, 216, 219, 351.3, 356), calling such an assessment the responsibility of the employer and one of the areas of state activity in the field of labor protection.
At the same time, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation makes reference to a separate regulatory act - the law “On special assessment of working conditions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ, which is entirely devoted to this event. According to this document, based on the results of a special assessment, classes of harmfulness of working conditions for specific workplaces should be established (clause 2 of article 3). The procedure is mandatory and is carried out at least once every 5 years (clause 4 of article 8). A special assessment is not carried out only in relation to (clause 3 of article 2):
- homeworkers;
- remote workers;
- working for individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs.
Investigation of occupational diseases at the enterprise
The investigation of occupational diseases is regulated by Government Decree No. 967 (dated December 15, 2000). Which institution establishes a preliminary diagnosis of an occupational disease? The law allocates two weeks for the formation of a sanitary and hygienic characteristic (SHC) for a chronic disease. Within a month, the victim is given a final diagnosis, which must be submitted no later than three days:
- employer;
- FSS;
- Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance Center (TSGSEN);
- medical institution.
Rospotrebnadzor expert prepares SGH
The employer creates an investigation commission within two weeks, which includes:
- a lawyer or directly the head of the enterprise;
- representative of the labor protection department;
- members of the trade union committee;
- enterprise health worker.
Based on the results of the work, within three days, the commission draws up a report, five copies of which are sent to the authorities listed above. The document must reflect information about the degree of guilt of the employee (up to 25%).
Important! The act and all related documents are stored at the enterprise for 75 years. In case of liquidation of a legal entity, the case is transferred to the Center for Sanitary and Social Security.
Who heads the commission to investigate occupational diseases
The investigation and recording of occupational diseases is regulated by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 967 of December 15, 2000. According to the provisions of the document, the created commission is headed by the head physician of the Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance. As its chairman, he oversees the enterprise with a registered case of PD.
How to apply for recourse for an occupational disease
The insurance company monitors the submitted documents and makes a decision on the insured event. An employee is insured if he was performing professional duties when an occupational disease was diagnosed.
If the decision is positive, a claim for occupational disease should be filed.
Temporary or partial loss of ability to work is compensated in the form of insurance payments:
- one-time How much their size will be depends on the depth of the disease, the degree of loss of working capacity and the fault of the insured;
- monthly. If it is impossible to continue work.
The FSS provides a referral for an examination, a certificate of occupational disease, a work record book and an extract of wages, an agricultural record of working conditions, a certificate of occupational disease, and an outpatient card.
After checking the documents, the Social Insurance Fund determines the amount of accruals that the victim receives even in the event of dismissal from the enterprise. In this case, additional payment for treatment is also subject to compensation. In a situation where a person becomes disabled, the victim is awarded a social pension.
Note! If the death of an employee occurs, payments are due to his relatives.