Investigation of the circumstances of occupational diseases
Performing work duties often causes occupational diseases.
If such consequences arise, the employee may qualify for various compensation payments from the employer and the state. How to register an occupational disease and what diseases are considered such, we will consider in this article. ConsultantPlus TRY FOR FREE Get access The procedure for establishing an occupational disease at work, as well as other details of this issue, are stipulated in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 15, 2000 No. 967, as well as in Article 184 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
How to register an occupational disease
If the result of work activity nevertheless led the employee to an occupational disease, then he has the right to compensation payments from the insurance company. However, first it will be necessary to prove that the disease was acquired during the period of work at the enterprise. In the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 15.
The answer to the question of how to register an occupational illness is simple: the employee needs to seek medical help.
Registration is carried out according to a certain algorithm. First of all, you need to make an appointment with your local therapist. This is the first step; it is needed to obtain a referral to a clinic for examination by specialized specialists.
After a thorough medical examination (or series of medical examinations), a diagnosis is determined.
Further steps involve:
- Contact Rospotrebnadzor. This body immediately begins an inspection of the place of work.
- Obtaining an extract from the labor protection inspector.
- Receiving the commission's report on the work.
- Contact the pathological center (this is where the final conclusion is issued).
In order for the work of the pathological center to be as complete as possible, it is necessary to submit all collected certificates and documents. In addition, for an objective conclusion from the center’s specialists, a full range of analyzes and, possibly, additional studies are necessary.
Occupational disease: where to start
Occupational diseases are health disorders that are gradually or overnight caused by unfavorable production factors. A set of measures aimed at preventing the occurrence of these disorders is the prevention of occupational diseases.
Since the law provides for social insurance against accidents and occupational diseases, as well as compensation payments from the employer, the victim will have to prove that the illness or injury was actually acquired in connection with the performance of professional duties. To establish this fact, a special investigation is being carried out, the procedure of which is defined in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 15, 2000 No. 967.
The investigation is carried out in relation to the following categories of employed citizens:
- persons with whom an employment contract has been concluded;
- persons working under a GPC agreement;
- students undergoing internship under an employment contract;
- convicts forced to work;
- other persons working for individual entrepreneurs and organizations.
Prevention of occupational diseases
In order to prevent and timely diagnose occupational diseases, preventive measures have been developed.
For certain categories of workers performing labor functions related to the negative impact of HPF, annual and upon employment mandatory medical examinations are prescribed at the expense of the employer (Part 1 of Article 24 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of November 21, 2011 No. 323-FZ “On Health Protection”). Employers are also recommended to introduce technologies that are safe for personnel or that minimize the harmful effects of the working environment.
Recording and investigation of occupational diseases
An employee whose health has been damaged in some way at work must know the following algorithm of actions taken in this case and consisting of several stages:
- Contacting a medical facility.
- Doctors notify the employer about the treatment and transmit this information to the organization exercising sanitary and epidemiological control.
- Within 24 hours, the controlling organization carries out inspection activities at the enterprise and issues a conclusion.
- If the employer or employee is dissatisfied with the conclusion, they state their complaints in writing, which are attached to the document.
- The conclusion is sent to a health care institution, where a conclusion is made as to whether the disease is occupational.
- The medical organization sends the victim to the center of occupational pathology (institute of occupational diseases), where a final conclusion is made based on the documents received and the state of health.
- The final conclusion is sent to the employer and the insurance company.
It is worth mentioning separately that the diagnosis, treatment and study of occupational health disorders are mainly carried out by specialized institutions. For example, the Moscow Institute of Occupational Hygiene and Occupational Diseases named after Academician N.F. Izmerova.
After receiving a conclusion from the occupational pathology center, the employer must, within 10 days, organize a commission to investigate the circumstances of the occurrence of the disease. For this purpose, a corresponding order is issued. The investigation is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Creation of a commission.
- Researching documents and other materials, conducting examinations and surveys of employees.
- Based on the materials reviewed, the commission establishes the causes of the occupational disease and determines the circle of persons responsible for the incident.
- Issuing a report on a case of occupational disease.
- Within a month, the employer issues an order to implement measures to prevent occupational diseases.
What documents must be provided for the investigation?
The following documents are required for the investigation:
- order to create a commission;
- sanitary and hygienic characteristics of working conditions;
- information about medical examinations performed;
- extracts from journals on the conduct of briefings and knowledge tests of workers;
- protocols of employee explanations and interviews with colleagues;
- expert opinions, research results;
- medical reports on the nature and extent of health damage;
- documents confirming the issuance of PPE.
In addition to these materials, the commission may require the provision of other papers.
Who heads the commission to investigate occupational diseases
The commission includes representatives of the sanitary and epidemiological surveillance body, trade union and medical organization. The commission can be headed, according to Article 229 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, by a representative of the employer, and in particularly difficult cases - by a state labor inspector or the chief physician of the Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance.
The commission evaluates the working conditions of the victim and also interviews other workers.
In how many copies is the occupational disease investigation report signed?
As a result of the investigation, an act is drawn up in the form approved in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 15, 2000 No. 967. Based on it, the employer then issues an order on measures to prevent the occurrence of occupational diseases. The report is drawn up within three days from the completion of the investigation in five copies. They are transmitted:
- employee;
- employer;
- to the insurer;
- Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance;
- center of occupational pathology.
The document is certified by the signatures of all members of the commission, as well as the seal of the center for sanitary and epidemiological surveillance. The report, together with the investigation materials, is stored for 75 years in the organization and in the center of sanitary and epidemiological surveillance.
Chronic occupational disease
If a preliminary diagnosis of “chronic occupational disease” is established, then the medical institution is obliged to notify the Center for Sensitive Diseases within 3 days about the fact of its registration. And the period for preparing the sanitary and hygienic characteristics of the employee’s working conditions increases to two weeks.
To establish a final diagnosis, the medical institution where the patient is served is obliged to send him with all documents for an outpatient or inpatient examination to an occupational pathology center (OPC) or other specialized health care facility within a month.
The center draws up a conclusion and within 3 days sends a notice to the Center for Sanitary and Social Security, the employer, the Social Insurance Fund and the medical institution at the place of observation of the patient.
One copy of the report is issued to the employee against signature, and one copy is sent to the insurer and to the health care institution that referred the patient.
What are occupational diseases?
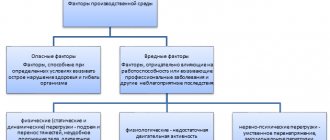
An occupational disease is a disorder in the functioning of the human body due to exposure to harmful production factors. The first PZ was described in the 17th century by the Italian physician B. Ramazzini. In his study “On Diseases of Workers,” he described 52 specialties in one way or another associated with harmful factors, drew parallels and linked the presence of certain diseases among workers with their working conditions (for example, asthma was detected in flour millers, and skin diseases in chimney sweeps) . Thus, with the development of industry and technology, more and more new occupational diseases appeared, which confirmed the fact that diseases are connected with factors of the labor process and the nature of work.
In the USSR, in the early 1920s, the Institute of Occupational Hygiene and Occupational Diseases was created, which became the flagship in the study of this segment, and its main task was and remains to protect the health of citizens at work. An important factor in the Soviet era was the presence of dispensaries created on the basis of medical units of enterprises. They were built everywhere to improve the health of ordinary factory workers. Funding came from trade unions and the organizations themselves, but after the collapse of the state, most of the institutions closed due to a lack of financial resources and the difficult situation. And this, among other things, was the reason for the increase in cases of occupational diseases in the 1990s.
What influences the occurrence of PZ?
The regulation of the health of industrial workers is carried out by a number of regulatory legal acts, including Federal Laws “On Compulsory Social Insurance” No. 125, “On Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare” No. 52, “On the Fundamentals of Labor Safety” No. 181, resolutions of the Government, the Ministry of Labor, Rospotrebnadzor and so on. Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 302n dated April 12, 2011 approved the list of hazardous production factors that affect the conduct of mandatory medical examinations within established periods of time. These factors include:
- Chemical;
- Biological;
- Labor process;
- Physical.
For each factor, the frequency of examinations by specific medical specialists is provided, a set of laboratory tests is established that must be completed, and contraindications to work are also listed. For example, a labor process factor is working with optical instruments. According to the Order, such employees are required to undergo a medical examination once every 2 years by an ophthalmologist and, according to his indications, by an allergist and neurologist. Contraindications for working in such conditions include various eye pathologies, including myopia, astigmatism, and so on.
The category of physical factors includes different types of radiation (ultraviolet, ionizing and others), vibrations, industrial noise, air temperature, gravity, environmental pressure. In the last 2 cases, medical examinations are required once a year by at least 7 specialists, and ultrasound examinations are mandatory. The list of contraindications for such work is huge. Biological includes interaction with toxins, poisons, dust, viruses (including hepatitis, HIV), respectively, in most cases the frequency of medical examinations is once a year with at least 6 specialists, including an infectious disease specialist, an allergist, an oncologist, an ENT specialist, a neurologist and etc. Persons with respiratory diseases are strictly not allowed to participate in such activities.
Chemical factors have the most extensive list of circumstances and substances, when working with which citizens are required to check their health once or twice a year. Such factors are divided into 3 subtypes: the first includes substances that have a pronounced effect on the human body (carcinogens, silicates, aerosols, etc.), the second includes chemical compounds (ammonia, aluminum, chlorine and others), and the third includes complex chemicals. mixtures (pesticides, synthetic polymeric materials, etc.). Of course, the main study that workers in this field must undergo is a study of respiratory functions and blood tests.
What forms and types exist?
According to Government Decree No. 967 of December 15, 2000 “On approval of the Regulations on the investigation and recording of occupational diseases,” there are two types - acute and chronic. The first are caused by a single (or short-term) exposure to any of the above factors, causing temporary or permanent disability. The second type, in contrast to the first, occurs after prolonged exposure. The first can occur in a fairly short time (even within a couple of hours or a work shift) and is most often caused by non-compliance with safety precautions in the workplace, any accidents, and so on. In addition to this classification, the system-organ principle is widely applicable. Occupational pathology distinguishes:
- Damages of the blood system, for example, anemia;
- Hepatobiliary system syndrome, for example, jaundice, cholelithiasis;
- Damage to the kidneys and urinary tract, for example, nephropathy;
- Lesions of the nervous system, for example, VSD syndrome, encephalopathy;
- Skin diseases, for example, eczema, dermatitis.
This classification into groups allows for a more in-depth analysis of the impact of a hazardous production factor on the human body. Grouping allows not only to clarify clinical symptoms, but also to diagnose diseases in time and provide timely and adequate treatment. Thanks to the differentiation of known occupational diseases and the constant analysis and study of newly identified ones, a list of occupational diseases was formed, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 417n dated April 27, 2012.
An example could be:
- toxic anemia, hepatitis;
- radiation sickness, lesions;
- radiculitis, diseases of the nervous system.
The list of occupational diseases is a document with which you can confirm the diagnosis. Based on this, the commission issues a verdict of incapacity for work.
| Didn't find the answer? Ask your question to lawyers 8835 lawyers are waiting for you Quick response, free! |
| RECORDING AND INVESTIGATION OF OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES |
Documents for registration of occupational diseases
An occupational disease is a chronic or acute illness of an employee resulting from exposure to harmful production factors and resulting in temporary or permanent loss of professional ability. An acute occupational disease (poisoning) is understood as a disease that is, as a rule, the result of a single (for no more than one working day, one work shift) exposure of an employee to a harmful production factor (factors), resulting in temporary or permanent loss of professional ability to work.
Features and essence of chronic diseases
In 2021, the greatest risk of loss of disability due to the manifestation of mental illness was noted in mining enterprises, metallurgical plants, agricultural and construction enterprises. At the same time, the incidence rate decreased by almost 2 thousand cases compared to 2012. But the high level of chronic occupational pathology remained - 4,719 recorded cases, that is, 99.2% of the total number of occupational diseases (in 2016 - 5,489, that is, 99.4%), despite the fact that the acute form was established only in 37 cases (out of there are 9 of them in women).
The bulk of chronic occupational pathologies are a consequence of exposure to dust, chemicals and other substances. Thus, the share of dust bronchitis is 21.54%, while asthmatics account for 17.63%. Chronic respiratory diseases also include pneumoconiosis arising from silicon dust - their share is 25.87%. The chronic form of labor problems most often in 2021 arose due to imperfect technological processes (49.24%), design flaws in equipment (39.38%), unsatisfactory condition of workplaces (2.02%) and other things.
Occupational diseases caused by exposure to unfavorable production factors are strictly controlled by authorized government bodies. Inspections and monitoring of working conditions of citizens are carried out at established intervals, as well as prevention of diseases and treatment of already acquired health problems. All these measures contribute to the annual reduction in the number of cases.
We recommend reading: The procedure for establishing the presence of an occupational disease 0/5 (0 votes)>How to register an occupational disease
What is an occupational disease
According to Federal Law No. 125 of June 24, 1998, an occupational disease is a disease the occurrence of which is provoked by harmful working conditions. Occupational diseases are:
- Spicy. They are formed as a result of a short-term influence on the employee’s body of harmful (dangerous) production factors (poisoning, intoxication with chemical compounds, gases).
- Chronic. Formed due to prolonged exposure to harmful factors. One of the signs of such a disease is its protracted nature. These include encephalopathy and disorders of the autonomic nervous system, tuberculosis and lung cancer, decreased hearing and vision, problems with joints, bones, and skin.
In the acute form of the disease, it is easier to prove its connection with harmful production factors. If there is a release of harmful substances at an enterprise and an employee is poisoned, the cause-and-effect relationship is obvious. It is a little more difficult to prove a similar connection in a chronic disease.
Social insurance against accidents and occupational diseases
Art. 212 Labor Code of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2001 No. 197-FZ, art. 5 Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ regulates the obligations of employers to ensure safe conditions and labor protection, as well as compulsory social insurance in relation to persons performing work under an employment contract, sentenced to imprisonment and involved in work, as well as performing work on the basis of a civil contract, if the customer pays insurance premiums to the insurer.
Legislation
Which workers may develop an occupational disease (list of professions), what responsibilities do employers have, are there state guarantees for sick citizens - these and other points are stipulated in several regulations of the Russian Federation:
- general information is provided by the Federal Law “On compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases” dated July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ;
- The procedure for registering an occupational disease is established by the Regulations on the investigation and recording of occupational diseases, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 967 of December 15, 2000;
- Resolutions of the USSR Cabinet of Ministers dated January 21, 1991 and the Council of Ministers dated August 22, 1956 approved two lists of positions and professions that were entitled to additional leaves, early pensions, and other benefits. List No. 1 contains professions identified by the Ministry of Labor as particularly difficult and dangerous. List No. 2 indicates specialties that negatively affect the health of employees, but are not considered particularly harmful;
- Order 417n is a list of occupational diseases, upon detection of which an investigation is initiated, the employee is provided with additional benefits, and free medical care is provided.
New list of occupational diseases
About the new list
About occupational diseases
Property interests associated with loss of health, professional ability to work, or death of an employee due to an occupational disease are the subject of compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases.
The legal, economic and organizational foundations of compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases in the Russian Federation are established by Federal Law No. 125-FZ of July 24, 1998. The same law determines the procedure for compensation for harm caused to the life and health of an employee during the performance of his duties under an employment contract and in other established cases.
Let us recall that an occupational disease is a chronic or acute illness of the insured person. It is the result of exposure of the specified person to harmful production factors and entails temporary or permanent loss of professional ability to work.
Investigation of occupational diseases
The regulation on the investigation and recording of occupational diseases was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 15, 2000 No. 967. According to it, an occupational disease that occurs in an employee who is subject to compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases is an insured event.
Acute and chronic occupational diseases (poisonings) are subject to investigation and recording in accordance with the mentioned Regulations.
Acute occupational disease (poisoning) is understood as a disease that is, as a rule, the result of a single (for no more than one working day, one work shift) exposure of an employee to harmful production factors. It entails temporary or permanent loss of professional ability to work.
A chronic occupational disease (poisoning) is a disease that is the result of long-term exposure of an employee to harmful production factors, resulting in temporary or permanent loss of professional ability to work.
When a preliminary diagnosis is made of an acute occupational disease (poisoning), the health care institution within 24 hours sends:
- emergency notification of an employee’s occupational disease to the Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision, which supervises the facility where the occupational disease occurred;
- message to the employer.
It is the employer’s responsibility to organize an investigation into the circumstances and causes of an employee’s occupational disease.
A report on a case of occupational disease is a document establishing the professional nature of the disease that occurred in an employee at a given workplace.
Tax consultant O.L. Alekseeva
5. The diagnosis of an acute occupational disease (poisoning) can be established taking into account the conclusion of specialists from the Center for Occupational Pathology.
6. Only specialized treatment and preventive institutions and their divisions (Occupational Pathology Centers, clinics and occupational disease departments performing their functions) that have the appropriate license and certificate have the right to make a diagnosis of a chronic occupational disease (or intoxication) for the first time.
7. When deciding whether a given disease is occupational, it is necessary to take into account the nature of the current etiological factor and the work performed, the characteristics of the clinical form of the disease, specific sanitary and hygienic conditions of the production environment and the labor process, work experience in harmful and dangerous working conditions.
8. In case of mixed etiology of occupational diseases, expert questions should be resolved as for an occupational disease.
9. Determination of the degree of loss of professional ability in percentage is entrusted to MSEC (medical and social expert commissions of the Ministry of Social Protection of Russia). If there are grounds determined by MSEC, the appropriate disability group is established and the victim’s need for additional types of assistance is determined.
10. In order to most rationally resolve issues related to the examination of work ability, when formulating a diagnosis of an occupational disease, the main clinical syndromes and the degree of impairment (compensation) of the functions of the affected organs should be indicated.
11. When giving an opinion on labor recommendations, it is necessary to take into account that recognition of a disease as occupational does not always mean a violation of general ability to work. In case of initial and mild forms of occupational diseases and intoxications, in the conclusion on the ability to work, recommendations may be given on the need to stop working in specific production conditions and rational employment without reducing qualifications and earnings.
12. Control over the establishment of a connection between the disease and the profession, the correct application of the List of Occupational Diseases and the Instructions to it is entrusted to the territorial health authorities, as well as the Federal Expert Council on Occupational Diseases at the Research Institute of Occupational Medicine of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences.
Head of Department
preventive medicine
S.I.IVANOV
Head of Organization Department
medical assistance to the population
A.A.KARPEEV
List of occupational diseases for 2019
The list of occupational diseases for the current year was approved by the Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated April 27, 2012 (appendix to the Order). Among its authors are the Institute of Occupational Hygiene and Occupational Diseases (Moscow), Rospotrebnazdor, other structures and individual specialists involved in disease prevention.
In the list, diseases are divided into 4 large sections, each of which describes the names of diseases, forms of their manifestation, possible causes (harmful factors). Here are the groups of diseases identified by officials and the Institute of Occupational Diseases:
- associated with exposure to chemical factors (dust, aerosols, gases, chemical compounds);
- associated with exposure to physical factors (various radiation, electromagnetic field, pressure, noise);
- associated with exposure to biological factors (microorganisms, allergens, viruses);
- associated with physical overload and functional overstrain of individual organs and systems (heavy lifting, visually intense work).
Please note that the list of the Ministry of Health (appendix to Order No. 417n) does not indicate all diseases without exception, but the most common ones are included there.
Occupational diseases
Application
to the List of professional
diseases
By Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated December 10, 1996 N 405, it was approved for the application of the List of Occupational Diseases.
INSTRUCTIONS
ON THE APPLICATION OF THE LIST OF OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES
1. The list of occupational diseases is the main document that is used when establishing a diagnosis of an occupational disease, connecting it with the work or profession performed, when resolving issues of examination of work ability, medical and labor rehabilitation, as well as when considering issues related to compensation for damage caused to an employee by injury health.
2. The List includes diseases that are caused exclusively or predominantly by the action of harmful, dangerous substances and production factors.
3. Acute occupational diseases (poisonings) include forms that developed suddenly, after a single (during no more than one work shift) exposure to harmful and dangerous production factors, the intensity of which significantly exceeds the maximum permissible concentration or maximum permissible limit.
4. Chronic occupational diseases (poisonings) include those forms of diseases that arose as a result of prolonged exposure to harmful, dangerous substances and production factors. The immediate and long-term consequences of occupational diseases (for example, persistent organic changes in the central nervous system after carbon monoxide intoxication) should also be classified as chronic.
Recording and investigation of occupational diseases at work: procedure
Employees who have been diagnosed with a disease included in the list of the Ministry of Health are entitled to compensation. To receive them, the employee must confirm that his illness is associated with the influence of harmful (hazardous) production factors. The investigation process must be initiated by the medical facility (hospital or clinic) where the worker is being observed.
In case of acute occupational illness
When a preliminary diagnosis of “acute occupational disease (poisoning)” is established for a patient, the medical institution within 24 hours sends an emergency notification of the occupational disease to the Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance (TSGSEN) and a message to the employer. Rules for issuing a notice can be found in Order of the Ministry of Health No. 176 dated May 28, 2001.
The Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision, which has received the notification, within 24 hours from the moment of its receipt, begins to clarify the circumstances and causes of the disease, upon clarification of which it compiles a sanitary and hygienic description of the employee’s working conditions and sends it to the clinic to which the employee is attached. In case of disagreement with the points of the characteristics, the employer can formalize his objections in writing by attaching his statement to the paper.
The final diagnosis of the patient can be made by the clinic. Doctors examine the sanitary and hygienic characteristics and assess the patient’s condition. After this, a medical report is issued.
In case of chronic illness
The establishment of an occupational disease is carried out in the following order:
- At a medical institution, doctors conduct an examination of the patient and establish a preliminary diagnosis. The results obtained in the form of a notification are sent to the Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision and to the employer. The deadline for sending notifications in the chronic form is 3 days.
- Within 2 weeks from the date of receipt of the notification, the Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiology provides the medical institution with a sanitary and hygienic description of the employee’s working conditions.
- If a chronic disease is detected, the patient undergoes additional examination. To do this, the medical institution sends the employee to the Occupational Pathology Center within a month.
- After examining the patient and reviewing available documents (referrals from the medical institution, characteristics of sanitary and hygienic working conditions, copies of the work record book, extracts from the outpatient card, medical examination data), specialists from the Center for Occupational Pathology establish a final diagnosis. After this, they draw up a medical report and send a notification within three days:
- to Rospotrebnadzor;
- employer;
- insurer (FSS);
- to the medical institution that referred the patient.
Medical report on the presence of an occupational disease:
- issued against signature to the employee;
- sent to the insurer (FSS);
- sent to a medical facility.
Acute occupational disease
If such a preliminary diagnosis is made by doctors of the medical organization that recorded this case, a notification must be sent to the center of state sanitary and epidemiological surveillance (TSGSEN) and the employer within 24 hours. The notification form was approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated May 28, 2001 No. 176.
The Center for Sensitivity and Epidemiology examines the details and reasons for the occurrence of the disease. The center is given one day after receiving the notification to begin the inspection. Then a sanitary and hygienic description of the employee’s working conditions is compiled, which is sent to the medical institution at the place of observation of the employee.
If the employer does not agree with the conclusions set out in the characteristics, he must record his comments in writing and attach them to the conclusion.
In the medical institution where the employee is observed, the diagnosis is either confirmed and a medical report is drawn up or refuted.
Employer's actions
An employee has been diagnosed with an occupational disease, where should the employer start? The employer is obliged, by order, to form a commission to investigate all the circumstances of the occurrence of the disease and to facilitate its work in every possible way. He is given 10 days to do this from the date of receipt of the medical report. Who heads the commission to investigate occupational diseases? A representative of the Center for Sanitary and Epidemiology, but the commission itself consists of:
- employer representative;
- occupational safety engineer;
- a representative of the medical institution that made the initial diagnosis;
- trade union representative.
Based on the results of the commission’s work, an act on the case of occupational disease is drawn up (the form of the act is approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 967).
In how many copies is the occupational disease investigation report signed? The document is drawn up in 5 copies. It is certified by the signatures of the persons who took part in the inspection and the seal of the organization. One copy of the act remains with the employer. The rest are sent:
- employee;
- to an insurance company;
- in TsGSEN;
- to the medical institution from which the request came.
The storage period for the act in the Central State Sanitary and Epidemiological Service and in the employer’s archive is 75 years. Upon liquidation of an enterprise, documents are transferred to the Central State Sanitary Service.
To prevent the occurrence of new cases of occupational diseases and implement the commission’s instructions, the employer issues an order to take appropriate measures. The order must stipulate that the production must plan for the prevention of occupational diseases among workers. The employer is given one month to carry it out.
Employee payments
From the organization
The employee has the right to claim sick leave payment from the employer. The procedure for calculating benefits is similar to payment for ordinary disability, with the exception of the following:
- the benefit is always assigned in the amount of 100%, regardless of length of service;
- the maximum amount is four times the amount of payment established by clause 12 of Art. 12 125-FZ;
- indexation of benefits in 2021 was carried out on February 1, and now the maximum monthly insurance payment is RUB 77,283.86;
- benefits for all days are paid at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund. If the benefit is assigned before February 1, then indexation in 2021 must be taken into account. After this date, payment of the benefit must be made taking into account the changes.