Working conditions (W) are considered harmful according to experts. Before assigning them such status, the expert must make sure that the position is present in the List. If it is present, a special assessment cannot assign working conditions the status of acceptable or optimal. The list of professions associated with hazardous production is enshrined in law. Changes and additions have been made to it over the years.
Legislative framework and regulation
Initially, occupational hazards were outlined in the Resolution of the USSR Cabinet of Ministers, dated January 26, 1991. It received a second edition on October 2 of the same year. The document approves lists of people entitled to early retirement pension. The procedure for its approval is defined in Art. 30 of the Federal Law “On Labor Pensions” of 2013 and Resolution No. 665 of the Government of the Russian Federation.
Lists of professions with harmful factors
The class of hazardous working conditions is also regulated by other documents:
- Labor Code;
- Resolution No. 198P/122;
- Law No. 426 “On special assessment of working conditions”;
- Resolution No. 188.
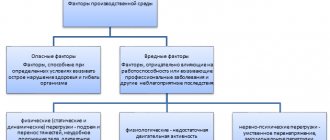
The classification of working conditions allows us to determine how production factors affect a person.
Classification of working conditions
Depending on the factors that a person faces, all working conditions are divided into four categories:
- optimal, when the microclimate is positive, labor productivity does not interfere with anything (manager, accountant);
- acceptable, in which the influence of harmful labor factors does not exceed the norm;
- harmful, when production issues can worsen human health;
- dangerous, associated with an increased risk of threat to life and injury.
Order No. 695 on psychiatric examination: list of professions
Particular attention is paid to harmful and dangerous working conditions. Those categories of exposures that affect reproductive function, reduce immunity and negatively affect a person’s psychological state are considered harmful.
For your information! Hazardous factors can directly provoke a sharp deterioration in health, resulting in the death of an employee. Most often this happens due to a violation of safety regulations at work.
The last two categories of working conditions can have varying degrees of influence:
- mild degree. When the influence of harmful factors ceases, the level of health is restored;
- the worker often goes on sick leave, chronic diseases are discovered;
- the health impairment is irreversible;
- persistent deterioration in the functioning of internal organs leads to disability and loss of the ability to work.
The degree of threat to the health and life of an employee depends on whether he uses protective equipment, takes regulated breaks, and takes measures to improve his health after a shift and prevent occupational diseases.
Worker in hazardous industry
There are certain harmful working conditions that lead to deterioration of health. Harmful working conditions, the list of professions for 2021, related to list Nos. 1 and 2, were compiled taking into account the effect of hazardous production factors on the worker.
If your work activity involves working in harmful or dangerous conditions, then you need additional rest time to restore your strength and health. You may be granted such leave if you work:
• in underground mining;
• in open-pit mining in open pits and quarries;
• in areas of radioactive contamination;
• at other jobs that adversely affect your health (physical, chemical, biological factors);
• you are a medical, veterinary and other worker directly involved in the provision of anti-tuberculosis care, as well as employees of organizations for the production and storage of livestock products serving farm animals with tuberculosis (Federal Law of June 18, 2001 No. 77-FZ “On preventing the spread of tuberculosis in RF").
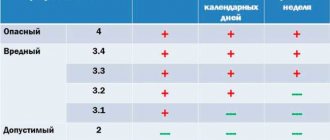
The minimum duration of annual additional paid leave for employees engaged in work with harmful working conditions of 2, 3 or 4 degrees or hazardous working conditions is set at no less than 7 calendar days (by virtue of Article 117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the presence of harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions must be confirmed by the results of a special assessment of working conditions.
It is worth saying a few words about the special assessment of working conditions and changes in legislation that were adopted at the end of 2013. Until 2014, the concept of “special assessment of working conditions” did not exist in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation. Previously, employers were required to carry out “certification of workplaces according to working conditions,” and the articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regarding the provision of additional leave to “harmful workers” looked somewhat different. Previously in Art. Art. 117 and 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation it was stated that the amount of additional leave (as well as other compensation) is established by the Government. For a number of reasons, the Government of the Russian Federation did not fully establish the necessary guarantees and compensation, and therefore acts of the USSR regulating these issues were applied. Readers can learn more about the history of legal regulation here – https://trudprava.ru/expert/article/protect/657. In addition, additional leave was previously granted to all employees who, based on the results of certification at the workplace, were found to have harmful conditions (or dangerous working conditions).
Important!
At the end of 2013, laws were adopted that significantly changed the current labor legislation. In the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in particular in Art. 219, it was directly stated that guarantees for “harmful persons” are prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and are not established by the Government, as it was before. In Art. 117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation established the right of “harmful workers” to a minimum additional leave of 7 calendar days. Thus, since the level of guarantees was clearly established in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in our opinion, the application of acts of the former USSR establishing the level of guarantees and compensation for “harmful workers”, including the List of industries, workshops, professions and positions with hazardous working conditions, work which gives the right to additional leave and a reduced working day, approved. By Decree of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR, the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated October 25, 1974 No. 298/P-22, it is no longer mandatory for employers.
Since the acts of the USSR, for example, in the already named List, established significant additional leaves for workers, many of them have now experienced a significant decrease in the level of compensation provided to them. Employers strive to reduce the additional leave of “harmful workers” to the minimum set forth in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, i.e., to 7 calendar days. At the same time, it is important to know that according to the Law that amended labor legislation (see paragraph 3 of Article 15 of Law No. 421-FZ dated December 28, 2013), the level of guarantees of those employees who were already working at the time of adoption of the changes should not be reduced In the organisation. We consider these provisions of the Law discriminatory; it turns out that for “previously employed workers” the same level of guarantees is maintained, and for those adopted in 2014 and later - in accordance with labor legislation as of 01/01/2014. At the same time, this Law and it is quite possible to refer to it. Note that it is enough for the employer to agree with the employee on dismissal, and then re-accept him, so that the employee ceases to be considered a “previously employed” employee and receives a smaller guarantee.
Attention!
If the collective agreement concluded in your organization states that when determining the amount of additional vacation of “pests”, the 1974 List is applied or an additional amount is established. vacation exceeding that established in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then the employer has no legal grounds not to comply with this condition of the collective agreement. In other words, if the collective agreement contains a reference to the List when determining additional leave, then the List is mandatory for use by the employer.
It is also quite curious that according to current legislation, not all employees who have been identified as harmful can apply for additional leave. This privilege is deprived of employees who, based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, have been identified as hazardous to the 1st degree. Special assessment, as mentioned above, replaced the certification of workplaces based on working conditions. A special assessment is mandatory for all employers (except for individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs. It is also not carried out for homeworkers and remote workers). The procedure for conducting a special assessment of working conditions is regulated by the Federal Law “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ. According to Art. 14 of this Law, working conditions can be: optimal, acceptable, harmful and dangerous. Additional leave under Art. 117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation considers workers with harmful or dangerous working conditions. Harmful working conditions are divided into 4 degrees. If before 2014, an employee who was diagnosed with any degree of harm could apply for additional leave, now additional leave. Leave is not provided for 1st degree harm (these employees receive only a cash supplement). This looks very strange given the fact that, according to clause 1, part 4, art. 14 Federal Law “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” harmful working conditions of the 1st degree - working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, after exposure to which the altered functional state of the employee’s body is restored, as a rule, in a longer period than before the start of the next working day (shift), the cessation of exposure to these factors increases the risk of damage to health.
That is, the legislator himself indicates that in such workplaces workers require a longer recovery period after exposure to harmful factors, and, accordingly, longer rest, but deprives these workers of a reduced working day and additional leave, providing only small monetary compensation. However, the fact remains that this category of workers is no longer provided with additional leave.
You must be familiarized with the results of the special assessment at your workplace by your employer. He is obliged to familiarize the employee with them against signature in accordance with Part 5 of Art. 15 of the said Law. If, based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, no harmful and (or) dangerous production factors are identified, then the employee does not have the right to additional leave, which follows from Part 4 of Art. 219 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
So, unless otherwise provided by the employment contract, collective agreement or Federal Law, “harmful workers” are entitled to 7 calendar days of additional leave.
Important!
Despite the fact that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes minimum amounts of additional leave, some Laws of the Russian Federation and by-laws adopted in their implementation establish increased amounts of additional leave for certain categories of employees. For example, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 22 of the Federal Law “On preventing the spread in the Russian Federation of the disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV infection)” and with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 06.06.2013 No. 482 established an increased duration of additional leave for medical and other workers who diagnose and treat HIV-infected people, as well as persons whose work involves materials containing the human immunodeficiency virus. The same Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation established increased additional leave for harm to employees involved in the provision of psychiatric and anti-tuberculosis care.
Among other conditions necessary to receive additional leave, it should be taken into account that the length of service giving the right to additional leave. vacation, only the time actually worked under the relevant conditions will be included. That is, if you do not work in hazardous conditions all the time, leave should be calculated in proportion to the time worked.
Interesting fact!
According to paragraph 12 of the Instruction on the procedure for applying the List of industries, workshops, professions and positions with hazardous working conditions, work in which gives the right to additional leave and a shortened working day, approved by the Resolution of the State Committee of Labor of the USSR and the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated November 21, 1975 No. 273/P- 20, the length of service required to provide additional leave includes only those days when the employee actually worked at least half the working day under appropriate conditions. According to the same paragraph of the Instructions, the List could contain an indication that the employee is “permanently employed” or “permanently employed” in the appropriate conditions. In this case, only full-time work was counted toward the length of service for additional leave.
Similar provisions are not contained in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, and the List and Instructions for it, as we wrote above, contradict the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and should not be applied.
However, we do not think that the approach of the courts and regulatory authorities on this issue will change. It seems that the length of service that gives you the right to leave for harmful conditions will include only those days when you worked in harmful (dangerous) conditions for more than half of the working day.
An example of calculating vacation in proportion to the time worked (Dates in the examples are given arbitrarily):
For example, on January 11, 2006, an employee joined the organization. From January 11 to June 17, 2007, the employee was temporarily transferred to a workshop with hazardous working conditions, work in which gives him the right to additional leave of 7 calendar days per year of work in such conditions. From June 18, 2007, the employee was granted basic paid leave, to which must be added additional leave for work in hazardous working conditions, calculated for the period of work from January 11 to June 18, 2007:
1). We calculate the number of days worked by an employee in a workshop with hazardous working conditions for the period from January 11 to June 17, 2007:
The employee worked in a workshop with hazardous working conditions for 107 working days according to a 5-day working week calendar;
2). We determine the average monthly number of working days in 2007.
In January 2007 - 17 working days
In February 2007 — 19 working days
In March 2007 — 21 working days
Etc. according to the production calendar for the corresponding calendar year.
(17+19+21+21+21+20+22+23+20+23+21+21) / 12 months. = 20.75 days.
3). We determine the number of full months worked in a workshop with harmful working conditions,
107 workers days: 20.75 days = 5.15 months. (or 5 months and 3 working days). 3 days are less than the average monthly number of working days, so they are not counted. In total it turns out to be 5 months.
Consequently, the employee has the right to additional paid leave for work in hazardous working conditions for the duration of:
7 days / 12 months * 5 months = 2.916 days.
If employees worked in different industries, workshops, professions and positions, each of which gives the right to additional leave, but of different durations, the calculation of the time that was worked in harmful conditions is carried out separately for each job, based on the law, labor or collective agreement on the length of additional leave for employees of such industries, professions, industries, workshops.
For example, from September 18 to December 31, 2005, the employee worked in a workshop with hazardous working conditions, under which, according to the collective agreement concluded in the organization, he has the right to additional leave of 14 calendar days per year.
From January 1 to May 15, 2006 the employee was engaged in loading and unloading dust-laden cargo, which gives him the right to additional leave of 7 calendar days per year.
Then the worker was transferred to a workshop with normal working conditions.
In August 2006, the employee is granted basic leave, to which additional leave must be added, the duration of which must be calculated based on the following:
1). During the period from September 18 to December 31, 2005. the employee worked in a workshop with hazardous working conditions for 74 working days. The number of full months will be: 74 days / 21 days (where 21 days is the average monthly number of working days in 2005) = 3.52 months. Surpluses amounting to more than half a month are rounded up to the nearest full month.
Thus, the employee must be given additional leave for 4 months of work in a workshop with harmful working conditions, which will be: 14 days: 12 months* 4 months. = 4, 667 days – duration of additional leave.
2). On loading and unloading operations from January 1 to May 15, 2006, the employee worked 85 working days or 4.05 months (85 days / 21 days). Surpluses amounting to less than half a month are discarded.
Thus, the employee is entitled to leave for 4 months of work on loading and unloading operations, which in days will be: 7 days / 12 months. * 4 months = 2.333 days.
3). The total duration of additional paid leave for work in harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions will be 4.667 days + 2.333 days = 7 days.
ATTENTION!
If the main annual paid leave is prohibited from being provided for two years in a row, then the employer is obliged to provide additional leave for work in harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions annually. The employer does not have the right to try to recall the employee from this additional leave, nor does he have the right to replace this leave with monetary compensation, except in cases of dismissal of the employee.
Annual additional paid leave for the special nature of the work
You may be given additional paid leave if the work you do is significant. We are talking, for example, about general practitioners (family doctors) and nurses of family practice doctors (family doctors) for continuous work in these positions for more than 3 years - they are granted leave of 3 days (Regulation of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 30, 1998 No. 1588 “On establishing for general practitioners (family doctors) and nurses of general practitioners (family doctors) an annual additional paid 3-day leave for continuous work in these positions”).
In general, the list of categories of employees who can be granted such additional leave, its minimum duration, and the conditions for its provision are determined by the Government of the Russian Federation.
ALL MATERIALS IN THE SECTION “RELAXING ACCORDING TO THE RULES”
By what criteria are professions included?
Bibliography on occupational health and safety
It is impossible to quantify harmful factors in the workplace. The criteria for including professions in the list are as follows:
- working in dust;
- constant contact with paint and other chemical sprays in industry;
- influence of radiation;
- working in noise;
- contact with microbiological material (in medicine);
- high level of humidity;
- constant vibration in the workplace;
- temperature changes.
For your information! Depending on the concentration of harmful factors in the surrounding space, a list of professions classified as harmful and dangerous has been determined.
What indicators are assessed when conducting a production commission?
When determining the hazardousness of production, the state commission evaluates the following factors:
- Volume of noise effects of the enterprise;
- High concentration of dust in the air. A significant content of dust in the environment leads to its settling in the lungs, which gradually destroys the respiratory structures of the body;
- Poor lighting. In such working conditions, mental health suffers the most. There is greater sensitivity and irritability, disturbances in the employee’s mood and general condition;
- Pathological exposures;
- Excessively high or low ambient temperature;
- Working with chemicals;
- Significant level of vibration during operation;
- Severely polluted working conditions;
- The severity, duration and level of stress of labor specialties.
A significant amount of dust in the environment leads to its settling in the lungs
Hazardous professions according to lists No. 1 and 2
Working conditions class 3 subclass 3: additional pay and benefits
Harmful professions (list Nos. 1 and 2) were created 60 years ago and remain relevant to this day. The first list includes particularly dangerous and difficult activities that pose a threat to life. List No. 2 - professions associated with contact with harmful labor factors. Due to this, employees involved in the areas receive permanent health problems during long-term interaction. Therefore, to obtain the right to benefits, it is necessary to comply with the conditions for working time in hazardous conditions.
Important! The difference between the groups lies in the degree of impact on the body. The second group poses less danger.
List No. 1: particularly harmful conditions
“Pests” in lists No. 1 and 2 are prescribed in the corresponding government decree. The first includes professions associated with the critical impact of harmfulness on the body, bordering on a threat to life:
- employees working above ground level in mining;
- workers in the production of ferrous and non-ferrous metals;
- gas and oil producers;
- involved in the production of building materials, as well as repair and restoration work;
- chemical production workers;
- employees of a glass processing plant;
- healthcare workers;
- involved in the printing business.
Professions with hazardous working conditions where additional leave is required
According to this list, there is a list of professions that are directly related to harmful ones. For example, a driver at a metallurgical plant will also qualify for early retirement if he has worked the required number of years. Teachers who teach the rules of handling chemicals and reagents are also included in the first list. The second list of hazardous occupations includes a smaller number of specialties.
List No. 2 of preferential professions
This list includes persons:
- processing metals and coal (welders, shop workers, rolled metal production);
- signalmen;
- employees of food factories;
- railway workers;
- social service workers;
- pharmaceutical production workers.
The specific list includes the following professions:
- electricians;
- geologists;
- agricultural machinery drivers;
- reinforcement workers, concrete workers;
- rolling stock drivers, conductors;
- workers installing communications equipment and maintaining stations;
- workshop for the production of metal pipes, chain-link mesh.
For your information! In order to avoid mistakes and correctly determine which category an employee belongs to, all professions are divided into lists. They are constantly adjusted according to the economic needs of the state.
Professions that give the right to early retirement
Early retirement guarantees not only employment in hazardous industries, but also a certain length of service devoted to this type of activity, as well as an individual pension coefficient of at least 30 for working years.
The procedure for early registration of pensions for such citizens is regulated by two lists. These are the so-called professions of lists 1 and 2, which give the right to early registration of pension benefits (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 16, 2014 No. 665).
The first list identifies professions that can cause serious harm to health. This includes, for example, the following areas of work activity:
- rock development;
- ore beneficiation and roasting;
- production of ferrous and non-ferrous metals;
- specialists involved in the coke industry;
- employees associated with generator gases and chemicals;
- involved in the production of ammunition and explosives;
- oil and gas production and processing;
- metalworking specialists;
- manufacturers of building materials;
- workers engaged in the manufacture of products from glass, porcelain, artificial fibers;
- pulp and paper mill workers;
- representatives of motor transport enterprises;
- persons involved in printing;
- pharmacists;
- work with radioactive substances, specialists in the field of nuclear energy and industry.
To obtain a pension, representatives of the professions listed in the first list must fulfill the following conditions (clause 1, clause 1, article 30 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ “On Insurance Pensions”):
- Men - work for at least 10 years in a hazardous enterprise, retire at 50 .
- Women who have worked for at least 7 years and 6 months at such enterprises receive a pension at 45 years of age .
This is important to know: What does freezing the funded part of a pension mean: how to receive payments
Download for viewing and printing:
The second list includes less harmful professions, but long-term employment in this area can negatively affect health. These include:
- positions related to mineral processing;
- metallurgy;
- gas-electric welders;
- railway transport workers;
- persons employed in food industry enterprises;
- healthcare workers;
- peat extraction;
- employees of agrochemical complexes;
- communications enterprises;
- electrical engineers and specialists involved in the repair of electrical equipment;
- construction specialties.
The following conditions for early registration of pension provision apply here (clause 2, clause 1, article 30 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ “On Insurance Pensions”):
- Men - at least 12 and a half years of experience, retirement at age 55 ;
- Women - at least 10 years of experience, retirement at age 50 .
Download for viewing and printing:
Important! Both lists do not require additional documentary evidence of employment in hazardous and life-threatening industries. To apply for benefits and reduce the retirement age, an entry in the work book is sufficient.
Features of retirement conditions based on harmfulness
For an employee to be eligible for early retirement, several conditions must be met. Professions belonging to list No. 1 may stop working earlier provided:
- men aged 50, if their work experience has reached 20 years, of which 10 are in hazardous work;
- women aged 45 years, subject to a total work duration of 15 years, half of this period in dangerous work.
If you work in a hazardous industry, early retirement is possible if:
- men reach the age of 55 years, the total work experience must be 25 years, of which 12.5 years in hazardous production conditions;
- women over 50 years of age, with a total work history of 20 years, half in hazardous conditions.
If an employee has worked the required amount of time in a complex production, but the total length of service does not reach the required level, the employee can leave earlier in proportion to the number of years worked (not at 50, but at 53, for example, two years before the age pension).
Conditions for early retirement for lists No. 1 and 2
Benefits for an employee in hazardous work
Federal legislation provides benefits for all professions that have unfavorable working conditions.
Employees of such enterprises are assigned the following benefits:
- Increased wages. The increase in official salary is made by at least four percent;
- Additional vacation. This category of workers can take out additional leave every year, which will be paid by the employer. The vacation period must be at least seven days;
- Opportunity to retire earlier. Men can legally retire at fifty-five years of age, and women at forty-five, if they are included in the first list, and fifty years for women and fifty-five years for men, if they are included in the second list;
- The duration of the shift should be from six to eight working hours, and no more than thirty-six hours in seven days;
- Nutrition. Before starting work, the employer is obliged to provide workers with a hot breakfast, and after the shift - with milk or fermented milk products;
- Free medicines and personal protective equipment;
- As well as other preferential benefits provided in certain regions.
Preferential pension provision according to lists No. 1 and 2
The procedure for calculating pensions is determined by Federal Law 400-FZ “On Insurance Pensions”. An employee will be accrued a preferential pension if the employer has made contributions to the state for all the years. There is no additional increase in the level of contributions. The size of the pension can be higher only taking into account the fact that wages in hazardous industries are higher compared to other areas.
Starting from 2015, the employer must pay an insurance payment of at least 9% of the employee’s income to the fund, otherwise the length of service will not be counted as work in hazardous working conditions. Due to changes in the retirement age, under the new legislation, persons who were previously supposed to retire in July 2021, and according to the new rules in January 2021, will be sent to retire six months earlier, that is, according to the old deadlines.
Thus, these lists play a significant role in the lives of many workers. They are important for arranging early retirement and related payments. They are no less interesting for the employer to know how to properly organize production activities.
List of benefits and compensations
Expert opinion
Davydov Alexander Yurievich
Civil law consultant with 20 years of practice. Author of numerous articles on legal topics
Representatives of dangerous and hazardous professions are provided with a number of benefits that must be strictly observed by the employer. This includes the following points:
- free and regular provision of work clothes, footwear and personal protective equipment in accordance with the regulations of the enterprise (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- provision of additional days to paid annual leave (Article 117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- additional payment for special working conditions: at least 4% of the official salary (Article 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- shortened working week: such citizens cannot be employed more than 36 hours a week (Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- issuance of medical nutrition: dairy and fermented milk products, financial compensation is allowed, paid monthly (Article 222 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- annual medical examination at the expense of the enterprise; in some cases, additional medical examination is allowed before performing certain duties (Article 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
These measures are mandatory for every employer whose employees are involved in industries that are hazardous to health and life. Enterprise managers do not have the right to refuse to provide employees with medical nutrition or financial compensation for failure to receive it.
In addition, the employer cannot oblige such employees to purchase personal protective equipment and other equipment necessary for the safe performance of work at their own expense.
When faced with such violations, employees can complain to the labor inspectorate or the prosecutor's office. As legal practice shows, in such situations the law is 100% on the side of the employee.