Normative base
Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 08/18/2011 N AS-4-3/
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08/27/2012 N 03-04-05/6-1006
Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 N ММВ-7-11/ “On approval of codes for types of income and deductions”
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 17, 2016 N 03-04-05/8718
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 16, 2014 N 03-04-05/64847
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 2, 2016 N 03-04-05/71785
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 20, 2017 N 03-04-06/2414
Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated August 20, 2015 N 304-KG15-9468 in case N A45-16187/2014
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02.09.2014 N 03-03-06/1/43912
Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 15, 2016 N BS-4-11/
Tax-free financial assistance 2021
Who can receive financial assistance at work? To give financial assistance or not to give is the right of the employer. Financial assistance may also be paid selectively. During a calendar year, an employee has a non-taxable limit of financial assistance of 4,000 rubles for various purposes. The limit of 4,000 rubles does not depend on the connection in which the money was issued. It could be:
- wedding;
- birthday;
- financial assistance for the anniversary (taxation 2020);
- acquisitions;
- treatment, etc.
Taxation of financial assistance in 2021 and insurance premiums from it vary depending on whether payments exceed 4,000 rubles.
The only exceptions are:
- death of an employee or his relative;
- birth of a child;
- natural disasters and terrorist attacks.
When a subordinate becomes a parent, he can be paid up to 50,000 rubles without calculating insurance premiums. Financial assistance in connection with the death of a family member, compensation for damage due to injury, terrorist attack, emergency or accident are not included in the base for calculating insurance premiums and personal income tax. Thus, taxes on financial assistance and the maximum amount in 2021 remain unchanged for now.
Please note that one-time financial assistance is considered a payment for certain purposes, accrued no more than once a year on one basis, that is, on one order (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. AS-4-3/13508). How a person receives the money - all at once or in parts throughout the year - does not matter (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03-04-05/6-1006).
Financial assistance to someone not working in the organization
There is no need to impose contributions on financial assistance to individuals with whom the company does not have labor relations or civil contracts. Payments of financial assistance to a person who does not work in the company are not subject to taxation (clause 1 of Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This applies to payments to former employees (including pensioners), as well as to relatives of a deceased employee.
Document:
Insurance premiums in 2021
Order a free collection
materials from ConsultantPlus “Insurance premiums from calculation to report”! In the selection you will find the procedure for calculating insurance premiums, basic and reduced rates, examples of calculating contributions for injuries, refunds and credits for overpayments on insurance premiums, and much more.
Financial assistance: taxation 2021, insurance premiums
Is financial assistance subject to insurance premiums in 2020? Since financial assistance does not relate to income related to the employee’s performance of his work duties, it cannot be subject to contributions. However, this provision has a number of limitations. That is, the manager cannot pay his employees any amount as financial assistance. Since 2021, issues related to fees for employee insurance are explained in Chapter 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Situations when you do not have to pay are contained in Art. 422 codes. Amounts from one-time financial assistance paid under the following circumstances are not calculated:
- the employee received money to compensate for damage caused by a natural disaster or emergency;
- the victim of a terrorist attack on the territory of the Russian Federation was compensated for damage to health;
- the employer helped with money in the event of the death of a member of his family;
- an amount of up to 50,000 rubles was paid as support for the birth of a child. Not only each parent, but also the adoptive parent and guardian have the right to it;
- the amount of financial assistance does not exceed 4,000 rubles during the year.
We remind you that 4000 rub. - this is tax-free financial assistance (2020). If payments are higher, they are subject to insurance premiums. In this case, the goals may be different, for example, for partial compensation of expenses for additional education, to cover the costs of purchasing medicines, for vacation. Note that the situations listed apply to all existing types of compulsory insurance: pension, medical, social, as well as injuries. In addition, they apply to assistance in both in-kind and cash forms. So, 4000 rubles for financial assistance. (taxation 2020) insurance premiums are not charged
How is it taxed?
Financial assistance is subject to mandatory taxes. But there are certain restrictions on different types of deductions from wages when they will not be taxed. Insurance contributions to social funds will not be charged on the mat. help in the following cases if:
- the employee terminated the contract for the performance of his professional duties with the organization;
- the employee's family member died;
- the employee was influenced by unforeseen circumstances or natural disasters;
- the employee has a child and/or financial support is provided after the birth within twelve months from the date of birth;
- the amount of assistance is no more than four thousand.
Personal income tax on mat. assistance is not awarded in the following cases, if support is provided:
- in connection with the appearance of a new member in the family and within twelve months from the date of his birth, and the amount of payments for the entire period does not exceed fifty thousand;
- a resigning employee due to disability or upon reaching retirement age;
- employees to pay for study, recreation or medical procedures and the amount of assistance should not be more than 4,000 rubles per year;
- in connection with the death of someone close or the employee himself.
If there are other reasons for dismissal, mat. assistance is subject to personal income tax. You also need to know that the amount of financial assistance is not taken into account when calculating income tax. For any questions that you have after reading this article, you can contact our website consultants.
Expert opinion
Korolev Konstantin Georgievich
Practicing lawyer with 7 years of experience. Specialization: criminal law. More than 3 years of experience in document examination.
Extra money never hurts, so it will be useful to know how to get financial assistance at work, in what cases is it issued and what is the amount?
Financial assistance up to 4000 (taxation 2020)
Let's consider the taxation of financial assistance to an employee in 2021. Is financial assistance subject to personal income tax (2020)? The withholding of personal income tax is indicated in Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation specifies whether financial assistance is subject to personal income tax. If you carefully read this article, it will become clear that income tax for individuals is not withheld in the same cases when insurance premiums are not collected. We are talking about the payment of money upon the birth of a child or the death of a family member, amounts up to 4,000 rubles (for any purpose). At the same time, we must remember that the 2-NDFL certificate will have different income codes and deduction codes each time - depending on the type of financial assistance provided and taxation or collection of insurance premiums (Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/).
Here are some more interesting points:
- According to the Ministry of Finance, monthly financial assistance to a person on maternity leave can be subject to personal income tax, taking into account standard tax deductions, the amounts of which are contained in paragraphs. 4 clause 1 of Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Letter dated 02/17/2016 No. 03-04-05/8718). In other words, if an employer pays extra every month to a woman on maternity leave, he can reduce the amount of the extra payment by the so-called child deduction. Since this form of support may be a general type of financial assistance, and not a one-time payment in connection with the birth, although one reason is the birth of a baby;
- financial assistance, tax-free in 2021, is provided by the employer to family members of a deceased employee or former employee who previously retired due to disability, age or old age, or to the employee (pensioner) himself if one of his family members has died (Letters from the Ministry of Finance dated 16.12 .2014 No. 03-04-05/64847, dated 12/02/2016 No. 03-04-05/71785);
- if the fact of an emergency or terrorist act is not confirmed, the employer takes personal income tax from compensation (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 20, 2017 No. 03-04-06/2414).
Features of taxation of financial aid
If the amount of financial assistance does not exceed 4,000 rubles per year for any reason, personal income tax on financial assistance in 2021 is not withheld. But there are several special cases, which we will consider in detail.
1. Financial assistance that is completely exempt from personal income tax is financial assistance, which is issued in the case of:
- death of a close relative of an employee, death of a former employee;
- emergency circumstances, including natural disasters;
- prevention, suppression and other actions to prevent the commission of a terrorist act.
2. Non-taxable within the limit of 50,000 rubles:
- employees at the birth (adoption, establishment of guardianship) of a child.
According to paragraph 28 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, such one-time financial assistance is excluded from the tax base for personal income tax; with regard to insurance contributions, the position of the Ministry of Finance is identical. The material assistance code in the 2-NDFL certificate up to 4,000 rubles is indicated in the Federal Tax Service order No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] dated 09/10/2015. This includes:
- income code 2760 (material for employees, former employees who left upon retirement);
- income code 2710 (other types of financial assistance not related to code 2760).
The deduction code for any material income code also depends on the basis for charging the employee.
IMPORTANT!
If material support exceeds the limit, then financial assistance is subject to personal income tax only on the excess amount.
The legislation establishes a number of cases in which material is completely excluded from the base for calculating tax, regardless of the amount:
- One-time payments to victims or family members of those killed as a result of a natural disaster or emergency (clause 8.3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Assistance to citizens injured as a result of a terrorist attack on the territory of the Russian Federation, and family members of those killed under these circumstances (Clause 8.4 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- One-time assistance to an employee in connection with the death of a member of his family. The payment can be made to a former employee who has retired (clause 8 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Material for the birth of a child or his adoption. The legislation sets a limit - no more than 50,000 rubles for each child, and per each parent per year (clause 8 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Such clarifications were given by representatives of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in a letter dated July 12, 2017 No. 03-04-06/44336. Officials withdrew previous clarifications that required providing a 2-NDFL certificate from the spouse’s place of work in order to receive the material.
- One-time financial assistance to an employee and a retired person to pay for medical services (Clause 10, Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In order for the tax authorities to recognize this payment as financial assistance, it is necessary not only to document the circumstances, but also to make the payment exclusively from the net profit of the enterprise (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated January 17, 2012 No. ED-3-3 / [email protected] ).
Support for quitting employees
An interesting question: what to do with insurance deductions from payments to ex-employees. Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation will help answer this, which states that contributions are accrued for remuneration under employment agreements or GPC agreements. Since there are no such relationships with those who quit, there is no need to retain anything. At the same time, inspectors may have questions on what basis financial support was provided. Organizations need to keep this point in mind when discussing financial assistance (taxation 2021, insurance premiums).
The procedure for obtaining financial assistance in an organization
To receive money, the employee writes a free-form application. In some cases, he will have to prove his right to financial assistance of 4,000 rubles. (taxation 2021, insurance premiums) and provide relevant documents, such as a birth or death certificate, a certificate of accident, etc. Based on the application, the manager issues an order. Below are samples of documents that can be used when applying to an employer for financial assistance at the birth of a child.
Sample application for financial assistance
Sample order for financial assistance
When an employer pays financial assistance
Situations when employees need to provide financial assistance are determined by the employer himself. It could be:
- employee's marriage,
- the birth of a child in his family,
- treatment of the employee or his children (for example, purchasing expensive medicines, receiving paid medical services),
- death of a family member of the employee (for example, mother, father, spouse),
- employee's retirement.
All grounds for receiving financial assistance are usually prescribed in a local regulation or collective agreement. They also indicate what documents the employee needs to bring, how much money they will give, and within what time frame they will be transferred.
The employer can provide both specific amounts of financial assistance and a range, for example, 20,000 ₽ - 100,000 ₽.
If the conditions of financial assistance are not specified anywhere, the head of the organization, upon request of the employee, can decide on payments personally.
Financial assistance in tax accounting
In tax accounting, financial assistance is not reflected (clause 1 of article 252, clause 23 of article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The Ministry of Finance made only one exception. Material assistance can be taken into account in labor costs if it is provided for in the company’s internal personnel documents and is related to the performance of job duties (Letter No. 03-03-06/1/43912 dated 09/02/2014). An example is financial assistance for vacation.
Accounting for financial assistance
The reflection of financial assistance in accounting depends on whether it is stated in local documents.
If, for example, the payment of financial assistance is provided for by the Regulations on remuneration, then it should be accrued on the credit of account 70 “Settlements with personnel for remuneration”.
If financial assistance is paid at the request of the employee and is not provided for by the organization’s local regulations, then it must be accrued as a credit to account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations.”
When providing financial assistance to former employees or relatives of an employee, settlements with them are reflected in account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors.”
The order for the provision of financial assistance must indicate the source of payment. If this is the profit of previous years, then the debit of account 84 “Retained profit (uncovered loss)” is used, if the current profit is the debit of account 91 “Other income and expenses” (sub-account “Other expenses”) or the debit of cost accounting accounts - 20, 26, 44 (if financial assistance is recognized as part of wages).
Financial assistance to low-income families in 2021
Financial assistance to low-income citizens of the Russian Federation is currently provided in several forms. The most common option is cash payments that the state makes monthly. In addition, there is one-time monetary assistance in the form of a grant for training, a scholarship, assistance for the purchase of basic necessities, assistance in kind (food, medicine, etc.). A low-income family may be exempt from paying all taxes and fees when calculating material assistance in the form of benefits and subsidies.
Children who are raised in a family with low-income status have the right to receive education in higher and secondary educational institutions, taking part in a general competition for applicants. They can also count on help from the state, but for this at least one of the following conditions must be met:
- if the child is raised by only one parent who is recognized as a disabled person of the second or first group;
- if a child from a low-income family has scored the minimum number of points based on the exam results, which allows him to take part in the competition, since the exams are considered to have been passed successfully;
- the age of the child who wishes to enter a higher education institution does not exceed 20 years.
There are a number of innovations specifically for children raised in low-income families:
- out of turn children must be admitted to educational preschool institutions;
- in schools, children must have two meals a day, which are paid for by the state;
- Children should receive both a uniform for school and clothing for sports free of charge;
- Children under 6 years of age can receive the necessary medications for free, but only with a doctor’s prescription.
Parents who are part of a low-income family can count on the following benefits:
- preferential employment;
- lowering the retirement age;
- exemption from paying registration fees;
- obtaining a garden or summer cottage plot out of turn;
- obtaining a mortgage loan on preferential terms.
Taxation of financial assistance to an employee
Each employer has the right to independently decide on the issue of financial assistance to its employees. It may be provided for by a collective agreement, be part of the remuneration system, or an employee could simply turn to the employer for it in a difficult life situation.
Payments to employees are classified as financial assistance if the following criteria are present:
- payments are made to employees when special circumstances arise;
- the payment is made not as part of the employee’s performance of his labor functions and does not depend on the individual results of his work;
- payments are not regular.
Thus, financial assistance is not stimulating or compensatory in nature and is not considered an element of remuneration.
GOOD TO KNOW
The amount of financial assistance, as a rule, is established by the management of the organization depending on each specific situation and the financial capabilities of the organization. In this case, the conditions for the payment of financial assistance and its specific amounts are determined by the local regulations of the organization.
Payment of financial assistance is usually made when the following main circumstances arise:
1. Financial assistance at the birth (adoption) of a child.
This type of financial assistance can be paid in the amount of up to 50,000 rubles. during the first year after birth (adoption) for each child and is not subject to personal income tax (clause 8 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The payment can be made to one or both parents, provided that the total amount does not exceed RUB 50,000. The employer has the right to request a certificate of income in form 2-NDFL from the place of work of the second parent in order to control the amount of financial assistance paid to both parents, although by law the employee is not required to submit it independently. The employer may also request a copy of the work record book to confirm that the second parent is not employed. A certificate from the employment service may also be requested (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 1, 2013 No. 03-04-06/24978). Another feature of this type of financial assistance is that it may not be one-time, but it will still not be subject to personal income tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated August 27, 2012 No. 03-04-05/6-1006, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 28. 2013 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] ).
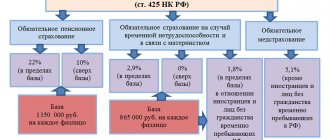
Insurance premiums for this type of financial assistance are not charged in accordance with clause 3, part 1, art. 9 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ and paragraphs. 3 p. 1 art. 20.2 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ.
GOOD TO KNOW
When a positive decision is made to satisfy an employee’s request for payment of financial assistance, an order must be issued indicating his last name, first name, patronymic, as well as the grounds for payment of financial assistance and its amount.
2. Financial assistance in connection with the death of a member (members) of the employee’s family.
This type of financial assistance is also not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions.
3. Financial assistance in connection with the death of the employee himself (or a former employee who has retired) to family members.
Likewise, it is not subject to personal income tax or insurance premiums.
4. Material assistance in connection with a natural disaster or other emergency in order to compensate for material damage caused to employees or harm to their health, as well as to individuals affected by terrorist attacks on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Not subject to personal income tax, not subject to insurance premiums.
5. Financial assistance to persons affected by terrorist attacks on the territory of our country, as well as citizens who are family members of persons killed as a result of terrorist attacks on the territory of the Russian Federation.
This type of financial assistance is completely exempt from paying personal income tax (clauses 8.3 and 8.4 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and insurance contributions.
GOOD TO KNOW
When including amounts of financial assistance paid to an employee in the personal income tax tax base, it is necessary to take into account the provisions of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
6. Financial assistance in connection with going on vacation.
This financial assistance is subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions, as it depends on the amount of wages, labor discipline and, as a rule, is established by labor and collective agreements. The employer, in turn, can include this type of financial assistance in expenses related to wages (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated September 2, 2014 No. 03-03-06/1/43912).
7. Financial assistance for no particular reason.
Not subject to personal income tax and insurance premiums up to 4,000 rubles. during the billing period. In excess of 4000 rubles, according to the authorities of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund (letter dated July 29, 2014 No. NP-30-26/9660, 17-03-10/08-2786P) and the Ministry of Labor of Russia (letter dated January 20, 2014 No. 17-3/ B-13), it is necessary to impose insurance premiums on the amount of financial assistance. But judicial practice has developed exactly the opposite. According to the courts, if this payment is not of an incentive nature, is not paid depending on the qualifications of the employee, the complexity and quality of the work performed, working conditions, or is paid in connection with a collective agreement, then it is of a social nature and insurance premiums should not be charged on it (see, for example, Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 14, 2013 No. 17744/12, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated July 31, 2014 No. A33-15536/2013).
8. Material assistance to the trade union organization.
If there is a trade union in the organization, the amount of swearing provided. assistance is established by his decision. There are no insurance premiums. Personal income tax is not assessed only if it was issued to a direct member of the trade union.
GOOD TO KNOW
From the provisions of Law No. 212-FZ it follows that material assistance paid not on the grounds named in clause 3 of part 1 of art. 9 of this law, is subject to insurance premiums if the payment amount exceeds 4,000 rubles. per employee per billing period.
Methods for establishing financial assistance for employees
Financial assistance to employees, as mentioned above, is established by decision of management. It can be provided for in an employment contract, a collective agreement, or in the case where the employee simply turned to the employer for help, while the application to the LLC or JSC was considered at the general meeting of the company’s participants and documented in the minutes of the meeting (Clause 6, Article 37 of the Federal Law dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies”, Article 63 of the Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ “On Joint-Stock Companies”), mainly if it was decided to issue financial assistance at the expense of the profits of previous years . If there is only one participant in the company, his decision is also formalized in writing.
Financial assistance can be established depending on the employee’s salary, qualifications, working conditions, labor discipline, complexity and quality of work performed, or it can be of an incentive nature, paid upon the birth of a child or provided in connection with the death of a close relative.
GOOD TO KNOW
Financial assistance can be paid both to the employee himself and to a member of his family (for example, in the event of the death of the employee). Tax consequences will vary, and the specific tax benefit depends on the reason for providing financial assistance.
Assessing the effectiveness of the form of financial assistance
| Form of financial assistance | Grade | pros | Minuses |
| Regular financial assistance to an employee | Safe form. There will be no claims from inspectors | No tax risks | In general, the amount is over 4,000 rubles. per year per employee is subject to personal income tax (NDFL) and insurance premiums, but there are exceptions |
| Ordinary financial assistance to a family member of an employee | Safe form. There will be no claims from inspectors | Insurance premiums are not charged | It is necessary to charge personal income tax on the full amount and submit form 2-NDFL to the tax authority |
| One-time social bonus | Safe form, does not save on taxes | No tax risks | The full amount is subject to personal income tax and insurance premiums |
| Interest-free non-repayable loan | The most risky form for both the employer and the employee. Tax optimization does not justify the risks. We do not recommend using | Insurance premiums are not charged on the loan amount; Personal income tax on material benefits for using an interest-free loan and on the amount of the loan itself is not calculated | Tax disputes are possible. Risks of retraining in remuneration with corresponding taxation. Tax risks in case of recharacterization of the operation as debt forgiveness. Risks for the employee in terms of uncertainty that the employer will not demand repayment of the debt |
| Giving money under a written gift agreement | A completely legal, but attention-grabbing form. Should not be used regularly | A significant amount (in general - 34% of the payment) is exempt from insurance premiums | A sum of money over 4000 rubles. subject to personal income tax. Attracts the attention of the tax office. Risks of reclassification into regular financial assistance with corresponding tax consequences |
Is financial assistance a remuneration system?
Not all financial assistance relates to wages. Material assistance of a social nature cannot in any way relate to the wage system, but material assistance related to the performance of labor functions will. A striking example of material assistance, which is a system of remuneration, is material assistance in connection with an employee going on vacation, since it depends on compliance with labor discipline and wages, and other economically justified types of material assistance provided for in labor or collective agreements, aimed at generating income activities (clause 1 of article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
GOOD TO KNOW
When calculating average earnings, the time of vacations and periods of temporary disability, as well as amounts accrued during this time (vacation pay, temporary disability benefits) are excluded from the calculation period. Social payments (financial assistance, etc.) are also excluded from the billing period.
Financial assistance for pensioners in 2021
Many pensioners are interested in the question of whether the government will repeat the one-time payment of 5,000 rubles, as it did in 2017. No, no such payment is planned. This was a single measure taken by the government in order to compensate for losses from rising prices.
From January 1, 2018, insurance pensions were indexed; the increase was 3.7 percent. In monetary terms, this is approximately 300-500 rubles.
Social pensions, received by those who do not have a single day of work experience (disabled people, disabled children, those who have lost their breadwinner, etc.), have increased by 4.1 percent since 04/01/2018. Depending on the disability group, this ranges from 175 to 500 rubles. Pensioners who are officially employed may not count on indexation in 2021.
Financial assistance to large families in 2021
Today the state provides large families with:
- material support for the construction of a house;
- benefits for obtaining housing using social rent;
- land;
- subsidies for payment of utility bills;
- targeted benefits.
In the coming year, 2021, benefits will be provided as before. Assistance will be provided to each family subject to the same conditions:
- presentation of a certificate of large families issued by social security authorities;
- age of children (set separately by regions);
- if parents do not shirk their responsibilities.
Financial assistance to military personnel in 2021
Financial assistance to military personnel is accrued in the amount of their salary after submitting a report to the superior. If assistance is not received, it is accrued at the end of the year along with wages. The payment is issued based on the signing of the order by the commander. Financial assistance to military personnel is paid:
- when going on vacation;
- at the birth of a child;
- in case of wedding;
- in the event of the death of a relative;
- when the employee’s financial situation is difficult.
Financial assistance is calculated based on the following components on the 1st day of the last month of the year: monthly salary, taking into account military rank; monthly salary based on position.
FAQ
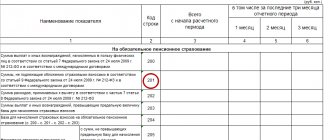
Financial assistance 4000 rub. - income code in certificate 2-NDFL
Financial assistance paid in connection with the death of an employee or a member of his family is not subject to personal income tax, therefore, it does not need to be reflected in the 2-NDFL certificate.
Financial assistance paid for other reasons is reflected in 2-NDFL in full amount according to the codes:
- 2762 - at the birth of a child;
- 2760 - for treatment, anniversary, for other reasons.
At the same time, a deduction for financial assistance is indicated with the following codes:
- 508 - at the birth of a child (maximum 50,000 rubles);
- 503 - for other reasons (RUB 4,000).
Financial assistance 4000 rub. and income tax
Material assistance is not included in the enterprise’s expenses when calculating profit tax (clause 23, article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But insurance premiums calculated on the amount of financial assistance exceeding 4,000 rubles can be included in other expenses associated with production and sales (clauses 1, 45, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
How to make postings in 1C 8.3
Financial assistance is reflected by the posting: Debit 91 Credit 73 (76). To reflect it in 1C 8.3 you need to:
1. Set up the additional accrual “Financial Assistance” in the “Salaries and Personnel Management” section.
2. Then, in the “Methods of reflecting wages in accounting” section, create a method for reflecting financial assistance and write down the corresponding entries.
3. Select the correct method of reflecting the previously created additional accrual on the “Accounting and UTII” tab.
Income code and deduction code in 2021
| Index | Code |
| Financial assistance at the birth of a child | 2762 |
| Financial assistance for treatment, anniversary, etc. | 2760 |
| Deduction for payment of financial aid at the birth of a child (RUB 50,000) | 508 |
| Deduction for payment of other financial assistance | 503 |
Financial assistance 4000 under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”
When applying the simplified tax system, financial assistance cannot be taken into account in expenses (clause 2 of article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How many times a year can financial assistance be given in 4000
The number of financial assistance payments to one employee is not limited in any way. But you need to keep in mind that the deduction is only provided in the amount of 4,000 per year for all payments. For example: Ivanov I.I. financial assistance paid:
- in March - 2000 rubles;
- in June - 5,000 rubles;
- in August - 1000 rubles.
Material assistance paid in March will not be subject to personal income tax; in June, 3,000 rubles will need to be taxed. (that is, the balance of the annual deduction in the amount of 2000 rubles has been provided), and financial assistance in August will be taxed in full.
Financial assistance 4000 rub. in 6-personal income tax from 2021, tax-free
Financial assistance is reflected in 6-NDFL as follows:
| Basis for payment of financial assistance | The order of reflection in the report |
| Due to death | Not included in the report in full. |
| In connection with the birth of a child | In the non-taxable limit (up to 50,000 rubles), the Federal Tax Service allows it not to be reflected in the report (Letter dated December 15, 2016 No. BS-4-11/). But if you don’t want discrepancies with 2-NDFL certificates, then you can reflect it by analogy with other financial aid (see below). |
| Other financial assistance | In section 1: line 020 reflects all financial assistance (both taxable and non-taxable parts), line 030 - only the non-taxable part (deduction); in line 040 - the amount of calculated personal income tax. In section 2: in lines 100 and 110 - the date of payment; in line 120 - the next business day after payment; 130 - the amount of financial assistance together with personal income tax; in line 140 - the amount of tax withheld. If the entire amount of financial assistance is not subject to personal income tax, enter “0” in line 140. |
Financial assistance 4000 rub. when calculating sick leave
When calculating average earnings, only material assistance for which insurance premiums were calculated is taken into account. The following are not included in the calculation of the amount of financial assistance:
- in connection with death;
- in connection with the birth of a child in the amount of 50,000 rubles;
- financial assistance for other reasons in the amount of 4,000 rubles. for every year.
When you don’t need to think about personal income tax and insurance premiums
Paid financial aid will not become the basis for calculating personal income tax and deducting insurance premiums from it in cases specified by law. Depending on the annual amount and some special reasons for the assessment, there are several situations where the tax agent does not need to collect regular personal income tax from these amounts and withhold contributions to the Pension Fund and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
- The amount of financial assistance paid to the same employee does not exceed 4 thousand rubles per year (clause 28, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 11, part 1, article 9 of Federal Law No. 212, clause 12, clause 1, article 20.2 Federal Law No. 125). Aid in excess of this limit will be subject to personal income tax and insurance premiums, like other income.
- Help is assigned to the parent or adoptive parent into whose family a child was born (in the first year of the baby’s life). If employers allocated no more than 50 thousand rubles for both parents at the same time (based on one order) for such a joyful occasion, taxes and contributions do not matter (clause 8 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated July 1, 2013 No. 03 -04-06/24978). You will need a certificate from the other parent’s work about the amount of financial assistance accrued there.
- Financial assistance provided to an employee, including a former employee, regarding the death of a family member, and, conversely, assistance to the relatives of a deceased employee will not require taxation (clause 8 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subparagraph b, clause 3, part 1, art. 9 of Federal Law No. 212, paragraph 3, clause 1, article 20.2 of Federal Law No. 125). Such a relative (who has died or turned to the enterprise for help) can be the employee’s husband or wife, his parents or children, as well as brothers or sisters if they lived together. If assistance is provided to other family members, it will be subject to normal taxation.
- If assistance is allocated in connection with certain emergency events, then in this case personal income tax will not be collected from it (paragraph 2, paragraph 8, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If a natural disaster, catastrophe, fire or other emergency of a force majeure nature occurs and management decides to financially support the affected employees, then the amount of such assistance is not limited. It can be given to either the employee or a close family member if the employee dies as a result of a disaster.
- Assistance to victims of a terrorist attack (paragraph 6, clause 8, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This terrible circumstance, which could overtake an employee or a member of his family in the territory of the Russian Federation, will not require the employer to impose personal income tax on the assistance paid to the victims.
- A pensioner who became such as a result of disability or age will receive tax-free and contribution-free financial assistance from the enterprise upon leaving (paragraph 4, paragraph 28, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of such assistance for “tax-free” accrual should not exceed the required 4 thousand rubles. per year, but the requirement for a one-time accrual is not necessary.
Naturally, the sad event, as well as the degree of relationship, must be documented, and the payment must be made in a lump sum, that is, according to a single order.
Any payments issued not directly to employees, but to other persons who are not in an employment relationship with the employer (for example, family members of an employee, etc.), are under no circumstances subject to social contributions.