Compensation for delayed payment of wages under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
In times of crisis, many Russian companies, often small businesses, are increasingly delaying wages (hereinafter referred to as wages) to their employees.
In most cases, this is not the fault of the company: each of them is a link in a dependent chain of counterparties. Consequently, as soon as payment interruptions (payment under contracts from customers/purchasers are not received on time) occur in one link, this automatically affects all subsequent ones. As a result, this may lead to the fact that employees of one, or perhaps several levels, will not receive salaries on time. If this happens and the employees do not receive the wages due to them on time, then the employing company will subsequently be obliged to pay the employees not only their wages, but also compensation (which in its content represents interest on late payments). This is stated in Art. 236 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
IMPORTANT! Failure to pay wages on time, among other things, gives the employee the right to temporarily suspend the performance of his labor functions, as well as apply for compensation for moral damage (Articles 142, 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Compensation for late payment of wages is accrued from the day following the established payment deadline until the day the employer repays the debt to employees, inclusive.
Example 1
If the salary, for example, was supposed to be paid on the 5th, but was actually paid on the 12th, then the compensation will be calculated for 7 days (from the 6th to the 12th inclusive).
If a delay did occur, the employing company will have to pay the employee appropriate compensation, regardless of whether it is directly to blame for the delay in the salary or not.
NOTE! Today, the situation is especially relevant when, due to the revocation of the license, the bank did not transfer the salary to the employees of the organization - the payroll client. This circumstance does not relieve the employer of the risk of falling under Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, since the fact of guilt does not matter. Therefore, in order to minimize this risk, the company should more carefully select a bank for its salary project.
Moreover, if, for example, the bank is to blame for the delay (in particular, it did not fulfill the payment order of the client organization on time to transfer the salary to employees), then the company should remember that it has the right to make a recourse claim to the bank for the fact that it did not timely transferred the salary to the employees, which means he violated the terms of the salary project with the company. However, you will still need to pay workers' compensation first.
What you need to know
Due to the unstable economic situation in Russia, many employers may delay wages for their staff.
As a consequence, this leads to a deterioration in financial well-being, and in some situations - non-payment of debt obligations on loans, utilities, and so on.
To be able to defend personal interests, Russian labor legislation has provided for compensation payments for delayed wages.
Thanks to this, many employers try their best to pay employees on time.
Basic moments
As noted earlier, the instability of the economic situation in the country creates many negative trends, including delays or complete disregard for the payment of wages to hired staff by employers.
Such points are clearly described in federal legislation, which also provides for the need to charge payments for any type of activity in accordance with previously reached agreements.
If Russian citizens have a document that can confirm the presence of official employment with a specific employer, then there is every chance of counting on compensation payments established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The process of registering this kind of additional financial assistance is directly related to the acquisition of legal force by new Regulations in Russian legislation.
As a consequence, this entailed:
| Fixing a new list in relation to the dates of accrual of official wages | In case of violation of the period established by the norms of the Law, Russian citizens have the right to count on the accrual of compensation |
| Formation of disciplinary sanctions | From the direct employer in case of violation of the employment agreement and the norms of current labor legislation |
| The process of calculating a specific percentage on official wages | Thanks to this, it is possible to significantly minimize the inconvenience that employees were able to experience due to late payment of wages |
These features provide an opportunity to specifically regulate cash flows and thereby force direct employers to approach the procedure for accrual and calculation of this type of payments with full responsibility.
For what reasons are wages not paid on time?
The norms of Russian legislation specifically differentiated the conditions for the purpose of receiving compensation payments for late payment of wages.
Due to the fact that direct employers assume responsibility for calculating the payments in question no later than the 15th day of the next calendar month, identified violations of this condition automatically entail liability in the form of the accrual of penalties for the purpose of calculating compensation payments to the hired staff.
For a sample order for the appointment of a person responsible for fire safety, see the article: order for the appointment of a person responsible for fire safety. How to remove a seizure from a car imposed by a bailiff for alimony, read here.
The provision under consideration is also supplemented by the fact that direct employers take responsibility for paying funds every 15 days, and this is of a regular nature.
Such moments imply that employers are forced to fully comply with the procedure for calculating wages.
Otherwise, the portion of the unpaid wages must be subject to interest payable in the following calculations.
Monthly delays automatically entail an increase in compensation payments. Speaking about the reasons for the occurrence of salary arrears, among them are:
- lack of funds flowing into the company;
- decline in the company's production capacity;
- lack of sufficient level of product sales, and so on.
In other words, the reasons can be very diverse. Regardless of the reasons for the delay, when calculating the amount of compensation payment, the established refinancing rate of the Central Bank is taken into account.
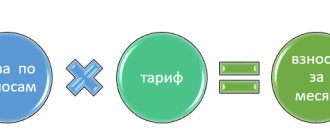
The formula looks like:
Based on this formula, we can conclude that employees can easily make a preliminary calculation of the payment themselves, which will eliminate the possibility of various misunderstandings with their immediate employer in the future.
Legal basis
From a legal point of view, the issue under consideration is regulated by various norms of Russian legislation. It is recommended to consider some of them in more detail.
For example, the main regulatory document is considered to be the Labor Code of Russia, in particular Article 142.
It sets out in detail the responsibility placed directly on the employer to the hired staff in the matter of accrual of official wages in a timely manner.
The presence of such a clause provides employees with the opportunity to stop employment until their existing debt obligations are repaid, taking into account some features.
This may even be stated in the collective agreement. Additionally, it is recommended that you read Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in accordance with which a material penalty is assessed from the direct employer in the event of a delay in payments.
Additionally, it details the existing features of compensation payments.
We should also not forget about the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, in which some articles describe the features of holding an employer liable.
Video: changes in 2021 for accountants In particular, Art. 145.1 describes in detail the features of non-payment of numerous types of financial assistance and wages, among others.
In accordance with the provisions of this article, the employer may face:
- large fine;
- or imprisonment.
The basis for prosecution is the application filed by the employee to law enforcement agencies.
Calculation of monetary compensation for delayed wages
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not establish in what specific amount the company must pay compensation to employees for delays in wages. The legislator gave organizations the right to independently determine this in a collective agreement.
At the same time, the lower limit of compensation has been determined - not less than 1/150 of the key rate for the period of delay in the salary, calculated for each day of delay:
MRK = ZPnach × Kl.St. / 150 × Dpr,
where: MRK is the minimum that the employer is obliged to pay to the employee for a delay in salary;
ZPnach - the amount of wages that should have been paid to the employee on a strictly established day (minus personal income tax);
Class.St. — refinancing rate (key rate) of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for the period of delay;
DPR - the number of days for which the employer was late in paying employees wages.
In the collective agreement, the company can only increase the amount of compensation for delay; the organization does not have the right to set it in a smaller amount than according to the above formula.
IMPORTANT! For information on the size of the key rate (refinancing rate), see here.
Example 2
Salary in the company is paid, according to the collective agreement, on the 5th (for the second half of the previous month) and the 20th (for the first half of the current month) of the month. The collective agreement does not contain special provisions regarding compensation for late wages.
For the first half of February, the employee was accrued salary in the amount of 30,000 rubles. However, it was actually paid only on March 6.
The refinancing rate in force during the period under review (conditionally) was 7.5%.
Under these conditions, the organization should pay the employee on March 6, in addition to the salary, also compensation for delay for 15 calendar days in the minimum amount:
MRC = 30,000 × (100% – 13%) × 7.5% / 150 × 15 = 195.75 (rub.)
However, it is not enough to simply correctly calculate the amount of compensation for late salary payments. It is also important for an organization to clearly know whether personal income tax should be withheld from such compensation, whether insurance premiums should be charged and paid for such an amount, and what to do with expenses for profit tax purposes.
Personal income tax on compensation for late payment of wages
On the one hand, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that it is not necessary to pay personal income tax to the budget on compensation if it must be paid to an employee due, in particular, to the performance of labor functions in the company (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
On the other hand, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation limits the scope for establishing a specific amount of compensation to a minimum limit. The upper limit is not standardized. Consequently, the employer can set arbitrarily high compensation by fixing it in the collective agreement.
The question arises: will the amount of compensation be subject to personal income tax (both in terms of the minimum and in terms of exceeding the minimum under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)?
Regarding the minimum amount of compensation, the answer is transparent: it will not be subject to personal income tax. This has been confirmed more than once by the regulatory authorities in their explanations (letters of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 06/04/2013 No. ED-4-3 / [email protected] , Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 02/28/2017 No. 03-04-05/11096, 01/23/2013 No. 03- 04-05/4-54, etc.).
In the case of exceeding the minimum allowable amount, controllers take a similar position: the amount of excess is not subject to personal income tax, but only if such excess is consistent with an employment or collective agreement (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 28, 2008 No. 03-04-05-01/450, dated 06.08 .2007 No. 03-04-05-01/261).
NOTE! If a company abuses this exemption and, under the guise of compensation, pays, for example, the salary itself to employees, then this is fraught with disputes with inspectors and additional personal income tax amounts being assessed during the inspection. In this case, the court will most likely side with the inspectors, since content has priority over form: regular payments of compensation in an amount significantly exceeding the amount of wages accrued to employees prove that wages were actually paid. This means that it is necessary to pay personal income tax (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated November 30, 2012 No. F09-11655/12 in case No. A60-7589/2012).
Whether it is necessary to accrue personal income tax when paying other compensation payments, read the materials in the section “Compensation and personal income tax” .
Is income tax withheld?
Clause 3 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that compensation payments are not subject to taxation within the framework of the norms related to the performance of labor duties.
From this point we can draw conclusions:
- The amount of compensation is 1/150 of the Central Bank refinancing rate, as well as large penalties for non-payment (if they are determined by an employment or collective agreement) are not subject to income tax. There is no need to withhold or pay personal income tax from them.
- If the employer has not established a specific amount of compensation in an employment or collective agreement, but pays it in an amount greater than 1/150 of the Central Bank refinancing rate, personal income tax will have to be withheld from an amount exceeding the norm by law.
Example:
The employee was paid compensation in the amount of 1/100 of the Central Bank refinancing rate. There is no clause in employee contracts indicating the amount of the penalty for late wages.
Then, only part of the payment will be subject to taxation, above the established norm: 1/150 - 1/100 = 1/50 of the Central Bank refinancing rate - personal income tax will need to be withheld from the amount of the penalty calculated at the specified rate.
Important! The amount of compensation in excess of the excess norm is subject to income tax in accordance with the general procedure.
Is it subject to insurance premiums?
The procedure for levying insurance premiums from 2021 is determined by Ch. No. 34 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Art. No. 422 of the specified normative act does not contain in the list of non-taxable amounts the compensation amount for late payment of wages. Therefore, according to the code, such payments must be subject to contributions.
However, in court proceedings, judges take the opposite opinion.
This type of compensation relates to the financial responsibility of the organization, is paid on the basis of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and ensures the protection of the labor rights of personnel when performing physical labor.
Based on this, representatives of the judicial authority decide that the employer does not have to pay insurance premiums.
An example is Resolution No. 11031 / 31 of December 10, 2013.
In order to avoid litigation, many organizations pay contributions to the budget based on the tax code.
Payment deadlines
In order not to enter into disputes with the tax authority, many organizations pay insurance premiums from compensation payments for delayed salaries.
According to Art. 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the transfer of contributions must occur no later than the fifteenth day following the reporting month.
When the amount of the penalty paid for non-payment of wages exceeds the norm and is not stipulated in the contracts, the employer is obligated to pay personal income tax on the excess amount. Payment of income tax under Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation must be made no later than the day of the actual payment of the amount of money to the employee.
Example of taxation
Let's look at specific examples of how the compensation amount is subject to taxes and contributions.
How personal income tax is withheld:
Let's assume that the employer has not established, using regulations, the amount of compensation for non-payment of wages.
In fact, he pays it in the amount of 1/50 of the Central Bank rate.
The payment was delayed by 3 days, the amount of wage arrears is 15,000, the rate is 7.25%.
Income taxation:
- First, let's calculate the amount of compensation payment from which personal income tax is taken:
- 1 / 150 – 1 / 50 = 1 / 100;
- 15000 * 1 / 100 * 7,25% * 3 = 32,63.
- We calculate personal income tax: 32.63 * 13% = 4.24.
- The employee will receive the following amount of compensation:
- 15000 * 1 / 50 * 7,25% * 3 = 65,25.
- 65,25 – 4,24 = 61,01.
How are contributions assessed:
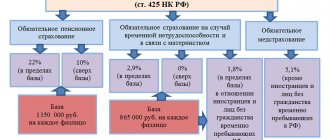
If the employer decides to make insurance contributions in order to avoid litigation, the rates will be identical to the salary: 22% - OPS, 5.1% - Compulsory Medical Insurance, 2.9% - VNiM.
To calculate, let’s take the compensation from the previous example, it is equal to 65.25:
- OPS = 65.25 * 22% = 14.36.
- Compulsory medical insurance = 65.25 * 5.1% = 3.33.
- VNiM = 65.25 * 2.9% = 1.89.
Insurance premiums for payment of compensation for late wages
If a company pays personal income tax as a tax agent, that is, at the expense of an employee, then the burden of insurance premiums falls directly on the organization.
So, is interest on late payments subject to insurance premiums? There are two points of view on this issue.
One is that amounts of monetary compensation for violation by the employer of the established payment deadline are not subject to inclusion in the base for calculating insurance premiums. This conclusion was reached, for example, by the judges of the Arbitration Court of the Far Eastern District dated December 21, 2017 No. F03-4860/2017 in case No. A73-2697/2017 (the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated May 7, 2018 No. 303-KG18-4287 refused to transfer the case to the court Collegium for Economic Disputes).
The arbitrators motivated their decision by the fact that compensation for late payment of wages is not remuneration, but a type of financial liability of the employer to the employee, which is paid by force of law to an individual in connection with the performance of his labor duties, providing additional protection of the employee’s labor rights. For this reason, compensation for late payment of wages is not subject to insurance contributions on the basis of subclause. “and” clause 2, part 1, art. 9 of Law No. 212-FZ (since January 1, 2017, similar provisions are given in paragraph 2 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
See also “Compensation for non-payment of wages on time: contributions”.
Another point of view is that the types of payments not subject to insurance premiums are listed in Art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Compensation for late payment of wages in Art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is not given, therefore, contributions must be calculated from this payment. This position is adhered to by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in letter dated March 21, 2017 No. 03-15-06/16239.
As you can see, this issue is controversial. And it's up to you to decide.
Personal income tax for delayed wages
In practice, there are often situations where organizations fail to pay wages to their employees on time. In this case, the company must pay them “salary” compensation. The question arises: is it necessary to pay personal income tax on such compensation? Let's look at the nuances of calculation using practical examples.
M. Antonova As is known, all types of compensation payments (within the limits established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation), related, in particular, to the performance of work duties by the taxpayer, are not subject to personal income tax (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Compensation is not taken into account when calculating income tax, since it is not related to work hours or working conditions (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 12, 2003 No. 04-04-04/131). Unified social tax and pension contributions are not accrued for this payment (clause 2 of article 238 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, interest on delayed wages is not taken into account when calculating contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for accident insurance (clause 10 of the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 7, 1999 No. 765).