Conducting activities (business) is not always limited to one region. Therefore, employees are often sent on business trips to complete assignments. In this article, we analyze a very common situation with daily allowances in excess of the norm on a business trip, and also what is directly connected with this: the concept of a place of permanent work, norms and rules for paying daily business trips for 1 day, are they subject to insurance premiums, code of income per diem in excess of the norm .
Also see:
- How to draw up and execute an order for daily allowance on a business trip
- How to calculate daily allowance when traveling abroad
general information
In accordance with the provisions of Art. 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a business trip is a trip by an employee at the direction of his employer to perform an official task outside his place of permanent work for a specific period.
Place of permanent work is the legal or actual address of the company (division) where the employee performs his duties in accordance with the employment contract.
Here are the basic rules for paying daily allowance:
- The company pays the employee per diem for each day of travel, incl. weekends and holidays, travel time and temporary stops.
- Daily allowances are issued until departure on a business trip. The employee must receive travel allowances in advance, otherwise he has the right not to go on a business trip. The accountant issues money to the employee, making a debit entry to account 71.
- When a business trip involves a trip to a nearby area, and the employee intends to return home every day after the end of the working day, per diem is not paid .
- Per diem is paid even if an employee gets sick on a business trip, which is confirmed by sick leave. In addition to the daily allowance, the sick person will be paid a disability benefit.
The specifics of employees going on business trips are established by the Regulation “On the Peculiarities of Departing on Business Trips”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation on October 13, 2008 No. 749.
As for business trips for 1 day , for a long time there were different opinions about whether it is necessary to pay daily allowances, as well as how to pay taxes and insurance premiums on them.
Now we recommend that internal regulations provide for the payment of these expenses, moving away from the concept of “per diem” . In this case, the accountant can include payment of these costs in income tax expenses - according to clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 26, 2014 No. 03-03-06/1/24916.
If there is a documentary justification for the expenses incurred, there is no need to impose insurance premiums on payments for one-day business trips (letters of the Ministry of Finance dated May 17, 2018 No. 03-15-06/33309, dated October 2, 2017 No. 03-15-06/63950, determinations of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated August 11. 2017 No. 310-KG17-10343, dated January 26, 2015 No. 310-KG14-7400).
One-day business trips are practically no different from ordinary ones, so it is also important to document them correctly. Payment for such business trips due to the lack of daily allowances has its own characteristics , characteristic only for business trips for one day.
Changes in daily allowances above tax standards in 2021
In 2021, a reform was carried out on insurance premiums in relation to daily allowances in excess of the norm. Recent innovations oblige enterprises to pay taxes on the income of their employees along with insurance premiums in case of exceeding the limits on the amount of daily allowances that are withheld by law.
Changes in the field of taxation were made in accordance with the fact that from the beginning of 2021 the Federal Tax Service is responsible for insurance payments. The only exception is if you are injured. All insurance transfers according to the new rules are made to the tax service, and not to the Social Insurance Fund.
The latest tax changes in 2021 establish that daily allowances in excess of the norm must be correctly processed both when traveling on business in the Russian Federation and in other countries. Everything must be done in strict accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In 2021, adjustments were made to Article 422; they are dedicated to daily allowances in excess of taxation standards in 2021. They also need to pay personal tax. However, in addition to these tax contributions, companies are required to make payments to the Social Insurance Fund. The exception is payments that are related to employee injuries.
The Federal Tax Service does not establish the amount of standards for payments per day. In other words, each company can independently determine them for the time spent on a business trip.
The tax office sets limits on the amount of refunds that are not subject to taxation. If the limit is exceeded, the organization must pay compensation for personal income tax on daily allowances in excess of the tax rate in 2021. The company will also have to pay contributions for health insurance and the Pension Fund.
A significant number of enterprises set their own amounts of travel allowances, which exceed the standards defined by law. As a result, they are ready to make insurance payments.
Rationing daily allowances
To calculate and pay insurance premiums starting from 2021, you must be guided by paragraph 2 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The daily allowance standards established by law sometimes do not allow a business trip employee to feel comfortable during a business trip. In this case, the company, by decision of management, can establish its own standards.
do not need to be documented . Perhaps supporting documents may be required to confirm the advance payment. Such as:
- air, railway, bus tickets, trains;
- online checks and receipts;
- hotel registration invoice;
- other documents for the employee’s residence;
- agreements, acts;
- travel package;
- office notes;
- marks in the passport about border crossing.
Based on information from primary documents, the traveler fills out an advance report. Further, on its basis, the accountant will reflect in accounting the expenses for the completed business trip under Kt 71 .
Based on the interpretation of Art. 167 of the Labor Code, when an employee is sent on a business trip, he is retained and reimbursed:
- place of work (position), as well as average salary;
- business travel expenses.
Business travel expenses include:
- travel (round trip);
- rental of residential premises (hotel or apartment);
- daily allowance;
- other expenses that the employee made with the permission or instructions of the employer.
The amount of income on which personal income tax must be calculated is determined by the accountant at the time of approval of the advance report.
KEEP IN MIND
Daily allowances in excess of the established norm are their amount exceeding the norm specified in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Regardless of the fact that the amount of daily allowance is established in the internal documents of the enterprise.
That is, excess daily allowances are subject to insurance premiums and personal income tax if they exceed:
- 700 rubles – for each day on business trips within the Russian Federation;
- 2500 rubles – for each day on a foreign business trip.
These excess amounts are considered income received by an employee of the enterprise.
The daily allowance income code in excess of the norm for filling out official certificates and reports is 4800 “Other income”.
Reflection in RSV-1
All legal entities, including individual entrepreneurs, should send to the Pension Fund branch, in addition to their own personal information, a document in the form of a certificate drawn up in accordance with the RSV-1 form.
This form is a report containing information regarding accrued or paid insurance transfers. It stores a lot of data that is necessarily transmitted to the Pension Fund and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
Line 201, located in the RSV-1 form in subsection 2.1, displays the amount of payments and compensations that are not subject to insurance transfers for compulsory pension insurance.
All managers of enterprises and entrepreneurs with any tax regimes need to study all the main provisions and information regarding the certificate drawn up in the RSV-1 form.
Insurance premiums for daily allowances in excess of the norm
Daily allowances in excess of the norm were subject to taxation by the Unified Social Tax (UST) until 2010. Then it was replaced by insurance premiums.
Insurance companies pay in the month the manager approves the advance report. Because until this moment it is not possible to determine the exact amount that the employee will spend. These clarifications were given by the Ministry of Finance on May 29, 2017 in letter No. 03-15-06/32796.
If daily allowances are paid to an employee in foreign currency, the amounts must be recalculated into rubles at the Bank of Russia exchange rate on the date of approval of the advance report by the director.
And insurance premiums in case of work-related injury and occupational injury. illnesses (injuries) are not included in the daily allowance within the limits established by the employer’s internal orders .
The Regulations established in Article 20.2 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ are still in effect.
We reflect daily allowances in 6-NDFL
Clause 3 art.
217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that there is a limit for daily allowances, from which personal income tax is not paid. This is 700 rubles. per day for business trips around the country and 2,500 rubles. per day for foreign business trips. If, according to internal regulations, the employer issues large amounts of daily allowance, then everything issued in excess of the limit is subject to personal income tax. Accordingly, taxable income must be reflected in 6-NDFL. Read more about the rules for paying daily allowance here .
We show the amount of income on line 020 only to the extent of the excess. The option in which the full amount of income is shown on line 020 and a deduction for the amount of the limit on line 030 is not suitable, since in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 08/01/2016 No. BS-4-11/13984 (question 3) it is explained that in line 030 amounts fall in accordance with the codes of the types of deductions listed in the Federal Tax Service order dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
The date of receipt of income (p. 100) in the form of daily allowance is recognized as the last day of the month when the manager approves the advance report (subclause 6, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This date cannot be the day the money is issued, since at that moment there is still no supporting document, the accomplished fact of the business trip, and the employee receives an advance, which can be returned in case of early arrival back or cancellation of the trip.
The employer must withhold tax (p. 110) when the next payment of funds to the employee occurs after the date of receipt of income (clause 4 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The Federal Tax Service does not allow tax to be withheld before this date (letter from the Federal Tax Service dated July 25, 2014 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] ).
As a rule, personal income tax on excess daily allowances is withheld on the day the salary is issued for the month in which the advance report is approved. The tax transfer (page 120) is made the next day after the withholding (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
See also “How is a one-day business trip paid?”
Check whether you correctly reflect various payments to employees in 6-NDFL using the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Excess daily allowances and their taxation
When an employer sends his employees on a business trip, he guarantees that his subordinates will retain their jobs, their average earnings, and the company will reimburse them for travel expenses, including daily allowances.
This concept can be defined as the employer covering the daily expenses of employees that arise as a result of their living away from home. If daily allowances are paid within the limits established by the Tax Code, then personal income tax should not be withheld from them. When excess daily allowances are paid, payment of personal income tax is mandatory.
Correct calculation of daily allowance for a person on a business trip is an important aspect of accounting activities. In order to make payments correctly, the accountant must have information about the established amount of daily allowance, the period for which they are paid, the withholding of tax on the payment and the deduction of insurance premiums.
What it is
When an employee is sent on a business trip to another location in Russia or abroad, the organization must pay him a monetary remuneration calculated for each day. It's called "daily allowance".
The employer must pay them in the following situations:
- the employee is sent on a business trip;
- the employee is on a business trip, which is traveling in nature or the work within which takes place directly on the road;
- when working in the field or participating in an expedition.
The following definition is enshrined at the legislative level: a business trip is a business trip, the terms and conditions of which are determined by the employer. An important condition is that the place of work is remote from the location of the organization in which the seconded person works.
Payment of excess daily allowances involves the employee receiving an amount that exceeds the norm established by law. Special attention should be paid to expenses that do not qualify as daily allowance, but must be paid by the employer.
Among them:
- transportation costs (types of transport, the costs of which will be compensated, are determined by each employer independently);
- expenses associated with living in another city;
- additional expenses resulting from the fact that the employee lives away from home.
The remaining expenses are covered by the employee from the daily allowance paid by the employer. Their amount may be increased at the discretion of the organization’s management. In such a case, we must not forget that excess daily allowances are subject to taxation. If this rule is neglected, you can become a defendant in a lawsuit.
What norms are provided by law?
The issue of excess daily allowances is regulated by two main legislative documents - the Labor and Tax Codes.
The Labor Code regulates the following aspects:
- Article 168 obliges the employer to reimburse expenses of employees associated with living outside their permanent place of residence;
- the amount of daily allowance can be determined by the employer independently, and it must be fixed in a local regulatory document or collective agreement;
- The trip of an employee whose work officially involves the implementation of field activities is not considered a business trip;
- when a person is on a business trip, his salary must be accrued to him in the established amount, and his job must also be retained.
Article 168. Amount of tax presented by the seller to the buyer
The Tax Code establishes the following standards:
- the fact that daily allowances higher than the norm established by the Russian Government do not reduce the income tax base (Article 264);
- Article 217 limits the amount of daily payments that are not subject to taxation;
- The procedure according to which personal income tax is withheld is determined by Article 226.
Article 264. Other expenses associated with production and (or) sales
Article 217. Income not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation)
Article 226 Peculiarities of calculation and payment of tax by tax agents when carrying out transactions with securities
Important regulatory documents are decrees of the Russian government, which address the problem of paying daily allowances to employees.
In the first document, number 93, you can find information about the daily allowance standards that can be paid.
The second, numbered 729, displays the amount of reimbursement for expenses incurred during a business trip, which should guide budget structures.
Excess daily allowance and form 6-NDFL
The Tax Code of Russia determines that the daily allowance for trips within the country is 700 rubles; foreign business trips require the payment of a daily allowance in the amount of 2.5 thousand rubles.
If a person is paid amounts in excess of the established norms, they are subject to personal income tax.
However, the organization does not have the right to withhold this tax at the moment when it gives a person funds in the form of an advance, since it is not known for certain exactly what amount will be spent by him.
If a person returns from a business trip ahead of schedule, her expenses will be less, but if she is delayed on a business trip, her expenses will increase accordingly. Considering that finances provided to a person on the basis of an advance request cannot be considered the person’s economic benefit, it would be unlawful to charge personal income tax at the time of payment.
Form 6-NDFL
Thus, when the question arises of calculating personal income tax on an employee’s daily allowance, you need to adhere to the following sequence of actions:
- provision of a report by the employee;
- calculation of the exact amount of a person’s income that is subject to taxation;
- personal income tax calculation;
- withholding tax, which is calculated on the amount received by the employee as additional income.
Dates
To reflect the amount of daily allowance that exceeds the established norm in form 6-NDFL, you need to clarify which dates should be indicated in the second section of the calculation.
For taxable daily allowances, the date on which the actual income was received is the last day of the month in which the advance report was approved after the employee returned from a business trip.
It is this date of the month that should be indicated in line 100 of form 6-NDFL (the date on which the income was actually received).
In line 110 (the date when the tax was withheld) you should indicate the date when the income from which personal income tax was withheld was paid.
It is important to know that this date is not allowed to come earlier than the last day of the month, since the withholding of personal income tax is not allowed if the income was not received by the employee.
Since the receipt of income occurred on the final day of the month, tax withholding may occur when the next payment is made.
Based on this, we can conclude that the transfer of personal income tax from excess daily allowances must occur no later than the working day that follows the day when personal income tax was withheld from the daily allowance.
Insurance premiums
Daily allowances that do not exceed the standards established by Russian legislation are not subject to insurance premiums.
In order to avoid controversial situations with the tax service, the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund, the company should specify the rules by which daily allowances are calculated. This can be done in any local regulatory document, for example, in the Regulations on Business Travel or a collective agreement.
For daily allowances that exceed the established standard, insurance premiums are charged. However, such a rule clearly applies only to those business trips whose duration exceeds 24 hours.
As for one-day business trips, there are two different opinions:
- The opinion of the Social Insurance Fund is that contributions should be calculated in any case.
- The Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia expresses the opposite opinion (decision dated June 14, 2013). It is based on the fact that the daily allowance that an employee receives for being on a business trip is not the person’s income. These are funds that compensate a person for the inconveniences that appeared in his life as a result of fulfilling the employer’s instructions.
Display in accounting
Payment of excess daily allowances must be reflected in the financial statements. The documents must reflect both direct daily allowance payments and withheld insurance premiums, as well as personal income tax.
For example, an employee is sent by the employer on a business trip within Russia for 7 days. His daily allowance is 1,200 rubles, which is 500 rubles higher than the established norm. For the days allotted for a business trip, the employee will be paid an amount of 8,400 rubles.
In the calculation table it looks like this:
| No. | Debit/Credit | Sum | Operation | date |
| 1 | 208.12; 201.34 | 8400 | An amount was issued from the organization's cash desk for daily expenses | Date on which the daily allowance was paid |
| 2 | 401.20; 208.12 | 8400 | The daily payment by the date of approval of the advance report is shown in expenses | Date when the expense report was approved |
| 3 | 302.11; 303.01 | 455 | Personal income tax is withheld from the employee’s salary (8400 – 700*7)*0.13=455 | The date of the next salary payment |
Similar rules for indicating payments and expenses are contained in the Instructions for the use of budget accounting plans of accounts, approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in 2010.
The question often arises, which 1C income code should be used when it comes to excess daily allowances. In this case, code 4800 is used; it is intended for other expenses for which personal codification is not provided.
Changes from 2021
From the beginning of 2021, the law on insurance premiums No. 212 has ceased to apply. It was replaced by a new section 34 of the Russian Tax Code. In this regard, the employer should forget about independently rationing daily expenses.
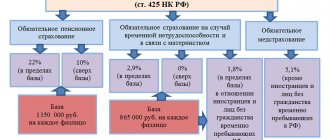
According to the provisions of Article 422, an updated procedure is established according to which daily allowances will be subject to insurance contributions when the limits established for personal income tax are exceeded. The size of such limits depends on whether the employee is going on a business trip within Russia or whether it is a business trip abroad.
Article 422. Amounts not subject to insurance contributions
Excessive daily insurance premiums are subject to the general procedure. The only exception is insurance premiums for injuries, from which daily allowances are exempt.
Attention!
- Due to frequent changes in legislation, information sometimes becomes outdated faster than we can update it on the website.
- All cases are very individual and depend on many factors. Basic information does not guarantee a solution to your specific problems.
That's why FREE expert consultants work for you around the clock!
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
Source: https://buhuchetpro.ru/sverhnormativnye-sutochnye/
How are daily personal income tax and insurance premiums assessed?
The taxation procedure for SRs exceeding those established in Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the general one applies. For personal income tax, the rate is set at 13%. Let us remind you that not the entire amount is taxed, but only the difference exceeding the permissible limit.
The amount of insurance coverage is determined individually. This means that if a company has benefits and applies reduced rates for SV, then in order to tax daily allowances above the norm, insurance premiums for 2021 will be calculated at reduced rates. We described in more detail what benefits are valid in 2021 in a special article “Who is entitled to reduced SV tariffs in 2021”.
For example, a company operates in the field of IT technologies and has the right to reduced insurance rates:
What travel expenses are not subject to personal income tax?
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation stipulates what is not included in the employee’s income subject to income tax. This includes, among other things, compensation by the employer for the following expenses (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the cost of travel to the place of performance of the official assignment (regardless of the place of departure for the business trip) and back, including the cost of services in luxury cars;
See also “The dates on the tickets do not match the dates of the business trip - the Ministry of Finance reminds about personal income tax.”
- commission for airport services;
- the cost of travel to the place of departure (train station, airport), destination or transfers;
- baggage transportation.
Compensation for these expenses is not subject to personal income tax if the expenses are documented. If such documents are missing, the compensation paid is exempt from personal income tax only within the established norms (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, the employee must be reimbursed for the costs of renting housing on a business trip (paragraph 3, part 1, article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the employee submits supporting documents, then such expenses will be compensated in full and are not subject to personal income tax. In the absence of documents, income tax will not be imposed on the amount within the limits specified in paragraph. 10 clause 3 art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
For information on how travel expenses are taken into account, read the article “Procedure for accounting for travel expenses in 2018-2019.”