Accounting with the Principal
All expenses incurred by the Agent in the process of executing the agency agreement in the accounting of the Principal will be expenses associated with ordinary activities. They are reflected in accounting as the report is received from the Agent, with supporting documents attached. The agency fee will also be an expense, the calculation of which will be made and indicated in the report.
Income will be considered the amount from the sale of goods (work, services) that are reflected in the Agent’s report as of the date of preparation of the report.
If the Agent acts on his own behalf, the Principal in this case does not issue invoices, certificates of work (services) performed, invoices, invoices, other documentation to third parties, and he does not issue them to the Agent either. The Agent's report will be a supporting document for the sale of goods (works, services).
Agent Accounting
Expenses incurred by the Agent under the agency agreement, which are reimbursed by the Principal, are not taken into account in expenses and income.
Only the remuneration received for the execution of the agency agreement from the Principal will be included in the taxable base. This reward will be income. Reflected on account 90 “Income from ordinary activities”. If the agency type of activity is other income for the Agent, then the income is reflected in account 91 “Other income and expenses”
Goods received from the Principal are accounted for in account 004 “Goods accepted for commission”. Goods purchased by the Agent himself are accounted for in account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping.” All goods until they are sold by the Agent to third parties are the property of the Principal.
If the Agent, under an agency agreement, enters into transactions with third parties on his own behalf and at the expense of the Principal, then he can immediately withhold his commission when making settlements. That is, transfer to the Principal the funds received from third parties minus the remuneration due. (Note: Unless the parties have specified a different payment procedure in the agreement).
Documents are issued to third parties on behalf of the Agent. It should be remembered that in accounting, documents on the sale of goods (work, services) are issued no later than five calendar days from the date of their sale.
Accounting entries under the agency agreement with the principal
An agency agreement is an alternative to a commission agreement. The essence of an agency agreement is to instruct an intermediary (company or individual) to carry out any operations on behalf of the guarantor organization or on its own. Let's consider how to record services under an agency agreement and transactions under an agency agreement with the principal.
Signs of an agency agreement
Just like a commission agreement and a surety agreement, an agency agreement is an intermediary agreement.
An agency agreement combines the features of a commission agreement and a guarantee agreement - depending on the type of agreement, transactions can be concluded both on behalf of the principal (guarantor) and the agent (performer).
The principal is the party that requires agency services, the agent is the party that performs these services. The principal pays for the agent's services by transferring the agent's remuneration.
Mandatory terms of the agency agreement:
- Subject of the agreement. For example, rent, utilities, electricity, etc.;
- On behalf of whom the agent will act;
- Contract time;
- The amount of the agent's remuneration, the procedure and timing of its payment;
- Rights and obligations of the parties;
- Termination dates, etc.
Agency agreement report
The agent's report is the main document by which the agent reports to the principal about the expenses incurred. To confirm them, copies of primary documents evidencing the costs incurred are attached to the report. The agent report form is not regulated; each organization has the right to develop its own form to reflect the information it needs.
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
Sample agent report:
Accounting for the principal
In accounting for an agency agreement on behalf of both the principal and the agent, the costs of its execution are accounted for by the principal.
All expenses of the agent for the execution of the contract with the principal are accounted for in account 76. Accounting for VAT on contract services is reflected only by the principal, even if the services are provided on behalf of the agent. The agent takes into account VAT only on the agency fee.
An example of accounting for services under an agency agreement for a principal with postings
Master LLC, which owns residential premises, entered into an agency agreement with Vector LLC. According to the terms of the agreement, “Vector”, on its own behalf, leases the premises of a shopping and entertainment center owned by “Master”.
The contract specifies a fixed amount of agent remuneration in the amount of 500,000 rubles. At the end of December 2021, the amount of sales (rent) for all premises amounted to 12,600,000 rubles, including VAT of 1,922,033 rubles.
The terms of the agency agreement provide for the withholding of the amount of remuneration by the agent when transferring proceeds.
Postings under the agency agreement with the principal Master LLC:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 62.1 | 90.1 | Revenue from sales (rent) is reflected | 12 600 000 | Implementation Act |
| 90.3 | 68(VAT) | VAT charged on sales (12,600,000*18/118) | 1 922 033 | Invoice issued |
| 20 | 60(76) | The amount of the agent's remuneration is reflected (500,000 - 500,000*18/118) | 423 729 | Accounting information |
| 19 | 60(76) | VAT on the amount of the agent's remuneration (423,729*18%) | 76 271 | Accounting information |
| 68(VAT) | 19 | VAT is accepted for deduction | 76 271 | Book of purchases |
| 51 | 62.1 | Receipt of funds from rent minus agent's remuneration is reflected | 12 100 000 | Bank statement |
| 76 | 62.1 | The offset of the agent's remuneration against payment is reflected | 500 000 | Accounting information |
Another option for accounting for agent remuneration would be to transfer the remuneration directly to the agent:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 60(76) | 51 | Remuneration transferred to the agent | 500 000 | Payment order ref. |
| 51 | 62.1 | Receipt of rental income | 12 500 000 | Bank statement |
Income tax on the principal
Under an agency agreement, the principal's income is revenue, and the agency fee is an expense.
Source: https://BuhSpravka46.ru/buhgalterskie-provodki/buhgalterskie-provodki-po-agentskomu-dogovoru-u-printsipala.html
Accounting Settings
If an organization operates within the framework of commission trading or agency services, then in the program “1C: Accounting 8” (rev. 3.0) it is necessary to make the appropriate settings.
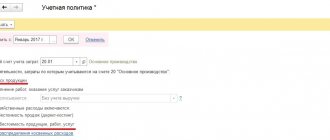
You can configure accounting settings from the Directories and accounting settings section using the hyperlink Setting up accounting settings on the navigation panel.
To organize ZAO TF Mega, in the Accounting Parameters Settings, on the Commission Trading tab, set the flag Activities are carried out under commission sales agreements (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Setting up accounting parameters for commission trading (agency services).
VAT accounting for the parties to the agency agreement
An agent acting on his own behalf and at the expense of the Principal when selling goods (works, services) to third parties issues an invoice to them on his own behalf. The Agent enters this invoice into the book of issued invoices. At the same time, he sends this document to the Principal, who in turn issues an invoice to the Agent on his own behalf in the name of a third party, where he duplicates all the information on the invoice received from the Agent.
Note: An agent acting on his own behalf and at the expense of the Principal, issued invoices for the sale of goods (work, services) to third parties, as well as invoices issued for funds received for future deliveries of goods (work, services) to third parties (advances) are not reflected in the sales book.
The Agent issues an invoice to the Principal for the agency fee, and the Agent registers this invoice in the sales book. The principal records it in the book of purchase invoices and in the book of received invoices.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Termination of the contract by agreement of the parties sample
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from Scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) purchased by {amp}gt; 8000 books |
How to re-issue an AD invoice
Since the agent acts as an intermediary between the actual suppliers and purchasers, they are responsible for re-issuing the invoice. An intermediary who sells the customer's goods on his own behalf indicates himself as a seller in the invoices. If the intermediary purchases products (goods, services) on behalf of the customer, he is obliged to indicate information about the supplier in the reissued SF.
Consequently, the intermediary will have to issue invoices to both parties to the transactions, as well as issue an additional invoice to pay remuneration for his services. All SF must be reflected in Part 1 and Part 2 of the Account Journal.
Sample of a reissued invoice under an agency agreement
VAT accounting for the parties to the agency agreement
Revenue from the provision of intermediary services is income from core activities. Goods purchased by the agent on behalf of the principal are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping.” When the principal transfers goods to the agent for subsequent resale, they are recorded in off-balance sheet account 004 “Goods accepted on commission.”
Income in the form of property and funds received in connection with the fulfillment of obligations under an agency agreement is not considered an agent’s income. Also not expenses of the agent are expenses reimbursed by the principal.
Transactions under the agency agreement are reflected on the basis of the agent's reports. Until the agent sells the goods, it is recorded on the principal’s balance sheet.
Agency fees are subject to VAT if the agent is a tax payer and are included in income when calculating income tax. If the agent acts on his own behalf, then he issues invoices to third parties with VAT (if the goods are subject to VAT and the principal is a tax payer), even if he himself is not a tax payer.
The principal's income, taken into account when calculating income tax, is the amount of proceeds from the sale of goods by the agent, minus VAT, as of the date specified in the agent's report. The payer of VAT on the amount of income under an agency agreement is the principal, even if invoices to third parties are issued on behalf of the agent. Agency fees are taken into account as expenses when calculating income tax.
To reflect transactions for the sale of the principal's services, the accrual of VAT on sales, as well as the accrual of agent remuneration and its deduction from the principal's revenue, the document Commission Agent (Agent) Sales Report is intended, which is available from the Purchases and Sales section via a hyperlink on the Commission Agents Sales Reports navigation panel.
The document form consists of several tabs (see Fig. 2). Let's look at filling out the document details on the Main tab:
- the document number and date are filled in in accordance with the agent’s report number and the date of its approval;
- In the Contract field, you need to select an agreement with an agent for the provision of services. Please note that in the contract selection window only those contracts that have the form With commission agent (agent) for sale are displayed;
- The method for calculating agency fees is selected from the field of the same name. As a rule, this field is filled in automatically according to the conditions defined in the contract. If the calculation method is not selected, then you must indicate one of the three proposed options: Not calculated, Percentage of the difference between the sales and receipt amounts, or Percentage of the sale amount. In our example, the calculation method is set as Percentage of the sale amount, and the reward percentage is set as “10%”;
- the VAT rate on the commission agent’s remuneration in our example is set to “18%”;
- registration of an invoice for agent remuneration is carried out through the field of the same name, after which a hyperlink is created to the created document Invoice received for receipt;
- to accurately indicate how the calculated amount of remuneration will be taken into account, use the details Account of remuneration costs and Cost Items, which in our example are filled out as “44.02” and “Agency remuneration” with the tax accounting expense type “Other expenses”;
- the amounts in the Total and VAT (including) fields both in relation to the principal's sales and in relation to the agent's remuneration are calculated automatically according to the data filled in on the Goods and Services document form tab.
Rice. 2. Filling out the title details of the agent’s report
The Products and Services tab contains two interconnected tabular parts (Fig. 3):
- at the top of the document there is a table of buyers - third parties to whom the agent sold the principal’s services;
- at the bottom of the document the name, quantity and cost of goods and/or services sold by the principal through the agent, as well as the agent’s remuneration, are indicated.
Rice. 3. Services sold to third parties through an agent
In accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation, the services provided by the agent are indicated in the context of end buyers and the date of the transaction, that is, the date indicated in the invoice issued by the agent to the end buyer. After recording the document for the same dates, the program will automatically create invoices issued by the principal to the agent.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Pass to appeal a court ruling
In our example, we add a record in the buyers tabular section and select the buyer User 1 from the Counterparties directory. Since the agent issued an invoice to the buyer, we set the Invoice flag, and in the Invoice Date field we indicate the date the document was issued.
In the lower table on the Services tab, add a record and select an element from the Nomenclature directory - Information service type 1, indicate its quantity, price and cost, as well as the VAT rate - 18% according to the agent’s report. The remuneration amount is calculated automatically for each item sold.
In the same way, add User 2 to the top table of the buyer and fill in the services sold to him in the bottom part of the table.
On the Cash tab, information about funds received from buyers for the services of the principal is indicated based on the agent’s report. Upon approval of the report on funds received, the obligation to pay VAT in the case of prepayment passes to the principal. Information about the funds received is entered into the document Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales manually. One of three payment options is possible, which must be selected in the Payment report type field: Advance, Payment, Advance offset.
According to the agent’s report, the funds received from customers were credited within five days; the principal has no obligation to charge VAT on prepayments, so the tabular part is filled out as follows (see Fig. 4):
- a new record is added and Payment is selected in the Payment report type field;
- in the Buyer field, select User 1 from the Counterparties directory;
- in the fields Date of event, Amount with VAT (rub.), % VAT, VAT (rub.), the date and amount of funds received from the customer, including VAT, are indicated, according to the agent’s report;
- For the second buyer, the fields are filled in similarly.
Rice. 4 Registration of funds received from third parties
Filling out the Cash tab is important if you receive an advance payment from the customer, as well as if this advance payment is offset. In our situation, the information reflected on the Cash tab is for reference only.
On the Settlements tab, settlement accounts with the agent for the principal’s services sold, as well as settlement accounts for the agent’s intermediary services are indicated (see Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Accounts with the agent
Settlement accounts are set by default in accordance with the accounts specified in the Settlement accounts with counterparties setting in the navigation panel (Purchases and sales section).
When posting the document Commission Agent (Agent) Sales Report, the following transactions are generated in the program:
Debit 76.09 Credit 90.01 - for the total amount of the principal’s services sold for January; Debit 90.03 Credit 68.02 - for the amount of accrued VAT on the sale of the principal’s services; Debit 60.01 Credit 76.09 - for the amount of agency fees withheld from the principal’s revenue; Debit 44.02 Credit 60.01 - for the amount of accrued agency fees excluding VAT; Debit 19.04 Credit 60.01 - for the amount of VAT on agency fees.
In order to determine the agent's debt after deducting the agent's remuneration, you can use the report Balance sheet for account 76.09 “Other settlements with various debtors and creditors” (Fig. 6).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Federal Tax Service canceling electronic invoices. Long live UPD! #legislation #EDS #ECMJ
Rice. 6. SALT for account 76.09
As can be seen from the balance sheet, the debit of account 76.09 “Other settlements with various debtors and creditors” reflects the receivables of TF Mega CJSC in the amount of 54,000.00 rubles.
The debt will be repaid upon reflection of the payment received from the agent for the services performed. Payment can be registered with the document Receipt to the current account based on the document Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales.
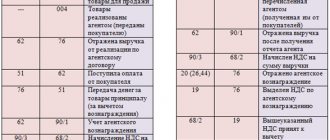
Debit Credit Basis
51 62 Reflected funds received from third parties
62 76 Reflects the sale of goods (work, services) under agency
Agreement
76 51 Funds were transferred to the Principal with withholding
commission
76 62 Commission reflected
62 90 Income for agency fees is reflected
90 68 VAT charged on agency fees
Receipt of goods under an agency agreement with the principal
And he cannot enter into a sales contract with himself. After all, a contract requires at least two parties - the transferor and the recipient, and a contract is an agreement of at least two persons. 1 tbsp. 420, paragraph 1, art. 454 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
When an agent acts on behalf of the principal, he is his representative. And the representative does not have the right to make transactions in relation to himself personally. 3 tbsp. 182 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
We buy and receive the goods. Inform the principal that you want to keep part of the goods for yourself, agree with him to purchase it at a discount in the amount of the agent's fee that would be due to you, and ask for an invoice and a delivery note.
And after signing the purchase and sale agreement or receiving shipping documents, write off the goods from off-balance sheet account 004 “Goods accepted on commission” and capitalize it at the agreed price. 1 tbsp. 433 Civil Code of the Russian Federation; Chart of accounts, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n.
- Outdated food purchase and sale contracts threaten fines, No. 23
- The store has moved - the sales tax is paid twice, No. 22
- Exchange rate on the date of shipment, but with a caveat: accounting with the seller, No. 22
- Do you need to disassemble the goods?, No. 21
- Buyer's bonus from the seller, No. 19
- We receive a retro discount and adjust expenses, No. 18
- The seller gives a retro discount, No. 17
- When goods become materials..., No. 17
- Looking for discounts, No. 16
- How can an accountant take into account controversial issues when providing discounts, No. 16
- “Accounting” consequences of working with a payment aggregator, No. 15
- Clarifications for alcohol retailers, No. 13
- Rospotrebnadzor told how to draw up price tags in retail trade, No. 11
- The authenticity of alcohol can be checked using EGAIS, No. 11
- Calculations in y.
Important
The actions of the contractor under the contract must be documented in a corresponding report.
Subject and parties of an agency agreement An agency agreement is a bilateral agreement, according to which one of the parties undertakes to perform any work and services on behalf of the other party for a fee.
Such work, as a rule, includes consulting, legal, notary, logistics, analytical and other services that are not related to the main activity of the enterprise, but are necessary for its conduct.
The parties to the contract are the agent and the principal. The agent is the person who has assumed the obligation to perform services, while the principal acts as their direct customer. According to the law, parties to an agreement can be both legal entities and individuals.
Accounting for agency agreements in “1s:accounting 8”
Attention
The intermediary fee will be taken into account in income in the usual manner - on the date the principal signs the agent’s report. Let's consider the accounting records of the agent when purchasing services for the principal, where account 76.у is the account of settlements with the principal for purchased services, and 76.
c – account of settlements with the principal for the agent's remuneration: Accounting record of the transaction D 76.у К 60 Debt of the principal for payment of services to the supplier D 76.в К 90.1 Accrued agent's remuneration D 90.03 К 68 VAT on the amount of remuneration D 51 К 76.у, 76 .
c Money was received from the principal as remuneration and payment for services D 60 K 51 Money was transferred to the supplier for services provided Features of VAT accounting for intermediaries Intermediaries under the general taxation regime are required to calculate and pay VAT on the amount of their remuneration.
In the invoice for remuneration, VAT is charged at a rate of 18%.
Accounting entries under the agency agreement with the principal
In this case, you will take into account the cost of the goods in “profitable” expenses only after receiving a delivery note from the principal. 1 tbsp. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. And you will use the VAT deduction only after receiving the invoice. 1 tbsp. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
*** For more information on accounting for goods received without accompanying documents, see: 2009, No. 21, p. 72 If you have not yet agreed on the price of a product with the principal, and you urgently need this product for work, you can take it into account without waiting for the conclusion of the contract.
Then you receive it on the basis of the acceptance certificate drawn up by you at the conditional cost specified in the agency agreement (for example, at the minimum selling price or the cost that you must compensate to the principal in case of loss of the goods).
And when you have the contract or shipping documents in hand, you will, if necessary, adjust the data reflected in the accounting pp. 40, 41 Methodological instructions, approved.
Postings under the agency agreement with the principal
Therefore, he must issue an invoice for the intermediary fee within five calendar days from the date of shipment. The agent records this invoice in the invoice journal and the sales ledger. He transfers one copy of the invoice to the principal, who registers it in the journal of received invoices and the purchase book.
After which the principal, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 171 and paragraph 1 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation receives the right to deduct “input” VAT on intermediary remuneration.
Income tax The costs that the principal incurs in connection with the sale (purchase) of goods under an agency agreement consist of two components. Firstly, this is the amount of the agent's remuneration.
And secondly, the agent’s expenses reimbursed by the principal. Of course, such expenses must be economically justified and documented.
Accounting for agency agreement
Income in the form of remuneration is recognized on the date of signing the intermediary’s report to customers of goods or services. This payment method is beneficial to the intermediary, since large sums of money do not pass through his current account.
Currently, there is an unspoken rule about attracting attention for money transfers over 600 thousand rubles. Let's consider the accounting entries from an agent who is not involved in the calculations: Accounting entry for transaction D 002 Commissioned goods accepted for accounting K 002 Purchased goods transferred to the customer D 76 K 90.
1 The agent’s remuneration is recognized as income D 90.
03 K 68 VAT on the amount of remuneration D 51 K 76 Agent remuneration received Accounting from an intermediary when purchasing services for the principal Often in practice there are situations when, in addition to the purchase of goods, the intermediary is charged with purchasing related or separate services.
Agency agreement for the purchase of goods. Accounting with the principal Consultations Agency agreement for the purchase of goods. Accounting with the principal 02/04/2012 The intermediary acts on his own behalf. The right to deduct “input” VAT on goods (work, services) purchased on the basis of an intermediary agreement belongs to the principal. Of course, if the purchase is made on behalf of an agent, the supplier will issue an invoice in the name of the agent.
Therefore, the agent, having received this document and registered it in the journal of received invoices, reissues it to the principal. The intermediary does not have the right to apply deductions for VAT claimed by the supplier. He does not register the supplier's invoices in the purchase book, nor does he make an entry in the sales book about the invoice reissued to the principal.
Settlements with other debtors and creditors." Based on the agent’s approved report, in the principal’s accounting, the amount of remuneration due to the agent is recognized as expenses for ordinary activities (clause 5 of PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization”).
Debit 76 of the account “Settlements with the agent” Credit 51 – Transferred funds to the agent for the purchase of goods; Debit 10 Credit 60 – Goods received from supplier; Debit 19 Credit 60 – VAT accrued on purchased goods; Debit 10 Credit 60 – Agency fee included in the cost of goods; Debit 19 Credit 60 – VAT accrued on remuneration; Debit 60 Credit 76 ac/account “Settlements with agent” – The debt to the supplier has been offset; Debit 60 Credit 76 account “Settlements with the agent” – The debt to the agent is offset; Debit 68 Credit 19 – Accepted for VAT deduction; Debit 51 Credit 76 account “Settlements with the agent” – Received the balance of funds.
Source: https://advokat-na-donu.ru/oprihodovanie-tovara-po-agentskomu-dogovoru-u-printsipala/
Accounting for agency agreements
Reflection from the Principal
Debit Credit Basis
62 90 Revenue from the sale of goods (work,
services) based on the submitted Agent’s report
90 68 VAT accrued for payment to the budget on sales
according to the Agent's report
20 76 Agency fee accrued to the Agent
19 76 VAT is reflected for reimbursement from the budget
according to agent's remuneration
68 19 The amount payable to the VAT budget was reduced due to reimbursement
90 20 Write-off of agency fees
51 62 Reflects the amount from the sale of goods (works, services), which
Transferred by the Agent to the Principal's account, minus
76 62 Reflected payment of commission to the Agent
due to the receipt of money from third parties
Accounting in 1C
On February 03, the Organization, under an agency agreement, acting on its own behalf and at the expense of the principal, purchased a consignment of goods:
- A4 paper – 500 pcs. in the amount of 105,000 rubles. (including VAT 20%) - for the principal;
- A4 paper – 100 pcs. for the amount of 21,000 rubles. (including VAT 20%) - for your own needs.
On February 10, the Organization transferred to the principal his part of the goods.
Receipt of goods
In the Purchases - Receipts (receipts, invoices) section, reflect the receipt of goods from the supplier with the document Receipt (receipt, invoice) transaction type Goods, services, commission.
Indicate in the header of the document:
- Counterparty - name of the supplier, selected from the Counterparties directory;
- Contract - an agreement with a supplier, selected from the Contracts directory.
Specify on the Products :
- Accounting account : for the principal’s goods - 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping”;
- for own goods - an account in which goods purchased for oneself are recorded (in our example, 10.01 “Raw materials and supplies”).
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 10.01 Kt 60.01 - own materials are accepted for accounting;
- Dt 002 - the principal’s goods are accepted for off-balance sheet accounting;
- Dt 76.09 Kt 60.01 - reflects the debt of the principal for his part of the goods;
- Dt 19.03 Kt 60.01 - VAT on own materials is accepted for accounting.
Register the supplier's invoice by indicating its number and date at the bottom of the Receipt document form (act, invoice ), click the Register .
Invoice document will be automatically filled in with the data from the Receipt document (act, invoice) .
- Operation type code - “Drafting or receiving an invoice by a commission agent or agent when selling or purchasing both own and commission goods at the same time.”
If the document has the Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt checkbox selected , then when it is posted, entries will be made to accept VAT for deduction on the part of your own goods.
Transfer of goods
The transfer of goods to the principal is reflected in the document Report to the principal, type of transaction Purchase report based on the document Receipt (act, invoice) (or from the section Purchases - Reports to the principal - button Report to the principal - Purchase report).
The data on the Main will be filled in according to the document Receipt (act, invoice) .
Specify in the Commission :
- Calculation method - method of calculating the agency fee under the contract (selection from the drop-down list);
- % of remuneration - percentage of the agent's remuneration;
- % VAT - VAT rate on the amount of the agent's remuneration;
- Remuneration service - name of the service, selected from the Nomenclature directory;
- Income account - an account in which income from intermediary activities is recorded;
- Nomenclature groups - nomenclature group for intermediary activities.
Register an invoice for agency services using the Write invoice .
- Transaction type code - “Shipment or acquisition of goods, works, services, rights, including transactions taxed at a rate of 0%, shipment or acquisition under a commission (agency) agreement, return of goods by the buyer and receipt of them by the seller, preparation or receipt unified adjustment SF (except for operations under codes 06, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16, 27).”
The data on the Goods using the Fill will be automatically filled in based on the Receipt document (act, invoice) only with goods purchased for the principal.
After clicking the Write , the program will automatically create an issued Invoice .
Please indicate:
- Operation type code - “Drawing up or receiving an invoice by a commission agent or agent when selling or purchasing both own and commission goods at the same time.”