Last modified: February 2021
Labor relations between an employee and an employer do not always mean the signing of an employment agreement. If management does not consider it necessary to expand the staff due to one-time needs for the work of specific specialists, they draw up a civil contract with the employee.
Relations under the civil contract (hereinafter referred to as the civil contract) provide for the employee to perform a specific type of work, the provision of a service in a clearly defined scope. Since the rights of the contractor under the GPA are limited, unlike an employment contract, this form of registration is not welcomed by citizens, and for employers this option is more profitable, but is not always possible.
Samples of GPC agreement
Standard GPC agreement with an individual
Sample form for a contract with an individual: example 1 and example 2
Civil contract with an individual for the provision of services: download form and sample 2021
Sample act on the provision of services under a civil law contract concluded with a citizen in 2021
What is it (concept)
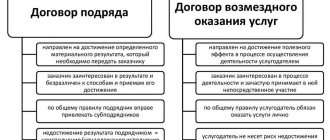
A civil contract is an agreement between the parties to perform certain works or provide services, regulated by the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The parties to a civil law contract can be state and municipal bodies, organizations, individual entrepreneurs and ordinary citizens.
Depending on the subject of the contract, there are:
- agreements aimed at the transfer of property and property rights (purchase and sale agreements, exchange, donation, rental, leasing);
- contracts for the performance of work (construction or household contract, contract for the provision of contract and survey work, etc.);
- contracts for the provision of services (agency contract, insurance contract, transportation, storage, commission, etc.).
What is a civil contract?
A GPC agreement is a transaction where, based on the agreement of the parties, their obligations and rights in relation to each other are established, changed or terminated in accordance with Articles 153, 154 and paragraph 1 of Art. 420 GK.
This type of agreement between a legal entity and an individual determines their relationship related to the result of the work. In this case, the parties do not enter into an employment relationship; in relation to each other, they are the customer and the contractor.
A civil law contract is concluded according to the rules of the Civil Code and its main difference from an employment contract is the ability to prescribe any conditions that do not contradict the law and suit both parties. This rule is prescribed in Art. 421 Civil Code.
Performance of work and provision of services by an individual
If we talk about contractual relations between citizens, they are regulated using the provisions of Chapter 37 of the Civil Code. These norms indicate that a citizen takes upon himself the obligation to fulfill orders voiced by customers. At the same time, the finished work must be handed over, for which you will receive money. The second party is responsible for accepting the result of such work.
When forming the act in question, it is necessary to take into account the conditions classified as essential. Including:
- the period during which the result must be submitted;
- subject, this concerns the content of the ordered work, its volume and the expected result.
However, in this case, the value under the agreement cannot be attributed to the named group of conditions. The services themselves under the type of agreements under consideration are implemented based on the provisions of Chapter 39 of the Civil Code.
Agreements that provide for the provision of services on a reimbursable basis include communications, medical services, consultations, provision of information, training, and others.
Regardless of what type of agreement is used, the subject matter must be included in the essential conditions in any case.
Types of GPA
A GPC agreement can be concluded with an individual:
- Contract. The parties are the customer and the contractor. The customer gives the contractor a task, the result of which he undertakes to accept and pay for at the cost established in the agreement. The contractor guarantees the completion and delivery of the task within the framework of the contract within a certain period. At the same time, it is permissible to involve other persons (subcontractors), the only important thing is compliance with deadlines and the quality of the work performed.
The result of acceptance of the work is an act signed by both parties. The amount and procedure for payment must be strictly specified in the GPA.
- For the provision of services . Parties to the contract are the customer and the contractor. The contractor is obliged to provide services in accordance with the terms of the agreement, and the customer is obliged to pay for them. All general provisions that are valid for a contract are applicable to such an agreement.
- Author's order. The author, on the one hand, and the customer, on the other, enter into an agreement that the author agrees to create a work of art, literature, science, etc. and transfer it to the ownership of the customer. The customer is obliged to accept it and pay. The agreement stipulates the deadline for delivery, the amount and procedure for payment.
In each case, the contract is of a compensatory nature, i.e. an individual receives remuneration for work or services. The difference from other types of contractual relationships is that the contractor receives a result that is separate from the work itself.
How to avoid problems with supervisory authorities?
Sometimes employers make a grave mistake by registering an employee hired on a permanent basis not with an employment contract, but with a GPA.
The motives for such behavior are obvious, because a civil agreement allows you to pay a lower amount of insurance premiums, avoid providing the employee with social guarantees and compensation, etc. However, regulatory authorities easily detect this violation, which ultimately leads to not the most pleasant consequences.
So, in order to avoid making such a mistake, customers need to adhere to the following recommendations:
- To register a GPA, there must be a legal basis. A specific specialist should be hired to perform one-time work that is not of a regular nature.
- It is important to format all documentation correctly - a typical mistake by customers is to use the following wording in the GPD text: “employee” and “employer” instead of “customer” and “performer (contractor)”, “wages” instead of “contract price” or “remuneration for work”, etc. It should be remembered that these terms are acceptable only in labor relations.
- If there are any doubts about what kind of contract to formalize for this or that employee, it is recommended to first analyze judicial practice in similar situations.
Thus, civil law is a fairly broad area of law, affecting a variety of types of legal relations between the parties (performance of work, transportation of people and goods, conducting research, etc.). At the same time, it is very important to be able to distinguish them from the labor relations that arise between an employee and an employer in order to avoid problems with supervisory authorities.
Contracts, both construction and household, require proper drafting. You can find out how to conclude such an agreement, as well as the specifics of its termination by agreement of the parties and unilaterally, on our website.
Differences between a GPC agreement and an employment contract
GPA has significant differences from an employment agreement, since the subject of the agreement in the first case is precisely the result of the labor of an individual, and not the labor function itself. The contractor under the GPC agreement is obliged to do the work and transfer its result to the customer, while he runs the risk of producing it in sufficient quality and within the specified time frame.
Whereas an employee under an employment contract:
- included in the regular staff;
- is obliged to comply with the work regime specified in the contract;
- accepts responsibilities to perform work in accordance with the job function;
- submits to and is controlled by the management of the employing organization;
- receives wages based on a time sheet.
Labor Code in Art. 15 does not allow the replacement of an employment contract with a civil contract if, in fact, an individual and an employer have an employment relationship. At the same time, the employer must not only determine a specific list of work for the position in accordance with the staffing table, establish the amount of wages, and the working day schedule, but also provide the employee with working conditions that meet labor law standards and other regulations (Article 15 of the Labor Code).
The content of the employment contract must comply with the requirements of Art. 57 of the Labor Code, the drafting of a GPC agreement is regulated by the Civil Code.
Conditions of a civil law agreement that distinguish it from a labor agreement
There are a number of differences between a civil law agreement and an employment agreement.
| Comparable parameters | Civil | Labor |
| NPA | Ch. 37, ch. 39 GK | Ch. 10 – 13 TC |
| Parties (name) | Customer and contractor (performer) | Employer and employee |
| Item | Result and its transfer | The process of labor, performance of work, provision of services |
| Nature of work performed | Manufacturing (processing) of a thing, certain actions and transfer of the result to the customer | Work in a specific specialty, position in accordance with TD |
| Working hours, labor discipline | Performs work (provides services) independently | Compliance with work schedule and administration orders |
| Duration | Contracted for completion date | Consists:
|
| Calculations | Payment based on completion results after signing intermediate and final acceptance certificates | Regular payments in accordance with TD |
| Labor organization, interaction between parties | The customer has the right:
| Working conditions are provided by the employer in accordance with the TD and the collective agreement |
| Privileges | Guarantees and benefits are not provided | The employee is provided with all benefits and guarantees in accordance with, paid for:
|
| Termination | Possibly unilaterally, on the initiative of:
| Unilaterally only at the initiative of the employee. At the initiative of the employer in the cases provided for in Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Taxation |
|
|
Use for free a review of judicial practice on concluding work contracts in ConsultantPlus.
Advantages and disadvantages
For an individual, concluding an agreement has the following positive aspects:
- there is no subordination, the agreement rather regulates partnership relations;
- the contractor has the right to complete the work at a time convenient for him without the need to comply with the internal labor regime;
- the result must be paid in accordance with the terms of the contract or the customer will be held liable.
But not everything is so simple, so we will list the negative aspects:
- lack of social support;
- the workplace must be equipped independently;
- you will have to take into account the costs of tools and materials that will be required to obtain the final product under the contract.
Filling out a civil contract for the provision of services
The form of such an agreement between the customer and an individual can only be written in order to avoid situations where one of the parties in the process refuses to complete the task, and the customer refuses to accept or pay for it.
The contract should not contain language related to labor relations - “employer”, “salary”, “employee”. Otherwise, he may be reclassified as a labor worker, and this threatens the organization with a fine.
Any use of materials is permitted only with a hyperlink.
The document form is not regulated by law and is drawn up in a simple form. But it must contain:
- details of the parties indicating the name of the customer organization, its manager or other official who has the right to sign contracts, as well as information about the individual performing the work or services;
- the subject of the contract with the wording of the specific task, address of execution and properties of the final result;
- conditions of execution, including qualitative characteristics of the final result, scope of work or services, deadlines, conditions for monitoring the stages of execution, as well as issues of provision of materials and equipment;
- the procedure for delivery and acceptance of work or services performed;
- order cost and payment procedure;
- liability of both parties with the establishment of parameters for the application of a penalty in case of failure to fulfill their obligations for both parties;
- establishing the validity period of the contract and the procedure for making changes to it;
- full details of the parties to the contractual relationship.
All changes to the terms of the GPC agreement that could occur during its execution must be documented in an additional agreement. This document is an integral part of the main agreement, so it must indicate the number and date of the original agreement. All changes are written down point by point and certified by the signatures of both parties.
The document is drawn up in one copy for each party and certified by their signatures. The organization affixes the signature of the head with a seal.
Attention! A multi-page GPC agreement is certified by the signatures of the parties on each sheet.
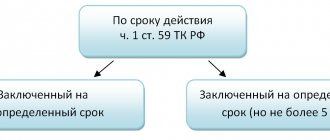
Duration of the GPC agreement
The specific validity period of the agreement is fixed in its corresponding paragraph, while the maximum term of the GPC agreement with an individual is not limited by law (Part 1 of Article 708, Part 1 of Article 781 of the Civil Code). Additionally, intermediate deadlines may be provided.
In practice, the customer and the contractor are interested in completing the work (providing the service) as quickly as possible and generating income. Therefore, although according to the law the period can be calculated in decades, it has reasonable limits. The duration is determined based on the actual ability to fulfill the terms of the contract.
Storage of contracts is determined by the provisions of Art. 23 of the Tax Code and Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ and is 5 years.
How to avoid recognition of the GPA as an employment contract?
Practice shows that when concluding a civil law contract, typical mistakes are made that can cause it to be recognized as a labor contract. The relationship between a legal entity and an individual can be considered labor if:
- a labor function is indicated (for example, regular cleaning of office premises), while the GPC agreement is a one-time one with the goal of obtaining only results;
- It is the specific result that is subject to payment, not the labor process. Remuneration should be paid only on the certificate of completion of work;
- specifying in the contract the requirements for compliance with job descriptions and labor regulations of the organization;
- ensuring working conditions at the expense of the customer without reflecting the corresponding costs in the contract;
- provision of social insurance.
Civil legal relations can turn into labor relations, then the employer is obliged to formalize them with an employment contract and set the start date from the moment of conclusion of the Civil Agreement (Part 2 of Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If it turns out that the civil contract in fact regulates labor relations, then the employer, within the framework of the Administrative Code, is liable in the form of a fine:
- from 5 to 10 thousand rubles per entrepreneur;
- from 50 to 100 thousand rubles from a legal entity;
- from 10 to 20 thousand rubles per official.
In what cases can a civil law contract be reclassified as an employment contract?
A civil law contract can be forcibly reclassified as an employment contract if:
- The text of the contract includes conditions characteristic of labor relations or indicating them (provisions on regular wages, vacation, social guarantees, sick pay, personal performance of work, work schedule and subordination to labor regulations, information about position, specialty, profession, etc. .);
- the implementation of work under a civil law contract is permanent and not one-time in nature;
- there is no document confirming the fact of performance of work under a civil contract (if its execution is mandatory as required by law);
- the contract was renegotiated several times after its expiration;
- remuneration is paid on the same basis as full-time employees, according to the tariff schedule, at least twice a month.