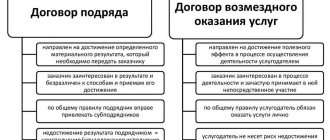
The difference between a GPA and an employment contract
When concluding a civil law contract (CLA), it is necessary to carefully ensure that its terms exclude even the small possibility of being classified as a form of employment agreement.
In judicial practice, such requalification is not uncommon, and its consequences are fraught not only with the payment of an administrative fine, but also with additional assessment of insurance premiums and penalties for their late payment. IMPORTANT! Labor relations with an employee are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and civil relations with an individual are regulated by civil law.
To avoid possible problems, the following features must be observed in the terms of the contract:
1. The subject of the GPA is the provision of a certain service, performance of work or transfer of property rights, and not the performance of a labor function by profession. The result of the work should be a tangible result in the form of, for example, a completed project or assembled equipment. Accordingly, the basis for payment is not a time sheet, application or order, but an act of work performed (services rendered).
2. An employee under such a contract is not a full-time employee, which means that he cannot be subject to requirements for compliance with internal regulations and subordination in accordance with the hierarchical structure of the company, as well as standards for setting salaries in accordance with the staffing table. This means that there will be no such conditions in the GPA.
3. The procedure for payment under the GPA is determined by agreement of the parties and is not regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, payment of remuneration is possible only after completion of the work (their stages) stipulated by the contract or transfer of rights to property, unless its conditions indicate the need for an advance payment.
4. Unlike an employment agreement, such an agreement, regardless of its subject matter, status of the parties and special conditions, always has a finite period of validity.
5. In the case of providing services under the GPA, special attention should be paid to the frequency of their provision. If, under the contract, certificates of work performed or services provided are regularly issued for amounts of a comparable amount, this will be considered a clear sign of a disguised labor relationship and will attract the attention of inspectors.
About situations in which the courts regard the GPA as a labor one, read the material “GPA with an individual for the provision of services - the risk of reclassification as a labor one.”
What is a contract
A work contract (civil contract of civil law nature) is an agreement in which one party (contractor) undertakes to perform certain work on the instructions of the other party (customer) and deliver its result to the customer, and the latter undertakes to accept the result of the work and pay for it (Art. 702 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The work contract is considered one of the oldest civil law contracts. It was already known to Roman law, which defined it as hiring work and was divided into three types - hiring of things, contracting, hiring of services.
After the revolution in Soviet legislation, contracting was identified as a separate contractual type. According to the Civil Code of 1922, under a contract, one party (contractor) undertakes, at his own risk, to perform certain work on the instructions of the other party (customer), and the latter undertakes to provide remuneration for completing the task. The Civil Code of 1964 defined a contract as an agreement under which the contractor undertakes to perform, at his own risk, certain work on the instructions of the customer from his or his own materials, and the customer undertakes to accept and pay for the work performed (Article 350).
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation of 1994 identifies the types of construction contracts (Chapter 37):
- domestic;
- construction contract;
- contract for design and survey work;
- contract work for government needs.
A contract with an individual can be used in cases of one-time work. Examples: legal services, office renovation, fence painting, etc.
Calculation of insurance premiums under GPC agreements in 2019-2020: features
One of the most important advantages of registering relations with an individual in a civil law manner is the possibility of reducing the amount of accrued insurance premiums, and sometimes the complete absence of the need to accrue them.
To understand which payments are subject to contributions and which are not, it is necessary to clearly define the subject of the agreement and its compliance with one of the categories listed in Art. 420 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
| Subject of the agreement | Is the remuneration subject to insurance premiums? |
| Contracting, provision of services | Taxable |
| Royalties | Taxable, minus the amount of confirmed expenses |
| Alienation of rights to the results of intellectual activity | The amount reduced by the amount of confirmed expenses is taxed. |
| Transfer of ownership or temporary use of property (including lease agreements, donations) | Is not a subject to a tax |
| Reimbursement of expenses of volunteers in charitable organizations | Not taxed, with the exception of food expenses exceeding the daily allowance in accordance with clause 3 of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Reimbursement of expenses for professional training, including student contracts | Is not a subject to a tax |
In the case of concluding an agreement with a mixed subject, for example, providing for both the sale or transfer for use of property and services associated with its transfer, contributions must be accrued only for that part of the remuneration that is subject to taxation. Therefore, in such GPAs it is necessary to distinguish between the amounts of an individual’s income into taxable and non-taxable parts.
ConsultantPlus experts have prepared detailed explanations on the calculation of insurance premiums for payments under a vehicle rental agreement with and without a crew. Go to the Ready-made solution by getting free trial access to the system.
The calculation of contributions does not depend on the form in which the GPC agreement is concluded: on paper or electronically .
Find out when to pay advance payments to the “physicist” contractor here .
See also “Reimbursing the expenses of a “physicist” under the GPA - should I pay fees? .
When a contract is concluded, its main terms
But first, it is worth studying in more detail other specifics of this agreement - in what cases, by whom and on what conditions it is concluded.
Let's start with the parties: there are two of them in the contract, respectively, the customer and the contractor. In both capacities, ordinary citizens, individual entrepreneurs, and legal entities can act - but when drawing up a document there will be its own characteristics, depending on which of these categories the parties belong to.
The form of the agreement can be:
- oral;
- written.
Yes, an oral form is indeed acceptable, but only if the total transaction amount under the agreement does not exceed 10 thousand rubles. However, even if the amount is less, it is allowed to draw up a written agreement, but it will not be necessary to have it certified - but for a larger amount, notarization is already required.
The most important features of the contract:
- The agreement is concluded by the parties voluntarily.
- The hired contractor is not part of the hiring company's staff; records of work performance will not be entered into his work record; there is no need for orders to accept and then dismiss; hours are not included in the time sheet; the cost of work is not estimated according to the standards accepted by the customer company.
- The contractor does not have to obey the work schedule of the enterprise, his schedule is free, and payment is made for completing the work and is in no way tied to the time spent, it is only important to meet the deadline and the level of quality.
- A contractor hired under a contract is not entitled to any benefits provided to employees of an enterprise.
Required conditions:
- The subject of the contract is the result that the employer needed the contractor to achieve. Here it is important to note once again that this is precisely the result, and not the work as such - payment for a contract is made not for the fact of work, but for its result, and in its absence, the fact that the contractor worked does not play any role, and he will not be able to receive even part of the payment, referring to this (unless there is the good will of the customer himself).
- Deadline – it is necessary to indicate both the start time of the work and by what date it must be completed. Sometimes the completion dates for individual stages are indicated separately. The contractor is responsible for meeting deadlines; by agreement with the customer, they can be changed. If there is a result, but it was not possible to meet the deadline, then the customer may also refuse to accept and pay for the work.
These are two key conditions, and the rest are already introduced by the parties at their discretion.
Sometimes the contractor may involve subcontractors - then he will become the general contractor and will be responsible for the actions of the subcontractors.
If losses were caused due to the actions of subcontractors, the work turned out to be of poor quality, or deadlines were missed - in all cases, the responsibility lies with the general contractor.
As for the price of the work, it includes two components:
- Costs incurred by the contractor during its course.
- His reward.
There are different options for determining the price:
- immediately in the text of the contract;
- at the current market rate;
- according to the contractor's estimate approved by the customer.
They also provide an approximate and fixed price. In the first case, the price may increase if additional work is needed, and therefore costs. If the need for this is justified, then the customer still has the right to refuse, but then he will have to pay for the part of the work already completed. But if a fixed price is set, then its revision cannot then be demanded.
A work contract was often concluded instead of an employment agreement due to the fact that this way customers reduced the taxes they paid, but starting from 2021, they also have to pay insurance premiums - with certain exceptions. There is no requirement to make only payments to the Social Insurance Fund - this is left to the discretion of the parties.
It is possible for the FSS to go to court in order to recognize the contract as an employment contract and collect the contribution, and also a fine. To avoid such a development of events, you should, while still drawing up the contract, abandon any controversial provisions in it, due to which it can then be defined as a labor contract. To clearly identify a document as a civil document, you should:
- Indicate the exact period allotted for completing the work.
- Register the exact amount of remuneration for the entire scope of work, without dividing into several amounts for certain periods.
- Do not provide any references to the company’s job descriptions and do not link contract work to its operating hours.
- Acceptance of work should be confirmed by an appropriate act signed by the parties.
- The work must be one-time in nature.
Exceptions to the general rule
Chapter 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, among other things, provides for a number of features in the taxation of insurance premiums relating to both the status of the insured person and the type of contract concluded with him:
1. Remunerations under the GPA, regardless of the subject of the agreement, are not subject to contributions for insurance against temporary disability or in connection with maternity (subclause 2, clause 3, article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
2. Amounts of income accrued to freelance employees are not subject to contributions for insurance against accidents and work-related injuries, unless this is expressly stated in the terms of the contract.
3. Remunerations to foreign citizens who have the status of temporary residents, in accordance with subparagraph. 15 clause 1 art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not subject to insurance premiums, unless this is expressly provided for by federal laws on specific types of insurance.
4. Income under the GPA of foreign citizens working in company divisions abroad of the Russian Federation is not subject to insurance contributions.
Read about the nuances of calculating contributions on the income of foreigners in the material “Insurance contributions from foreigners in 2021 - 2020.”
5. If a GPC agreement is concluded with an individual in the status of an individual entrepreneur, then he is obliged to calculate and pay insurance premiums independently. This is due to the fact that in the light of Art. 419 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, private entrepreneurs are allocated to a separate class of payers.
Read about the specifics of calculating and paying individual entrepreneur contributions here.
About the pros and cons of the GPC agreement
When concluding a civil law contract, you will need to sign certificates of acceptance of services. The paragraphs of the document indicate the customer’s registration data, deadlines, and personal information of the employee. It is not recommended to issue conclusions for a long period.
Advantages of registration under a civil law contract:
- A small package of documents (passport, SNILS, TIN).
- The customer does not control the time spent at the workplace; the main thing is to deliver the work on time.
- The work experience of the performer is preserved, since deductions for him are transferred to the Social Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation.
- No proof of worker qualifications is required.
The disadvantages of GPC agreements include:
- Entries are not entered into the work book.
- Social guarantees such as weekends, holidays, sick leave and vacation are not provided.
- Difficult processes for resolving the issue of insurance premiums.
- There is no compensation for closing a business due to bankruptcy.
- When the contract is closed, by decision of the contractor, a penalty will be paid to the customer.
Advice! It is advantageous to conclude civil law agreements in the case of one-time cooperation. It is recommended to draw up an employment contract for a long period of time.
Expense limit for reducing the taxable base for insurance premiums
In the case of royalties, as well as contracts for the alienation of rights to the results of intellectual activity, the amount of expenses by which the taxable base can be reduced must be documented and have a direct connection with the receipt of such income (clause 8 of Article 421 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) . The volume of expenses not confirmed by documents is limited (clause 9 of Article 412 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The limits are set as a percentage of the accrued remuneration:
- for the creation and execution of literary works, scientific developments and works - 20%;
- for the creation of musical works not related to the theatrical sphere or audio design for video films - 25%;
- for the creation of artistic, architectural, audiovisual works, photographs - 30%;
- for inventions, discoveries and creation of industrial designs - 30% of the amount of income of an individual received during the first 2 years of using the results of work;
- for the creation of sculptures, decorative and design graphics, as well as musical works intended for theater or films - 40%.
Read about the cases in which income under the GPA is not subject to personal income tax.
Insurance premium rates for GPC in 2019-2020
According to established Art. 425 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of insurance premiums for calculation from the amounts of remuneration under GPC agreements is:
- for compulsory pension insurance - 22%, taking into account the maximum base for calculation and 10% on income exceeding it;
- for compulsory health insurance - 5.1% (there is no limit on the income base for these contributions).
The maximum base for calculating insurance contributions for pension insurance is equal to:
- in 2021 - RUB 1,150,000. (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 28, 2018 No. 1426);
- in 2021 - RUB 1,292,000. (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 6, 2019 No. 1407).
However, the size of the marginal base and the tariffs depending on it cease to play their role if the policyholder has the right to apply reduced premium rates.
Application of reduced and additional GPA contribution rates
In Art. 427, 428 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation clearly regulate cases when the payer can use reduced rates of insurance premiums or, conversely, must apply an additional rate.
The situation with a reduced tariff in relation to civil law contracts is quite simple: if the payer exercises the right to reduce insurance premiums for full-time employees, it has the right to apply the same tariffs under civil contracts.
Note! Starting from 2021, the list of persons entitled to preferential rates on contributions has been significantly reduced; in particular, the majority of simplifiers have lost this right. Since 2021, this list has decreased even more, at the same time, individuals have appeared who can reduce the general insurance premium rate to 15%.
A more complex analysis is required before a decision is made on the assessment of additional contributions. As you know, this applies to work that is carried out in hazardous and unhealthy working conditions: the legislator lists professions that are subject to additional contributions for pension insurance in paragraphs 1–18 of Part 1 of Art. 30 of the Law “On Insurance Pensions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ.
Thus, if the GPC agreement covers work related to the performance of duties in such professions, or it directly states that the work is carried out in hazardous conditions, then additional contributions are necessary. The same approach must be followed in the case where the place of work is the territory of an enterprise, which, as a result of a special assessment of work, has been assigned a certain class of danger or hazard.
However, in a situation where the contract does not indicate the location of the work or the wording of the subject of the contract is vague and does not directly indicate that work is being carried out in conditions of increased danger, the enterprise may not charge additional insurance premiums. But, taking advantage of this opportunity, it is necessary to understand that in case of an audit, you need to prepare to defend your position in the judicial authorities.
Payment and reporting of GPA insurance premiums in 2019-2020
Currently, reporting on insurance premiums (with the exception of contributions for insurance against accidents and industrial injuries, the calculation of which continues to be accepted by the Social Insurance Fund) is submitted to the Federal Tax Service. The form of this calculation is common to all contributions supervised by the service. For 2021, the ERSV is submitted according to the form approved. by order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 10, 2016 No. ММВ-7-11/551. As of reporting for the 1st quarter of 2021, a new ERSV form is in effect - from the Federal Tax Service order dated September 18, 2019 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] The calculation must be submitted no later than the 30th day of the month following the end of the reporting quarter/year.
This report does not highlight the amounts of payments under the GPA, so the main thing for the accountant is to correctly determine the part of the income paid that is taxable and non-taxable with insurance contributions.
Read more about the rules for filling out the new calculation here.
Reporting on insured persons is not limited to a single calculation form submitted to the Federal Tax Service. On a monthly basis, it is necessary to submit a report to the Pension Fund in the SZV-M form, which must indicate not only all employees who worked in the organization during the reporting period, but also all individuals with whom GPC agreements were concluded.
Among other things, all payers are obliged annually, before March 1 of the year following the reporting year, to provide personalized data on the length of service of insured persons to the Pension Fund in the form SZV-STAZH, approved by Resolution of the Board of the Pension Fund of December 6, 2018 No. 507p.
Required tax and other deductions
Cooperation on a contract can be formalized not only with an individual, but also with a legal entity. person or individual entrepreneur. As a result of this fact, taxation rules change. Article 346 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation clarifies the concepts of who can act as a tax agent.
The contractor himself must pay taxes under the contract, regardless of his status (individual entrepreneur or individual). However, for an individual, the customer will act as a tax agent, and for a legal entity, an individual entrepreneur.
Reporting forms (personal income tax-1, personal income tax-2)
According to Articles 208 and 209 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income received for performing services under a contract is subject to taxes. The personal income tax-1 tables contain data on the profit transferred to the contractor for the work, information on deductions and the amount of payments sent to the state treasury. The dates for transferring funds and withholding taxes for the performers specified in the agreement are indicated.
All persons to whom transfers were made from the customer must be indicated in the personal income tax form -2. Documents must be submitted no later than April 1 of the following year. The certificate indicates the full amount of income without deducting contributions, as well as the amount of tax transfers.
Amount of tax withheld and calculation procedure
The amount of deduction from payment for work done depends on the citizenship of the contractor or his individual entrepreneur. If the person performing the services is registered on the territory of the Russian Federation, then the income rate will be 13%. For foreigners and their organizations, deductions of up to 30% are charged.
Personal income tax percentages are specified in Article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In order to determine the correct wage, the contractor will need to make a calculation. The contract must indicate the total amount of payment for the work plus income tax on this payment. The salary can be divided into an advance and the remainder. Thus, it turns out that the payment for the service provided will be a little more than the remuneration that the contractor will receive.
You can give an example using a sample. The contractor agreed with the customer, an individual, that he would receive 12,000 rubles for the reconstruction of the building facade. To indicate the correct amount in the agreement you will need 12000/0.87 = 13793.1 rubles. As a result, the price of 13,793.1 rubles will be entered in the clause on payment for work.
Insurance premiums under the contract
Insurance premiums under a contract will have to be paid by the employer if the contractor is represented as an individual. face. Responsibilities for such payments are described in Federal Law 212. In situations where the employee is an individual entrepreneur, transfers of funds to the Social Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation must be carried out by the contractor himself. To avoid controversial issues, it is necessary to stipulate in the contract in a separate paragraph the obligations of the participants for insurance and tax payments. Transfer of funds to the Social Security Fund occurs upon payment of wages.
Payer of taxes and contributions
Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation describes the relationship between the hiring party and the contractor. According to the law, a tax agent will be considered a person who transfers payments to the contractor for work done.
If the contractor is a legal entity
Case one: if the performer is registered as a legal entity. Before concluding an agreement with such a contractor, you need to ensure his legal capacity. It comes in the following types:
- general (the company has the right to conduct any type of activity without a license);
- special (the performer must have permission to carry out the activity).
When an agreement is drawn up between the customer and a legal entity, insurance premiums and taxes are paid by the contractor independently. To prevent possible disagreements in the future, it is better to indicate the tax obligations of the parties in the clauses of the agreement.
The performer is an individual. face
When creating a contract with an individual, the customer is required to pay taxes for it. Therefore, when deciding the issue of wages, it is worth considering that the contractor will receive payment less than what is specified in the contract. The cost of services should be indicated increased taking into account tax deductions. The calculation of insurance premiums in the contract is also paid by the customer’s organization.
It is important to know! If the deductions have not been transferred, the contractor can remind the employer about this; another way is to contact a representative of the tax service. The time allotted for this is within 30 days from the date of payment for the work.
Concluding an agreement with a foreigner
When concluding a contract with a foreigner, you should pay attention to whether he is a resident of the country. If the performer is a non-resident of the Russian Federation, then the amount of tax deductions will be 30%.
In order to pay less tax for a foreign performer, he must become a resident of the country. To do this, he must officially be on the territory of the state during the last year for at least 183 days. Recalculation of taxes by 30% may occur if the contract is terminated before the expiration of 183 days.
Persons are not allowed to carry out activities if they entered visa-free. In order to get started, you will need to purchase a patent. In this case, tax deductions will have to be made by the contractor himself, as prescribed in Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The tax percentage also depends on the length of stay in the state. According to Art. 231 of the Tax Code, the organization should be notified of changes in the amount of contributions and their overpayment.
At the conclusion, you should explain and agree with the contractor that tax contributions will be included in the amount of remuneration. Accordingly, the contractor will receive a smaller amount. Or another option is possible. The agreement indicates the cost excluding taxes and stipulates that personal income tax deductions are made by the foreigner himself.
Agreement with individual entrepreneur
If the contractor is an individual entrepreneur, then he is responsible for insurance premiums. The system for paying contributions will depend on what taxation scheme the person has. When concluding a contract, it is necessary to register in a separate clause the persons carrying out these transfers.
The customer, in this case, is exempt from paying contributions to the state treasury. However, in practice, contractor-entrepreneurs already include funds to pay fees in advance in the cost of their services. If an individual entrepreneur does not have registered employees, contributions to the Social Insurance Fund are voluntary.
Results
Despite the obvious attractiveness of using GPA agreements due to the possibility of charging insurance premiums for the payments they provide for in a smaller amount, their legal component requires accuracy in the wording of the terms of the agreement. For an accountant, the presence of freelance workers will mean the need to carefully collect and study documents confirming the possibility of non-payment of insurance premiums, as well as work together with a lawyer to exclude language from civil liability agreements that implies negative consequences for the business.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 6, 2019 No. 1407
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 28, 2018 No. 1426
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 18, 2019 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 10, 2016 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
- Resolution of the Board of the Pension Fund of December 6, 2018 No. 507p
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.