An employment agreement is an agreement signed by the parties to perform certain work by one person for the benefit of another. In everyday life, such an agreement often means the conclusion of an employment contract. An employment agreement with an employee, a sample of which was drawn up in accordance with the requirements of current legislative norms, regulates all aspects of the labor relationship, including labor and its payment, rest, and the provision of benefits. If concluding an employment contract with an employer who is a legal entity or individual entrepreneur is a generally accepted practice, then signing such a document with an employer who is an individual does not yet have such widespread use today.
Key terms of the employment contract
An employment contract is concluded between parties called the employee and the employer.
An employee can be any capable person who has reached the age of 16 years. In turn, employers can be individuals (when hiring domestic workers), legal entities, as well as individual entrepreneurs. The contract must include the place of work - the exact address and name of the structural unit. If a legal entity has branches in the country, the municipality or region should be indicated.
The labor function must be clearly defined : it is necessary to indicate the list and nature of the work performed by the employee, as well as the employee’s position. It should be noted that if the work does not correspond to the job function, the employee may refuse to perform it on legal grounds. If due to work processes it is necessary to change or transfer responsibilities, it is necessary to sign an additional agreement to the contract or enter into a new employment contract.
The terms of remuneration in the contract must be fully described . You should not make references to internal acts or agreements regulating the amount of wages. If the employment contract does not contain a wage scale or does not indicate the exact salary of the employee, such an agreement will most likely arouse the interest of the inspection authorities.
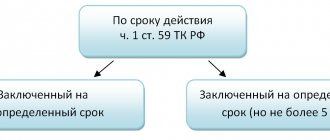
The most important element of the contract is its term . As a general rule, an employment contract is of unlimited duration, therefore, for a fixed-term contract, a direct indication of this is necessary in the text of the contract and compliance with at least one reason, a full list of which is specified in the law (Article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The most frequently cited reasons are:
- replacing an employee on maternity leave;
- performing seasonal work;
- going on a business trip abroad.
Employment agreement form
The conclusion of an employment agreement between an employee and an employer is primarily aimed at streamlining the relationship between the parties, as well as at fixing the most important points characterizing the work activity of a particular employer. For this purpose, a document is drawn up in written form.
The legislator, highlighting important points, enhances their significance and calls them essential (or mandatory) conditions of the employment agreement. Next we will reveal them.
And at this stage, the first conclusion that the employee must remember is that an employment agreement is a written document that is considered concluded if there are essential conditions in it.
The employment contract offered to the employee for signing is filled out by the employer on the company’s letterhead according to a model previously developed by him.
At the same time, when filling out the employment agreement form, you must always remember the mandatory conditions and, if necessary, supplement it or, conversely, exclude unnecessary ones.
The difference between labor relations and a civil contract
There are 4 distinctive features of an employment contract that distinguish it from a civil contract:
- Performance by the employee of a labor function. The employee must perform all actions and tasks personally (excluding any types of representation) and in a manner consistent with the staffing schedule and working conditions established by the employer.
- Submission to internal regulations. The employee is obliged to act in the interests of the employer, obey superior management and internal regulations.
- Ensuring working conditions. Each employer is obliged to provide appropriate working conditions provided for by the labor code. The workplace must comply with hygiene rules, be safe, comfortable and have the necessary set of tools. The employee has the right to days off, paid and maternity leave, as well as sick leave.
- Payment of decent wages not lower than the minimum wage. An employee has the right to decent pay, which will not be lower than the minimum wage (minimum wage). In this case, it is not the result that is subject to payment, but the process of fulfilling the employee’s obligations (this is, perhaps, the main difference between labor relations and civil law).
Legal aspects
A distinctive feature of standard agreements classified as civil law is that relationships are regulated, regardless of the status of the participants, by the Civil Code instead of the Labor Code. In accordance with Article 702 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a contract is a legal relationship obliging one party, called the contractor, to perform work for the other party, called the customer, with delivery within a specified time.
Work under a contract is regulated by Articles 740-757 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and is divided into the following types:
- household contracting - production of material goods to meet household needs;
- construction contract – new construction, repair or reconstruction of fixed assets, including installation and other related additional work;
- contract for design and survey work - preparation of design documentation, estimates for construction and reconstruction of fixed assets.
What is a work contract in essence and how does it differ from other legal relations of a civil law nature? A distinctive feature is the material form of the custom-made object, the ability to connect third parties, called subcontractors. Delivery of the finished object is carried out on the basis of a signed certificate of completion, according to which the contractor transfers the work to the customer, who undertakes to make payment in accordance with the conditions.
Additional terms of the employment contract
At the request of the employer, it is possible to establish a probationary period in the contract. The maximum possible period is 3 months, but for officials (chief accountant, his deputies and directors) this period can be 6 months. When the contract is of a fixed-term nature from 2 to 6 months, the trial period should be no more than two weeks. Establishing a trial period for a fixed-term contract of 2 months or less is prohibited. It is also prohibited by law (Articles 70, 207 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) to establish a probationary period for the following categories of citizens:
- Persons under the age of 18;
- Pregnant women;
- Persons with children under 1.5 years of age;
- Persons invited to work by transfer from another employer;
- Persons elected through a competition to fill the relevant position;
- Specialists who have successfully completed an apprenticeship, upon concluding an employment contract with the employer under the contract with whom they were trained;
- Specialists who have graduated from a higher educational institution no later than 1 year and are entering work for the first time.
It is important to specify the work schedule and designate rest days in the contract. A unified staffing table is created for the entire staff of employees in accordance with labor legislation. But if the schedule is different for a particular employee, the terms of the new schedule are best described in the contract.
If the specifics of the employer’s activities require it, he can specify a condition on non-disclosure of confidential information. In this case, the contract is supplemented with a corresponding section with a list of protected data or a link is established to regulations where this list has already been published. At the same time, the employer is obliged to create such conditions so that confidential information is protected from prying eyes:
- restrict access of unauthorized persons;
- encrypt information;
- mark electronic and printed documents;
- create safe conditions for storing data.
Some employers are ready to additionally insure their employees, improve their living conditions, or offer various forms of incentives. All this information is indicated in advance in the contract. Most often, employers are willing to compensate for housing rental costs, offer free trips to sanatoriums, or pay for gyms.
Conditions for improving the employee’s qualifications may also be prescribed, when courses, seminars or various training programs will be paid for by the employer. Often, enterprises are willing to pay even for higher education, but on the condition that after completing the training the person will work for some time with the employer or reimburse the full cost of training.
The employer and employee may specify other terms of cooperation if they do not contradict current legislation and do not infringe on the rights and legitimate interests of the employee.
Employment agreement (form and sample)
Sample employment agreement
Finally, all the interviews and tests are over, and you are hired for the job you want. The final completion of recruitment is the conclusion of an employment agreement with the employer. The employment agreement form does not have an officially approved form, therefore, as a rule, each employer uses its own form. However, drawing up such an agreement requires mandatory consideration of the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The sample provided will help the employee take into account possible nuances when signing it.
Responsibilities of the parties to the employment contract
The general responsibilities of the employee are formulated as follows:
- performing the work task accurately, efficiently and on time;
- compliance with established rules and daily routine;
- careful handling of the employer's property;
- compliance with safety regulations.
The tasks of a particular employee are determined by the employment contract, and a job description can be used as an addition explaining the procedure for their implementation.
General responsibilities of the employer:
- creating a comfortable and safe workplace;
- stable payment of wages to the employee;
- compliance with labor laws;
- product of all social payments.
Grounds for termination of an employment contract
The Labor Code establishes a number of grounds for termination of a contract:
- Employee initiative. On his own initiative, the employee may terminate the contract at any time and under any circumstances. The employee is required to write a resignation letter in accordance with general standards and submit it to the employer. After this, the employee is required to work for another 2 weeks fulfilling his duties. The employer pays all wages, as well as the cash equivalent for unused vacation.
- Agreement of the parties. A frequent case is when the employer and employee terminate the contract by mutual consent. Most often, this happens when the employer does not want to fire an employee due to a disciplinary offense, indicating the latter in the work book (“dismissed under the article”).
- Expiration of the contract. If the contract is fixed-term, it terminates after the end of the specified period. However, as a general rule, there is no provision for automatic extension of the employment contract.
- Employee transfer. The contract can be terminated if the employee expresses a desire to transfer to another employer or is transferred to work in another city, branch or division of the same employer.
- Change of conditions. When working conditions change, the employee has the right to terminate the employment contract and sign a new agreement with changed conditions. Most often, changes relate to work schedules, wages and responsibilities.
- Dismissal under article. A similar reason for termination of a contract is often related to the employee’s discipline: constant tardiness, absenteeism, drunkenness, inappropriate behavior, etc.
- Termination of probationary period. If an employee was hired under a probationary period, but was not hired for one reason or another, the employment contract is terminated.
- Company relocation. When an employer moves to a new location, employees have the right to refuse their duties and terminate the contract.
- Reasons beyond the control of the parties. The agreement can be terminated if the employee develops health problems or due to certain circumstances he is unable to perform his duties.
- Errors when concluding a contract. When an agreement was concluded with significant errors (contradiction with the law, forged signature, etc.), the agreement may be declared invalid in whole or in part.
Fixed-term employment contract for the period of performing a clearly defined job
Text of the agreement and template to fill out:
Fixed-term employment contract for the period of performing a clearly defined job
| city (place of conclusion of the contract) | (day month Year) |
(full name of the employer) represented by (name of position, full name), acting on the basis of (Charter, regulations, power of attorney), hereinafter referred to as the “Employer”, on the one hand and citizen ( ka) Russian Federation
(full name of the employee), hereinafter referred to as the “Employee”, on the other hand, collectively referred to as the “Parties”, have entered into this agreement as follows:
Subject of the agreement
1.1. Under this employment contract, the Employee undertakes to fulfill the duties of the profession/position (work by position is indicated in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications; specific type of work entrusted to the employee) at (place of work, and in the case where the employee is accepted for work in a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of the organization located in another locality - the place of work indicating the separate structural unit and its location), and the Employer undertakes to provide the Employee with the necessary working conditions provided for by labor legislation, as well as timely and full payment of wages .
1.2. Work under this agreement is the main place of work for the Employee.
1.3. Working conditions in the workplace in terms of the degree of harmfulness and (or) danger are (optimal (class 1)/permissible (class 2)/harmful (specify the class and subclass of harmfulness)/dangerous (class 4)).
1.4. The probation period for hiring is (specify the period)./The employee is hired without a test.
1.5. An employment contract is concluded for the performance of clearly defined work, the completion of which cannot be determined by a specific date.
1.6. The employee must begin work on (day, month, year).
1.7. The employment contract is terminated upon completion of the work assigned to the Employee.
1.8. The employee is obliged to complete the work assigned to him no later than (day, month, year).
Rights and responsibilities of an employee
2.1. The employee has the right to:
— conclusion, amendment and termination of an employment contract in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- providing him with work stipulated by the employment contract;
— a workplace that meets state regulatory requirements for labor protection and the conditions provided for by the collective agreement (if any);
— timely and full payment of wages in accordance with their qualifications, complexity of work, quantity and quality of work performed;
— rest provided by the establishment of normal working hours, reduced working hours for certain professions and categories of workers, the provision of weekly days off, non-working holidays, paid annual leave;
— complete reliable information about working conditions and labor protection requirements in the workplace;
— training and additional professional education in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— association, including the right to create trade unions and join them to protect their labor rights, freedoms and legitimate interests;
— participation in the management of the organization in the forms provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws, if any, and by the collective agreement;
— conducting collective negotiations and concluding collective agreements and agreements through their representatives, as well as information on the implementation of the collective agreement and agreements;
— protection of one’s labor rights, freedoms and legitimate interests by all means not prohibited by law;
— resolution of individual and collective labor disputes, including the right to strike, in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- compensation for harm caused to him in connection with the performance of his job duties, and compensation for moral damage in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— compulsory social insurance in cases provided for by federal laws;
— (other rights provided for by the current labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations).
2.2. The employee is obliged:
— conscientiously fulfill his labor duties assigned to him by the employment contract;
— comply with internal labor regulations;
— maintain labor discipline;
— comply with established labor standards;
— comply with labor protection and occupational safety requirements;
— take care of the property of the Employer (including the property of third parties held by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property) and other employees;
— immediately inform the Employer or immediate supervisor about the occurrence of a situation that poses a threat to the life and health of people, the safety of the Employer’s property (including the property of third parties held by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property);
— (other responsibilities provided for by the current labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations).
Rights and obligations of the employer
3.1. The employer has the right:
— conclude, amend and terminate an employment contract with the Employee in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— conduct collective negotiations and conclude collective agreements;
— encourage the Employee for conscientious, effective work;
— require the Employee to fulfill his job duties and take care of the property of the Employer (including the property of third parties owned by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property) and other employees, and compliance with internal labor regulations;
— bring the Employee to disciplinary and financial liability in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— adopt local regulations;
- create associations of employers for the purpose of representing and protecting their interests and join them;
— create a works council;
— (other rights provided for by the current labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations).
3.2. The employer is obliged:
— comply with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, local regulations, terms of the employment contract, agreements, collective agreement (if any);
— provide the Employee with work stipulated by the employment contract;
— ensure safety and working conditions that comply with state regulatory requirements for labor protection;
— provide the Employee with equipment, tools, technical documentation and other means necessary to perform his job duties;
— provide the Employee with equal pay for work of equal value;
— pay the full amount of wages due to the Employee within the terms established in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the collective agreement (if any), internal labor regulations, and the employment contract;
— conduct collective negotiations, as well as conclude a collective agreement in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
— provide employee representatives with complete and reliable information necessary for concluding a collective agreement, agreement and monitoring their implementation;
— familiarize the Employee, against signature, with the adopted local regulations directly related to his work activity;
— timely comply with the instructions of the federal executive body authorized to exercise federal state supervision over compliance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, other federal executive bodies exercising state control (supervision) in the established field of activity, pay fines, imposed for violations of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms;
— consider the submissions of the relevant trade union bodies, other representatives elected by employees about identified violations of labor legislation and other acts containing labor law norms, take measures to eliminate the identified violations and report on the measures taken to the specified bodies and representatives;
— create conditions that ensure the Employee’s participation in the management of the organization in the forms provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and the collective agreement (if any);
— provide for the Employee’s everyday needs related to the performance of his job duties;
— carry out compulsory social insurance of the Employee in the manner established by federal laws;
— to compensate for damage caused to the Employee in connection with the performance of his labor duties, as well as to compensate for moral damage in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
— (other responsibilities provided for by the current labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations).
Working time and rest time
4.1. The employee is assigned (a five-day work week with two days off/a six-day work week with one day off/a work week with days off on a sliding schedule/a part-time work week).
4.2. The duration of daily work/part-time work is (value) hours.
4.3. The start and end times of work, the time of the break and its duration (in the case of providing days off on a staggered schedule - alternating working and non-working days) are established by the internal labor regulations.
4.4. The employee is granted annual basic paid leave with a duration of (value) calendar days.
4.5. The employee is granted annual additional paid leave with a duration of (value) calendar days (indicate the basis for providing additional leave).
4.6. For family reasons and other valid reasons, the Employee, upon his written application, may be granted leave without pay, the duration of which is determined by agreement between the Employee and the Employer.
Terms of payment
5.1. The employee is paid a salary of (amount in figures and words) rubles.
5.2. Additional payments and allowances of a compensatory nature, including for work in conditions deviating from normal conditions, systems of additional payments and incentive allowances and bonus systems are established by a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
5.3. Wages are paid to the Employee (indicate specific dates of the calendar month)./ Wages are paid to the Employee at least every half month on the day established by the internal labor regulations.
5.4. When performing work outside the normal working hours, at night, on weekends and non-working holidays, when combining professions (positions), when performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee, the Employee is paid appropriate additional payments in the manner and amount established by the collective agreement and local regulations.
5.5. During the period of validity of this employment contract, the Employee is subject to all guarantees and compensation provided for by the current labor legislation of the Russian Federation.
Responsibility of the parties
6.1. In case of failure or improper performance by the Employee of his duties specified in this employment contract and job description, violation of the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as causing material damage to the Employer, he bears disciplinary, financial and other liability in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
6.2. The Employer bears financial and other liability to the Employee in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
Final provisions
7.1. Disputes between the Parties arising during the execution of this employment contract are considered in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws.
7.2. In all other respects that are not provided for in this employment contract, the Parties are guided by the legislation of the Russian Federation governing labor relations.
7.3. The employment contract is concluded in writing, drawn up in two copies, each of which has equal legal force.
7.4. All changes and additions to this employment contract are formalized by a bilateral written agreement.
7.5. This employment contract may be terminated on the grounds provided for by current labor legislation.
Details and signatures
| Employer (fill in what you need) (position, signature, initials, surname) M.P. | Worker (fill in what you need) (signature, initials, surname) |
I received a copy of the employment contract (day, month, year) (signature, surname, initials of the employee)
- Back
- Forward