Concept of part-time work
Working time is considered incomplete if the period is less than the normative and legally established one - an 8-hour working day with a 5-day working week of 40 hours. The establishment of part-time work occurs on special operating conditions mentioned in the work contract, and this amendment is made to the staffing table.
This work regime may relate to working days and weeks, distributed in equal shares with respect to each billing period.
These conditions should not entail any consequences for the employee: neither in determining the average wage, nor in establishing the next vacation, or social compensation. That is, there is no significant difference between employees who have different working hours, even if they are hired part-time or work as a result of transfer from another department. Moreover, each of them has the right to apply for part-time work if special circumstances arise.
In accordance with Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is customary to distinguish between three types of part-time work:
- working day or shift – the number of working hours for each day (or shift) is reduced equally;
- incomplete week - only a reduction in the number of working days for the entire week, while maintaining the established 8-hour working time;
- combined mode – part-time work every day and week: the number of working hours and days is reduced. Example: four working days per week, lasting 4 hours.
All of the listed types of part-time work can be applied to any employee, subject to the proper circumstances and taking into account the specifics of his work.
Need help from a labor lawyer?
We solve the most complex cases in favor of the client!
+7
Payment methods, procedure and calculation formula
To learn how to correctly calculate the amount of payments, you need to clearly understand how a certain type of salary is calculated.
| Forms of payment | Calculation procedure |
| Time-based | Depends only on the amount of time worked, the amount of products produced does not affect this form of payment |
| Piecework | The calculation procedure is inversely proportional to the previous form. Payments are made only for the amount of work done, regardless of the time spent on it. |
In addition, the salary can be divided into:
Main:
- salary or piece income;
- bonuses for a job well done;
- other surcharges.
Additional:
- payment for required vacation and sick leave in case of incapacity for work;
- reimbursement of expenses incurred in connection with travel, accommodation and meals (for example, during business trips);
- bonus payments that are not part of the main employment agreement.
The established calculation formulas are applied depending on the forms of remuneration:
- For piecework wages, the following calculation is used: Salary = cost of production specified in the contract * volume of products produced for the period + accrued bonuses + other additional payments – income tax – other deductions.
- Time-based payment is calculated using the formula: Salary = salary amount / total number of working days * number of days actually worked + bonus amount - personal income tax - withheld amounts . Read also the article: → “Calculating salaries for employees (piecework, temporary payment, calculation example).”
The above formulas are relevant when the employment contract states that the terms of employment are part-time and the employee has worked the required hours.
Payroll calculation for part-time work
When an employee has not fully worked the required hours, the calculation algorithm will be different:
| Period | Formula |
| Calculation for less than a month | Salary for an incomplete month = the value obtained by calculation using the formula for the standard calculation of payments due / number of working days for a certain period * number of days actually worked. |
| Calculation for the day worked | Wages for one day = value obtained by calculation using the formula / number of working days in the period. |
| Calculation for the year worked | Average salary per day = amount of salary for the year / number of months / 29.3. |
| Calculation of wages with a vacation break | Wages, if there was a vacation in the billing period = employee’s salary / total number of working days in the period * number of days actually worked in the month. |
Calculation of wages at a salary rate at a rate of ½ or ¼:
- Salary at ½ rate = salary at full rate*0.5
- Salary at ¼ rate = salary at full rate *0.25
Calculation example No. 1. Employee Kovalev A.A. drawn up under an employment contract, rate - ½, from November 11, 2016 to the position of equipment sales manager. The full salary for this position is 25,000, according to the staffing table. Calculate wages for less than a month.
First you need to determine the number of working days and weekends that fell in November:
- workers - 21 days;
- weekend - 9 days.
From November 11 to November 30, the employee worked 14 days. Next, the calculation is carried out according to the formula: 25,000 / 21 * 14 = 16,666.67 rubles - wages for the period from November 11 to November 30. The rate of Kovalev A.A is ½, accordingly the amount of payment will be:
Salary for November = 16,666.67*0.5=8,333.34 rubles
Under piecework conditions, the calculation is much simpler. It is enough to know the amount of payment per unit of production and the quantity of goods sold.
Established working modes
Regarding the Labor Code, the transition to part-time working hours occurs after the employee provides the required documents and issues an order signed by the head of the institution.
The employer's guarantee obligations and all benefits for the employee must be preserved in full, which he must not forget about and confidently declare his rights. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Part 3 of Article 93 states that the time actually worked by him is included in the total insurance period as full, and every weekend, as well as holidays and vacations, are provided to him without exception and on the usual basis.
Also, part-time work may be introduced for the entire organization, at the initiative of the director or employees.
Here, part-time work is calculated for each staff unit. This is advisable when a business is suffering losses and there is a choice - to reduce staff or reduce the duration of all working hours.
It is very important to adhere to the legislative rules when the administration initiates the introduction of such a regime, for the successful implementation of this measure and to avoid difficulties in the future.
Stages of introducing a regime by decision of the employer
Stage 1. Select suitable part-time options and positions (departments) for which the appropriate regime will be introduced.
Step 2: Invite eligible employees to switch to part-time work. For example, organize a meeting, video message, or write a general letter about planned events. It is important to convey information about upcoming changes as correctly as possible.
Stage 3. Distribute drafts of additional agreements on the transition to part-time work to employees and request consent to sign them (at least simply in the “Agree” or “Disagree” format).
Stage 4. Sign additional agreements with those employees who agreed and immediately transfer them to the selected part-time option.
Source:
HeadHunter
Heading:
Labor law
part-time part-time part-time part-time work week
- Yuri Donnikov, director of the legal department of HeadHunter
Sign up 6825
9750 ₽
–30%
Order on part-time work
The issuance of the order is preceded by the drawing up of an additional agreement for a new part-time working time to the existing employment contract with a specific employee. Its basis is the employee’s personal statement, signed by the manager and attached to the agreement.
The agreement states:
- duration of the working day (or shift);
- exact start time of work;
- end time.
A flexible (or “sliding”) schedule is fixed based on the results of the previous accounting period - year, month, etc. They are reflected in regulations for recording the summarized time worked (timesheet, etc.).
An order to establish part-time work must include the following information:
- name of company;
- location of the organization;
- date of issue of the order;
- mention of the relevant legislative act;
- list of supporting documents (application, additional agreement);
- number and date of the additional agreement;
- signatures of the manager and employee;
- seal of the organization.
In any budgetary institution, the order to establish part-time work is agreed upon, first of all, with the head of the trade union and the chief accountant. This regime is announced en masse when conditions arise that could provoke a series of layoffs.
The introduction of a part-time working regime is regulated by Article 74 of the Labor Code, according to which it can last up to 6 months to pursue the goal of preserving previous jobs in the institution.
Cancellation of the part-time regime occurs on the basis of a new order of the employer, by informing all employees. An important condition is the agreement of each employee with the changed regime introduced for him.
When and how an employer can establish part-time work
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for cases when a part-time working regime can be introduced by the employer without an application from the employee.
As a rule, the employer establishes part-time work for reasons related to changes in organizational or technological working conditions in the organization. In such situations, the law allows changes to the terms of the employment contract at the initiative of the employer while the employee continues to work without changing his job function.
If changes in working conditions in an organization may lead to mass layoffs of workers, then the employer, in order to preserve jobs, has the right to introduce part-time work for up to six months. But in this case, the employer must obtain the consent of the organization’s trade union body.
It is entirely possible that not all employees will be satisfied with part-time work. Therefore, if an employee refuses to continue working under the proposed conditions, then his employment contract with the employer is terminated. In this case, the employer is obliged to provide the employee with the guarantees and compensation provided by law.
Who applies for part-time work?
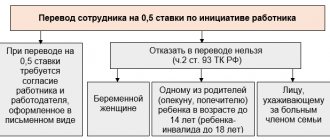
The following groups of workers have the right to apply for part-time work (Article 93 of the Labor Code):
- parent (guardian or trustee) of a child (children) under 14 years of age, or a disabled child under 18 years of age;
- caring for a sick relative who has a medical certificate in hand;
- female employees during pregnancy.
It should be noted that part-time work leaves the employee the right to receive social benefits from the state. Moreover, this can be not only the mother, but also any other close relative who provides care for the child (children), guardianship or trusteeship (Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Who also has the right to part-time work.
It must be said that the right to part-time work is retained by each employee throughout his entire working life and can be documented not only at the time of entry to work, but also at any other time, with supporting documents attached (certificate of pregnancy, doctor’s report and etc.).
All differences in the working regime of a particular employee from the accepted standards in the organization must be included in the employment contract (Article 57 of the Labor Code). Just as changes in the regime are listed in the additional contractual agreement for part-time work, concluded in writing (Article 72 of the Labor Code).
Part-time work for certain categories of workers.
For certain categories of employees, the employer is obliged to establish part-time working hours. First of all, these are the workers listed in Art. 93 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- pregnant woman;
- one of the parents (guardian, custodian) having a child under the age of 14 years (a disabled child under the age of 18);
- persons caring for a sick family member in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation.
In addition, by virtue of Art. 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, at the request of a woman while on maternity leave, she can work part-time or at home while maintaining the right to receive state social insurance benefits.
A similar right can be exercised by the child’s father, grandmother, grandfather, other relatives or guardian who is actually caring for the child.
The part-time working regime is introduced by the employer based on the employee’s application. Workers in these categories are not required to provide additional documents. An exception is for persons caring for a sick family member. They must attach to the application a medical report issued in the manner approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated May 2, 2012 No. 441n “On approval of the Procedure for issuing certificates and medical reports by medical organizations.” However, if employees did not provide the employer with documents about pregnancy or the presence of a child under the age of 14 (disabled child under 18) before submitting the application, they will have to be provided along with the application.
Here is a sample application.
To the Director of OJSC "Stroymarket"
V. M. Korotkov
from accountant I. V. Moreva
Statement
I ask you to establish a part-time working day for me during my pregnancy - to reduce the working day by three hours from December 14, 2015 until I go on maternity leave.
I am attaching a certificate from the Municipal Budgetary Institution "Women's Consultation No. 3" dated December 10, 2015.
12/08/2015,
Moreva
The employer also enters into an additional agreement with the employees who wrote the applications to change the working hours.
Additional agreement
to the employment contract dated October 13, 2014 No. 15/b
10.12.2015
Moscow
Open Joint Stock Company "Stroymarket" (OJSC "Stroymarket") represented by director V. M. Korotkov, acting on the basis of the Charter, hereinafter referred to as the Employer, on the one hand, and accountant Irina Vladimirovna Moreva, hereinafter referred to as the Employee, on the other hand, have agreed on the following:
1. Clause 2.2 of the employment contract dated October 13, 2014 No. 15/b should be stated as follows: “The employee is provided with a part-time working schedule:
- working week – five days, from Monday to Friday inclusive, with two days off (Saturday, Sunday);
- Duration of daily work – 5 hours, from 09.00 to 15.00;
- break for rest and food – 1 hour from 12.00 to 13.00.”
2. Clause 4.1 should be stated as follows: “Payment is made in proportion to the time worked based on a salary of 35,000 rubles. per month".
3. This agreement is valid from December 14, 2015 until the Employee goes on maternity leave.
4. This additional agreement is an integral part of the employment contract dated October 13, 2014 No. 15/b, drawn up and signed in two copies having equal legal force, one of which is kept by the Employer, the other is transferred to the Employee.
Employee: Employer:
Moreva
/Moreva I.V./
Korotkov
/Korotkov V.M./
A copy of the additional agreement has been received. Moreva, 12/10/2015
For employees listed in Art. 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the condition on the duration of work during part-time work is established by agreement with the employer. But if an employee on parental leave expressed a desire to fulfill his duties part-time, the employer must accept his conditions, since Art. 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation protects the rights of persons with family responsibilities that combine caring for young children with work, which is a source of income for them.
Thus, O.E., while on maternity leave, applied to the employer to establish part-time work of 39 hours a week. However, the employer issued an order and an additional agreement, which specified the duration of part-time work as 1 hour per day, from 8.00 to 9.00, and 5 hours per week.
As a result of the trial on O.E.’s claim, the court recognized that the employer’s actions to establish such a regime in the absence of the employee’s consent contradict labor legislation and violate the rights of an employee on parental leave. In this case, the court referred to the current Regulation on the procedure and conditions for the employment of women with children and working part-time, approved by the Resolution of the USSR State Committee for Labor, the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated April 29, 1980 No. 111/8‑51 (hereinafter referred to as the Regulation).
In accordance with clause 4 of the Regulations, part-time working time can be established by agreement of the parties, either without a time limit or for any period convenient for the employee - for example, until the child reaches a certain age. The provision is aimed at providing women with favorable conditions for combining the functions of motherhood with professional activities and participation in public life (clause 1).
Paragraph 7 of the Regulations notes that the work and rest regimes of women with children and working part-time are established by the administration, taking into account the wishes of the woman. In paragraph 8 - that labor regimes for part-time work may include, among other things, a reduction in the duration of daily work (shift) by a certain number of working hours on all days of the working week. When establishing part-time work schedules provided for by this paragraph, the length of the working day (shift), as a rule, should not be less than 4 hours and the working week - less than 20 - 24 hours, respectively, with a 5- and 6-day week. Depending on the specific production conditions, a different working time may be established.
Based on the foregoing, an employee who is on parental leave and has begun performing duties on a part-time basis has the right to choose a convenient working time during the shift, and the employer must take into account his wishes and establish a part-time work schedule of at least 4 hours and a working week of at least 20 - 24 hours, respectively, with a 5- and 6-day week (Appeal ruling of the Supreme Court of the Komi Republic of October 22, 2015 in case No. 33-5580/2015).
Remuneration for part-time work
When switching to part-time work, the payment of wages is reduced in proportion to the work completed or the period worked. This fact does not depend on the payment system adopted in this institution. But the total salary for an employee may not reach the minimum wage, because, according to the law, the condition for paying the minimum wage is the development of a standard working time per month.
When calculating payments to an employee, even the fact that part-time work was established for him in the middle of the billing period is absolutely not significant. The employer can introduce these conditions, if not at the insistence of the employee, then in the presence of extraordinary factors.
To pay for sick leave, maternity benefits, and others, travel expenses and regular vacations, average earnings are also taken into account, without restrictions when switching to part-time work. For involvement in activities outside the hours determined for the employee by order of the manager, this is paid in accordance with the procedure for paying overtime work (Article 99 and Article 152 of the Labor Code). As well as work on weekends, with the existing part-time work week (Articles 113 and 153 of the Labor Code).
Salary: part-time and combined schedule
Let's consider the situation using conditional examples.
Let the LNA establish a “five-day workday” and an 8-hour shift in the organization. day. The salary of a company accountant is 30 thousand rubles. In September, accountant Mikhailov, by agreement with management, switched to a part-time work week: he works 8 hours a day, but he has 3 working days per week - Monday, Wednesday and Friday.
He worked through September in this mode completely. With a five-day working week in September 2021, 20 rubles. days Of these, Mikhailov worked 12 rubles according to his personal schedule. days Mikhailov’s salary for September was 30,000/20*12=18,000 rubles.
Let Mikhailov work 5 hours a day under the same conditions. The standard working time fund in September 2021 is 160 hours. Mikhailov actually worked according to the schedule of 12*5 = 60 hours. Mikhailov’s salary for September was 30,000/160*60 = 11,250 rubles.
On a note! Wages are calculated similarly for part-time and full-time work, taking into account the latter circumstance.
Wages proportional to the volume of work actually means piecework payment. For example, the order picker is paid 200 rubles for each set order. If it produces 200 such orders per month, then the accrual will be 200*200=40,000 rubles.
How does the SZV-STAZH form indicate information about working in harmful and difficult working conditions on a part-time basis ?
Rights of part-time workers
In order to avoid possible misunderstandings and litigation, employees should be aware of their rights related to the concept of “part-time work”, and also correctly interpret the provisions of the Labor Code. So, for example, in such cases, when the initiator of the introduction of new rules regarding an employee (or several persons) is the manager, employees are warned about this in advance - no later than 2 calendar months.
An employee may be against having a part-time working regime introduced in relation to his activities.
Then the employer is obliged to immediately, as soon as possible, offer him another position that meets his professional skills and state of health, putting the offer in writing. In its absence, a vacant lower position with lower pay is offered.
If there are none in this institution, then the employment contract, if the employee does not agree to switch to part-time work, is terminated, in connection with clause 7, part 1, article 77 of the Labor Code. The employee is also notified in writing that there are no suitable vacancies and this entails termination of cooperation.
All benefits, compensation, guarantees for an employee switching to part-time (weekly) work are retained in full. This is provided for by modern legislation and cannot be violated.
Author of the article
What does this term mean?
In Russia, the current Labor Code provides for a traditional work week consisting of five days with two days off on Saturday and Sunday. The standard length of a classic working day for ordinary people is eight hours a day (with a lunch break it turns out to be nine hours) or hours a week. If an employee works more than 40 hours, he is paid an additional agreed amount for overtime. Some companies may have a 6-day work week, which must be negotiated during employment.
Part-time work is introduced both at the initiative of the employer and at the request of the employee
Let's consider what Russian legislation defines as working time. This is the time during which a person fulfills labor obligations in accordance with the terms of the employment contract or regulations. If the company does not need the classic eight-hour performance of work duties by an employee, then he can be transferred to a part-time or a week, depending on the current situation.
So, part-time is how many hours? In fact, an “incomplete” day is considered to be a day in which the employee worked less than 8 hours, and an incomplete week is less than 5 days, provided that the work is carried out according to a traditional schedule.
Attention:
The night shift may last less than 8 hours, but is considered full-time. The eight-hour limit is only available during the daytime during classic operating mode.
Note that the length of the working day is regulated by both the labor code and internal regulations. In order to formalize part-time employment, it is necessary to issue a new order or act, limiting the working day to certain values. In this case, wages are calculated either according to hours worked or according to the output of each employee.
Who has the right to work part-time?
Part-time working hours are established (Article 93, Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
| By agreement of the parties | Mandatory |
| For any employee | When contacting:
|
| For any period, including without restrictions | No more than the period of validity of the listed circumstances |