How is the dismissal of employees due to liquidation carried out?
An important point in successfully fulfilling the legal requirements regarding the dismissal of employees in connection with liquidation is the mandatory notification that is sent to each employee of such an organization two months before the date of its official final liquidation.
Such a written personal warning is prepared in any form. It does not have a fixed form. In most cases, a special form of the organization is used.
This notification requires the following information:
- About the reasons for the proposed dismissal and its date
- About the guarantees that an employee will be provided upon dismissal
Important: The fact of familiarization with the notification can only be confirmed by his personal signature.
Such notices are sent to each employee 2 months in advance, with the exception of those hired for seasonal or temporary service.
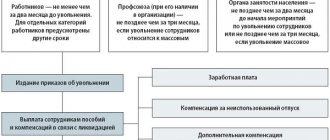
Next, the liquidated company and its personnel services should take the following actions:
- Inform the employment center about the emergence of new unemployed personnel in production
- If there is a trade union organization at the production site, notify its managers of the upcoming dismissal
- Calculate all mandatory payments to each employee that will need to be made directly on the date of dismissal or earlier than the date of dismissal
- Prepare appropriate orders
- Make appropriate entries in the work books of each employee
An important difference between dismissal due to liquidation of production is the need to formalize the termination of relations with each employee enrolled in the staff, regardless of the social guarantees that apply to him.
Including, as a general rule, relationships are terminated with such representatives of socially protected groups as:
- pregnant women;
- parents on maternity leave to care for a child;
- single parents;
- minor workers;
- those who were on vacation or had sick leave at the time of notification of liquidation.
All representatives of these categories on the established date of liquidation .
Upon dismissal, each employee receives an increased payment , calculated on the basis of average monthly earnings. Further, the average earnings are retained for two months, including severance pay, and can be retained for a period of 3 months by decision of the employment service authority.
True, the latter is assumed only in the case when the employee is registered with the employment service within two weeks after the date of official liquidation of production. This amount is paid if there is no information about acceptance to a new duty station.
Step-by-step instructions for the dismissal procedure
Dismissal of employees in a liquidated organization is a variant of the employer’s proactive actions in labor relations. Not mandatory, but allowing the liquidation of a company to be carried out in an organized, correct and timely manner, the procedure is the preparation of a comprehensive liquidation plan. Separate paragraphs of the plan provide for the dismissal of personnel and the implementation of all required payments.
The step-by-step procedure for dismissing employees during the liquidation process is as follows.
What regulatory documents should be used?
When formalizing such termination of an official relationship, the following are used:
- the first part of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (LC RF);
- Article 176 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Federal Law of November 14, 2002 No. 161-FZ “On State Municipal and Unitary Enterprises,” which defines the procedure for liquidating production for various legal reasons;
- Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which determines the terms of settlement with dismissed employees
- Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation assumes the employer’s liability for violating the terms of payment of wages and severance pay of the country’s Civil Code and some other regulatory and legislative documents.
Liquidation of an organization: concept
State policy in the field of labor relations can hardly be called balanced, since it pays much more attention to the rights of employees than to the rights of employers. This is especially true when management begins to lay off its employees en masse. At what moments does this happen?
Of course, during the liquidation of an enterprise, when a legal entity completely ceases its activities and does not transfer its rights to conduct business to anyone. A record of this event is made in the Unified Register - Unified State Register of Legal Entities. At the same time, the owner of the LLC is legally exempt from liability to government agencies, and creditors, for their part, do not have the right to demand fulfillment of loan obligations.
Causes
Termination by a business entity of its activities can occur on a voluntary basis or forcibly. The circumstances can be very different, but in practice the following are recognized as the most common.
At the initiative of the owner
In fact, he is not required to comment at all on his actions, but he usually voices one of the following:
- the business is not profitable;
- lack of funds on the balance sheet to pay taxes, issue earnings, and maintain document flow;
- desire to reorganize the company;
- contradictions that have arisen between the founders of the LLC;
- reluctance to engage in the development of this particular direction;
- expiration of the license or lease term.
Under duress
- lack of a license and other permitting documentation for the activities of the LLC;
- carrying out practices prohibited by law;
- violation of legal norms when establishing and running a business;
- Violation of deadlines for reporting and payment of taxes or deliberate refusal to comply with such requirements.
Experts identify a number of additional reasons leading to the cancellation of a company.
- Bankruptcy. Can only be recognized by a court decision.
- Human factor. Lack of interest in the company's activities and investing in its further development.
- Force Majeure. The company is recognized as unprofitable as a result of a natural disaster, economic crisis, or other circumstances.
- Negligence of management. Unfair performance of official duties.
Attention! Regardless of the reason, the employer is obliged to cancel the company according to the established regulations and in compliance with certain rules.
Legislative framework
The procedure for liquidating an organization is recognized by law and is regulated by the Constitution of the Russian Federation, as well as the Civil Code.
- Art. 61 explains in detail what liquidation of a legal entity is.
- Art. 62 lists the responsibilities of the commission dealing with this issue;
- Art. 63 describes the procedure for terminating activities without the possibility of succession.
- Art. 64 defines guarantees for the company's creditors.
In addition, the termination of the company’s existence is regulated by the following regulations:
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 439;
- Federal Laws No. 14, 125 and 129;
- Articles 23 and 89 of the Tax Code;
- Orders No. 7-6/362.
Mass layoffs of employees are also regulated by the provisions of the Code of the Russian Federation, but only the Labor Code, and not the Civil Code.
- ST. 81 characterizes the liquidation of an enterprise as the reason for termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer.
- Art. 178 contains the main provisions on severance pay, which are subject to mandatory payment.
- Art. 180 lists the compensation and guarantees that the manager is obliged to provide to dismissed employees, and also clarifies the notice period.
- Art. 127 obliges the employer to pay compensation for vacation that the employee did not have time to use.
- Art. 139 determines the procedure for calculating wages.
Thus, the law protects the rights of citizens dismissed due to the termination of the company’s activities without restoration. In addition to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the main provisions are also set out in the charter documents of the LLC.
Competently compiling an entry in the work book
The basis for such a record is the Order on liquidation of proceedings. On its basis, an entry is made in the work book.
In this case, information about the reason for dismissal is traditionally entered in column 3.
It states “dismissed due to the liquidation of the organization, paragraph one of part one of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.”
Column 4 indicates the date and number of the dismissal order.
Sample entry in the work book for dismissal due to liquidation of the enterprise
Issuance of an order
A dismissal order in a liquidated company is drawn up in forms T-8 (for one employee) or T-8a (for several employees).
The following details are entered in the document form in the appropriate sections and lines:
- full name of the organization;
- registration data;
- number of the employment contract, date of its termination (writing in Arabic numerals is allowed, for example, 07/21/2018 or in a verbal-numeric way, for example, July 21, 2021);
- Full name of the employee;
- number according to the report card;
- subdivision;
- position, specialty, profession;
- reason for dismissal and reference to Art. 81, part 1, clause 1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- grounds for dismissal, for example, decision (minutes) of a meeting, decision of the founders;
- registration data of the employee’s written notification;
- signature of the director or liquidator with a transcript;
- employee's signature and date.
Important
All information in the order form is entered without abbreviations.
Features of the procedure
Is it possible to fire everyone at the same time?
The simultaneous dismissal of all employees is usually not practiced, but occurs in several “streams”, since production shops are first liquidated, terminating employment contracts with those working in them. Then employees of administrative and economic services are fired.
Last of all, labor relations are terminated with specialists directly involved in the liquidation procedure, drawing up liquidation documents, balance sheets, and completing events that complete the company’s activities (HR officers, lawyers, accountants).
Dismissal of a manager
Occurs depending on whether he is appointed to the position of liquidator, managing the company during liquidation. The powers of the director terminate from the moment the decision on liquidation is made, and the management of the company is taken over by a liquidation commission headed by a chairman, who can be either the previous director or a third party.
If the manager is elected by the general meeting to the position of liquidator, he is the last to resign, after all activities of the enterprise are terminated and documented.
Pregnant women and women on maternity leave
During the liquidation of the company, these categories of employees cannot exercise the right to remain at work in accordance with legally established standards and are warned about dismissal on a general basis.
Pensioners, part-time workers and seasonal workers
Such employees are given notice of impending dismissal in accordance with the law and are entitled to severance pay. Part-time workers and pensioners have the right to expect benefits in the same amount as the main contingent.
For seasonal workers, the amount of severance pay is limited to 2 weeks' average earnings.
Payment of compensation
According to the provisions of Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 318 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a resigning employee must receive:
- salary for the last 2 months of work;
- all appropriate compensation for previously unused vacations;
- severance pay, which corresponds to two monthly salaries.
Approximate calculation of the amount of compensation for unused vacation
Let’s assume that an employee has worked at the company for 2 years, has never been on vacation, and his salary for the previous 12 months was 360,000 rubles. To calculate the total amount for payment, you need to determine the average daily earnings and multiply it by the number of days of unused vacation:
Compensation = 360,000 / 351.6 days according to the norm * 28 days * 2 years = 57,337.88 rubles.
Calculation of severance pay
Severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings for the previous 12 months is issued to all laid-off employees on the day of dismissal. If an employee cannot find a job within 2 months after dismissal, the employer is obliged to pay him another average monthly salary. This rule applies only to those who registered with the employment center within 20 days from the date of dismissal. If 3 months have passed, but the dismissed employee has not found a job, the city employment center will pay him benefits for the third month.
Liquidation of an enterprise is not a reason to refuse due compensation payments