Home / Labor Law / Employment / Employment contract
Back
Published: 07/15/2016
Reading time: 11 min
0
810
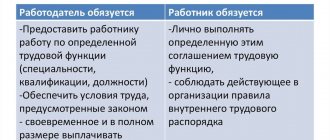
In Article 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the concept of an employment contract is defined as a bilateral agreement between an employer and an employee, implying the mutual fulfillment of obligations and conditions and the receipt of certain rights.
The employer must provide work and working conditions that meet the norms of labor legislation and other legal acts (agreements, local legal acts, collective agreement, this agreement), and pay the employee wages on time.
The employee must perform this work and comply with all labor regulations.
The law prohibits the inclusion in an employment contract of conditions that could worsen the employee’s situation.
- Features of the employment contract
- Main types of contracts Term
- Nature of the relationship and scope of work
- Type of employer
- Working conditions
Features of the employment contract
Despite the external similarity with other labor-related contracts (contracts, assignments, etc.), they are different and should not be confused.
The distinctive features of an employment contract are:
- Its subject is the employee’s work activity itself, and not the final result.
- It involves the personal performance of work by a specific person, without the possibility of replacing him.
- One of its conditions is the employee’s compliance with the internal regulations established by the employer.
- The employer’s responsibility is to organize the employee’s work and provide safe conditions.
The content of the contract is a list of conditions that can be divided into two large groups:
- mandatory. Without them, the employment contract will not have legal force. These are conditions about the work itself, the position, the scope of responsibilities, the place where the employee carries out his work activity, and the duration of the contract;
- additional.
Some conditions of the employee’s everyday life may be stipulated, for example, providing him with housing, food, placement of the child in a preschool educational institution, etc.
If such conditions are not specified, the contract will still be considered concluded and have legal force.
Requirements for a written contract
All employment contracts must contain the following information:
- information about the parties to the agreement;
- conditions of a contract;
- details and/or contacts.
The contract is drawn up in two copies, one of which is given to the employee, and the second remains with the manager. The employee must leave his signature on the manager’s copy, this will confirm that the second copy of the contract is with the employee. If the employee is under 14 years old at the time of concluding the contract, then the signature must be left by one of his legal representatives (parents, guardians).
According to the rules established in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employment contract must be concluded in writing.
If the manager does not have the status of an individual entrepreneur, then he needs to register an agreement with the employee with local authorities. This requirement is published in Article 303 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. But the consequences for the manager if this condition is not met are not described anywhere.
The employment contract is concluded in writing, but there are some differences in the sequence of registration of employment. Actual permission to work. An employee can begin to perform his duties with the knowledge of the manager. In this case, a special form of employment contract must be drawn up in writing no later than three days after the start of cooperation. In this case, the agreement may indicate the principle of starting activities “with the knowledge” or “on instructions”. “with the knowledge” means that the manager does not oppose the employee’s employment and acts as a passive party to the contract.
The wording “on instructions” implies an active position of the manager in relation to the employee.
The difference in these terms should be understood as follows: if an employee began work on behalf of a manager, then he can demand from the manager full payment for his work and the further conclusion of an employment contract precisely from the moment the work actually begins. If an employee started work with the knowledge of the manager, then he cannot demand any incentives from the manager, because He began working of his own free will, but with the notification of management. In this case, the manager can conclude an agreement “today”.
Official permission to work. This form of employment contract involves employment in the “correct” order: first the written employment contract, and then the start of work. That is, the manager enters into an employment contract with the employee, and only after that the employee begins to fulfill his duties. In this case, the employee can begin to perform his duties either the next day after the conclusion of the contract, or on the day specified in the contract.
Main types of contracts
Employment contracts are divided into several types depending on the characteristics that unite them.
Term
Depending on the period for which the contract was concluded, they are of the following types:
- with an indefinite validity period. This is the main type of contracts concluded.
- for a specified period of up to five years. It is concluded in the event that it cannot be signed for an indefinite period, for example, if the nature of the work performed is temporary or seasonal, there is a certain amount of work that needs to be completed, or if it is concluded to replace a woman on maternity leave.
This type is called a fixed-term employment contract.
If at the end of the specified period the parties do not terminate the contract, it becomes concluded for an indefinite period.
Nature of the relationship and scope of work
Depending on the nature of the labor relationship and the volume of work performed, these may be the following contracts:
- at the main location. The employee constantly carries out labor activities for this employer at the hours established by him. This type of agreement involves keeping the work record book with the employer;
- at the same time. An employee performs a certain amount of work, usually proportional to the number of working hours, in his free time from his main job. This can be either internal (with the same employer) or external part-time work;
- about seasonal work. It is concluded to perform a certain type of work that can be performed in a limited time, for example, harvesting or hotel business;
- about temporary work. Concluded for a period of up to two months, for example, to replace a sick employee;
- about working from home. An employee performs a certain amount of work without being provided with a workplace by the employer.
Type of employer
Depending on the type of employer, contracts can be:
- with organizations. Concluded between an employee and an individual entrepreneur or legal entity;
- with individuals who do not have individual entrepreneur status, for example, working as a nanny or other service personnel for private individuals.
Working conditions
Depending on the nature of the conditions under which the employee performs work, the contract may be:
- with normal conditions. This is usually a day shift with an eight-hour workday (office work);
- with the condition of performing work at night (factories, shops);
- with harmful and dangerous conditions (underground, rescue work, work with chemicals, etc.);
- subject to the condition of performing work in climatic zones with a severe climate (regions of the Far North and areas equivalent to them).
How to write a term paper on speech therapy
07.09.2010 199465
These guidelines are compiled to help students gain an understanding of the content and structure of coursework in speech therapy.
Logopedia of pedagogical science that studies anomalies of speech development with normal hearing, explores the manifestations, nature and mechanisms of speech disorders, develops the scientific basis for overcoming and preventing them means of special training and education.
The subject of speech therapy as a science is speech disorders and the process of training and education of persons with speech disorders.
The object of study is a person suffering from a speech disorder.
The main task of speech therapy as a science is the study, prevention and elimination of various types of speech disorders.
Coursework in speech therapy is a student's scientific and experimental research. This type of educational activity, provided for by the educational and professional program and curriculum, contributes to the acquisition of skills in working with literature, analyzing and summarizing literary sources in order to determine the range of insufficiently studied problems, determining the content and methods of experimental research, processing skills and qualitative analysis of the results obtained. The need to complete coursework in speech therapy is due to the updating of knowledge concerning the content, organization, principles, methods and techniques of speech therapy work.
As a rule, during their studies, students must write two term papers - theoretical and practical.
The first course work should be devoted to the analysis and synthesis of general and specialized literature on the chosen topic. Based on this analysis, it is necessary to justify and develop a method of ascertaining (diagnostic) experiment.
In the second course work, it is necessary to provide an analysis of the results obtained during the ascertaining experiment, as well as determine the directions and content of speech therapy work, and select adequate methods and techniques of correction.
So, let’s present the general requirements for the content and design of coursework in speech therapy.
The initial and most important stage of working on a course project is the choice of a topic, which is either proposed by the supervisor or chosen by the student independently from a list of topics that are consistent with the areas of scientific research of the department.
Each topic can be modified, considered in different aspects, but taking into account a theoretical and practical approach. Having chosen a topic, the student needs to think through in detail its specific content, areas of work, practical material, etc., which should be reflected both in the formulation of the topic and in the further construction of the study. It should be recalled that the chosen topic may not only have a purely theoretical orientation, for example: “Dysarthria. Characteristics of the defect”, “Classification of dysgraphia”, but also take into account the practical significance of the problem under consideration, for example: “Speech therapy work on speech correction for dysarthria”. It should also be taken into account that when formulating a topic, excessive detail should be avoided, for example: “Formation of prosodic components of speech in preschoolers of the sixth year of life attending a preschool institution for children with severe speech impairments.”
The course work includes such mandatory parts as: introduction, three chapters, conclusion, bibliography and appendix.
The text of the term paper begins with the title page . An example of its design can be seen here.
Then the content of the work is given, in which the names of chapters, paragraphs, and sections are formulated in strict accordance with the content of the thesis. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the text, each subsequent chapter and paragraph begins on a new page. At the end of each chapter, the materials are summarized and conclusions are formulated.
The introduction reveals the relevance of the problem under consideration in general and the topic being studied in particular; the problem, subject, object, and purpose of the study are defined. In accordance with the goal and hypothesis, objectives and a set of research methods aimed at achieving the objectives must be defined.
The relevance of the topic lies in reflecting the current level of pedagogical science and practice, meeting the requirements of novelty and usefulness.
When defining the research problem, it is important to indicate what practical tasks it will help to implement in training and educating people with speech pathology.
The object of research is understood as certain aspects of pedagogical reality, perceived through a system of theoretical and practical knowledge. The ultimate goal of any research is to improve this object.
The subject of research is some part, property, element of an object, i.e. the subject of research always indicates a specific aspect of the object that is to be studied and about which the researcher wants to gain new knowledge. An object is a part of an object.
You can give an example of the formulation of the object, subject and problem of research:
– The object of the study is the speech activity of preschool children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The subject of the study is the features of intonation speech of children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The research problem is to determine effective directions for speech therapy work on the formation of intonation expressiveness of speech in the system of correctional intervention.
The purpose of the study contributes to the specification of the object being studied. The goal of any research is to solve a specific problem. The goal is specified in tasks taking into account the subject of research.
The research objectives are formulated in a certain sequence, which determines the logic of the research. The research objectives are set on the basis of a theoretical analysis of the problem and an assessment of the state of its solution in practice.
The first chapter is an analysis of literary sources, which examines the state of this problem in historical and modern aspects, and presents the most important theoretical principles that formed the basis of the study.
When writing the first chapter, you should pay attention to the fact that the text of the course work must be written in a scientific style. When presenting scientific material, it is necessary to comply with the following requirements:
– Specificity – a review of only those sources that are necessary to disclose only a given topic or solve only a given problem;
– Clarity – which is characterized by semantic coherence and integrity of individual parts of the text;
– Logicality – which provides for a certain structure of presentation of the material;
– Reasoning – evidence of thoughts (why this and not otherwise);
– Precision of wording, excluding ambiguous interpretation of the authors’ statements.
A literary review of the state of the problem being studied should not be reduced to a consistent presentation of literary sources. It should present a generalized description of the literature: highlight the main directions (currents, concepts, points of view), analyze in detail and evaluate the most fundamental works of representatives of these directions.
When writing a work, the student must correctly use literary materials, make references to the authors and sources from which the results of scientific research are borrowed. Failure to provide required references will reduce your coursework grade.
As a rule, in coursework on speech therapy, references to literary sources are formatted as follows: the number of the cited source in the general list of references is placed in square brackets. For example: General speech underdevelopment is a speech pathology in which there is a persistent lag in the formation of all components of the language system: phonetics, vocabulary and grammar [17].
When using quotations, in square brackets, in addition to indicating the source number, the page number from which this excerpt is taken is indicated, for example: Speech rhythm is based on a physiological and intellectual basis, since, firstly, it is directly related to the rhythm of breathing. Secondly, being an element that performs a communicative function, “correlates with meaning, i.e. controlled intellectually” [23, P.40].
However, course work should not be of a purely abstract nature, so you should not abuse the unreasonable abundance of citations. Quoting should be logically justified, convincing and used only when really necessary.
In the second chapter , devoted to experimental research, the organization should be described and the program of the ascertaining experiment should be presented. The survey methodology, as a rule, consists of a description of several series of tasks, with detailed instructions, visual and lexical material, the procedure for completing tasks by experiment participants, and scoring criteria. This chapter also provides a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the results obtained.
When analyzing the results of an experiment, it is necessary to use a scoring system. Examples of various criteria for quantitative and qualitative assessment are presented in the following works:
– Glukhov V.P. Formation of coherent speech in preschool children with general speech underdevelopment. - M.: Arkti, 2002. - 144 p.
– Fotekova T.A. Test methodology for diagnosing oral speech of primary schoolchildren. - M.: Arkti, 2000. - 56 p.
– Levchenko I.Yu. Pathopsychology: Theory and practice. - M.: Academy, 2000. - 232 p.
In order to visually present the results obtained during the experimental study, it is recommended to use tables, graphs, diagrams, etc. Histograms can be used in a variety of ways - columnar, cylindrical, planar, volumetric, etc. An example of the design of tables, figures, and histograms can be found here.
The third chapter provides a rationale for the proposed methods and techniques and reveals the content of the main stages of correctional work.
The conclusion contains a summary of the material presented and the main conclusions formulated by the author.
The bibliography must contain at least 25 sources. The list includes bibliographic information about the sources used in preparing the work. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the application you can present bulky tables or illustrations, examination protocols, observation records, products of activity (drawings, written works of children), notes from speech therapy classes, etc.
The volume of one course work must be at least 30 pages of typewritten text.
In general, coursework in speech therapy is the basis for a future thesis, in which the study of the begun problem can be continued, but from the standpoint of a different approach or a comparative analysis of the disorders being studied in different age categories of people with different types of speech disorders.
The content and format of theses in speech therapy can be found here.
Literature:
1. How to write a term paper on speech therapy: Methodological recommendations. Educational and methodological manual / Comp. Artemova E.E., Tishina L.A. / Ed. Orlova O.S. – M.: MGOPU, 2008. – 35 p.
2. Research work of students in the system of higher professional pedagogical education (specialty 031800 - Speech therapy). Methodological recommendations for completing the thesis / Compiled by. L.V. Lopatina, V.I. Lipakova, G.G. Golubeva. - St. Petersburg: Publishing house of the Russian State Pedagogical University named after. A. I. Herzen, 2002. - 140 p.
Order of dismissal, entry in the work book
The following items must be included in the order:
- Order number, date
- Last name, first name, patronymic of the employee
- Employment contract number and validity period
- Specify the date of dismissal
- The grounds on which the employment contract was terminated
An entry in the work book is made on the day of dismissal, and the basis for the dismissal is indicated.
| Entry no. | date | Information about hiring, transfer to another permanent job, qualifications, dismissal (indicating reasons and reference to the article, clause of the law) | Name, date and number of the document on the basis of which the entry was made |
| Limited Liability Company "Mercury" (LLC "Mercury") | |||
| 1 | 01.06.2011 | Hired as a leading specialist in the accounting department | Order dated 01/01/2015 No. 3 |
| 2 | 10.06.2016 | The employment contract was terminated due to the expiration of the employment contract, paragraph 2 of part one of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Order dated January 1, 2015 No. 8 |
| Accountant Safonova O.V. | |||