Is it possible to fire an employee due to lack of confidence?
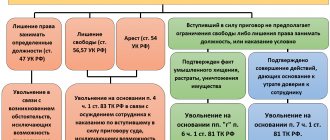
Clause 7 of Part 1 of Article 81 of the Labor Code provides, as grounds for termination of an employment contract, such guilty actions of a subordinate, in connection with which the employer loses confidence in him.
However, not any employee can be fired on this basis, but only the one who is engaged in servicing inventory items. This must be stipulated in the employment contract with the employee, his job description, as well as in a special agreement on full financial liability, which the employer has the right to conclude with some employees.
Termination of working legal relations due to mistrust occurs at the initiative of the employer. There are restrictions established by labor legislation: in particular, the dismissal of persons on vacation or sick leave, pregnant women, and minor employees is prohibited.
What does the law say about dismissal due to loss of confidence?
Dismissal due to loss of trust in an employee is one of the grounds that allows you to unilaterally terminate an employment contract with a dishonest employee. This possibility is enshrined in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (clause 7, part 1, article 81).
As a document confirming that the dismissed employee was engaged in servicing goods or funds, the contract concluded with him (Article 244 of the Labor Code):
- Employment contract.
- Agreement on financial responsibility.
- Job description.
To successfully dismiss on this basis, you must:
- Identify and record damage or shortage of property, as well as establish the employee’s guilt.
- Get a written response from him.
- Draw up a report after an internal investigation.
- Issue an order.
- Make appropriate entries in the employee’s card and his employment record.
Article of the Labor Code “Dismissal for loss of trust”
After dismissal under the article Loss of trust, it is difficult to regain your reputation
In accordance with Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 7, guilty actions committed by an employee regarding the property or finances of the employer are considered to be a loss of trust.
Dismissal with this wording will adversely affect the employee’s future career, because his reputation will suffer greatly. With such an entry in the work book, it will be extremely difficult to get a job in the future.
To fire a person for such an unpleasant article, the employer must have compelling reasons. If you do not take into account all the subtleties and nuances, then the dismissal will most likely develop into numerous lawsuits.
Grounds under the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The Labor Code does not contain a list of actions that an employer can or should regard as grounds for showing distrust of an employee. However, based on the interpretation of clause 7, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, termination of legal relations under this provision is possible in the following cases:
- a subordinate has committed a guilty offense;
- he is responsible for commodity, material assets;
- the actions of the subordinate served as the basis for a loss of trust on the part of the company's management.
Dismiss the employee on the basis of clause 7, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is possible provided that the actions that served as the basis for mistrust were committed not at the workplace or in connection with the performance of a work function (paragraph 2, paragraph 45 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of March 17, 2004 No. 2).
Facts that, if revealed, may lead to dismissal of an employee
Before dismissing an employee on such grounds, the manager must carefully check all the facts, and if they are confirmed, initiate the procedure for terminating the employment contract.
In the Labor Code, the basis for dismissal is “committing guilty actions.” It is the determination of guilt that is one of the difficult issues.
In the classical sense, such actions include:
- Acts related to various forms of theft (embezzlement, embezzlement, theft, etc.).
- Loss of money and material assets.
- Actions that create a threat of theft or loss.
As actions that create a threat, we can consider the activities of a warehouse security guard who fell asleep while on duty. These actions did not entail the consequences described in paragraphs 1 and 2, but created a threat to their occurrence.
Consider terminating a contract due to loss of trust with a government employee. The law establishes an exhaustive list of what may cause a loss of trust, including:
- Unresolved conflict of interest.
- Failure to provide a completed declaration of income, expenses and property at all or incompletely.
- Participation in the management of a commercial enterprise.
- Engagement in entrepreneurial activity.
- Availability of accounts in foreign banks.
- Participation of civil servants in the management of public and political organizations. For example, it is prohibited to be the chairman of a branch of any party.
List of employee’s guilty actions
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other special acts do not provide a complete list of actions that may lead to the dismissal of an employee due to loss of trust. It is possible to terminate an employment contract at the request of the employer if the fact of a disciplinary offense is revealed and the procedure for bringing the guilty employee to justice is followed.
The list of grounds for dismissing an employee - due to distrust of him on the part of the employer - includes the following actions:
- which resulted in the loss or theft of the company’s material assets: equipment broke down, money disappeared from the cash register, safe deposit box, safe, etc. – such facts may become grounds for dismissal of an employee, including with the participation of the courts.
- threat of theft - if the employee did not take the measures necessary to preserve the organization’s money and property, ignored his immediate job responsibilities, left valuable property unattended, etc.
- bribery, fraud, commercial bribery, an official going beyond the limits of regulated powers - concluding transactions bypassing the enterprise, transferring funds to the accounts of shell companies, dummy individuals.
Dismissal may also follow if the above actions were not committed at the workplace. The Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation No. 2 of 2004 states that they must be of a selfish nature, i.e. committed for the purpose of obtaining illegal personal gain, profit, bypassing the interests of the employer or to the detriment of the company’s reputation. For specialists not associated with financial responsibility, dismissal may follow if the official committed an act that discredits the civil service, representatives of law enforcement and military structures.
Procedure for dismissal due to loss of confidence
If it turns out that the employee’s guilt is due to his dishonest performance of his official duties, then termination of the employment contract is possible as liability for a disciplinary offense. The grounds for applying penalties are established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - Art. 193.
Evidence will be required to confirm that the employee actually committed actions that resulted in a loss of trust. If the head of the company decides not to write a statement to the police, then he must initiate his own investigation. The employer has the authority to create a special commission, which includes authorized officials of the enterprise, auditors, and experts.
The basis for starting the dismissal procedure may be a memo from the boss under whose subordination there is an employee who has committed a disciplinary offense associated with loss of trust. During the investigation, an inventory may be carried out necessary to establish the fact of theft and (or) shortage. Before the procedure, you can take a receipt from the employee stating that the funds entrusted to the employee have been accounted for in advance, and those that have left the organization’s balance sheet have been written off.
During an investigation, as part of a disciplinary offense, the employee must be required to provide an explanation in writing. They are provided to the employer within two days from receipt of the written request. If explanations are not received within the allotted two-day period, then the fact of their absence must be recorded in a separate act. If an employee ignores the requirement to submit an explanatory note, the employer may begin the dismissal procedure without this document. The results of the investigation performed are recorded in the report. There is no standardized form for this.
The act contains information about:
- organizations;
- employee;
- the circumstances of the offense;
- results of the investigation.
The recommended penalties for the offending employee are also indicated. The document is signed by the members of the commission and its chairman.
The decision to dismiss is made by the head of the company. If the offense that resulted in loss of trust was not committed at work, then there is no need to bring the employee to disciplinary liability, but there must be documents confirming or reliably suggesting the presence of guilt in the employee’s actions - a protocol on bringing to administrative responsibility, extracts from the criminal case materials, court solution and other information.
What document confirms that the employee dealt with material assets?
The manager cannot claim that the employee’s job duties were related to the turnover of material assets if there is no documentary evidence. That is, the boss’s words alone are not enough for an employee to trust the organization’s assets. It is necessary to draw up a corresponding document.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows the financial responsibility of an employee to be specified in an employment contract. If the contract does not provide for this fact, it will be necessary to conclude an additional agreement on the full financial responsibility of the employee (hereinafter referred to as PMO) or the team.
Form of agreement on full individual financial responsibility of an employee ()
You can fire a specialist if a PMO agreement has been concluded with him. Moreover, a collective agreement is not suitable. The thing is that if a theft is discovered, it is impossible to identify the specific culprit. Then workers who have entered into a collective agreement can be subject to disciplinary action and may be limited to a fine. A standard form of a contract for personal assistance services for one employee has been approved by the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation. It can be found in the second schedule 85 of the departmental order that came into force in 2002.
Agreement on full financial responsibility
Sample of filling out an agreement on the financial responsibility of an employee ()
The employee's PMO agreement is filled out on a pre-prepared form, printed using computer technology, or written by hand in legible handwriting with a blue, purple, or black pen. It is necessary to spell out important provisions.
| Section number | Section name | Section Contents |
| Name of the agreement and its number. | Filled in the middle of the sheet. Below, on the right side, write the city where the agreement was concluded, and on the right, the date. | |
| Subject of the agreement. | The parties to the agreement, as well as its subject, are specified. | |
| 1 | General provisions. | The position of the employee, as well as his main responsibilities for the safety of valuables. |
| 2 | Responsibilities of the employee and the employer. | The main job functions of an employee related to the turnover of valuables, as well as the employer’s responsibilities to provide items of labor related to the safety of assets. |
| 3 | Type of financial responsibility of the employee. | Each case is specified for which the employee is responsible. |
| 4 | Conclusion. | Cases when the employee does not bear financial responsibility, as well as the validity of the contract. |
| 5 | Details of the parties. | Address, basic details of the enterprise, place of residence, passport details of the employee. |
| Conclusion of an agreement. | The fact of concluding an agreement is certified by the signatures of the manager and employee. |
Important! Upon receipt of the contract, the employee is required to sign on it, which means the start of the agreement.
Sample of filling out an agreement on full financial liability
Reasons for loss of trust
Dismissal due to loss of trust is possible if the employee caused direct damage to the employer’s property, that is, the available property decreased in quantity or its condition worsened. In this case, the perpetrator will have to compensate for the restoration or fully compensate for the damage. But remember that lost profits cannot be recovered.
In addition, an employee can be fired due to loss of confidence if he has committed illegal actions not related to the performance of official duties. In this case, the employer must establish the fact of the crime and receive a copy of the court verdict that established the employee’s guilt.
How to fix the bases
Dismissal due to loss of confidence is a set of actions that must be strictly followed in order to avoid violation of labor laws.
If an employee has committed actions related to the performance of job duties, his dismissal is a disciplinary measure. When terminating an employment relationship on this basis, it is necessary to strictly follow the disciplinary procedure established by the organization, including deadlines.
The manager must require a written explanation from the employee. The form of explanation is not established by labor legislation. If the employee is ready to write an explanatory note, there is no need to require him to give an explanation in writing. If the situation is conflicting, then the notification must be issued in writing and handed to the subordinate against signature. If you refuse to sign, a document is drawn up.
The legislation gives the employee two working days to provide explanations. The period is counted from the date following the day the claim is submitted.
How to conduct an investigation and document its results
To confirm the detected violations, a commission is created for an internal investigation. It should include who are not interested in the outcome of the proceedings. Its number is at least 3 people . To do this, issue an order in any form, which indicates:
- positions and names of persons involved in clarifying all the circumstances of the offense;
- powers of commission members;
- objectives of the investigation;
- its duration.
The commission must:
1. Identify all the conditions under which the violation was committed.
2. Establish a list of valuables that are lost or damaged.
3. Inspect the place where the violation occurred.
4. Assess the amount of direct actual damage.
5. Identify the guilty employees and obtain evidence of their guilt.
6. Establish the circumstances that contributed to the commission of the offense.
All members of the commission are introduced to the order against signature.
Based on the results of the actions taken, an act is drawn up. It provides the following information:
- a list of employee actions that give grounds for mistrust;
- conditions for committing unlawful acts;
- the amount of damage caused or possible damage caused by them;
- the degree of guilt of the employee and proposals for applying punishment to him.
The act is signed by all members of the commission, and the employee gets acquainted with it against signature. If he refuses to familiarize himself, this is also documented in a separate act.
Execution of orders and terms of dismissal
The order is issued in the general manner - on the basis of Art. 84.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The employee must be familiarized with the contents of the document against signature within three days from the date of execution of the order. If the employee does not want to sign the order, then the employer will need to draw up a separate written act.
An employee can be dismissed due to loss of trust within 1 month from the moment the disciplinary offense is discovered. The period does not include periods of temporary disability and vacation of the employee. It is possible to terminate an employment contract within 6 months from the date of discovery of a disciplinary offense. Based on the results of the audit, the employee can be dismissed no later than two years after committing illegal actions. If discipline is violated not at the place of work, then the employee can be dismissed no later than one year from the date of notification of the employee’s behavior.
An entry is made in the employee’s work book indicating the number, full date, and information about hiring. The reason for dismissal is indicated with reference to clause 7, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. You will need to indicate the order number for the hiring and dismissal of the employee. The work book is signed by a specialist from the HR department (with a transcript of the signature). From November 27, 2016, it will be necessary to certify the dismissal record with the employer’s seal only if it is available. A similar entry is made in the employee’s personal card (Form T-2).
Upon dismissal, the employee receives all payments guaranteed by the remuneration system:
- calculation;
- compensation for unused vacation;
- accrued but not paid bonuses.
The consequences for an employee when fired for loss of trust are often negative. If an employee desires subsequent employment, he receives a justified refusal from other employers due to an entry in the work book. Officials dismissed from public service are deprived of their social and housing benefits due to their length of service. Unlawful dismissal can be challenged administratively and judicially.
Answers to frequently asked questions
In the process of dismissing an employee due to loss of trust, both employees and employers may have questions that are typical.
Question 1. I hired a seller, but we did not have time to conclude an agreement on full financial liability. They only drew up an employment contract. The girl stole money from the cash register, which she does not admit now. How can I fire her due to loss of trust?
Answer 2. If the employment contract stipulates the obligation to preserve material assets, then the dismissal procedure is the same as if there is an agreement on material liability. Otherwise, the employee will have to be fired under another article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and the fact of theft will be dealt with by the investigative authorities.
Who can be counted and how?
Due to the loss of trust by the employee, that is, under Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (clause 7, part 1), not all employees can be fired. This rule applies to persons who:
- are financially responsible;
- committed guilty actions (inaction).
Only if these conditions are met will the termination of an employment agreement with an employee be legal. Dismissal on this basis is one of the types of disciplinary sanctions; accordingly, it requires the employer to comply with the imposition procedure.
Salesman
With whom agreements on full material (individual or collective) liability can be concluded is determined by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2002 No. 85.
The position of the seller is included in this list - when performing his job duties, the seller services commodity and material assets, therefore, when hiring him, a liability agreement is concluded with him. Therefore, under certain circumstances, the seller may be fired in accordance with clause 7, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Termination of legal relations with the seller will be legal only if the following conditions are met:
- monetary shortages or absence of goods must be confirmed by an inventory carried out in accordance with legal requirements;
- in addition to the shortage or absence of goods, the seller’s guilt must be established and confirmed;
- there is a cause-and-effect relationship between the actions (inaction of the seller) and the resulting consequences in the form of causing material damage to the organization.
Failure to comply with these conditions may result in the seller turning to the courts, declaring the employer’s actions illegal, reinstating the employee at work, or bringing the employer to financial or administrative liability.
Chief Accountant
Since the activities of the company's chief accountant are inextricably linked with the maintenance of material and commodity assets, he can be dismissed under clause 7 of part 1 of art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if his actions cause the employer to stop trusting him. The actions that the employer identifies as the reason for the loss of trust must be culpable.
Guilt may be confirmed by the results of an audit or related inspection.
Other employees
Any employee who is engaged in the maintenance of material or commodity assets at work may be dismissed due to loss of trust if an appropriate agreement on liability has been concluded with him.
For example, when applying for a job, a warehouse manager entered into an agreement with the employer on full financial responsibility. A few months later, the employer conducted an audit and discovered a shortage in the warehouse.
We conducted an inspection - recordings from CCTV cameras and witness testimony confirmed that the warehouse manager did not always securely lock the premises when leaving work. Because of this, third parties were able to enter the warehouse and take things from there. These actions allowed the employer to fire the warehouse manager due to loss of trust.
Another case: the manager received money from the cash register to buy gifts for the team for the New Year, but lost the gifts. The employee did not enter into an agreement on full financial liability. An employer can recover damages from an employee, but it cannot be fired due to loss of trust - this is not a person who directly serves material assets.
Who cannot be fired on the basis of loss of trust
From the current legislative norms it naturally follows that an employee who has not signed an agreement on full financial responsibility cannot be fired due to loss of trust. However, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for cases when, on the same basis, it is impossible to remove an employee from a position, even if the appropriate conditions exist.
- It is prohibited to fire an employee who is in an interesting position, even if she is found guilty. This rule is regulated by Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- You cannot dismiss employees who are away from the workplace, for example on a business trip, on sick leave or on vacation. The prohibition also applies in cases of dismissal for other reasons. However, upon arriving at the workplace, the employee can receive an order from management at any time.
- It is prohibited to dismiss employees under 16 years of age. But, if a minor employee is found guilty, management can contact the labor inspectorate, as well as the commission for children under the age of majority, to coordinate this action.
Thus, it is prohibited to dismiss minors, pregnant women and those employees who have not signed an agreement on full financial responsibility due to loss of trust, even if their work activity is related to the turnover of the company’s financial resources.
When you can’t fire someone due to loss of trust
Not all people who have committed any offense can be fired on this basis. There are exceptions:
- It is prohibited to dismiss pregnant employees (according to Article 261 of the Labor Code).
- An employee who has taken vacation or sick leave cannot be deprived of his or her job. While he is absent, it is impossible to dismiss him, so he will be on the staff until he returns (Article 81).
- Dismissal of persons under 18 years of age is not permitted if the implementation of this decision has not received approval from the labor inspectorate and the commission for the protection of the rights of minors (Article 269 of the Labor Code).
When is a full employee payout made?
On the final day of work, the employee has the right to receive payment in full. He should be given not only all the earnings due to him, but also compensation for all unspent vacation days, including for previous years.
If an employee does not show up for work on the final day, payments must be made to him by bank transfer. If the employer does not have the technical ability to make the transfer, he must pay the money to the employee on the day of his request, and if this is not possible, then on the next day.
What is the procedure for dismissal due to loss of confidence?
The general procedure for dismissal due to loss of confidence must be applied taking into account compliance with the procedure for bringing to disciplinary liability (Articles 192 and 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Notification
The employee receives notice of upcoming dismissal. Moreover, the mandatory two-week period does not have to be fulfilled. If illegal acts are discovered, the employer can get rid of the culprit any day he wishes.
Notification shall be made exclusively in writing. Upon delivery, the employee must sign. In case of refusal to do this, a special act is drawn up.
Order
If it is established that a guilty act has been committed, a special order is created in the standard T-8 form. The wording in the order and in the work book must be the same.
Calculation
Upon dismissal, on the very last working day, the employee is given everything that is required in such cases:
- work book with the corresponding entry;
- certificate of income for the last year;
- wages that the employee earned for the entire period, including the last day;
- all bonuses and other monetary payments due under the remuneration system;
- if the vacation days required by law were not used, then compensation is issued for them. If the employee used vacation days in advance, then the previously issued vacation pay will be withheld from him.
Important! If an employee knows for sure that he did not commit any illegal actions and his dismissal is illegal, then he has the right to go to court and be reinstated in his job.
What documents are needed and how to prepare them?
Regardless of the reasons why the employer terminates the legal relationship with the employee, he is obliged to issue the dismissed person with a package of documents required by law on the last day of work:
- a copy of the dismissal order;
- work book and information about the employee’s work activity;
- certificate in form 2-NDFL;
- documents relating to personalized accounting and the amount of insurance premiums paid;
- certificate of earnings for the previous 3 months;
- upon receipt of a written request - copies of official inspection reports, orders for employment, internal transfers, etc.
The employer is given 3 days from the date of receipt of a written request to issue the dismissed employee with documents related to the performance of his labor function.
Grounds for dismissal
The calculation and dismissal of a police officer can be carried out on the following grounds:
- the presence of one’s own desire (a dismissal report is written);
- upon reaching a certain age established by law;
- if an applicant for a police vacancy provided false information about himself in advance (education, previous position, work experience, etc.), which was later found out;
- repeated disciplinary action received in the presence of an existing offense recorded in writing and not yet removed by management;
- according to length of service sufficient for a police officer to retire;
- in accordance with the expiration of the concluded contract;
- if the clauses of the employment contract were violated by one of the parties;
- sending a police officer to duty (alternative/military);
- dismissal due to reorganization of the employer's organization (staff reduction);
- in connection with the liquidation of the employer's organization (staff reduction);
- an accusation was made in court and it entered into legal force;
- deterioration of health, according to which the person will no longer be able to continue working in the internal affairs bodies (a medical certificate is required);
- deterioration of health, according to which it is impossible to perform job duties in full and it is also impossible to transfer to another position (a conclusion from a medical commission is required);
- establishing a person’s inadequacy for the position held based on the results of the certification;
- gross violation of labor regulations/discipline;
- the person’s inconsistency with the requirements for service in the internal affairs bodies (the personal and service qualities of the employee are assessed);
- trust in the employee has been lost, the policeman has committed an offense that discredits the honor of an employee in the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
In each case, the consequences of dismissal will be different. In any situation, the dismissal of a police officer is significantly different from the termination of an employment contract with an ordinary employee.
Committing an offense discrediting honor
Service in the internal affairs bodies involves protecting the safety of citizens and complying with/protecting legal norms. Modern laws do not provide a clear concept of the “honor and dignity” of a police officer. Honor is understood as the personal qualities of a person during non-working hours and his behavior in the performance of official duties. The concept of honor can also be revealed as the attitude of society towards an individual, that is, how others see and evaluate a person. In turn, dignity is a person’s perception of himself. Loss of honor is most often accompanied (or one might even say initiated) by loss of dignity.
If you turn to Federal Law No. 342, adopted on November 30, 2011 (more precisely, to Article 113 of the above law), you can become familiar with one of the basic requirements for the behavior of a police officer on duty and outside of it. An employee of the Department of Internal Affairs/Ministry of Internal Affairs is obliged to behave with dignity, without damaging the honor of his personal and internal affairs bodies as a whole.
It is unacceptable to make decisions and perform actions for the purpose of obtaining personal gain. Every action must be accompanied by an objective and fair reflection.
Committing actions that discredit the honor/dignity of a law enforcement officer will lead to an inevitable result - dismissal for negative reasons. The same Federal Law 342, which regulates the service of police officers (Article 82, Part 3, Clause 9), tells us that termination of a contract in the event of committing acts discrediting honor and dignity is inevitable. It is possible to simultaneously apply administrative punishment and disciplinary liability. For example, a police officer caught driving while drunk not only behaved negatively, which is unacceptable for law enforcement officers, but also violated the norms of the Code of Administrative Offenses and Traffic Regulations.
Loss of trust
Federal legislation in the field of official relations between law enforcement officers does not provide a clear concept of “loss of trust.” Article 82, Part 4 of the Service Law more or less “sheds light” on this aspect. Loss of trust in a police officer occurs in the following cases:
- if the employee in the current situation has his own benefit, and no measures have been taken on his part to eliminate this conflict of interest;
- if close relatives of the police officer (wife, children under the age of eighteen) or the internal affairs officer himself violated the laws regarding investing/storing funds in foreign bank accounts;
- if the boss knew (could have known) about the personal interest of his subordinate and did not take any actions aimed at resolving the current situation;
- if the police officer indicated false or incomplete information in the income declaration (including about the income of the spouse and children under eighteen years of age);
- if a police officer is engaged in commercial activities (namely managing an organization) with the aim of generating income/profits in circumvention of the adopted legislation;
- if the employee combines police service and entrepreneurship;
- if a police officer is a member of the management bodies of foreign organizations engaged in non-profit activities in our country.
A police officer can be fired on this basis only if there is intent (that is, the act was committed purposefully) and if there is a court decision/results of an internal audit/investigation. After a person has to “resign” for such an unpleasant reason, information about the fact of dismissal and the offense committed will be entered into a special register.
Violation of discipline
A police officer may be dismissed on the basis of a disciplinary violation.
The procedure for labor conduct for current police officers is determined by more than one legal document:
- federal regulations;
- instructions appropriate to the position of a police officer;
- charter of employees in the internal affairs department;
- internal regulations adopted in the department where the “culprit” works (and higher departments in general);
- prohibitions established for police officers in general and for a specific position on an individual basis (depending on job responsibilities defined by law);
- violation of the obligations assumed by the police officer when signing the contract and taking the oath;
- establishing requirements for the manifestation of personal and official qualities of a police officer in accordance with official duties;
- failure to fulfill one's official duties to the required extent, their performance with violations, or a complete refusal to work without reasonable grounds;
- orders, decrees, orders of immediate superiors in the process of performing their work as a police officer.
The legislation contains such a concept as gross violation of labor discipline. Such an act includes:
- violation of the legislation of our country (prohibited actions/restrictions specified for police officers);
- absence from one's workplace (except for cases arising in connection with official necessity or another reason that the law considers a valid reason) for more than 4 hours in a row;
- a statement by a person serving in the police towards the government, power structures, superiors, etc. in an unflattering manner (except in cases where public speaking is included in the terms of the police officer’s contract);
- consumption of alcohol/drugs/other intoxicants directly during work or before starting to perform duties in accordance with the concluded contract;
- failure to provide information received by a police officer as a result of requests from citizens of the Russian Federation to him for the purpose of obtaining personal gain;
- violation of the rules for storing information entrusted to him (unless such an act is punishable under articles of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation);
- violation of the rules for storage and use of service weapons and additional components (cartridges);
- a police officer’s refusal to undergo a medical examination, the necessity of which is stipulated by the legislation of our state;
- disagreement with undergoing certification, the results of which affect further service;
- damage to government property, with intent - that is, purposefully;
- violation by a police officer of all types of security requirements, resulting in serious consequences (fire, injuries, accidents, etc.) or creating a real threat of such consequences (except for cases where the actions of a police officer fall under the criminal code);
- violation of the rules for working with money and/or other valuables, as a result of which management’s trust in the employee was lost;
- committing illegal actions against ordinary citizens, which entailed a violation of their constitutional rights (except for cases where the actions of a police officer fall under criminal liability).
In case of gross violations of discipline, the police officer faces the only penalty - termination of the contract with an unflattering mark in the work book.
Depending on the category of police misconduct, measures may be as follows:
- verbal warning;
- reprimand (with or without entering in a personal file);
- assessment for non-compliance with the duties performed;
- demotion in position/rank;
- dismissal with varying degrees of consequences (up to and including refusal to reinstate).
The degree of guilt and responsibility will be determined based on the results of the official investigation.
Violation of contract clauses
Violations of contractual obligations by police officers must be understood as violation of job descriptions, abuse of granted rights, failure to fulfill (or incomplete fulfillment of) assigned duties. The management of the Ministry of Internal Affairs/Internal Affairs can say goodbye to a subordinate if the following laws were violated at the time of registration of the employment relationship:
- when the contract was concluded, a court decision prohibiting this person from holding certain positions had already entered into force in relation to the job applicant;
- when concluding a contract, a medical certificate has already been issued in relation to the job applicant, on the basis of which the person is contraindicated to occupy this position;
- the job applicant does not have the required level of education;
- and so on. in accordance with the legislation in this area.
It should be understood that a violation of the terms of the contract can be committed not only by the employee, but also by the employer.
False documents upon entry into service
It is mandatory to dismiss for this reason immediately after it is discovered that a police officer has provided false documents. What could it be - a school certificate, a diploma from a higher educational institution, a work record, etc. Providing false documents during employment may result in criminal liability.
Conviction for a crime
If a police officer has committed a crime, he will definitely be fired.
The main motivation for terminating an employment relationship is a court decision, after the established deadline for appealing it has passed. Provided that before such a decision on guilt was made, the police officer was taken into custody, the date of termination of employment with him will be the date of his arrest.
Dismissal of an employee due to loss of trust. Deadlines
Whenever it comes to terminating an employment contract, it is extremely important to adhere to certain deadlines. So, according to the clauses of the Labor legislation, if an employee continues to work after the date indicated in the order and notification, and besides, he was not given any money or documents, then the contract with him is automatically extended.
If dismissal cannot be avoided, then all the measures taken will have to be repeated all over again. Typically, an employer wants not only to get rid of a negligent employee, but also to receive compensation for the damage caused. In this case, it is important to ensure that the employee receives written notice, and on the last day of work the necessary payment is made to him.
The manager must be firmly convinced that he completed all the necessary documents correctly and on time, thereby depriving the former employee of the opportunity to win the case when going to court.
There are often situations when an employee does not agree with the wording of dismissal and writes a statement “of his own free will.” If the employer does not hurry up and does not complete all the necessary documents within the established time frame - within two weeks, then it will be considered that the dismissal procedure was carried out under Article 80, as stated by the employee.
Dismissal due to loss of trust can put an end to a person's future career. If the employee is really at fault, then he should try to resolve everything peacefully and resign “of his own free will.” This way you will be able to maintain your reputation, which is very important when looking for a new job.
Dismissal on the initiative of an employee of the Ministry of Internal Affairs
The employee has the right to resign before the expiration of the contract. To do this, you will need to submit a report addressed to your boss no later than 1 month before the date of termination of the employment relationship. The report can be withdrawn after submission - before the expiration of the work period.
Important! It is impossible to withdraw a report if another specialist has already been invited to replace the dismissed employee.
Upon completion of the service period, the employee has the right to stop performing his job duties, provided that:
- surrendered weapons;
- certificate;
- token;
- other property managed by a specialist.
An employment contract can also be terminated after the expiration of the period allotted for work, with the consent of the boss and in the absence of departmental obstacles. A dismissal report can be signed earlier, for example, when an employee was elected to an elective position or if he cannot continue to serve for family reasons - due to the illness of a close relative, the need to care for a child, etc.
In some cases, it is prohibited to submit a notice of dismissal:
- in the event of an armed conflict or a counter-terrorism operation;
- during an established martial law or state of emergency;
- when eliminating the consequences of an emergency.
You can then submit a report for dismissal after removing such obstacles. You can also leave at your own request if the employee is recognized by the military medical commission as unfit for service in the internal affairs bodies.
Recording in labor
A mandatory entry must be made in the work book that confirms the reason for dismissal. For this:
- In the column with information about dismissal, they write something like this: “dismissed for committing guilty actions, after which the trust of the employer was lost.” At the end, they refer to the relevant legal norm (Article 81 of the Labor Code). The wording must be similar to that contained in the order.
- In the column with the grounds indicate the date and number of the issued order, thanks to which the termination of the contract was formalized.
Issuance of employee documents.
On the employee’s final day of work, management is obliged to give him documents, including a work book.
If the employee refused to receive them, or was unable to show up for work on that day, the employer must notify him of the need to come for his documents, or give permission to send them by mail.
Such notice may be sent in a manner that allows the employee to later prove its receipt. Otherwise, the employer may be held liable for withholding the employee's documents after his dismissal.
Nuances
This procedure has important points that you need to know immediately before dismissing an employee on this basis.
Dismiss on the basis of Art. 81 Labor Code accountants and economists should be careful. Since this basis involves working with property and finances, you need to make sure in advance that the employment agreement requires them to work with them. For example, they perform the functions of a cashier and accountant.
Attention
If such an obligation is not provided, the employee will prove his case in court. It will be restored, and the employer will be required to pay compensation.
Some types of activities (state and military service, etc.) provide that dismissal due to loss of confidence must be carried out not only in compliance with the Labor Code, but also other federal acts (“On the Police”, etc.). But even then you will need:
- Prove the worker's guilt.
- Follow all stages of the dismissal procedure.
Important
An employee dismissed for corruption is registered in the register of persons on the GIS website. The validity period is 5 years. If other violations are committed, a person may also be temporarily or permanently prohibited from engaging in certain types of activities.
Appealing dismissal and going to court
If a person disagrees with the management’s decision and believes that he was fired illegally, he has the right to file a claim with the judicial authorities within one month. Labor legislation also makes it possible to pre-trial resolve conflicts between the employer and subordinates. To do this, you need to put your requirements on paper in two versions and transfer them to management, observing the organization’s document flow rules. One copy with the date of acceptance and incoming number will remain with the subordinate.
A common mistake made by managers when terminating a contract on the initiative of one party (the management) is violating the deadlines for conducting an internal investigation. Another problem is the inability to determine in time what type of disciplinary punishment should be applied to the offending employee. It is mandatory to comply with the following requirements for service verification:
- order of conduct;
- deadlines;
- paperwork.
If the deadline for the manager to publish documentation on disciplinary punishment in the form of dismissal from the authorities is violated, such punishment will be declared invalid in court.
It is worth considering that the timing of disciplinary action may vary significantly depending on the offense committed. For example, if a police officer committed an act that discredited his honor and dignity, but was not on duty at the time the offense was committed, then he can be punished within a year. The countdown begins from the day when management learned of the misbehavior of its subordinate.
In addition, a person cannot be held accountable for official misconduct if he is on vacation or sick leave.
Although periods of temporary incapacity for work are not included in the period allotted for the preparation of documents for imposing a disciplinary sanction.
A police officer can appeal against illegal termination of a contract within a month from the date of receipt of the order. It is necessary to write a statement of claim taking into account the jurisdiction and jurisdiction of the courts. In this situation, you need to go to court in accordance with the territorial location of the employer. To correctly fill out the statement of claim, it is better to familiarize yourself with the sample.
What to do if you were fired due to lack of confidence?
Dismissal due to loss of trust is one of the disciplinary measures and carries negative consequences for the employee. If a person believes that there were no grounds for terminating an employment contract with him or that during the dismissal process there were violations of the procedure or procedure for holding him accountable, he has the right to appeal the decision made by the head of the enterprise.
A statement of disagreement with the dismissal can be sent to the labor inspectorate , and a statement of claim for reinstatement to work can be sent to the court. If, after considering a complaint from a former employee, the labor inspectorate concludes that the employer committed violations, it may hold him administratively liable in the form of a fine.
In order to be reinstated at work, the dismissed person must submit a corresponding statement of claim to the court. If, based on the results of the consideration of the civil case, the court comes to the conclusion that the employer did not have grounds for dismissal or committed violations in the process of terminating legal relations, it decides to reinstate the former employee in his position.
You must contact the court before the expiration of a month from the date of receipt of the work book or familiarization with the order to terminate the legal relationship. The missed deadline can be restored by the court, but the plaintiff will have to prove that there were good reasons for missing the deadline.
Dismissal due to loss of confidence is a disciplinary measure and can be applied only to a certain category of employees with whom agreements on full financial responsibility have been concluded.
In order for the termination of legal relations to be lawful, the employer must prove that the employee committed guilty actions, and also that these actions provide grounds for further mistrust. Violations of the dismissal procedure by the employer are grounds for reinstatement of the employee to his position.
Can dismissal be challenged?
The employee has the right to disagree with this decision and defend his rights in:
- Court.
- Labor Inspectorate.
The inspection authority will pay attention to 3 points to make a decision:
- Does the victim belong to the persons to whom the property and funds are entrusted?
- Whether a misdemeanor or serious offense was committed, after which the employer lost confidence.
- Has the legal procedure for dismissing an employee been followed?
Information
To prove that he is right, he must provide documents proving that he did not commit any illegal actions and that he was fired unreasonably.
For employers who wrongfully get rid of an employee on this basis, penalties are provided. If a complaint is filed against the employer in court, a claim for illegal dismissal is filed, then he will most likely be returned to his previous place. Plus, the employer will have to (according to Articles 237 and 394 of the Labor Code):
- Pay the victim compensation for the period of absence (based on average salary).
- Pay for moral damages.
- Cancel entries in documents.
If a complaint is filed with the labor inspectorate, then the employer will have to pay a fine for illegal dismissal (closed in Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code):
- 30,000 – 50,000 rubles – for legal entities.
- 1000 – 5000 – for authorized persons who made such a decision and individual entrepreneurs.
Illegal dismissal
In the event that an employee believes that his rights have been violated, he has the right to resort to their protection as follows:
- Judicial order.
- Administrative.
In court, the person demands that the dismissal be declared illegal and reinstated at work. It is important to immediately note that civil servants, military personnel, prosecutors and other persons appeal orders of dismissal in accordance with Chapter 22 of the CAS RF.
In addition, if the court finds the dismissal illegal, the employee is due payment for forced days of absence and legal costs.
In an administrative manner - contact the prosecutor's office, as well as the State Inspectorate, which will conduct an inspection, and based on its results, the employer may be held administratively liable under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Arbitrage practice
Lawsuits regarding dismissals for lack of confidence are quite varied. Offended workers are trying to restore their rights and good name. Firm owners try to protect their property from unscrupulous employees. The final results of disputes depend on the completeness and correctness of the evidence presented to the judiciary on both sides. Issues that are subject to study and analysis in court:
- classifying the employee as a person to whom the relevant article of the law can be applied, establishing grounds for dismissal due to loss of trust;
- the fact of committing a disciplinary offense, administrative or criminal offense related to theft, bribery and other mercenary offenses, giving the employer grounds for loss of confidence in the employee;
- compliance with the procedure for dismissing an employee by the employer.
Thus, by the appeal ruling of the judicial panel for civil cases of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug dated 02.10.2012 in case No. 33–4375/2012 on the appeal of KRS Eurasia LLC against the decision of the Kogalym City Court dated 27.07.2012, which canceled the Order of LLC "KRS "Eurasia" on dismissal, confirmed the legality of the appealed decision on the basis that the employee was not a financially responsible person.
As follows from the case materials and established by the court of first instance, the parties had an employment relationship, the plaintiff worked at KRS Eurasia LLC as the head of the underground well repair workshop, and an agreement on full individual financial liability was concluded between the parties. In fact, the basis for the plaintiff’s dismissal was the fact that the plaintiff signed fictitious waybills. When making a decision, the court proceeded from the fact that the plaintiff is not a person directly servicing monetary or commodity assets; an agreement on full financial liability in itself will not be a confirmation that the employee directly services material assets; it is necessary that the scope of work duties employee, recorded in the employment contract or in the job description, included work with inventory items. The signing of waybills does not indicate the plaintiff’s direct service of monetary or commodity valuables. Thus, the plaintiff, by virtue of his position, does not belong to the category of persons directly servicing monetary and commodity assets, and therefore could not be dismissed on the basis of paragraph 7 of part one of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
As we see, the law is on the side of the workers. However, dishonest employees are also common. From my experience in trade, I know that collective financial responsibility is divided among all members. One person can steal, but everyone will have to pay for the losses. That is why management should carefully conduct an inspection and identify the culprit. The rest will not be so offended by the unfair punishment. Well, if you can’t do this with your own resources, it would be useful to contact the prosecutor’s office. They will quickly find and bring to justice the culprit.
The procedure for recording a violation and creating a commission for investigation
Dismissal due to loss of trust is a rather complicated procedure. Before terminating the employment relationship, the manager needs to prove the employee’s guilt. Otherwise, dismissal based on this fact will be illegal. And this threatens the company’s management with trouble. The collection of evidence begins with an internal investigation, the basis of which will be an internal report on the employee’s misconduct, drawn up, for example, by the head of the department.
Service memo about the fact of violation
The internal memo provides for the following design rules:
- At the top, in the left corner is the name of the department that delivers the information.
- In the upper right corner the addressee, his position, surname, and initials are indicated.
- In the center or near the left border of the sheet in capital letters - the name of the document.
- The next line contains the date and index of the report. The date is written in Arabic numerals, for example 02/21/18, the day on which the document was drawn up and signed.
- The information that needs to be conveyed to the manager is stated.
- In conclusion, the position, surname, initials, and signature of the writer of the note are written (all on one line).
A well-written report on the violating employee will help in collecting evidence for regulatory authorities.
The text of the memo against the employee lists the facts of violations
Explanatory note from an employee
As soon as the manager has received a memo against an unscrupulous employee, the first step is to demand that the latter explain the reason for his actions. This must be recorded in writing. In other words, the employee is asked to write an explanatory note within 2 days after the violation is detected . In case of refusal to give written explanations, a report is drawn up where the employee’s actions are recorded.
If an employee refuses to give an explanation for the violation, a report about this is drawn up
In practice, in situations of employee deception and fraud, management does not pay attention to small details when dismissing employees. In a fit of anger, people are fired indiscriminately and without explanation. Then the company owners try to prove the fraudsters’ guilt in the courts, but, alas, to no avail. Hence the conclusion - every little thing must be recorded in writing. In court, it is the nuances that will help achieve the truth and punish the culprit.
The best option would be a written explanation, preferably in handwritten form, addressed to the manager, indicating the reason for the violation, signature, and date.
If an employee explains the violation with a valid reason, he cannot be considered guilty
An explanatory note must be registered in the office and the date of reception must be marked on it. After becoming familiar with the cause of the violation, the manager makes a decision on disciplinary measures for the employee.
Creation of a commission to investigate the violation
Taking into account the information received about violations and the explanations of the offending employee, the manager issues an order to conduct an internal investigation with the creation of a special commission, the composition of which is determined independently. The number of committee members present must be at least three.
The creation of a commission is necessary for an objective investigation of the violation
The order must necessarily contain:
- date and purpose of creation;
- Full names and positions of commission members;
- the period for conducting the official investigation;
- signatures of the commission members.
The order must be signed by the head of the company and certified with a seal.
End of internal investigation
After all the formalities, the commission begins an internal investigation. It is important that the inspection team impartially examine the facts and causes of the violation, assess the losses, identify those responsible, collect a sufficient amount of evidence and determine the degree of guilt. At the end of the internal audit, a report is drawn up, to which written evidence obtained during the work is attached. A verdict rendered by the commission not in favor of the employee is a valid reason for dismissal due to loss of trust.
The commission report presents the results of the internal investigation
If it is impossible to investigate the violation on its own, the owner of the company turns to law enforcement agencies. In this scenario, the culprit will be punished much more severely.
In what cases is dismissal possible?
Dismissal is the logical conclusion of a discovered labor violation. For the employer’s sentence to take effect, a number of conditions must be met :
- identifying the fact of a violation (conducting an inspection or investigation, personal recognition of the employee, inventory results, etc.);
- proof of the employee’s guilt (the manager independently decides to contact the competent authorities or conduct an internal investigation);
- the possibility of recovering the material damage caused (if the employee at fault does not have funds or property sufficient to cover the damage, it is advisable not to dismiss him until full compensation from his salary).
What does an employer face in case of illegal dismissal due to loss of trust?
If an employee is fired illegally, and especially for such a serious reason as loss of trust, the consequences for the employer can be quite serious:
- Imposition of penalties. The amount of the fine varies from 1,000 to 50,000 rubles, depending on who the fine is imposed on (organization, individual entrepreneur or official).
- Reinstatement of the employee to his position and payment for all time of forced absence at the average salary.
- Compensation for moral damage in the event of an employee going to court.