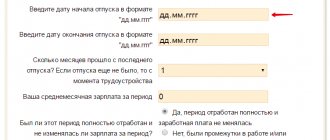
Using the calculator
The rules for calculating compensation provided for in Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation apply not only to wages. The employer is obliged to compensate for delays in any payments due to employees in connection with the performance of their labor duties, namely:
- wages;
- redundancy benefits;
- vacation pay;
- compensation for harmful working conditions;
- maternity payments, etc.
In accordance with the requirements of labor legislation, the calculator calculates compensation based on the key rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for the period of debt formation.
The key rate is a constantly changing indicator. For example, during 2021 alone it was changed four times. The calculator constantly monitors changes made by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, and therefore its calculations will always be accurate provided that the user enters the correct payment delay period.
Compensation for delays is set by law at 1/150 of the key rate. The calculation will be made in accordance with the rate in effect during the period that you specify and for each overdue day. The delay period begins from the day following the day on which payment should have been made until the day of actual payment. If there was a change in the key rate during this period, the calculator will take this into account.
The amount owed will be considered the amount actually due for payment. That is, the amount of debt will be equal to the salary for the period of delay. If there is a two-month delay in salary equal to 25,000 rubles, the amount of debt will be equal to 50,000 rubles.
Insurance premiums for payment of compensation for delayed wages
The issue of calculating insurance premiums from the amount of compensation for delayed wages under the legislation of the Russian Federation is in a controversial situation. There is no clear solution in any legislative act. The Ministry of Finance, in its letters dated September 24, 2018 No. 03-15-06/68161 and dated September 24, 2018 No. 03-15-05/68049, clearly states that insurance premiums from compensation for delayed wages must be calculated in the same way as from wages . However, the Supreme Court (ruling No. 303-KG18-4287 dated 05/07/2018) does not agree with the Ministry of Finance and believes that compensation for delayed wages is not subject to contributions.
Therefore, if you do not want to enter into legal proceedings with the Federal Tax Service and the Social Insurance Fund, then mandatory insurance contributions from the amounts of compensation for delayed wages must be calculated and transferred to the budget.
Compensation options
Before you begin calculating compensation, you must be sure to familiarize yourself with the conditions written down in the employment or collective agreement. It is quite possible that the contracts provide for other compensation rates. The fact is that Article 236 of the Civil Code stipulates the minimum amount of compensation, while the employment contract may provide for higher percentages.
Please note: It does not matter to the employee why the payments were delayed. This could be the illness of the accountant or the dishonesty of the employer’s business partner, that is, the delay may occur through no fault of the employer. But this does not relieve him of the obligation to pay compensation.
New title
What to do if the company does not have enough money to pay salaries and compensation
The well-known advice of the Prime Minister will not work in such a situation. The law does not relieve the employer from the obligation to pay wages to the employee even if business activities are temporarily suspended due to financial difficulties.
If employees do not go to work due to non-payment, using their right enshrined in Part 1 of Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then according to the law (Part 3 of Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), this situation is recognized as downtime. And downtime is paid in an amount not lower than 2/3 of the average salary of workers. Compensation will also have to be paid.
What should employees do if their salaries are delayed?
Here's what a worker can do to get their money.
This is also important to know:
How is the average salary collected during forced absence?
Pause work. If a person is not paid a salary, he is not obliged to work for free. After 15 days of delay, he has the right to suspend work until he is fully paid off.
This rule does not work automatically. The employee is obliged to notify the organization in writing of his intention to suspend work. After this, he may not appear at work. Moreover, such a strike occurs at the expense of the employer: the employee sits at home, but his salary is still calculated based on average earnings.
There are exceptions. It is prohibited to suspend work:
- Civil servants.
- Military.
- Law enforcement officials and the Ministry of Emergency Situations.
- People responsible for providing the population with gas, electricity, and heating.
- Ambulance workers.
- People who work in hazardous types of production and with dangerous equipment. For example, an engineer from a nuclear power plant will have to wait for his salary at his workplace.
When the employer is ready to pay the employee, he must give him written notice. It can be sent by registered mail or delivered in person against signature. The employee is required to return to work on the next working day after receiving such notice. If it doesn’t work out, he will be given absenteeism. And the employer must pay the employee in full on the day of departure.
Write complaints. There are three recipients:
- State Labor Inspectorate. After receiving the request, inspectors will conduct an inspection. If inspectors find violations, they will draw up a report and bring the employer to administrative responsibility.
- Prosecutor's office. She will organize an inspection, collect documents confirming the violation, and transfer them to the State Tax Inspectorate for administrative liability. If the inspectors find signs of a crime in the employer’s actions, they will send the materials to the investigative committee to initiate a criminal case.
- Investigative committee. It makes sense to come here if your salary has not been paid for more than 2 months. Or when they give out less than half of your salary for 3 months. As a rule, after the initiation of a criminal case, the employer suddenly has money to cover the salary debt.
Go to court. The employee has the right to file a claim in court and recover from the organization arrears of wages, compensation for delays and moral damages. It is free - employees are exempt from paying state duty.
If the employee wins the court, then after the decision comes into force he will receive a writ of execution. It must be taken to the bailiffs, who will initiate enforcement proceedings and forcibly collect the debt from the organization.
Olga worked for an individual entrepreneur - she sold watches in a store. They did not sign an employment contract with her; all the conditions were discussed in words. One day Olga got sick and went on sick leave. The boss didn’t like this - the seller was fired remotely through correspondence on VKontakte, and the salary was not paid. Olga went to court demanding to collect back wages and compensate her for moral damages.
If the employment contract was not drawn up in writing, it does not matter. It is still considered concluded when the employee began work with the knowledge and consent of the employer. An individual entrepreneur provided Olga with a workplace and a product - a watch - for sale. She constantly went to work and performed work duties.
The employer did not come to court and did not refute Olga’s arguments in any way. The court decided that Olga was right and should receive unpaid wages and compensation for moral damage.
Is it necessary to levy personal income tax compensation and pay insurance premiums?
Compensation for delayed payment of wages is not subject to personal income tax (clause 3 of article 217 of the Tax Code). This has been confirmed more than once by the regulatory authorities in their explanations (letters from the Federal Tax Service dated 06/04/2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] , Ministry of Finance dated 02/28/2017 No. 03-04-05/11096, dated 01/23/2013 No. 03-04 -05/4–54, etc.). Personal income tax is also not charged for an increased amount of compensation, but only if such an excess is consistent with an employment or collective agreement (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated November 28, 2008 No. 03-04-05-01/450, dated August 6, 2007 No. 03-04-05-01 /261).
As for the calculation of insurance premiums, financiers believe that compensation for delayed wages does not apply to compensation payments related to the employee’s performance of work duties. It is not exempt from insurance contributions, since Article 422 of the Tax Code, which names payments not subject to contributions, does not mention such compensation. This means that the institution has no reason not to pay insurance premiums (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated September 24, 2018 No. 03-15-05/68049, dated March 21, 2017 No. 03-15-06/16239).
The courts, in their decisions, still adhere to the opposite point of view: insurance premiums are not charged (Decision of the Supreme Court dated 05/07/2018 No. 303-КГ18-4287). Thus, the Social Insurance Fund lost another dispute regarding the additional assessment of contributions for compensation for delayed salaries. The judge indicated that compensation is a type of financial liability of the employer, therefore, there is no need to pay contributions (resolution of the North-Western District Court of January 22, 2019 in case No. A13-8431/2018).
The employer is obliged to pay, but does not pay
Calculating compensation due to an employee is sometimes purely academic, especially when the employer is in financial trouble. That is, the employer knows that he owes, but is not going to or cannot pay the debt.
In this case, the employee has only one option - to court.
You can draw up a statement of claim yourself using tips from the Internet. The requirements of the statement of claim should include:
- collection of net wage arrears;
- recovery of compensation based on calculator calculations;
- recovery of moral damages (optional, upon request).
It is very important not to miss the statute of limitations, which for these categories of claims is shortened and is only three months. Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation determines the beginning of the limitation period from the moment when the employee learned about the fact of the delay.
As a rule, the employee learns about the fact of a delay in payment on the day when the payment should have taken place according to schedule. However, there are exceptional cases when information is received late, for example, in the case of an employee’s illness, due to which he could not call work, could not clarify whether the money was transferred to the salary card, and did not contact any of his colleagues.
The delay in payment of severance pay begins to be calculated from the moment the employee was given the work book. In connection with the transition to electronic work books planned by the Government of the Russian Federation, perhaps we should expect changes in the Labor Code regarding the calculation of the delay in payments upon dismissal.
Advice! Remember that your employer is not going to play the role of a lamb in court. It is possible that he will try to prove that you missed the deadline for filing a claim. It's not that difficult to do. For example, provide testimony that the sick employee was notified of the delay in salary personally by the chief accountant. Therefore, it is best not to delay going to court, especially since labor disputes are not subject to state duty.
What are the acceptable deadlines for salary payments?
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
The entire list of restrictions on the dates of transfer of payment for work done is enshrined in Art. 136, 140, 141 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, the timing of salary payment depends on the specific circumstances of its accrual:
- For amounts for work performed, both systematic and one-time, the following parameters must be adhered to: Payment occurs every half month;
- The transfer of money is carried out no later than 15 days after the end of the time period for which the accrual was carried out.
There are no provisions in legislative acts allowing for delays in employee salaries.
Consequences of missing a deadline
If the statute of limitations is missed, the case will not be considered and the judge will make a decision to reject the claim without examining the circumstances of the case.
Therefore, if it happens that you missed the deadline out of laziness or ignorance of the law, then before filing a claim in court, take care of several things:
- Think about how you might motivate missing a deadline. To extend the period, the reason must be valid - illness, caring for a sick family member, funeral, wedding, administrative arrest, etc. But the reason will have to be confirmed. As an option, think about your chronic illnesses, run to the doctor, tell him that you have been feeling bad for two months now, but you have been patient, and let him write it all down in your chart.
- Indicate in the statement of claim that you are asking to reinstate the missed deadline for a valid reason.
- Attach to the claim documents confirming valid reasons for missing the deadline. Perhaps the court will believe you.
If you could not come up with a good reason, then there will be little chance of winning the case. However, you can still file a claim. And at the same time hope that the employer will not come to court and the decision will be made in his absence or that the employer will simply admit your claim.
What fines may be imposed?
If payment rules are violated, the organization is subject to not only financial liability in the form of compensation, but also administrative liability, which involves issuing a warning and imposing a fine. The amount of sanctions is indicated in parts 6, 7 of article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
The amount of the administrative fine is:
- 10-20 thousand rubles. - on officials;
- 1-5 thousand rubles. - on individual entrepreneurs;
- 30-50 thousand - for organizations.
In case of repeated violation, the amount of sanctions increases:
- 20-30 thousand or disqualification for 1-3 years - for officials;
- 10-30 thousand rubles. - on individual entrepreneurs;
- 50-100 thousand - for organizations.
The exact amount of the sanction depends on the degree of guilt of the employer, the scale of the damage caused, and the number of similar offenses within the company.
The withheld fine is transferred to the municipal fund or the state treasury.
Criminal liability for violation of payment terms is regulated by Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the sanctions include:
- In case of partial non-payment for more than 3 months - a fine of up to 120 thousand rubles, forced labor for up to 2 years or imprisonment for up to 1 year.
- In case of complete absence of payments for more than 2 months - collection of 100-500 thousand rubles. or forced labor for up to 3 years or imprisonment for up to 3 years. If there are serious consequences from the offense, the period of loss of freedom can increase to 5 years.
It is also possible to introduce restrictions on entering into management positions or conducting specified activities.
Appeal to other authorities
It should be remembered that only a court can recover money from an employer. It is quite possible that you will be advised to file a complaint with the Prosecutor's Office or the labor inspectorate, and it is quite possible that these authorities will help you. However, please remember that:
- The prosecutor's office and labor inspectorates are extremely slow structures. The period for considering citizens' applications there is a month, but by the time you receive an answer, it may well take a month and a half.
- The orders of these authorities cannot oblige the employer to pay you.
- Contacting labor inspectorates does not suspend the running of the statute of limitations. If we assume that you waited a month and a half for the employer to pay voluntarily, then waited a month and a half for the inspectorate to wag its finger at the employer, then you have already missed the deadline for going to court.
- The court may recognize the missed deadline as valid due to the fact that you were waiting for a response from the labor inspectorate. Or maybe he won’t admit it. Just remember that the courts are overloaded with work, and every new lawsuit is a tragedy for the judge. Therefore, almost any judge will do everything possible to get rid of both you and your claim.
Documents attached to the application
The statement of claim will need to be accompanied by documents indicating, firstly, that you have an employment relationship with the employer, and secondly, documents confirming your claims.
Thus, in general terms, the list of attached documents should look like this:
- An extract from the work book, which can be obtained from the personnel service or from the accounting department of the enterprise.
- Employment contract.
- Interest calculations that you can do using the calculator.
- Optional documents, for example, indicating that you missed a deadline for a good reason or the costs of a lawyer that you are asking to recover from the employer.
- Copies of statements of claim at the rate of “one for the court, one for the defendant.”
When submitting an application, it would be useful to have an additional copy with you, on which the court employee will put a mark of acceptance.
When should vacation pay be paid if an employee goes on vacation?
Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates the timing and place of all payments due to an employee, states that the payment of vacation pay must be made at least three days in advance. At the same time, it is not reported which days the legislator has in mind, calendar or working days.
The Ministry of Labor put an end to this issue, which indicated that the period should be calculated in calendar days. Therefore, this period will include weekends and holidays.
This condition must be taken into account by the employer, especially if the employee’s vacation will begin after holidays combined with weekends.