In accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the organization of labor protection work at the enterprise must be carried out by the employer. The purpose of this activity is to create safe working conditions for employees, maintain their health and performance while performing their job duties (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In this article we have prepared for you a kind of guide to the site’s materials. It lists the main areas of work in the field of labor protection and provides links to articles that will provide more detailed information. This convenient rubricator allows you to quickly get the information you need.
Approval of labor protection regulations in the organization
At the initial stage, each employer must develop regulations on labor protection in the organization. If the number of employees exceeds 50 people, then it is necessary to allocate a position for a labor protection specialist or create such a service. Otherwise, appoint a person responsible for labor protection by order and assign him the duties of a labor protection engineer.
Occupational safety - expensive and not necessary?
Order on approval of the standard regulations on the occupational safety management system
Occupational Safety and Health Responsible
Occupational Safety and Health Commissioner
Labor protection in the institution
Organization of labor protection in dentistries, clinics and medical centers
Organization and management of labor protection
Regulations on the labor protection management system in the organization (sample)
The organization of the labor protection commission is carried out by the head. He issues an order in which he indicates the person responsible or all representatives together with the chairman. The chairman, in turn, keeps records of ongoing systematic events and meetings, develops a schedule and briefings. The chairman has the right to recall members of the commission and recruit new ones in their place. Making decisions about changing the chairman is the prerogative of the manager.
OSMS subsystem at the company
If an organization has many departments/branches, several responsible persons or services may be appointed for coordination and will carry out their activities in the controlled area.
Labor protection service at the enterprise, its functions and main tasks
The OSMS has the following main tasks:
- Monitoring the state of labor protection at the enterprise;
- Development of preventive measures, administrative documents and new proposals to improve the working environment;
- Participation in the development of instructions, manuals and other documents within the organization.
Among the rights and functions, there is an analysis of the state of the current occupational safety, the causes of injuries and illnesses, staff turnover, and the occupational safety and health management system organizes briefings, certification of equipment and some inventory, organizes special events, including charitable ones, in order to convey the importance of maintaining labor safety. If accidents occur, the OSMS should participate in the investigation of the causes. The OSMS performs reconnaissance of the condition of equipment and workplaces through inspections and maintenance, and monitors the legality of management and employees.
Planning work on labor protection
Organizing planning is the responsibility of the chairman. Necessary measures and development plan should be carried out in scheduled meetings. Members of the commission discuss the current problems of the organization and methods for solving them. If the organization is involved in transportation by freight or rail, members of the commission must also have a driver's license and experience in this field.
Note ! Representatives of the OSMS have the right not only to implement their plan, but also to attend meetings of senior management, as well as at meetings of lower levels of management of the institution. And also, report documentation to managers.
The frequency of briefings, training and educational activities must take place with the required frequency by law. For example, once a quarter, or once every six months, a year. For employees who have not been engaged in work activities for a long time, unscheduled and repeated briefings may be carried out.
Employee training
Training workers in safe methods and techniques for performing work, methods of providing first aid
It is mandatory to provide training on safe methods of performing work, as well as familiarize workers with first aid techniques for victims in the workplace.
Educational program for safety training for preschool employees
First aid in case of accidents at work
Internship on labor protection in the workplace
Employee training
Groups of occupational safety measures and their goals
Functions of the labor protection service and main tasks
Occupational safety measures are planned production work that is needed to ensure safe and effective work for workers that does not pose a risk of injury. They are divided into appropriate groups and recorded in the OHS materials.
Legal group
The legal group of activities is aimed at creating a system of legal norms and standards for safe UT. It is based on constitutional excerpts, by-laws, regulations and local acts that are adopted in each specific organization.
Socio-economic group
The socio-economic group includes measures aimed at government incentives for employers to increase the level of occupational safety, establish compensation and benefits when performing work, provide protection for a socially protected category of workers, establish social insurance with compensation payments if workers experience occupational diseases and work-related injuries .
Organizational and technological group
The organizational and technological group includes activities aimed at establishing a unified policy and goals for occupational safety, as well as safe production technologies.
Group
Sanitary and hygiene group
This includes activities of a sanitary and hygienic nature. Aimed at ensuring that work takes place in places favorable to life and health and that occupational diseases are rare.
Treatment and prevention group
This includes preliminary, periodic and extraordinary medical examinations, mandatory psychiatric examinations, and the provision of preventive nutrition.
Rehabilitation group
A set of measures aimed at ensuring that workers regain their health and ability to work if they suffer from acute illness or contract a disease associated with their professional activities.
Conducting labor safety briefings
The employer is also responsible for conducting various types of labor safety briefings with employees: introductory, primary, repeated, targeted, unscheduled.
How to conduct instruction and training on labor protection without errors?
The procedure for conducting labor safety briefings
Who should conduct induction training for the director or head of the institution?
Initial briefing: How many mistakes in documents have you already made?
Repeated briefing on labor protection: features of implementation, frequency and necessary documents
Main stages of implementation
The implementation of an OSMS is divided into the following stages:
- Preliminary analysis. The type of activity of the organization is analyzed, whether it is included in any occupational risk class, the safest type of production process is determined, equipment and production lines are selected, the territory is prepared, etc. PPE is selected for employees, and preliminary and periodic medical examinations are organized. Guarantees and compensation for work in dangerous or harmful conditions are prepared;
- OHS planning. The concept, goals and objectives in the field of labor protection are determined;
- Development and application. Responsibilities are assigned and personnel are trained and trained. Availability of information is ensured and documentation is prepared. Measures are being taken to prevent occupational diseases and injuries;
- Checking the OSMS. Both current and reactive control are provided. An OSMS audit is being carried out.
- Functional analysis.
The employer needs to analyze the work of the OSMS at certain intervals, as this will ensure its constant adequacy of the situation and effectiveness. During the analysis, opportunities for improvement and the need for changes are necessarily assessed.
The following information is used for analysis:
- audit results;
- complaints and other communications from interested parties;
- enterprise performance in the field of occupational safety;
- the degree of fulfillment of the goals set for the OSMS;
- the results of investigations carried out at the enterprise, as well as actions to correct and prevent industrial injuries;
- results of previous analyses;
- description of changing circumstances, including new legal requirements;
- list of recommendations for improvement.
After the analysis, decisions may appear or actions may be taken aimed at changes in the parameters of the OSMS, which are aimed at improving it. In this case, all conclusions must be documented and brought to the attention of responsible persons and the labor protection committee.
Development of a training and knowledge testing program in occupational safety
The organization must create a list of employees who need to undergo an occupational safety knowledge test. It is also necessary to approve the training program, develop exam papers and a schedule for testing knowledge. The inspection commission draws up a protocol and enters information about the inspection into the certificate of the established form.
Occupational Safety Training: Questions and Answers
Three Types of Training You Should Know!
Civil defense training
Structure of Methodological Recommendations for checking the OSMS in an organization
The document consists of the following sections and appendices:
I. General provisions.
II. Algorithm for checking the creation and operation of a labor safety management system:
Description of the main elements of the Algorithm for verifying the creation and ensuring the functioning of the occupational safety management system.
III. Algorithm for checking the creation and operation of a labor safety management system during an accident investigation.
IV. Filling out individual paragraphs of the report on the investigation of a group accident (serious accident, fatal accident) form 4.
V. Inspector response measures when identifying violations of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
Appendix - Flowchart.
Regarding the Flowchart. In accordance with paragraph 7 of the Methodological Recommendations, state labor inspectors are invited to organize an inspection based on a sequential consideration of a set of interrelated and interacting elements that form the OSMS, given in the Flowchart, namely:
a) the main elements that make up the OSMS (Block A of the Flowchart);
b) procedures related to the specifics of the employer’s economic activity, the implementation of which is necessary to establish goals and objectives in the field of labor protection, as well as to introduce in the organization the prevention and prevention of industrial injuries and occupational morbidity (Block B Flowcharts);
c) procedures that must be implemented by the employer to ensure compliance with state regulatory requirements for labor protection, as well as the safety and health of workers in the process of work (Block B Flowcharts).
In accordance with paragraph 8 of the Methodological Recommendations, it is proposed to divide an unscheduled inspection of an employer into 2 parts:
Part 1 - checking the OSMS documents;
Part 2 - checking workplaces.
At the same time, as part of the verification of OSMS documents, it is recommended to study the requested local regulations of the employer and other documents (magazines, acts, registers, etc.) confirming the compliance of the OSMS created with the requirements of the Standard Regulations of the OSMS and other regulations containing state regulatory requirements for labor protection .
As part of the inspection of workplaces, it is recommended to assess the compliance of these workplaces, equipment, vehicles, territories, buildings, structures, production and technological processes with state regulatory requirements for labor protection, as well as the practical implementation of OSH procedures.
Want to know what safety legislation changes have occurred in 2021? Come to our online conference! Participation is free.
Carrying out medical examinations
It is necessary to organize a preliminary (upon hiring) medical examination of the employee. Next, it is imperative to develop a list of employees and a schedule for periodic medical examinations, issue an order for medical examinations, and create a list of jobs that require a medical examination.
How to correctly formulate a contingent for a medical examination?
Mandatory psychiatric examination of workers (part 1)
Mandatory psychiatric examination of employees of public safety organizations (part 2)
The whole truth about medical examinations of employees
Changes in the procedure for conducting medical examinations of office workers
Development and approval of instructions and activities on occupational safety
It is necessary to develop, approve, and issue labor safety instructions to workplaces. All employees, without exception, must be familiar with labor safety instructions.
Planning occupational safety measures: starting work correctly
Development of labor protection instructions
Consolidated reporting calendar for 2021
Main tasks of labor protection
Occupational safety and health is a system aimed at ensuring a safe production process, preserving the health and life of the organization’s employees. It includes activities of a legal, social, economic, sanitary, hygienic, psychophysical, therapeutic, preventive and rehabilitation nature.
Occupational safety is aimed at studying occupational hygiene and reducing the impact of harmful production factors on the body of employees. The main method of OT is to use safety technology by creating or rebuilding special protective equipment, training manuals, machines and tools for safe work. The main task of labor protection is to achieve a reduction in the number of accidents and occupational diseases, ensuring labor safety by all available methods.
FROM
Providing workers with PPE
It is required to compile a list of professions and categories of workers who need personal protective equipment, timely fill out applications for receipt and maintain records of the issuance of personal protective equipment.
Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 9, 2014 No. 997n - Standard standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to workers in cross-cutting professions and positions of all types of economic activity
PPE issuance registration card
Selection of respirators for respiratory protection
Conducting a special assessment of working conditions
A special assessment of working conditions (SOUT) must be planned from the very beginning of the organization of production or enterprise activity. The employer is given 12 months to do this from the moment the new jobs are created.
It’s worth starting by issuing an order to create a commission on SAW and developing a list of jobs that need to be assessed. This work also includes concluding an agreement to conduct an assessment by a specialized organization, drawing up maps, protocols and reports of special equipment, creating lists of those entitled to additional leave and additional payments for working with harmful and (or) hazardous production factors.
Federal Law “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” dated December 28, 2013 N 426-FZ
Questions and answers on special assessment of working conditions
Article 216.1. State examination of working conditions
(introduced by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
State examination of working conditions is carried out by the federal executive body authorized to carry out federal state supervision over compliance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, and by executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in the field of labor protection in the manner established by the authorized Government of the Russian Federation federal executive body.
(as amended by Federal Laws dated July 23, 2008 N 160-FZ, dated July 18, 2011 N 242-FZ)
The provisions contained in part two of this article do not apply until July 1, 2012 in relation to documents and information used in the framework of public services provided by executive bodies of state power of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation or territorial state extra-budgetary funds, and municipal services, and in relation to documents and information at the disposal of state bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local government bodies, territorial state extra-budgetary funds or organizations subordinate to state bodies or local government bodies involved in the provision of state or municipal services (Part 5 of Article 74 of the Federal Law of 01.07.2011 N 169 -FZ).
If the documentation and materials for conducting the state examination of working conditions were not submitted by persons entitled to apply for a state examination of working conditions, the bodies authorized to conduct the state examination of working conditions independently request the specified documentation and materials from the bodies and organizations in in respect of which a state examination of working conditions is carried out, as well as in bodies providing public services, other government bodies, local government bodies and organizations subordinate to state bodies or local government bodies, if the specified documentation and materials are at the disposal of such bodies or organizations in accordance with regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal legal acts.
(Part two introduced by Federal Law dated July 1, 2011 N 169-FZ)
State examination of working conditions is carried out in order to assess:
quality of certification of workplaces based on working conditions;
the correctness of providing compensation to employees for hard work, work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions;
compliance of construction projects, reconstruction, technical re-equipment of production facilities, production and implementation of new equipment, introduction of new technologies with state regulatory requirements for labor protection;
actual working conditions of workers, including in the period immediately preceding the industrial accident.
State examination of working conditions is carried out on the basis of determinations of judicial bodies, appeals from executive authorities, employers, associations of employers, workers, trade unions, their associations, other representative bodies authorized by employees, bodies of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation.
Persons carrying out state examination of working conditions have the right:
in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, freely, with a standard identification card, visit any employers (organizations, regardless of their organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership, as well as employers - individuals) to carry out an examination;
request and receive free of charge the documents and other materials necessary for the examination;
carry out appropriate observations, measurements and calculations with the involvement, if necessary, of research (measuring) laboratories accredited in the manner established by federal laws and other regulations of the Russian Federation.
Persons carrying out state examination of working conditions are obliged to:
draw up, based on the results of the examination, conclusions on the compliance (non-compliance) of working conditions with state regulatory labor protection requirements and send these conclusions to the court, executive authorities, employers, associations of employers, employees, trade unions, their associations, other representative bodies authorized by employees, bodies Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation;
ensure objectivity and validity of the conclusions set out in the conclusions;
ensure the safety of documents and other materials received for the examination and the confidentiality of the information contained in them.
Conducting an assessment of the level of professional risk
In accordance with Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as with the standard provisions on the OSH (occupational safety and health system at the enterprise), it is necessary to develop and approve procedures for managing professional risks. Risk management means: identifying risks, assessing possible levels of hazards in workplaces, taking possible measures to reduce the level of possible risks and periodically monitoring the effectiveness of mitigation measures and current risk levels in workplaces.
Occupational risk assessment: what, why and how?
How will they be punished for OSHS in an organization?
Since the document is not scanty in content (about 30 pages), I will give only its motivating part, namely the fifth section - Inspector response measures when identifying violations of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
Here are the proposed response measures for detecting violations in terms of SOUT:
16. Issuance of orders to eliminate identified violations.
16.1. In the order issued after completion of the investigation, it is advisable to indicate the elimination of not only the violations that were the immediate causes (main), but also the violations that were the root causes (associated).
16.2. In the order issued after the completion of an unscheduled inspection, it is advisable to indicate the elimination of not only violations of state regulatory requirements for labor protection, but also the requirements of the employer’s local regulations, as well as violations related to OSH.
17. Bringing to administrative responsibility.
In accordance with Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to ensure the creation and operation of an OSMS, also in accordance with paragraph 2 of the Model Regulations, the creation and operation of an OSMS is carried out by the employer through compliance with state regulatory requirements for labor protection, taking into account the specifics of its activities, the achievements of modern science and the best practices adopted in obligations and on the basis of international, interstate and national standards, guidelines, as well as recommendations of the International Labor Organization on OSH and industrial safety.
Based on the above, it is obvious that violations in terms of failure to comply with the requirements of the Model Regulations, the absence of any elements of an OSMS, local regulations of the employer (must be developed in order to implement the requirements of the Model Regulations), as well as failure to comply with local regulations of the employer on the OSMS (if they are adopted) are violations of Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, for which liability is provided for in Article 5.27.1 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses (hereinafter referred to as the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, it is worth considering the fact that for some violations liability is provided for by different parts of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, for example:
The following violations were identified: in the employer's OSHS regulations there is no procedure for providing workers with personal protective equipment, flushing and neutralizing agents (clause 8, paragraphs 45 - 47 of the Model Regulations) (if the procedure is included in the OSHS regulations, then elements of this procedure may be missing), and workers are not provided with personal protective equipment.
Thus, it is advisable to bring the perpetrators to administrative liability as provided for in Part 1 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - for the lack of a procedure (or elements of the procedure) and Part 4 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - for failure to provide workers with personal protective equipment.
The same algorithm can be used for the procedures for training workers on labor protection, organizing and conducting assessments of working conditions, organizing and monitoring the health status of workers.
Using this example, let’s refresh our memory on the line of fine amounts:
Part 1 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Violation of state regulatory requirements for labor protection contained in federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, with the exception of cases provided for in parts 2 - 4 of this article, entails a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine:
- for officials in the amount of two thousand to five thousand rubles;
- for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from two thousand to five thousand rubles;
- for legal entities - from fifty thousand to eighty thousand rubles.
Part 4 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Failure to provide workers with personal protective equipment entails the imposition of an administrative fine:
- for officials in the amount of twenty thousand to thirty thousand rubles;
- for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from twenty thousand to thirty thousand rubles;
- for legal entities - from one hundred thirty thousand to one hundred fifty thousand rubles.
Let us repeat that the OSMS in the organization will be thoroughly checked by the GIT in accordance with the Methodological Recommendations in two cases:
- when state labor inspectors conduct accident investigations;
- during unscheduled inspections due to an accident.
As part of scheduled inspections, GIT are required to be guided by checklists, namely, in the OSH topic, checklist No. 31, according to which the following is checked:
- The employer has a Regulation on the occupational safety management system approved by order;
- The employer has an Occupational Safety and Health Policy.
At the same time, the Occupational Safety and Health Policy may be included in the provisions on OSH. This was discussed in the article - Occupational Safety and Health Policy and how to implement it.
Next, I suggest you download the Methodological Recommendations for checking the creation and operation of an OSMS in MS Word format and familiarize yourself with the document more thoroughly. Comments on this topic are very, very welcome!
DOWNLOAD DOCUMENTS
Order of Rostrud dated March 21, 2019 No. 77 “On approval of Methodological Recommendations for verifying the creation and functioning of a labor safety management system”
Organization of monitoring the state of working conditions in the workplace
The employer is obliged to monitor the state of working conditions in the workplace, maintain appropriate control logs, draw up quarterly reports and plan measures to eliminate identified deficiencies. This obligation is enshrined in Art. 212 TK. RF.
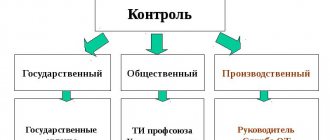
Occupational Safety and Health Commission
Production control: answers to questions
Monitoring working conditions at workplaces
What is the occupational safety and health department at an enterprise?
Enterprises are developing special OHSMS services (“occupational safety management system”), they are engaged in resolving conflicts, monitoring the legality of the production process, working conditions and finding profitable solutions to improve working conditions.
The service is created as a subsystem within the company itself and includes representatives from employees and employers. The main thing is that the activity should not contradict the law and worsen the social climate at the enterprise.
Work at the enterprise
Investigation and recording of accidents
To investigate accidents, an investigation commission is approved by order of the head. It is also necessary to document all investigation materials, create reports, and keep logs.
Just in case: an accident without permission
Accident investigation: list of questions
Investigation of student accidents
21 examples of fines for an accident
Payments in case of an accident at work
Carrying out work to ensure electrical safety
It is necessary to appoint a person responsible for electrical equipment, develop a list of professions and positions assigning them the corresponding electrical safety group, monitor the condition, create acceptance certificates and develop operating instructions for electrical equipment, electrical installations, buildings and structures.
Electrical safety instructions. Procedure and form of conduct
Typical violations of labor protection, electrical and fire safety requirements in a preschool institution
Carrying out fire safety work
It is required to issue an order on the fire safety regime in the organization, appoint those responsible for fire safety, develop evacuation schemes, means of agitation and arrange fire safety corners, monitor the maintenance of primary fire extinguishing equipment, form voluntary fire brigades, plan measures to ensure fire safety, and issue work orders in a timely manner -permits for hot work and keep a log of their registration.
Fire safety briefings: types, procedure, frequency
Everything you need to know about a fire extinguisher
Fines for violating fire safety requirements in 2020
Fire safety at school
Fire drills at school and preschool educational institutions