To ensure sanitary standards in organizations and enterprises, it is necessary to regularly clean premises. Mandatory cleaning areas are:
- workplaces;
- rest areas for workers;
- toilets and showers;
- places for eating and preparing food;
- warehouses;
- industrial premises;
- stairs, lobbies, halls;
- elevators;
- basements.
If the organization’s field of activity is food production, then in addition to routine cleaning, regular disinfection of all work surfaces, floors and walls must be carried out. This is necessary for storing food and will eliminate the likelihood of pathogenic bacteria and fungi appearing.
What cleaning work needs to be done
All organizations can be divided into several categories depending on the type of waste, according to which the cleaning standards for industrial premises per person are calculated. These are the productions:
- no waste;
- producing wood waste;
- producing liquid, lightweight and bulk waste;
- with metal waste;
- with fireproof waste, peat and coal dust.
To determine standards, cleaning is conventionally divided into basic and additional. The main ones include:
- sweeping and washing floors;
- garbage collection near workplaces;
- changing the cleaning solution;
- wiping and sweeping panels, window sills, heating pipes;
- delivery of waste to the designated location;
- cleaning sinks, taps and toilets.
Additional ones include:
- preparation of maintenance equipment and their delivery to and from the site;
- cleaning the janitor's workplace;
- receiving and handing over shifts;
- carrying out light repairs of equipment;
- And so on.
How often are rooms cleaned?
Full cleaning list:
- Floors must be wiped several times daily, or as needed.
- Shelves, walls and furniture are wiped down once a week on average.
- It is also necessary to remove objects and place them in their places every day.
- Furniture should be cleaned no more than once a week.
- Wipe window sills gently once a week.
- Cleaning of pipes and utility systems is carried out much less frequently - 4 times a year.
- Washing windows and wiping the ceiling - at least 2 times a year.
What standards exist for cleaning office premises?
If an organization cleans all premises on its own, then it must clearly define the job responsibilities of its premises cleaners. Each organization develops its own standards for cleaning office premises. Since the norms for the area to be cleaned relate to labor standards, they must be enshrined in the employer’s local regulations, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of workers (if one exists). This follows from articles 160, 162 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. They can also be enshrined in a collective agreement in accordance with Articles 40 and 41 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is also necessary to specify these standards in the employment contract or job description of the employee. Since the current legislation does not strictly provide for norms, one can focus on the norms approved in the USSR.
In order to develop such standards, you can focus on the following documents:
- Resolution of the USSR State Labor Committee of December 29, 1990 N 469 “On approval of time standards for cleaning office and cultural premises”;
- Resolution of the State Labor Committee of the USSR, the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated September 18, 1985 N 321/19-28 “On approval of standard service standards for cleaners of industrial premises of industrial enterprises”;
- Recommendations for standardization and remuneration of labor for workers in hotels, bathhouses and laundry facilities and funeral services for the population, approved by Order of the Ministry of Construction of Russia dated November 15, 1994 N 11;
- Standards of service for workers engaged in sanitary maintenance of households, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated June 24, 1996 N 38;
- Recommendations for determining the staffing level of employees of budgetary organizations based on labor standards approved by Roszdrav;
- Order of the Ministry of Justice of Russia dated 08/04/1999 N 227 “On organizational and staffing issues at training centers (points) of the penal system of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation”;
- Order of the Ministry of Culture of the USSR of October 19, 1984 N 552 “On approval of the standard staff and management structure of secondary specialized educational institutions of the system of the Ministry of Culture of the USSR and staffing standards for service personnel in hostels of these educational institutions”;
- Order of the USSR Ministry of Culture dated May 30, 1980 N 311 “On approval of temporary standard staff of rural centralized club systems of the USSR Ministry of Culture.”
How much equipment and detergents should be spent
To determine standards for the use of detergents, a special commission is created, which calculates the consumption of funds. To calculate, actual costs and engineering calculations are taken. To make it easier to develop space standards for office premises cleaners, you can use Order 1122 N. Also, manufacturers of household chemicals write recommendations on the expenditure of funds and the amount of product used for each cleaning.
Staff only
Note! The standards will differ for premises for different purposes: office and industrial. As a rule, labor standards for office cleaners in 2019 imply consumption is 2 times less due to the greater amount of dirt formation.
Some areas require special cleaning products. And the products should be different for different surfaces. The norm implies the number of days during which the product will be spent.
Standards for cleaning office premises per employee
Standards for cleaning premises per employee are set by organizations, as we have already understood, independently. Standards can be set based on the cleaning area per shift, or expressed in minutes per square meter. They may depend on the cleaning area, the clutter of the room being cleaned, and the type of waste being removed. Norms are also calculated taking into account the time spent on performing primary and additional work. Standards for cleaning industrial premises per person vary over a fairly wide range. The calculation can be made based on 400 sq. m. up to 1000 sq. m per person. If the occupancy is minimal, then the standard of service is approximately 560 sq.m. per shift per person, and if there is maximum occupancy, then the norm will already be 320 sq.m. per shift per person. For toilets the norm is 200 sq.m./shift per person, for showers – 300 sq.m./shift per person.
Norms can also be set based on the cleaning time of 1 square meter. With this approach, the norms can be determined as follows, for example, 0.2 minutes per 1 sq.m. for washing the floor using detergents or sweeping 0.6 min per 1 sq.m. For other enterprises, this indicator can be set depending on the mass of garbage removed per 100 square meters. m. So, with a mass of waste removed up to 50 kg, the sweeping rate without moistening will be, for example, 0.15 min, and with a mass of 120 to 200 kg - 0.35 min.
For premises cleaners, it is advisable to develop a cleanliness map for each zone, which can reflect the work route, the boundaries of the area, the frequency of cleaning, the types of work and the means used for them, and the time to complete these works. For employees to work effectively, it is also necessary that facilities maintenance supplies are stored in a special place and delivered by the premises cleaner to the work area independently.
Ventilation standards for premises in kindergartens
Children are the most vulnerable part of the country's population. They need constant monitoring, as well as monitoring their health. A growing body needs a constant supply of fresh oxygen and for this reason a special ventilation schedule was created in kindergarten according to Sanpin standards. An example of which can be expressed in the following rules:
- Airing or ventilation of the room in children's groups should be done at least once an hour;
- It is necessary to renew the air space with fresh air, taking into account the temperature outside;
- If the temperature outside the window is below 10 degrees Celsius, then in this case the fresh air circulation should be carried out as follows: in the morning, before the children arrive, air for 5-10 minutes; every hour and a half - open the window for one minute. It is worth remembering that children should not be near an open window with frosty air and conditions for a draft should not be created. It is advisable to transfer children to another room while airing.
Ventilation in a kindergarten must be carried out in accordance with the rules and regulations - If the temperature outside the window is from minus 5 to minus 10 Celsius, then ventilation should be done in the morning and evening, in the absence of children - 10-15 minutes. And while the group is in the room - one to two minutes every hour and a half.
- If the air temperature outside corresponds to parameters from zero to minus five degrees Celsius, then in this case ventilation is carried out as follows:
- morning, evening - 15-20 minutes before children arrive and leave the kindergarten; during classes and games - every hour and a half for 2-5 minutes.
- In the spring and autumn seasons, when the air temperature corresponds to parameters from zero to +5 degrees, ventilation is carried out much more often and longer: 3-7 minutes every hour and a half; 20 minutes before the group arrives and leaves; in warm weather from plus five degrees Celsius, ventilation of the room in the kindergarten should be done for 5-10 minutes every hour and at least 20 minutes before the arrival and departure of the group.
Ventilation is a very important aspect for the well-being of children
We can say that for a child’s body, the supply of fresh oxygen is a basic need for development and well-being. Air space that does not contain a large amount of carbon dioxide has a beneficial effect on the activity and curiosity of children, which all educators and parents should remember.
Detergent consumption rates
There are approximate consumption standards for detergents. Of course, they do not reflect all the needs of the organization, but they can be guided by. Typical detergents are:
- toilet soap, laundry soap;
- washing powder;
- buckets;
- brushes;
- toilet brushes;
- dust cloths;
- mops;
- brooms;
- scoops;
- rubber gloves;
- a variety of detergents and cleaning products.
Inventory is counted in pieces per person for a certain time. For an area of 400 square meters, the following amount of funds and equipment is required:
- washing powder – 1 kilogram;
- toilet soap – 200 grams;
- laundry soap – 400 grams;
- broom – 2 units for 30 days;
- brushes – 1 unit for 60 days;
- scoops – 1 unit for six months;
- rubber gloves – 1 unit for 30 days.
As for detergents and cleaning products, their consumption can be calculated based on the manufacturer’s recommendations, which are indicated on the label.
Who can clean office premises?
The law does not establish requirements for technical workers, their qualifications, work experience or education. Every company, entrepreneur and self-employed person has the right to determine who will clean the premises they occupy. The decision may be influenced by factors such as occupied space, financial well-being, and the specifics of the business entity’s activities. In general, there are 3 schemes that users of offices and industrial premises can resort to to maintain cleanliness:
- Small premises can be serviced by employees themselves, whose job responsibilities do not directly include cleaning, but may include the responsibility of maintaining the cleanliness of their workplace. Since there is no official technical employee in such companies, there is no need to regulate his activities with internal documents.
- The most common way to clean premises used for business and other activities is to employ a separate cleaner on staff. In this case, the work in the organization for such an employee may be the main one, or (if, for example, the areas are not large enough) he may be hired for part-time work. He can also perform work throughout the entire working day, or he can be hired only for a certain number of hours (part-time). Such work is regulated by local acts of the organization, taking into account current legislation and regulations.
- Concluding a contract for cleaning premises with a specialized organization. Since in this case the workers cleaning up are not part of the staff of the organization they are cleaning up, the latter is not responsible for them and their work. In such a situation, the work of technical workers is regulated by their employment contracts with the cleaning company and its internal documents.
SanPiN requirements for office premises: harmful factors when working with PCs
When working with a computer, employees are exposed to a number of harmful or dangerous influences:
- Electromagnetic radiation. May be caused by a missing or faulty grounding device.
- If the workplace is not organized correctly, static electricity may accumulate.
- The air environment is not sufficiently ionized.
- Since the worker is in a static position for a long time, this kind of load affects the body. At the same time, they can cause severe pain in the lumbar region, obstructed outflow of venous blood, depression and stress.
- Loads on the organs of vision.
These are physical factors whose indicators must be brought to normal. This is the employer's responsibility.
In which areas of the enterprise cleaning is mandatory?
Keeping the premises of an enterprise and the workplaces of its employees clean is the responsibility of the employer, arising not only from the duty of respect and care for employees, but also from the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, the employer is obliged to provide the everyday needs of his workforce and normal and safe working conditions. It is obvious that in order for employees to be healthy and able to work under normal conditions, regular cleaning of the premises should be ensured.
All premises in which employees carry out their work function, stay temporarily, and use them are subject to cleaning at one frequency or another. Such premises include:
- production;
- office (offices);
- public areas (corridors, elevators);
- sanitary facilities (premises for eating, sanitary rooms);
- warehouses and basements, etc.
The list of mandatory types of cleaning work is determined by departmental regulations and local instructions of the enterprise itself.
Important!
When engaging a third-party organization, the entire cleaning technology, as well as the list of objects that must be cleaned, indicating the corresponding areas, must be specified in the text of the contract (or provision of services) or as an appendix to it.
Ventilation system in office premises
Open windows promote ventilation. However, a lot of dust gets inside, and drafts “walk” around the room. Workers breathe polluted street air. The sad result is a lot of sick leaves on the manager’s desk. The ventilation system in office premises solves several problems at once and has many advantages.
Seven reasons to install:
- Creating the necessary conditions for high-quality work of the staff, which ensure the well-being of employees, helps reduce the number of colds.
- Improving the general tone of people's bodies and mental activity.
- Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity.
- Economical energy consumption.
- Reducing noise and dust levels in the office.
- Filtration of foreign odors, exhaust air outflow.
- Harmonious combination with the interior.
General requirements for cleaning office premises
Of course, any labor function is performed by an employee based on his job description. The same applies to cleaners, especially when it comes to manufacturing and similar enterprises. When hired and signed an employment contract, the employee gets acquainted with his job responsibilities against signature, and a copy of the job description is given to him so that he can always update his memory of what is included in his job function.
Important!
Currently, there is not a single regulatory document defining the rules for cleaning premises, or any standards and requirements. All existing documents have either lost their validity or are used solely as recommendations, but not mandatory. In this regard, the system for standardizing the work of a technical worker, as well as his job responsibilities, must be developed by each organization independently. When developing such a local act, it is possible to rely on the existing recommendations of government bodies in this area.
Work technology and labor organization
So, we can outline the following rules that must be followed by technicians, applicable to any premises:
- The responsibilities of the corresponding employee are divided into basic (direct actions to restore cleanliness) and additional (preparing detergents and cleaning products, preparing equipment, cleaning the office premises of the technical worker himself).
- An employee's inventory list consists of the types of work he needs to perform.
- Cleaning products should be stored in a separate room or specially equipped place (for example, a closet).
- Waste (if any) should be collected during the first stage of cleaning.
- Wet cleaning begins with the floor, which is divided into sections of no more than 12 m2.
- This is followed by wet cleaning of window sills, heating radiators and other surfaces in the room.
- The walls must be washed using special detergents, and the water itself must be changed as it becomes dirty.
- The waste is transferred by the cleaner to the place where it is stored or disposed of according to other rules (for example, placed in a garbage container).
Internal regulations of an enterprise may establish other rules or specify the above ones, taking into account the specifics of its activities. One way or another, the more detailed the cleaning technology is described, the less chance of a conflict arising in the future.
On the one hand, the employer does not have the right to demand the performance of actions that are not determined by the labor function (not specified in the contract or instructions). On the other hand, the employee is not obliged to fulfill newly arising requirements or remove additional areas, unless this is stipulated in his contract, and he was not notified of the expansion of duties 2 months in advance.
General requirements for workplace organization
When organizing a workplace, the main goal for the employer is to ensure high-quality and efficient performance of work by the employee while making full use of the equipment assigned to him in compliance with the established deadlines. In this regard, the workplace is subject to organizational, technical, ergonomic, sanitary, hygienic and economic requirements.
One of the most important requirements when organizing a workplace is to ensure safe, comfortable working conditions, and to prevent the occurrence of occupational diseases and accidents. It should be noted that the employer needs to organize workplaces, taking into account not only the specific type of activity, qualifications, but also the individual physical and psychological characteristics of each employee.
General requirements for the organization of workplaces are regulated by the Labor Code, sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations (SanPiN), as well as other legal documents.
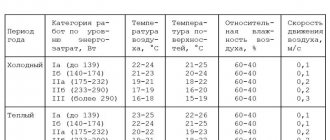
Currently, SanPiN 2.2.4.335916 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for physical factors in the workplace” is in force, approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated June 21, 2016 No. 81 (intended for citizens in labor relations, individual entrepreneurs and legal entities) . This document establishes sanitary and epidemiological requirements for physical factors of a non-ionizing nature in the workplace and the sources of these physical factors, as well as requirements for the organization of control, methods for measuring physical factors in the workplace and measures to prevent the harmful effects of physical factors on the health of workers.
In Letter dated February 10, 2017 No. 0924381716, Rospotrebnadzor indicated that from January 1, 2021, the previously valid SanPiN 2.2.4.54896 “2.2.4. Physical factors of the production environment. Hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises" (approved by Resolution of the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation dated October 1, 1996 No. 21) are applied to the extent that does not contradict SanPiN 2.2.4.335916.
The following sanitary standards and rules also apply to office workers:
- SanPiN 2.2.0.55596 “Occupational hygiene. Hygienic requirements for working conditions for women" (approved by Resolution of the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation dated October 28, 1996 No. 32);
- SNiP 2.09.0487 “Administrative and domestic buildings” (approved by Decree of the USSR State Construction Committee dated December 30, 1987 No. 313);
- SanPiN 2.2.4.129403 “2.2.4. Physical factors of the production environment. Hygienic requirements for the aeroionic composition of air in industrial and public premises" (approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation on April 18, 2003).
When working with a PC, you must additionally be guided by the following documents[1].
| Title of the document | Brief description of the circle of persons and (or) the list of objects in respect of which mandatory requirements are established |
| SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and organization of work” (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated 06/03/2003 No. 118) | Establish sanitary and epidemiological requirements for personal electronic computers (PCs) and working conditions |
| SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.219807 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization. Amendment No. 1 to SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003" (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated April 25, 2007 No. 22) | Amends SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003 regarding the operation of PCs in rooms without natural light |
| SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.262010 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization. Amendments No. 2 to SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003" (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Inspector of the Russian Federation dated April 30, 2010 No. 48) | Amends SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003 regarding instrumental monitoring and assessment of the levels of electromagnetic fields (EMF) from PCs |
| SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.273210 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization. Amendments No. 3 to SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003" (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated 09/03/2010 No. 116) | Amendments are being made to SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.134003 regarding the approval of the use of multi-lamp luminaires with electromagnetic ballasts |
| SanPiN 2.2.2.133203 “Hygienic requirements for organizing work on copying and duplicating equipment” (approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2003 No. 107) | Establish requirements for designed, built, reconstructed and existing production facilities, workshops, areas, individual premises with permanent and non-permanent workplaces, including a single set of copying and duplicating equipment. Designed for organizations that have the above-mentioned production facilities, as well as for design, construction and other organizations involved in the design, construction, reconstruction and operation of institutions where copying equipment is used |
If situations arise that are not regulated by SanPiN (the toilet is faulty, the roof is leaking, etc.), the employee has the right to refuse work. In this case, the employer is obliged to offer him other employment until the problem is resolved. Otherwise, according to Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to declare downtime with the payment of a penalty in the amount of at least 2/3 of the employee’s average salary.
Providing conditions for eating. The procedure for eating in the workplace is regulated by Art. 108 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, SNiP 2.09.0487:
- if the number of employees is less than 10 people, a space of at least 6 square meters is required. m, equipped with a dining table;
- with up to 29 employees, the required area is twice as large;
- if the enterprise employs up to 200 employees, it is obligatory to have a canteen-serving area;
- if the number of employees exceeds 200 people, the canteen must be provided with raw materials or semi-finished products.
Employer's liability. If the employer violates the established norms, the employee has the right to appeal to the trade union (Article 370 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the labor dispute commission (Article 385 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the State Labor Inspectorate in the subject of the Russian Federation (Articles 356-357, 360 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the court (Article 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) or the prosecutor’s office in a subject of the Russian Federation (Articles 10, 21 of the Federal Law of January 17, 1992 No. 2202I “On the Prosecutor’s Office of the Russian Federation”).
Administrative liability of the employer for violation of legally established standards and labor protection requirements is in the form of a fine in the amount of 2,000 to 200,000 rubles. (depending on the type of violation) or suspension of activities for a legal entity for a period of up to 90 days (part 1, 5 of article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).