When I was just starting my career in occupational safety, I had a lot of questions about how to properly organize the procedure for training workers in occupational safety at an enterprise, who needs to be trained and with what frequency.
There are small details that you begin to learn about only when you have already “got your head,” and not with the help of Resolution 1/29 “On approval of the Procedure for training in labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees of organizations,” which would be much easier.
So, in order for you to overcome difficulties and simplify your everyday life, we will consider training in occupational safety and health in an organization step by step with samples of completed documents, examples from personal experience and links to laws.
If you have anything to add or maybe just want to share your personal experience on how to avoid mistakes, I invite you to comment - it will be useful for everyone.
Who is responsible for preparation?
Occupational safety is an important component of any technological process, and it is not for nothing that management pays close attention to this. The main person responsible for maintaining this area is the OT engineer. The employer should treat the selection of such personnel with special attention, since the responsibility assigned to them is quite large.
The person responsible for conducting occupational safety training will help you avoid missing deadlines.
All specialists, management, as well as employees of an enterprise or other organizational structure must undergo periodic training.
To avoid missing deadlines for the next certification, it is recommended that the organization’s management take care of this in advance and appoint a person responsible for organizing and conducting training.
They can be assigned to any of the employees, for example, an occupational safety specialist or a human resources inspector.
How to monitor the implementation of the plan
An occupational safety specialist must regularly check the state of labor conditions and safety in the departments of the enterprise. For violations, officials and other responsible employees are issued orders with specific proposals and requirements to eliminate the identified violations. For each item of the order, a specific deadline for its implementation should be indicated. In order to involve the enterprise's trade union committee in monitoring the implementation of the labor protection work plan, it is recommended to give it a copy of the order. In the process of further work, the labor protection specialist provides methodological assistance to department heads in resolving issues specified in the instructions, informs the employer about the state of labor conditions and safety at the enterprise and proposes specific measures to eliminate shortcomings in labor protection. Upon completion of the survey, it is recommended to consider its results at a meeting with management employees of the enterprise, responsible engineering and technical workers and the trade union activists of the enterprise. The issue of drawing up a labor safety plan was considered by the head of the labor safety department of the State Unitary Enterprise MO "MOBTI" Ekaterina Zubareva. We also offer occupational safety plans in MS Word format.
DOWNLOAD SAMPLES
Plan of organizational measures to improve working conditions and safety
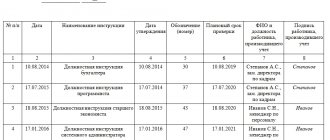
Sample occupational safety training schedule
The schedule for testing knowledge on OT can be arranged as follows:
- in the first column indicate the number in order;
- the second column contains information with the employee’s last name and initials;
- the third indicates the position held;
- then in the fourth the identification number is written;
- the fifth column contains the date when the knowledge test was conducted;
- in the sixth - the date of the next inspection.
Visually it might look like this:
| No. | Last name, initials | Position or profession | Certificate number | Certification date | Next certification |
| 1. | Ropanov Oleg Grigorievich | Senior master of forging and stamping production | 2–20-OT | 12.02.2015 | 12.02.2018 |
This form is approximate; another one can be developed, since there are no clear regulations for registration.
For information on organizing occupational safety training taking into account modern legal requirements, see here:
Commission for testing knowledge of labor protection requirements
In order to comply with the requirement of the Labor Code regarding occupational safety training, it is not necessary to send all employees to a training center and spend a lot of the employer’s money. The law does not prohibit saving.
For this purpose, a commission is created to test knowledge of labor protection requirements. The chairman must be the head of the organization or his deputy. You have every right to include a labor protection specialist, engineering specialists, for example, a chief engineer, a technologist, a mechanic, a power engineer, and so on, as members of the commission.
And also if there is a trade union at the enterprise, then a representative of the trade union or a representative of the interests of workers from your organization can take part in the work of the commission.
All members of the commission must be trained at a training center on labor protection. Otherwise, the protocol will be considered invalid.
An important point when preparing an order is the number of members. Three employees is the minimum number. You can read about this in paragraph. 1 clause 3.4 of the Training Procedure 1/29.
But I want to draw your attention to an important discrepancy. In para. 1 clause 10.7 GOST 12.0.004-2015 the commission must consist of at least five people, three of whom must be present at the knowledge test. So what is it really like?
The main document regulating the issues of occupational safety training is the Training Procedure. It is registered with the Ministry of Justice and is mandatory, but GOST 12.0.004-2015 is advisory. Of course, you can use it in your work, relying on the Procedure (Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated November 9, 2018 N 15-2/OOG-2749).
But in my practice, I always include at least five people in the commission, because there may be sick leave, business trips and other reasons why members may be absent, but a knowledge test must be carried out. Three out of five will probably be and that's enough.
At first, by the way, I doubted whether to count the chairman or only the members of the commission? A mistake is often made in the minutes - they include, in addition to the chairman, three members of the commission. This is a violation, because the chairman also makes the “Pass/Fail” decision and the number of votes and opinions must be odd.
The legal requirement to create a labor safety commission also applies to individual entrepreneurs - they must also conduct knowledge tests of their employees.
And if SOT is not provided due to the small number of personnel, then the commission can consist of only three employees. And they will be the chairman, his deputy and the secretary.
How to submit knowledge test results
Knowledge testing can take place either orally in the form of a question and answer, or in a test form. Based on the results, a protocol must be prepared, which must be drawn up in accordance with the form (clause 3.6 of Procedure No. 1/29).
Does it seem difficult to fill out the form? But very often mistakes are made, and if the inspector is principled, he may consider the protocol invalid and, moreover, issue a fine for violating the Training Procedure. Therefore, we prepare everything correctly and do not make mistakes. I will list the typical ones and those that I have encountered in practice:
- You cannot omit or omit the name of the occupational safety training program. Workers of several professions can take a knowledge test at once, and each of them must have its own protocol. It is also not allowed to list programs in one protocol separated by commas.
- The training hours are not indicated in the protocol, or they do not correspond to the number specified in the program.
- Protocols do not have serial numbers.
- It is necessary to fill in all lines and columns in the protocol; omissions are not allowed. In addition, it is also not allowed to edit the form at your own discretion, because it is mandatory.
- The protocol does not allow the use of abbreviations in recording positions, structural units, personal data of employees or members of the commission.
- The positions in the protocol must clearly correspond to the staffing table.
- Check the presence of all signatures in the protocol of both those being audited and members of the commission. Even if an employee “failed” the exam, he is required to sign an autograph.
Certificate of testing knowledge of labor protection requirements
In addition to the protocol, members of the commission prepare a certificate of successful inspection - a document confirming occupational safety training. It is considered valid if it contains the signature of the chairman of the commission and the seal.
When filling out, it is not allowed to shorten the name of the person being inspected and the position, or to make corrections with a pen; similar errors mentioned above are not made.
Employees of any enterprise who have successfully passed the knowledge test are required to have their ID with them at all times during working hours. In the event of an inspection, inspectors often ask employees of the organization to show their occupational safety certificate. And if he has nothing to show, then the government representative has every right to remove him from work without further thought. You will also face administrative liability.
It seems like a small thing, but it’s very unpleasant, considering the size of the fines. From my own experience, I found that it is difficult to convince employees to always carry their ID with them; they always left it in the locker. But several times they wrote explanatory notes due to absence and the situation changed. It is clear that these notes would not have been put into practice, but it was quickly possible to discipline employees without shouting and swearing.
The certificate form is mandatory and cannot be edited.
Working with a schedule
For the knowledge test schedule to really work, it must be used skillfully.
To do this you need:
- Look at it at least twice a month and make amendments. If a new employee appears or an employee is appointed to a new position, then during the first month of work he must be certified. This is the only way to ensure that you don’t miss a single employee’s certification and do everything in a timely manner.
- It is recommended to draw up a schedule at the end of the year for the next one, this will make it easier to navigate and plan the allocation of funds for training.
- It is recommended to draw up knowledge testing schedules in the same way according to the requirements of industrial safety rules.
Organization of training for blue-collar workers
- primary training in safe methods and techniques for performing work, providing first aid to victims - within a month after the worker is hired or transferred to another job. And if the work involves harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, then the employer must also organize an internship for the new worker at the workplace and pass exams;
- periodic training in safe methods and techniques for performing work and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for workers with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions;
- periodic, at least once a year, training of all workers to provide first aid to victims.
How often do you need to certify?
When drawing up a schedule, it is worth taking into account that certification occurs:
- Planned . Held once every three years. If an employee has not been certified in a timely manner, then he does not have the right to hold a position, as well as to conduct training and instruct workers at his site under his direct supervision.
- Unscheduled . This is a case when an unforeseen incident occurs - an accident, incident or emergency. And also if the employee was appointed to a different position, and it does not matter whether he had certification at that time or not, since the name of the position has changed and the previous knowledge test will not be valid.
Training and testing the knowledge of electrical personnel
Workers hired to perform work in electrical installations must have professional training appropriate to the nature of the work. In the absence of professional training, such employees must be trained (before being allowed to work independently) in specialized personnel training centers (training centers, educational and training centers).
Before being appointed to work independently or when transferring to another job (position) related to the operation of electrical installations, electrical personnel, as well as during a break in work as electrical personnel for more than 1 year, are required to undergo an internship (on-the-job training) at the workplace.
For training, the employee must be given a period sufficient to become familiar with the equipment, apparatus, operational schemes and at the same time study to the extent necessary for the given position (profession):
- rules for the design of electrical installations, safety rules, rules and techniques for providing first aid in case of accidents at work, rules for the use and testing of protective equipment, rules for labor protection during the operation of electrical installations;
- job and production instructions;
- labor protection instructions;
- other rules, regulatory and operational documents in force in this organization.
Training programs for electrical technical personnel, indicating the necessary sections of the rules and instructions, are drawn up by the heads (responsible for electrical equipment) of structural units and can be approved by the person responsible for the electrical equipment of the organization.
The training program for managers of operational personnel, employees from among operational, operational and repair personnel should include internship and knowledge testing, and for managers of operational personnel, employees from among operational, operational and repair personnel, also duplication.
An employee undergoing an internship (duplication) must be assigned by an appropriate document to an experienced employee in the organization (for managers and specialists) or in a structural unit (for workers).
The internship is carried out under the guidance of a responsible training employee and is carried out according to programs developed for each position (workplace) and approved in the prescribed manner. The duration of the internship should be from 2 to 14 shifts.
The head of an organization or structural unit may exempt from internship an employee who has at least 3 years of experience in his specialty and who moves from one workshop to another, if the nature of his work and the type of equipment on which he previously worked does not change.
Admission to an internship is issued by a relevant document from the head of the organization or structural unit. The document indicates the calendar dates of the internship and the names of the employees responsible for its implementation.
The duration of the internship is set individually depending on the level of professional education, work experience, and profession (position) of the student.
During the internship, the employee must:
- understand the requirements of operating rules, labor protection, fire safety and their application in the workplace;
- study diagrams, production instructions and labor protection instructions, knowledge of which is mandatory for working in a given position (profession);
- practice clear orientation in your workplace;
- acquire the necessary practical skills in performing production operations;
- study the techniques and conditions for trouble-free, safe and economical operation of the equipment being serviced.
Admission to duplication for operational personnel and independent work for administrative, technical and maintenance personnel is documented in the appropriate document for the organization.
After duplication, an employee from among the operational or operational-repair personnel may be allowed to work independently. Duration of duplication from 2 to 12 work shifts. For a specific employee, it is established by a decision of the knowledge testing commission, depending on the level of his professional training, length of service and work experience.
Permission to independent work for operational personnel is issued by a corresponding document from the head of the organization.
During the period of duplication, the employee must take part in control emergency fire drills with evaluation of the results and recording in the appropriate logs.
The number of training sessions and their topics are determined by the backup training program.
If during the duplication the employee has not acquired sufficient production skills or received an unsatisfactory assessment in emergency training, it is allowed to extend his duplication for a period of 2 to 12 work shifts and additionally conduct control emergency training. The extension of duplication is formalized by the relevant document of the organization.
If during the duplication period it is established that the employee is professionally unsuitable for this activity, he is removed from training.
During duplication, the trainee can carry out operational switching, inspections and other work in electrical installations only with the permission and under the supervision of the trainee. Responsibility for the correctness of the trainee’s actions and his compliance with the rules lies with both the trainee himself and the employee teaching him.