Help from a lawyer on this problem
Sooner or later, every person will retire. The size of the monthly social benefit for each pensioner is calculated individually and depends on a number of factors. One of them is the length of work experience.
Currently, Russian legislation has several definitions of length of service, or rather, its varieties. Each of these types gives the citizen the right to certain preferences in different areas of social security. So what is seniority, why is it needed and what types of it exist?
Types of work experience
According to labor legislation, today in Russia the following types of length of service are established:
- General.
- Special.
- Experience in a specific specialty.
- Continuous.
Total work experience refers to the entire duration of a citizen’s official work activity, from the first employment to retirement. The total length of service also includes some periods of time when a person de facto did not work for some good reason:
- Education in higher educational institutions.
- Leave to care for a child until he is one and a half years old.
- Leave due to pregnancy and childbirth (“maternity leave”).
- Temporary loss of work with official registration with the central bank.
- Compulsory service in the armed forces and other structures equivalent to them (internal troops of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the Russian Guard, border service).
- Caring for a disabled relative whose age has exceeded 80 years.
- Caring for a disabled minor child.
- Staying in the institutions of the Penitentiary Service (prison, correctional colony).
- Annual basic paid leave, leave at your own expense, sick leave.
- Wives of military personnel living with their husbands in remote garrisons without employment opportunities.
- Wives of diplomats living abroad without employment opportunities.
When calculating the total length of service, the time spent serving a prison sentence is counted only if the person was subsequently found innocent and rehabilitated. For women caring for young children, a maximum of 4 one-and-a-half-year periods are counted. That is, the time spent caring for the fifth and subsequent newborns will no longer be included in the total length of service. For wives of military personnel and diplomatic workers, this time limit is set at five years.
Special length of service was previously defined as a separately calculated type of length of service. This term, which appeared in the pension legislation adopted in 1990, is now excluded from the articles of the Law on Pensions. However, in fact, the provisions on special calculation of length of service continue to apply when calculating pensions in some sectors of the national economy. Thus, a special calculation of length of service is used for people employed in hazardous and hazardous industries, working in difficult climatic conditions (in the Far North and areas equivalent to it).
The length of service is considered continuous only if the period of time between dismissal from one place of work and employment in another does not exceed the established period. For different types of activities, this period may be different:
- 1 month is the standard period for workers and employees;
- 2 months - for persons who worked in the Far North after the end of the employment contract; for emigrants from other countries until employment in Russia; for persons who worked abroad in Russian companies, at the end of the contract.
- 3 months – for employees dismissed due to job elimination; for people with disabilities; primary school teachers.
Experience in a specialty determines the duration of work in a particular industry, in a particular position or profession. Allows you to determine a citizen’s work experience, and, consequently, the level of his labor skills when applying for a job.
Periods of activity
When calculating length of service, it includes the time during which the employee was engaged in work activities.
An important condition is the fact of payment of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund for it . In this case, not only periods of work on the territory of the Russian Federation, but also outside its borders (in some cases) can be taken into account.
The calculation may also include the following periods:
- undergoing military service (or other activities that are equivalent to it);
- care for each child until he reaches one and a half years old (but in total no more than 4.5 years);
- receiving unemployment benefits;
- caring for a disabled person or a person over 80 years of age;
- detention of illegally convicted citizens.
- receiving compulsory social insurance benefits in case of temporary disability;
- residence of military spouses together with their spouses in an area where there is no employment opportunity (but in total no more than 5 years).
An important condition for these periods to be included in the length of service is the mandatory official employment of the employee before their onset.
What does experience give?
Work experience, first of all, is necessary for calculating a pension to an employee. Not so long ago, its size and the worker’s retirement age completely depended on the duration and type of work experience. In recent years, in connection with the implementation of pension reform, the main factor influencing the size of the pension has become not the length of service, but the insurance period.
The insurance period begins to count from the moment a citizen concludes a pension insurance contract. A special personal account is opened for the insured citizen, to which the employer makes monthly contributions. Based on the amount accumulated by the time of retirement, the size of the basic pension paid to a person by the state will be calculated.
However, the length of work experience still continues to play a certain role in the calculation of pension payments. Let's consider what advantages this or that type of experience gives a person.
Calculation of work experience for individual entrepreneurs
An individual entrepreneur provides himself with the necessary work experience by paying the required insurance premiums. This length of service is the most important factor in determining the required pension.
An individual entrepreneur is recognized as an insured person when he makes all required payments for himself into the accounts of the pension fund. A pension is formed from a portion of such funds; for this reason, the periods of activity for which contributions are calculated and paid must be included in the length of service.
Keep in mind! The list of necessary documents to confirm the development of IP is present in Government Decree No. 555.
In accordance with the newly developed rules, the total length of service and the accrual of the required benefits for individual entrepreneurs are calculated in the same way as for employees. As a result of the reform, the required pension became an insurance one, as well as a funded one, the latter being formed from insurance payments and the profit received from their investment. Such a pension will be received by citizens at the age of 49 who have submitted an application for the transfer of a certain part of the insurance premiums paid to various non-state pension funds. Accrual is carried out according to previously existing rules.
The process of forming insurance-type pension accruals has changed significantly, so its size is influenced by the following factors:
- the amount of income of the individual entrepreneur for the annual period;
- seniority;
- the age of the citizen when applying to the Pension Fund for quick registration of the required benefit;
- type of required pension provision;
- the presence of time periods not included in the insurance period.
The formation of a businessman’s due pension is carried out from fixed amounts of payments, as well as the value of the accrued points. This cost is multiplied by an individual calculated coefficient, taking into account periods not included in the calculated insurance period.
Today, individual entrepreneurs, together with their hired employees, can receive a higher pension, whereas the previously performed calculation based on the minimum wage and without taking into account the insurance experience of the individual entrepreneur did not provide such an opportunity.
Total experience
The length of total work experience used to be the main condition necessary for assigning a pension to a citizen. The total work experience required for retirement varied significantly depending on the work specialty or working conditions. Thus, people working in hot shops or in difficult climatic conditions could qualify for early retirement. But since 2002, to calculate a pension, any citizen only needs five years of compulsory insurance coverage. Upon reaching this period, he can apply for the assignment of the minimum amount of pension established by law.
Interruption of service after the dismissal procedure
All conditions for how long the work experience will be retained after the dismissal procedure depend on the reasons for leaving work. The following situations stand out:
- Termination of an employment contract without sufficiently serious reasons at the request of one of the cooperating parties, but the employee will have to find a new job within a month after leaving work. Otherwise, his tenure will be interrupted.
- When working in difficult conditions in the north or abroad, a quit employee is given no more than two months for re-employment.
- If a citizen working outside the Russian Federation quits his job, he is given two months to get a new official job in Russia or in a country with which the Russian Federation has a social security agreement. Otherwise, the service will be considered interrupted.
Thus, after dismissal, the employee has no more than two months to find a job, and this time is included in the length of service. But further time will no longer be included in the working period.
Such situations relate to the actual termination of relations with the immediate employer precisely at one’s own expressed desire. In this case, after dismissal, the employee must find a job no later than one month to maintain his seniority. Even if he cannot get a job for a long time, the first month will be included in the period of service. Upon completion, the work experience will be interrupted.
Dismissal initiated by the employer indicates that the employee has committed a sufficiently serious offense, which becomes grounds for termination of the contract. Therefore, there is no reason to provide the required amount of time to find a new job while maintaining seniority. After all, the employee seriously violated labor discipline and demonstrated his inability to perform duties at his previous workplace. In this case, the accumulated experience will necessarily be interrupted immediately after dismissal and resumed after placement in a new job found.
What if the dismissal was not due to the employee’s fault, but also not on his initiative? For example, has there been a reduction in staff or numbers, or is the employee forced to leave for health reasons? In this case, the law maintains uninterrupted work experience for 3 months - during this time you should find a new job.
There is one category of workers for whom their service is not interrupted after dismissal: these are the spouses of those who were transferred to a new place of work in another city (region). It is logical that the husband or wife of the transferred person may not be able to find a job quickly, so their work experience is not considered interrupted until new employment.
Does continuity of service affect retirement?
Continuous work experience was very important in Soviet times. Today (since 2002) it has already lost its fundamental importance when calculating pensions. Priority is given not to continuous work, but to contributions to the Pension Fund, that is, insurance periods of service.
Why is the concept of continuity of service needed today? It is used in determining preferential periods of work with the preservation of the profession - in special conditions, in a specific area. For example, for work of a certain duration in the climatic conditions of the Far North, preferential pension supplements are provided. Also, employees of medical institutions who have worked in them continuously for a certain period receive some bonus.
So, the main function of continuous service is pension bonuses and preferential payments. Such length of service does not affect the size of the pension itself.
Special experience
The concept of “special work experience,” although absent from modern pension legislation, in fact continues to be used in a number of cases:
- For early calculation of pensions in accordance with the standards of compulsory pension insurance (Federal Law No. 400-2007).
- When calculating wage supplements as compensation for difficult working conditions (Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 822-2007).
- When establishing incentive bonuses for people working in hazardous industries or in difficult climatic conditions (Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 818-2007).
- To additionally provide paid annual leave to workers in heavy or hazardous production (Labor Code, Art. No. 121).
The list of professions whose employees are given special work experience is given in regulations approved by the government of the Russian Federation.
Main types
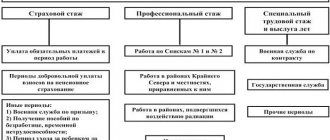
The legislation defines three types of length of service:
- General labor - all human activities recorded in documents (for example, in a work book), labor and other, socially useful. For example, it includes all registered and paid sick leave, service in the Armed Forces, and the like. You can read more about this here.
- Continuous – the sum of all periods of a citizen’s activity, if between them there was a break of less than a month or work in one place for a long time.
- Other activities - work in positions determined by law, for example, government, in a certain profession or special experience. It is valid, for example, for teachers, military personnel, carers, etc.
- Insurance is the recorded length of service during which contributions to the Pension Fund were paid. In other words, periods when contributions were not made are deducted from the total labor period; the remainder will be the insurance period.
Continuous experience
It is used when calculating compensation and providing other types of social guarantees. Today, having continuous experience is relevant:
- For workers working in the Far North and equivalent territories (Government Decree of 1993).
- For persons who served in the Armed Forces in areas with unfavorable climatic or environmental conditions (Government Decree of 1999).
- For medical workers employed in medical institutions with a high level of biological hazard (Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 463-2008).
In addition, continuous experience is necessary to establish additional pay for length of service for certain categories of employees of law enforcement agencies: the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, the FSB, the Ministry of Emergency Situations. By internal orders of the organization, employees with extensive continuous experience may also be provided with certain benefits - salary bonuses, additional paid leave, and so on.
Concept, legal meaning, types and legal basis of length of service.
Home Favorites Random article Educational New additions Feedback FAQ⇐ PreviousPage 2 of 4Next ⇒
Insurance experience: concept, calculation procedure, calculation methods and confirmation procedure.
General work experience and experience in relevant types of work.
Public service experience and length of service.
Continuous work experience.
– 1 –
Concept, legal meaning, types and legal basis of length of service.
Experience is a complex legal fact that gives rise to the emergence or change of legal relations in connection with the appointment and payment of all types of labor pensions, temporary disability benefits, as well as some other legal relations in social security.
Legal meaning of length of service in social security law:
1) Experience of a certain duration and nature can play the role of a basic legal fact
in a complex legal framework (for example, when assigning early labor pensions to teachers and other employees with special working conditions, pensions for long service to federal civil servants, military personnel, etc.).
2) Experience can be only one of the elements
complex legal-forming factual composition (for example, when assigning labor pensions for old age, loss of a breadwinner and disability, temporary disability benefits).
3) With length of experience
The size of
most types of pensions and individual benefits is related
Types of experience:
- insurance experience:
Ø general – indicates the total, total duration of labor and some other activity (the totality of periods of any labor
activities during the performance of which insurance premiums for compulsory social insurance were paid and (or) payable, periods of
other socially useful activities
and other periods recognized by the legislator as socially significant);
Ø special (professional) – is part of the general insurance experience
; the total duration of periods of labor activity with the payment of insurance premiums in workplaces with difficult or harmful working conditions, in special natural and climatic zones or territories with a special status;
- total work experience;
- experience in relevant types of work;
- experience in state civil service;
- length of service.
Legal basis of experience:
- International legal acts. Thus, if an international treaty of the Russian Federation establishes other rules for calculating and confirming, for example, the length of service for establishing labor pensions, the rules of the international treaty of the Russian Federation are applied. For example, the Agreement on mutual offset in the total length of service and length of service in the bodies and institutions of the prosecutor's office in the CIS member states.
- Federal Law dated 04/01/1996 No. 27-FZ (as amended on 03/12/2014) “On individual (personalized) accounting in the compulsory pension insurance system”[1];
- Federal Law of July 16, 1999 No. 165-FZ (as amended on December 28, 2013) “On the fundamentals of compulsory social insurance” [2];
- Federal Law dated 17.12. 2001 No. 173-FZ “On labor pensions in the Russian Federation” (as amended on December 28, 2013) [3] ;
- Federal Law of December 15, 2001 No. 166-FZ “On state pension provision in the Russian Federation”[4];
- Federal Law dated December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ (as amended on June 28, 2014) “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity”[5];
- Law of the Russian Federation dated 02/12/1993 No. 4468-1 (as amended on 12/28/2013, as amended on 06/04/2014) “On pension provision for persons who served in military service, service in internal affairs bodies, the state fire service, control bodies trafficking in narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, institutions and bodies of the penal system, and their families”[6];
- Law of the Russian Federation of May 15, 1991 No. 1244-1 (as amended on December 21, 2013, as amended on June 28, 2014) “On the social protection of citizens exposed to radiation as a result of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant”;[7]
- regulations:
ü Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 24, 2002 No. 555 (as amended on March 24, 2014) “On approval of the Rules for calculating and confirming the insurance period for establishing labor pensions” [8];
ü Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated September 20, 2010 No. 1141 (as amended on May 19, 2011) “On the list of positions, periods of service (work) in which are included in the length of service of the state civil service for the purpose of assigning a pension for length of service of federal state civil servants”[9] ;
ü Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 22, 1993 N 941 (as amended on May 5, 2014) “On the procedure for calculating length of service, assigning and paying pensions, compensation and benefits to persons who served in military service as officers, warrant officers, midshipmen and military personnel on extended service or under contract as soldiers, sailors, sergeants and foremen, or service in internal affairs bodies, the state fire service, institutions and bodies of the penal system, and their families in the Russian Federation"[10];
ü Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 12.08. 1994 No. 942 “On the procedure for calculating length of service, assigning and paying pensions to employees of bodies and institutions of the prosecutor's office of the Russian Federation and their families” (as amended on 12/07/2011, as amended on 04/03/2014)[11];
ü Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 02.02. 1998 No. 103 “On the procedure for calculating length of service for the appointment and payment of pensions and benefits to persons who served (worked) in the customs authorities of the Russian Federation, and their families”[12], etc.
– 2 –
Insurance experience: concept, calculation procedure, calculation methods
And the confirmation procedure.
The insurance period is an independent legal fact
in legal relations on social security and the most important element of the insurance pension system. It is he who is decisive in establishing a pension and determining its size.
The doctrine is based on the fact that insurance experience as a special type of experience
-
this is “the total duration of periods of work during which insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation had to be paid for a given person, and other activities taken into account when determining the right to a labor pension, taking into account which insurance contributions were reimbursed from the federal budget.”[ 13]
The insurance period has quantitative (duration in years) and qualitative (peculiarities of production conditions (harmful, difficult, etc.), climatic zones and territories in which labor activity was carried out (regions of the Far North and areas equivalent to them)) characteristics.
According to Article 3 of the Federal Law dated July 16, 1999 No. 165-FZ (as amended by the Federal Law dated March 5, 2004 No. 10-FZ, dated July 24, 2009 No. 213-FZ) “On the basics of compulsory social insurance,”
the insurance period is the total length of time for payment insurance premiums.
This definition does not make the insurance period in any way dependent on work or other activities.
Thus, the legislator does not link
the payment of insurance premiums directly with the work activity of the insured person.
An insured
in the field of compulsory pension insurance can be any person who has expressed a desire to pay insurance premiums for the insured, regardless of the existence of any legal relationship between them.
Insured persons can voluntarily enter
into legal relations under compulsory pension insurance related to additional payment of insurance premiums to the budget of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, in excess of the contributions paid for them by the policyholder, and independently pay insurance premiums for themselves.
Citizens also have the right to voluntarily enter into legal relations under compulsory pension insurance and pay insurance contributions to the budget of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation for another individual
.
In accordance with Art. 2 Federal Law dated December 17. 2001 No. 173-FZ “On Labor Pensions in the Russian Federation”
insurance period
-
the total duration of periods of work and (or) other activities during which insurance contributions were paid to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, as well as other periods, taken into account when determining the right to a labor pension counted towards the insurance period.
Consequently, there is a fundamental difference between the above legal definitions of insurance experience. In the first case, the payment of contributions is not related to work activity, which “contradicts the fundamental idea of social insurance.”[14] The second formulation, as an exception to the general rule, involves counting into the length of service periods during which work was not carried out and contributions were not paid. The Federal Law of December 15, 2001 allows for the payment of contributions without engaging in any work activity.
⇐ Previous2Next ⇒
Experience in specialty
The time a person works in a particular field of work does not imply the provision of any benefits, additional payments or other preferences. The main point of the length of work in a specialty is to make it clear to the employer when hiring an employee that he is faced with a person with certain experience and possessing certain professional skills. Accordingly, the more work experience in the required specialty, the higher the chances of such an applicant to get a job in the organization.
However, in a number of professions, the length of work in the specialty can also influence the employee’s career growth. For example, in the Armed Forces, in order to receive the next rank, an employee must have a certain period of service in a lower rank. Assignment of a subsequent rank. Extraordinary assignment of a title is possible only in the form of encouragement for any merits. And in certain positions, work experience is the main condition for employment.
Thus, in order to be admitted to the bar exam, a lawyer must have, in addition to specialized education, a certain amount of practical work experience. To be appointed to the position of prosecutor of a region or republic, a justice worker must work for at least 7 years in lower positions.
As we can see, despite the reform and the introduction of a new procedure for calculating pensions and salaries, length of service remains an important factor influencing the size and procedure of social payments.
Why do you need to develop it?
You should think about your future in advance, because now most people do not think about their work experience at all, and it is this that affects their future possible pension.
Or rather, it is influenced by the time during which certain contributions to the pension fund are paid for a citizen. If payments are not received, for example, during study or unofficial work, you can make payments to the Pension Fund yourself. To do this, you need to contact the pension fund with a statement of desire to voluntarily participate in pension insurance. This way you will take care of your future financial condition. Now many people work unofficially, for example, on the Internet, for which, of course, a pension is not accrued, so it is worth thinking about voluntary pension insurance.
Work experience is determined by the number of months that a citizen has worked. Let’s say you worked for less than a month, but the contribution was made no less than the minimum established amount, a full month will be counted.
By the way, not only the pension depends on the length of service. It also has an impact on your career. If a person has extensive experience in any field, he has a good chance of getting a decent position, because employers do not want to train employees, also at their own expense. So, the work book is an excellent confirmation of your vast work experience. When a citizen comes to an employer to get a job, he will ask about his work experience, which will affect his salary.
"Restoration" of experience
Unfortunately, it often happens that seniority is simply “lost.” This can happen if you lose your work book. Before the introduction of the electronic database of pension funds and pension insurance, it was the main document according to which both total and special work experience were calculated. Therefore, with the loss of a work book, there is a need to confirm one’s work activity before concluding an OPS agreement.
Confirming this is sometimes very difficult. It’s good if the enterprise where a person worked several decades ago is still preserved. But thousands of enterprises from the Soviet period did not survive the troubled 90s, and even today hundreds of large and small organizations go bankrupt and close across the country every year.
A professional lawyer specializing in labor relations issues can help you restore lost experience. The specialist will be able to competently draw up requests to the relevant authorities and help in collecting a package of supporting documentation. And if necessary, represent the client’s interests in any judicial and administrative authorities.
Calculation procedure
From the employee’s work book, it is necessary to write down all the dates of employment records and all the dates of dismissal, and then add them up to result in two amounts, one from the dates of employment, the second from the dates of dismissals. Then you need to subtract the first from the second amount.
In this case, one day from each place of work is lost, so to the amount received it is necessary to add a number equal to the number of entries in the work book. The resulting figure must now be converted into years, months and days, taking into account that the average number of days in a month is 30, and in a year there are 12 months.
Example:
It is necessary to calculate the OTC of Kravchenko P.F. until 2002. The work book contains the following entries about periods of work:
- June 25, 1995 – March 25, 1996 she worked as a secretary at OJSC Trade;
- March 30, 1996 – January 30, 1998 at Svet LLC;
- February 1, 1998 – December 4, 2001 at Yunus CJSC.
- Since January 11, 2002 Kravchenko P.F. worked in another organization.
Sum of hiring dates:
- 06/25/1995 + 03/30/1996 + 02/01/1988 = 11/56/5992 Sum of dates of dismissal from work:
- 03/25/1996 + 01/30/1998 + 12/04/2001 = 16/59/5995 We calculate the difference between the two amounts:
- 59.16.5995 – 56.11.5992 = 05.03.0003 Which means 3 years, 11 months, 3 days.
Since the employee had three hiring/dismissal periods, we will add three more days, and Kravchenko’s total work experience will be 3 years, 11 months and 6 days.
You need to calculate maternity benefits correctly! We will help you with this! Correctly calculating your sick leave during pregnancy has its own characteristics. You can learn about them and understand them here.
You will find out what the maximum period of time you can count on when receiving sick leave is if you follow the link and read our material.
Work experience: new items for 2021
Those who are planning to retire this year will receive it according to new rules, which have changed significantly compared to the past. The government has adopted a number of innovations that fundamentally affect the size and features of calculating old-age pensions.
Social pension for everyone?
Every citizen of the Russian Federation has the right to a social pension upon reaching a certain age - 60 years for women and 65 years for men. As you can see, the age for assigning this pension is 5 years older than for the insurance one. In addition, a possible increase in the retirement age has not yet been taken into account.
The size of the social pension is very small. If the total income of a social pensioner is less than the subsistence level, the federal budget allocates a supplement to the pension, along with which, from January 2018, the payment amounts to 7,990 rubles.
Most people who can count exclusively on a social pension are those who did not work or worked unofficially, receiving a salary or part of it “in an envelope” (without making contributions to the Pension Fund).
Insurance pension – why is it better?
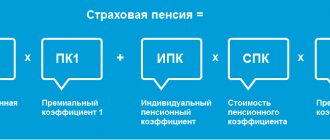
It is much more profitable to receive an insurance pension. It does not represent the same amount for all pensioners, but depends on several values. The size of the insurance pension is tied to the following factors:
- fixed “base” – 4983 rubles, intended for those who have the required pension experience and the corresponding minimum pension points;
- the number of points is multiplied by a coefficient, which in 2018 is 81.5 rubles per 1 point (50 accumulated points will give an amount of 4075 rubles;
- the funded component of the pension – for pensioners born after 1967, whose savings are placed in Vnesheconombank or a non-state pension fund. The amount in the account is divided by 246 months, and the federal coefficient is added to it.
Conditions for receiving an insurance pension
Not everyone is entitled to an insurance pension; it must be earned in the literal sense of the word. You need to work at an official job, because only this way guarantees contributions to the Pension Fund, or make these contributions yourself. The law requires simultaneous compliance with 3 conditions:
- reaching the age limit of 55 years for women and 60 years for men (it has not yet been increased, although the corresponding bill is already being considered, it may come into force in 2021);
- insurance experience of a certain duration (requirements for it have been growing annually since 2015, and in 2021 9 years of such experience are required);
- accumulation of pension points - special indicators accrued for the amount of contributions to the Pension Fund (1 monthly minimum wage paid to an employee during the year corresponds to 1 point accrued at the end of the working year); for 2021 you need to have at least 13.8 points.
The missing points and length of service can be gained by working some more time after reaching the pension threshold. Further work of those who have crossed the pension threshold brings them 1.5 times more points if they work after this time without a pension for another 5 years.
What else can you get points for?
Points are awarded not only for official work, but also for some specially designated periods, namely:
- conscription will bring 1.8 points per year;
- caring for a disabled person of group 1, an elderly relative over 80 years old, or a disabled child also brings 1.8 points per year;
- caring for the firstborn for 1.5 years will provide one of the parents with 1.8 points, for the 2nd child - 3.6 points, for the 3rd and subsequent ones - 5.4 points each.
Any citizen can view the number of accumulated points and years of insurance experience in their Personal Account on the official website of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation.
We hope that the theory presented in the article will help you better navigate the basic principles of Russian legislation regarding seniority. Thanks to this information, you will be able to better operate your civil rights, claiming all the well-deserved social benefits.