What is salary
All issues related to labor relations are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Section VI of the same name is responsible for payment and standardization of labor. In Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides a definition of salary, which can be divided into three parts and presented in the form of the following diagram:
As you can see, the legislation does not directly define what the variable part of wages is. Let us analyze the scheme in more detail and answer the question of which of it relates to the variable part of wages.
Remuneration for labor is understood as a fixed payment - salary, which is prescribed in the employment contract with the employee and can be changed only with his written consent. In addition, the salary cannot be less than the legally established minimum wage at full rate.
Compensation payments refer to payments guaranteed by the state to certain individuals or individuals working under certain conditions. These could be bonuses for work in the Far North, in territories exposed to radioactive contamination, etc.
Neither the first nor the second option can relate to the variable part, since they are quite strictly regulated either by the state or by relations with the employee.
Thus, the last component of the salary remains - incentive payments. This is the variable part of wages, and we will examine what exactly this refers to further.
Conclusion
In its pure form, the piecework form of remuneration is reasonable only when a person is an independent producer of a homogeneous product. In today's integrated and highly mechanized production, which prefers intellectual labor to physical labor, this situation is less common. Nevertheless, the piecework wage system is widely used in light industry and trade. In mass production, where workers perform simple routine tasks and the result of their work is easily measured quantitatively, piecework payment, as the main motivator, is still considered the most optimal option.
Fixed remuneration is more appropriate in circumstances where the result of a specialist’s work is not assessed by quantitative indicators. The salaries of scientists, engineers, doctors, teachers, lawyers, and programmers depend more on their professional reputation than on the amount of work they perform.
And although the size of wages is still considered by many as a key factor in professional motivation, from this article it becomes clear that it is not able to solve all the problems of personnel productivity. In addition to money, a specialist thinks about the prospects of his career, his reputation, and the stability of the company in which he works. And in this cherished balance between the interests of the employer and the interests of the employee, the main sign of economic progress is encrypted. Because in the end the consumer wins.
The variable part of the salary is incentive payments
Incentive payments - the variable part of the salary - include:
- Bonuses paid to employees.
Here we should make a reservation that the conditions for paying bonuses vary. If the payment is specified in an employment or collective agreement and is paid in a fixed amount or as a fixed percentage of the salary, and its payment is tied to a specific recurring event, for example, it is issued quarterly, then such a bonus should be classified more as a fixed payment. If the bonus is tied to the results of work, to any single events, for example, to exceeding the sales plan or to concluding a profitable large contract, then such a bonus can be safely attributed to the variable part of the salary. It should be approved by order of the manager and signed by all employees receiving the bonus.
- Various compensations not specified by law: transportation costs, mobile communications, food, visits to a fitness club, payment for any professional courses, etc.
- A separate line should be taken of the VHI policy, which is also very often offered by employers.
Differences between salary and salary
Salary and salary are different concepts.
The main difference between the amount of salary and salary is that salary is a fixed amount of remuneration for a specific position according to the work schedule. The salary amount is unchanged provided that the hired employee goes to work on all days of the calendar month.
The salary, in turn, may vary depending on the availability of bonuses and allowances, which add up to the salary amount. Thus, when calculating the salary, all compensations, bonuses are added to the salary amount and fines, if any, are subtracted.
What does the functionality of the variable part of the salary include?
The variable part of the salary is so called precisely because its size can be varied in order to achieve certain production goals. What can the variable part of the salary affect:
- Labor productivity and the presence of new clients for the company. A sales manager will work more zealously if he receives a salary increase from each new client.
- The attractiveness of the company in the market as an employer. Payment for travel, mobile communications, etc. is a significant advantage when choosing a place of work, all other things being equal.
- The reputation of a company that takes care of its employees by providing them with additional types of health insurance will increase.
- The variable part of the salary can be taken into account in the tax expenses of the enterprise (some within certain standards and subject to certain conditions), which is also beneficial for the company.
- If the company is doing worse, then in the economy mode this part of the salary can be easily reduced or reduced without going beyond the scope of labor legislation.
The variable part of the salary includes various payments in favor of the enterprise’s employees, made at the initiative of the employer, in addition to the fixed salary and established mandatory compensations. With the help of these payments, the manager can stimulate employees to achieve greater productivity or, if necessary, reduce them without any legal consequences.
You will also be interested in reading the materials that we wrote specifically for our Zen channel.
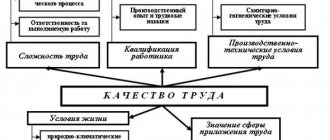
According to labor legislation, the concept of wages is considered as remuneration for work, which must be calculated and paid depending on the qualifications of the employee, working conditions, complexity, quantity and quality of the work process.
All allowances, additional payments, bonuses are included in the concept of wages, and therefore they are usually divided into basic and additional.
The main part depends on the qualifications of the employee and the type of work performed. It is established in a fixed form for the period of time worked or the number of works performed. The main part cannot be less than the established minimum wage (minimum wage).
Read also: The best mortgage offers
The procedure for calculating and the amount of additional wages, in contrast to its fixed part, can be established as a reward for work done or under special working conditions.
In accordance with Art. 135 of the Labor Code (LC RF), the procedure and amount of incentive and compensation payments are established by local acts and collective agreements based on labor legislation.
When issuing wages, the employer must notify employees in writing using a payslip of all payments due to him and their amount (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Fixed and variable payments underlie three types of remuneration systems: a fixed salary, a commission system and combinations of these systems.
Only a quarter of all firms use either a salary-only system or a commission-only system; the rest use a combination of the two methods, in which the ratio of salaries and commission payments varies widely.2 [p.629] Economics Management must also be able to assess how the organization's operations will be affected general changes in the state of the economy. The state of the global economy affects the cost of all inputs and the ability of consumers to purchase certain goods and services. If, for example, inflation is forecast, management may consider it desirable to increase the organization's supply of inputs and negotiate fixed wages with workers in order to contain the rise in costs in the near future. It may also decide to make a loan, since when payments become due, the money will be worth less and thereby partially compensate for losses from interest payments. If an economic downturn is predicted, the organization may prefer to reduce inventories of finished products, since there may be difficulties in selling them, lay off some employees, or postpone plans to expand production until better times. [p.125] The basic remuneration of banking personnel is a fixed official salary, a floating official salary, and operational wages. [p.322]
Additional remuneration for banking personnel fixed individual additional payments to the official salary one-time individual bonuses special bonuses for the bank management quarterly bonuses year-end remuneration. [p.322]
At the end of 1988, there were four tire repair plants in the industry and in 1989 one oil refinery and the Krasny Rezinshchik plant were transferred to lease relations. In our opinion, there are no big differences between the second model and the rental form of cost accounting, although even in case of rental, the enterprise’s wage fund is formed from the income remaining at its disposal after paying rental payments independently. But with the introduction of a normative relationship between the increase in income and the increase in the wage fund, this independence is lost. Probably, if we eliminate the standards for the distribution of profit retained by the enterprise under the first model, and self-supporting income under the second, and introduce fixed payments to the budget and the ministry under the first and second models, then the difference between the models will be lost. [p.125]
Under the conditions of a piecework form of remuneration, various systems for recording the output of piece workers can be used, in particular a system for operational accounting of output. It provides for the acceptance, calculation and recording of information about the output of a worker (or team of workers) in primary documents by a quality control inspector or a foreman after completing each operation. [p.140]
In conditions of inflation, financial statements of enterprises on the results of economic activities, financial condition and use of profits can be a source of biased information, since different elements of the balance sheet lose their value at different rates. For example, cash and accounts receivable, which are claims for payment of a fixed amount in the future, lose their value due to inflation and lead to losses for the enterprise in the amount of a decrease in the purchasing power of money. And, conversely, enterprises that increase their accounts payable, i.e. those withholding payment of supplier bills and other obligations (wages, budget, social insurance and other creditors) benefit from this because they can pay off their obligations with money with reduced purchasing power. [p.134]
Stimulating and motivating aspect of salary. The remuneration system must include effective means of incentives and motivation. Workers are given the opportunity to earn more than just a fixed salary. In this regard, additional payments are being introduced that are directly related to employee achievements. [p.169]
Contributions to pension plans administered on a group basis are accrued and paid as defined contribution pensions if the company is subject to any actuarial risk of co-payments, or on a straight-line basis if no such risk exists. State pension plans usually involve fixed contributions, in which the company is not responsible for the amount of pensions paid. This type of state pension system is used in Russia. These are defined contribution pensions. They are reflected in accounting, by charging a certain percentage to the accrued amount of wages, as a kind of special tax. [p.301]
Tariff rate (salary) is a fixed amount of remuneration for an employee for fulfilling a standard of work (job duties) of a certain complexity (qualification) per unit of working time (hour, day, month). [p.201]
Remuneration related to the employee’s performance has a number of varieties. Commissions can be set as a fixed percentage [p.222]
In contrast to tax deductions that were provided before January 1, 2001 and depended on the minimum wage, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines a system of clear and universal tax deductions provided for in firmly fixed amounts. [p.439]
The Time Sheet mode is intended for calculating wages for employees with a fixed salary or tariff rate. Only timesheets of employees with an incomplete number of working days in the reporting period are subject to processing. After selecting the required structural unit, information about the employees of the unit, their salaries (or tariff rates), days and hours worked for a given period, and the accrued amount of wages is displayed on the monitor screen. [p.288]
Figure 18-7 illustrates the effect of a fall in the price level when the nominal wage rate is fixed. In Fig. 18-7/1 a decrease in the price level from PQ to P entails an increase in the worker’s real wages. Thus, it provides more labor services, which can be illustrated by the movement along the /Vv graph. In Fig. 18-7, however, an increase in the price level means that at a given wage rate the worker is more likely to be willing to provide labor services in the same volume (since his real wage is higher). From different points of view, he is willing to receive a lower nominal wage for working a given number of hours. In any case, the labor supply schedule must shift to the right of the y-axis (on which the values of the nominal wage are plotted) when the price level falls from NS(PQ) to Ns(Pl). Both schedules, however, represent the same choice, so that a given worker's expected amount of work time will increase by the same amount in each case. [p.470]
Paying salespeople on a commission basis instead of paying a fixed salary. [p.410]
The fundamental difference between the newly established state duty rates and the previously existing ones is that they are determined not in fixed amounts, but as a percentage (or multiple) of the minimum monthly wage established by law, and thus to a large extent correspond to their purpose and the conditions of market relations. GOVERNMENT SECURITIES - bonds, treasury bills and other government obligations issued by central governments, local governments, etc. for the purpose of issuing loans and mobilizing monetary resources. [p.64]
After the calendar year, the amount of payment in connection with I. is included in the corresponding tariff rates and official salaries, state pensions, scholarships and social benefits. The source of funds for I. remuneration of employees of budgetary enterprises (health care institutions, public education, science, culture and others), social pensions and benefits are allocations from the corresponding budgets for remuneration of employees of enterprises selling products (services) at state fixed prices and tariffs, if there is a lack of funds for wages for reasons beyond their control - budgetary funds in the manner determined by the Council of Ministers of Russia for remuneration of workers of enterprises that independently determine prices for the goods they produce and services provided, public organizations (associations) and their enterprises - the enterprises' own funds and organizations of state labor pensions - funds of the Pension Fund of Russia, including funds transferred to this Fund from the Union budget for the payment of pensions and benefits to military personnel and their families, as well as categories of citizens equivalent to them in this regard and their families of social benefits paid from the Social Insurance Fund of Russia, - funds from this Unemployment Benefit Fund - funds from the State Employment Fund of Russia, state scholarships - allocations from the relevant budgets of income on government securities and government loans of Russia - allocations from the state budget of Russia of contributions to state insurance bodies - State Insurance of Russia from increasing interest rates on funds placed from these contributions. ENDORSEMENT (GIRO) - an endorsement on the back of a bill, check, etc., certifying the transfer of rights according to this [p.97]
Incentive systems The remuneration system in the United States is structured in such a way that a fixed salary can only [p.484]
Inflation punishes people who receive relatively fixed incomes and eats up citizens' savings. With high inflation, inflationary psychosis of the population may occur, which changes cash flows in the country. Understanding the negative impact of inflation, the state and employers increase wages when prices rise, which is called an inflationary spiral; rising prices entail rising wages, which pushes prices even higher, etc. [p.325]
One of the first wage laws was issued by King Edward II of England (1349). After the plague epidemic in 1348, two-thirds of the country's population remained, and a sharp reduction in labor resources led to an increase in prices. Edward II issued a law on fixed wages for labor and fines on feudal lords for increasing it in order to retain or lure workers. Workers who refused to work for a certain amount of pay faced imprisonment. [p.326]
A time-based system with a guaranteed minimum wage for labor provides a fixed amount of payment up to a certain minimum work time. This could be 50% of the standard schedule, 75% of the work time for the previous period, etc. If the work time is within the control volume, for reasons beyond the control of the worker, he is paid a guaranteed minimum wage. When working time exceeds the control volume, the system for calculating wages is transformed into a direct time-based wage system. [p.353]
Next, a company should determine the four components of compensation for its sales force—fixed salary, flexible pay, overhead reimbursement, and benefits. A fixed salary, a salary, must satisfy the employee’s need for financial stability. Flexible pay in the form of commissions, bonuses or company profit sharing is designed to stimulate and reward extra effort on the part of the employee. Overhead reimbursement allows sales representatives to be reimbursed for additional travel, hotel, food, and vacation expenses. Benefits such as paid time off, sickness and accident benefits, pensions and life insurance are designed to provide workers with security and a sense of job satisfaction. [p.751]
Trading management must determine the relative importance of these components. The most common view is that the fixed salary should make up about 70% of the employee's total income, with the remaining 30% allocated to the other three components. However, these are only approximate figures. Fixed wages are convenient if there are significant seasonal differences in sales volumes or the sales process depends on the work of a large number of people. Flexible payment is more important in cases where the level of sales is cyclical or depends on the personal initiative of the employee. [p.752]
Fixed and flexible wages give rise to three systems of material incentives for workers - fixed wages, piecework wages and their combination. Only a quarter of all firms use the first two systems. Three quarters use a combination of the two methods. [p.752]
For each of the proposed situations, determine what the remuneration system for sales workers should be based on (fixed, piece-rate, mixed). [p.776]
I would like to argue that a sharp decline in prices for agricultural products, accompanying a decrease in demand, will force many farmers to cease their activities, which will further reduce the total volume of production and soften the fall in yen and income. But agricultural production is little sensitive to price changes, since the fixed costs of farmers are quite high compared to variable costs. Rent payments, taxes and interest payments on a mortgage loan secured by land, buildings and equipment are the main costs of a farmer. These are fixed payments. Moreover, the supply of labor from the farmer and his family can also be considered fixed. While farmers remain on their farms, they cannot reduce these costs by, for example, firing themselves. This means that their variable costs go to pay only the relatively small number of helpers they could hire, plus the costs of seeds, fertilizers and fuel. Because there are so many fixed costs, farmers almost always benefit when they work their land rather than sit around and make only fixed payments. [p.727]
Insurance funds engage in a wide variety of investment activities. They work with sophisticated investors and are not subject to mutual fund laws. Managers are paid based on their performance rather than being a fixed percentage of assets. A more accurate name for such funds would be productive funds. [p.27]
The crisis in monetary circulation had a particularly hard impact on the population receiving a fixed wage. Their standard of living was declining at an accelerated pace, and if we take into account that this group of the population included a significant part of government employees, then the flourishing of bribery and various forms of misappropriation of state or society income is understandable - a kind of voluntary-forced redistribution of capital. [p.419]
It should be emphasized that the ratio of the fixed and floating part of the salary should vary depending on the employee’s place in the management hierarchy and the level of personal influence on the final result. It is obvious that the contribution of the process manager largely determines the success of the business, and the influence of an ordinary, low-skilled employee is minimal. It is most appropriate to apply fixed wages to the category of temporarily hired specialists used to solve specific and time-limited tasks. [p.188]
Having determined the ratio of fixed and bonus wages for various categories of workers, the designer must set reference values, which will subsequently serve as a guide in the implementation of the motivational component of the designed business model. [p.188]
Since the level of profit received by the process team is not static, the ratio of the fixed and bonus wage fund cannot correspond to the reference values of the schedule. [p.189]
Let's assume that the process team, conventionally called J-5, consists of 5 specialists. The wage fund (i.e., fixed) wages is known to us, as we know, the reference value of the bonus pay for each of the five specialists. However, the profit received from the economic activities of the process team is not enough to fully satisfy all team members in terms of bonus wages, which are not included in the costs of the process-oriented division and are formed from the profit received in an amount pre-approved by the company’s board of managers (as a percentage of the profit received, according to the data in the table below). [p.189]
By comparing the initial and received data, we will be able to find out how much the ratio of fixed and bonus wages has changed by making the appropriate calculations. [p.192]
The minimum tariff rate (salary) for employees of public sector organizations in the Russian Federation. Tariff rate (salary) is a fixed amount of remuneration for an employee for fulfilling a standard of work (job duties) of a certain complexity (qualification) per unit of time. [p.85]
If the work situation does not allow for a direct link between achievement and compensation, it would be wiser to separate the two aspects. In other words, we demand that assigned tasks be completed, but at the same time we pay a fixed salary, which does not provide for an increase as achievements increase. This means that the need for money can be satisfied (assuming that the reward is valued), but in reality we are only dealing with managing the process of achieving goals, uncomplicated by payment problems. In this way, the problem of remuneration, which negatively affects the morale of the employee, is eliminated. [p.135]
Typically, the system has several stable equilibrium states, associated, for example, with the use of vertical and organic structures, fixed and tied to the final result of the volume of remuneration. [p.23]
Incentive payments - payments at the discretion of the enterprise and from its funds; system bonuses (for the main results of economic activities and one-time ones, for example, for rationalization proposals for saving energy resources, materials, etc., are made 1-2 times a year); one-time bonuses for length of service (set by the state, in railway transport - a maximum of 30%) remuneration based on the results of work for the year (from the profit of the enterprise) professional skills (set for workers, IV category - 8%, V category - 8%, VI category - 12%) for combining professions expansion service areas or an increase in the volume of work performed (payments are made within the limits of wage fund savings) to foremen from among the workers and senior machinists who are not exempt from their main work (established for leading a team of up to 10 workers in the amount of 5 to 10% of the established hourly tariff rate, and with more than 10 people - up to 15%) road fixed surcharge to the minimum wage established in the industry for all road workers with the right to increase the average monthly wage depending on the growth of labor productivity and the implementation of specified planned indicators for the wage fund [p.133]
The question of the composition of payment, in particular its division into fixed and variable parts, is even more complex. Salespeople strive to receive a fixed salary and at the same time expect that the high efficiency of their work will certainly be rewarded, and the salary itself will increase as they gain experience. On the other hand, the company tends to use a payment system that stimulates the behavior of the seller that is beneficial to it, and uses its own scheme that reflects the balance between various goals. There are three main remuneration systems for sales representatives: a fixed salary, commissions and a mixed payment system. Let's take a closer look at them. [p.376]
The use of remuneration systems that combine fixed and variable payments allows companies to link the variable components of sales force compensation with various strategic goals of the organization. Some marketers note a new trend in assessing the effectiveness of sales services - a decrease in the importance of quantitative indicators and an increase in the importance of such factors as increased profitability, customer satisfaction and retention. For example, IBM rewards employees for customer satisfaction (the level of satisfaction is determined through customer surveys). [p.630]
Local authorities may establish a different procedure for determining the payment for trade in these goods - in the amount of a fixed rate from the minimum monthly wage established by law, both separately for each type of excisable goods, and for a group of goods as a whole. [p.165]
When recalculating pensions from February 1, 1998, in accordance with Federal Law No. 113-FZ, the Procedure for recalculating tariff rates, piece rates, official salaries, fees, bonuses, other types of remuneration, pensions, benefits and scholarships expressed in firm (fixed) terms is applied. ) amounts in connection with the change from January 1, 1998 in the face value of Russian banknotes, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia of October 1, 1997 No. 52. [p.681]
Let's see how to organize a payment scheme under the condition that the repairman maximizes their value minus the costs of exerting effort1. Let us first assume that the owners offer him a fixed fee. We can consider any level, so for simplicity we will take it equal to 0. (One could consider a pay level of 0 to be no higher than the salary of other comparable jobs.) With such pay, the repairman has no incentive to exert more effort. The reason is clear - he has nothing from the additional income received by the owners as a result of increasing his efforts. It follows that fixed wages lead to ineffective results. When a = 0 and w = 0, then the expected profit of the owner will be $15,000, and the repairman will receive zero net income. [p.481]
Piece wage (pie wage) is one of the forms of remuneration in which the employee’s wages are not fixed, but depend on the number of units of product of established quality produced by him. [p.213]
What parts does an employee's salary consist of?
Wages are calculated depending on working conditions and according to the payment system established by the employer. According to Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages include:
- Fixed part , which may consist of:
- salary (official salary) - set in a fixed amount and calculated for a calendar month;
- basic salary (basic official salary) - the minimum amount of payment without additional transfers, which is established for employees of the state or municipal service;
- tariff rate - calculation of paid labor occurs for a certain unit of time.
- Compensation payments are assigned when working conditions deviate from normal. Those employed in heavy work or under special climatic conditions that threaten health, also during overtime work, at night and on weekends.
- Incentive payments - bonuses, allowances and other incentives.
Modern types of remuneration and wage systems
Accounting, payment and labor regulation are responsibilities that every employer must fulfill. You can pay for work performed in different ways, but one way or another, each enterprise establishes certain rules according to which the work of personnel is taken into account, charged and rewarded. To understand exactly how material remuneration is paid, let’s briefly consider the main forms and systems of remuneration.
| Valentina Mitrofanova will tell you what's new in labor legislation this week. Watch the new episode of Personnel Review. |
There are three salary systems:
- Tariff.
- Tariff free.
- Mixed.
The most common today is the tariff system of remuneration, the types of which (“piecework” and time-based wages) are used by most employers. Under the tariff system, the salaries of workers of different categories are differentiated based on a number of conditions: the type and degree of complexity of the work performed, the intensity and nature of the work, natural and climatic conditions, etc. Non-tariff forms and systems of remuneration tie earnings not to clear tariffs, but to the final results of the work of the entire enterprise or structural unit in which the employee is registered, and the total amount of funds allocated by the employer to the wage fund. For each employee, their own coefficient of labor participation in the results of the team’s activities is established. Taking into account this coefficient, the individual salary is subsequently calculated.
Mixed remuneration has the characteristics of two other systems - non-tariff and tariff. On the one hand, the employer does not completely abandon tariff setting; on the other hand, it adjusts tariffs depending on the results of staff work and applies the labor participation coefficient when calculating individual salaries. In the modern economy, you can find different forms of remuneration related to the mixed system, in particular, “floating” salaries, dealership and commission payments.
Fixed part
The main mandatory component of wages is its fixed part. The establishment of remuneration depends on the qualifications of the employee, the complexity of the work process, the quantity and quality of the work performed. The fixed part includes only those payments that are accrued for the time actually worked or for the performance of job duties in accordance with the work schedule.
IMPORTANT
The salary cannot contain a fixed part, since, according to Art. 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if an employee has worked the full working hours, then the amount of remuneration cannot be less than the minimum wage.
Tariff rate
The salary at the tariff rate is calculated depending on the cost of fulfilling labor standards for a certain unit of time. Unlike salary, wage calculation at a tariff rate is established for the standard time worked , and not for the performance of work duties during a calendar month.
There are several time periods for calculating the tariff rate:
- Monthly - valid when the organization has established a strict work schedule; wages are calculated in the amount of the salary, regardless of the number of days in the month.
- Daytime - applies if the length of the working week is less than or more than five days, while the length of hours on working days is the same, but differs from the norm according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Hourly - used to evaluate each hour of an employee if the daily work schedule is irregular. When calculating an employee's total income, the actual time worked during a certain period of work is taken into account.
Additional Information
Features of the tariff system of remuneration are established by local acts of the employer's organization. To calculate the hourly tariff rate, it is necessary to divide the employee’s salary by the standard working hours for the month, in accordance with the production calendar.
The procedure for calculating wages according to the tariff system is established by the employer in accordance with the terms of labor legislation and on the basis of tariff and qualification directories of positions, works and professions.
Salary (official salary)
Salary is the established amount of remuneration, the main component of which is the employee’s performance of official duties during the working month. The salary part of the remuneration, as in the tariff calculation, does not include any other types of payments.
Salary is calculated based on the number of days actually worked in a calendar month. It is necessary to divide the salary amount established under the employment contract by the number of workers in a month, then the resulting amount must be multiplied by the number of days actually worked.
For example, if according to an employment contract the salary is 50,000 rubles , there are 22 working days in a month , and the employee worked 20 days , then 50,000 rubles are needed. / 22 days × 20 days = 43,478 rubles . (salary amount before deduction of personal income tax).
Basic salary (basic position salary)
The basic salary is part of the salary for workers and employees of the state or municipal service ; the amount and procedure for payments are established depending on the position, field of activity and qualifications of the employees.
According to Art. 144 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the base salary of employees cannot be less than the salary regulated by the government of the Russian Federation for the corresponding professional qualification groups. The size and system of remuneration are established on the basis of uniform recommendations adopted by the decision of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Labor Relations, as well as the norms of the unified qualification directory of works and professions and the directory of positions of managers, workers and employees.
What is included in the main (net) part of the salary?
The main part of the salary includes only the salary (tariff rate). This is a fixed part of the salary. It is reflected in the employment contract and the employer’s staffing table. The introduction of other payments to the salary (based on the law or at the will of the parties to the employment agreement) is additional, but in some cases the salary can only be a fixed salary. The opposite situation, when the salary consists only of additional payments without a salary (tariff rate), is not provided for by law.
Consequently, salary refers to the minimum amount of money that an employee has the right to claim when performing a certain job function for a specified period of time.
To set the salary level, the most important indicator is the qualifications of the employee. Its concept includes:
- having a certain level of education;
- previous practice of carrying out the relevant work;
- qualification category (if available).
Two other indicators - complexity and volume of work - are no less important, since qualifications are closely related to them. It is this that presupposes the possibility of performing a labor function with a certain level of complexity and volume. It is important not to confuse this level with personal indicators (for example, resistance to stress, independent decision-making). As a rule, personal indicators have a greater influence on the level of the position held than on the salary.
Compensation payments
Compensation payments that are accrued to an employee upon execution of an employment contract are of two types. Some are included in wages, others serve to reimburse employees for expenses incurred in the performance of work duties.
Read also: Payment to maintain the grace period
According to Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, compensation , which are part of wages, are accrued when a person works in working conditions that differ from standard ones or has special skills related to his profession. The amount of additional payments is established by the collective agreement and cannot be lower than that established by labor legislation.
Payment of compensation payments included in wages is accrued for work:
- in harmful or dangerous conditions - the amount of compensation must be increased by at least 4 percent of the tariff rate or salary (Article 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- in areas with special climatic conditions - the amount of payment increases depending on regional coefficients (Article 315 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- depending on the qualifications of the employee (Article 150 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- when combining positions or performing the duties of an absent employee - paid by agreement of the parties (Article 151 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- overtime - paid at an increased rate: for the first two hours - at one and a half times the rate, for subsequent hours - at double or more (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- on weekends and holidays - paid no less than double (Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- at night - from 22:00 to 06:00 an additional payment of 20 percent of the salary or tariff rate (Government Decree No. 554 of July 22, 2008).
Compensation payments not included in wages include:
- payment for business trips;
- compensation when moving to another job;
- additional payments when performing government duties;
- payment when combining work with education;
- payments upon termination of work through no fault of the employee;
- payment of annual paid leave.
Piece and time-based forms of remuneration: briefly about the main thing
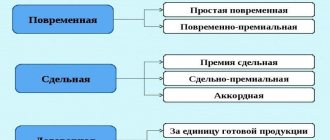
The main forms of remuneration within the tariff system are piecework and time-based. The difference between them lies in the method of accounting for labor costs: with the piecework system, the amount of products produced by the employee is taken into account, with the time-based system, the time worked. When setting a time-based salary for an employee, the employer primarily takes into account two factors: the qualifications of the specialist and the amount of time worked. This calculation scheme is most relevant when it comes to office, creative, research, scientific and any other work that is very difficult to standardize.
Time payment can be:
- Simple . Time worked is paid regardless of the amount of work performed.
- Time-based bonus . In addition to payment according to the tariff, the employee receives bonuses for the quality and efficiency of work.
- Salary . Depending on the qualifications of the employee and the category of work performed, a fixed salary is established.
| Advice To calculate wages without errors with a time-based form of remuneration, fill out a time sheet daily, noting employee attendance and absence, the number of hours and days worked, lateness and overtime. |
“Piecework” is used when the employer has a real opportunity to keep records of the products produced. In order to standardize the labor of personnel in a piecework system, output volumes are established.
6 types of piecework wages
- Straight . Fixed piece rates are used, and the employee’s salary directly depends on the volume of work performed or the number of products manufactured.
- Piece-premium . Bonuses are provided for exceeding production standards and the absence of defects in products;
- Piece-progressive . The results of labor within the established norm are paid at regular rates, and products produced in excess of the norm are paid at increased rates, but not more than double the rate;
- Collective piecework . Salaries are set for the entire team (team, department, group of specialists), and then redistributed among employees by decision of the team members;
- Indirect piecework . It is used mainly when calculating wages for employees servicing production equipment and main workplaces, and depends on the productivity of personnel working at the serviced workplaces;
- Chord . The complex of different works performed by employees is assessed, indicating the deadline for their completion.
Another common version of “piecework” is a salary set as a percentage of revenue received. Often used in retail and wholesale trade. The more products the company sells, the more the employee will earn.
Incentive payments (additional payments, allowances, bonuses, etc.)
The procedure and amount of incentive payments are established by local regulations or collective agreements of the organization. Since incentive payments are included in the additional part of the salary and are not mandatory, they can be accrued at the will of the employer.
Local acts of the organization indicate specific indicators , upon fulfillment of which incentive payments should be accrued. If such payments are specified in the employment contract as components of wages, then the employer does not have the right to refuse to accrue them.
The main types of incentive payments are considered to be:
- various types of surcharges and allowances;
- bonuses;
- other incentive payments.
Attention
The amount and procedure for calculating incentive payments to employees of state and municipal institutions is established on the basis of the list of payments for this category of employees in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated December 29, 2007 No. 818.
Additional payments and allowances
Additional payments and allowances are stimulating in nature and are awarded to the employee for special merits in work and high professional qualities. Their goal is to arouse interest in further development in their work activities. Can be installed when:
- having higher qualifications, for example, an academic degree;
- long work experience and length of service;
- special professional skills;
- performing particularly important work;
- for the safety of information that has a special secret.
Additional payments or allowances can be paid in a fixed amount of money, as a percentage of the salary, or calculated based on the tariff rate.
Employee bonus
The bonus is calculated on the basis of an assessment of the quality of work , for the employee’s achievement of special indicators in the performance of work duties. According to the provisions of the letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated September 21, 2016 No. 14-1/-911, bonuses can be paid for any period longer or shorter than a working month.
Payments are made on the basis of local acts of the organization. In the regulations on the procedure and amount of bonuses, it is advisable to indicate:
- positions of employees who are entitled to payment;
- amounts and conditions for accrual;
- frequency of accrual.
For your information
The bonus regulations indicate the exact date of payment or a certain period for accrual, for example, the 15th day after the reporting period. If the bonus is calculated based on the results of the working year, then you can specify the month in which the payment will be made.
In the context of the economic crisis, almost all companies are thinking about how to reduce costs and at the same time retain loyal staff. Reducing labor costs is one way to reduce costs. Reducing staff is an extreme measure, and it is quite possible to do without it, provided that the cost reduction will not be long-term. In practice, there are other legitimate methods of reducing the costs associated with employee wages. In any of the proposed options, it is important to follow the procedures and specifics of interaction with personnel in order to, if possible, avoid claims from inspection authorities, as well as from employees.
Incentive payments and salary supplements
For the most part, incentive payments are made through bonuses (we will focus on this in a separate subsection). But there are other ways.
For example, appropriate additional payments and bonuses are intended to encourage the employee to various achievements related to work through certain material incentives.
Let us give an example of one of the types of such payments: an allowance for length of service at one enterprise. In particular, it aims to:
- reward an employee for a long period of work in a particular organization;
- encourage him to continue working in this organization;
- to orient other employees to the fact that long work experience at this enterprise provides certain material benefits, and to deter them from looking for another job.
Another similar bonus may be established for the employee for regular professional development, acquisition of additional skills, and in other cases.
The procedure for such payments varies. For example, a payment or gift could be:
- one-time (for a professional holiday, anniversary) or periodic (based on the results of fulfilling the quarterly plan, etc.);
- set at a fixed amount or calculated as a percentage of the salary.
What does salary consist of?
In addition to wages, companies often offer employees a so-called compensation package, which includes a voluntary health insurance policy, payment for food, mobile communications, a gym, foreign language courses, etc.
When deciding to reduce labor costs, you should first consider options for reducing the compensation package and the variable part of wages. And only then should we consider reducing the permanent part of remuneration.
Read also: Cash loan secured by real estate
Let's look at the most popular and legal ways to reduce labor costs.
Analysis of the components of the compensation package
Voluntary health insurance (VHI) for employees is the most popular and widely used component of the compensation package; completely excluding insurance is not recommended for several reasons. Firstly, as a rule, the provision for voluntary health insurance is included in employment contracts, which means that they will have to be amended in the event of an exception. Secondly, spending on voluntary health insurance can reduce taxable profit (within 6% of the wage fund), which in itself is beneficial for the company. Secondly, the exclusion of voluntary health insurance from the compensation package will significantly reduce the employer’s position in the market for job seekers. In order to save money, the VHI program can be revised in the direction of reducing the volume of services provided, while retaining the necessary and vital services; in this regard, a survey of employees can be conducted and, based on the results, the ones that are in great demand can be left to choose from.
Part-time work
In the process of introducing part-time work, an important role is played by the fact that the transfer to part-time work must be justified, for example, by a change in the company’s technological processes. The decision to transfer part-time work is communicated to employees in compliance with the notification procedure of the State Labor Inspectorate at the place of registration of the company, in compliance with the deadlines. The procedure for notifying employees is also strictly regulated, which must be strictly observed in order to avoid the consequences of employees’ requests to protect their labor rights.
Reduction of the fixed part of wages
The salary reduction is carried out on the grounds that the company selects from a possible list for these purposes: a decrease in demand for products, a decrease in sales volume and, accordingly, a decrease in the volume of job duties, the exclusion of a number of job responsibilities, which will entail a change in the job description and a reduction in the permanent part of the salary. . This will require preparatory work with the involvement of line managers and HR specialists.
Employees must be notified in writing of salary reductions at least two months before the changes. The basis for notifying employees is the decision of the manager in the form of an order; upon notification, it is necessary to sign an additional agreement with the employees to change the terms of the employment contract. And based on this document, issue an order to change the salary (indicating the reason for the reduction) and the staffing table.
If the employee does not agree with the salary reduction, you can try to offer him one of two other possible options. The first is to temporarily transfer the employee to another position with a lower salary (Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The second is to establish a part-time or weekly work schedule in the company (see above). All this is also possible only with the written consent of the employee.
Important!
When reducing salaries, it is necessary to remember that the salary does not become less than the regional minimum wage.
Awards. If the employment contract states that the company pays a bonus in the form of a certain amount or a percentage of the salary, then such a bonus is considered a fixed part of the salary, therefore, the reduction of such bonuses must be notified to the employee at least two months in advance, the employee’s consent must be formalized in accordance with a procedure similar to the procedure for changing the salary with the preparation of the necessary documents.
The bonus provision may contain a condition that the bonus is guaranteed to be paid to employees based on the results of a certain period, in which case the bonus is also considered an integral part of wages. and, the procedure for its cancellation or reduction is the same as in the situation described above with a reduction in salaries and fixed bonuses. In addition to the notification procedure described above, the employer needs to approve the new Regulations on bonuses and familiarize employees with it against signature.
What functions does wages perform?
Salary has the following functions:
- motivational;
- reproductive;
- stimulating;
- status;
- production-share;
- regulating.
This function is the main one for an employee, since the salary allows him to satisfy his needs . Without material reward, a person would not waste his time on some kind of work activity.
The reproductive function is closely related to the motivational one, but serves for the benefit of the enterprise: the employee must eat well and be in good physical shape. His family also should not need anything, so that the employee could fully concentrate on his duties.
Sufficient monetary remuneration can increase employee productivity and ensure smooth operation of the company.
This function comes down to the fact that the employee must go to work with the understanding that wages primarily depend on the performance of his work. To do this, the employer must provide the person with work instructions, identify specific achievements and motivate the employee for exceeding them, for example, with a bonus.
Provides salary in accordance with the employee’s qualification level, knowledge and experience. The amount of monetary reward is an indicator of his place in a particular social group. For example, it is for this reason that electricians of different categories will have differences in salaries even with equal hourly output.
Requires the contribution of each employee to be taken into account in the final production costs.
Helps employees and subordinates interact effectively.
How else can you save money?
Unpaid leave. Another option is to send the employee on leave on your account. In this case, it is important that the employee writes an application with a specific period of leave. You also need to ensure that employees, for example, of one department, go on vacation one by one, and not all at once. Otherwise, mass unpaid leave may arouse suspicion on the part of labor inspectors.
Protect yourself from tax audits. An online course from a former employee of the Department of Economic Crimes, and now a well-known tax consultant, is now with a 50% discount. Now for only 2750 rubles.
You will learn to withstand the pressure of tax authorities, behave competently during interrogations and seizures, and protect yourself from criminals and subsidiaries.
Lots of practical advice and a minimum of theory. Training is completely remote, we issue a certificate. Hurry up to buy (we have five more courses at a discount).