27.08.2019
0
40
4 min.
Our country has developed several options for calculating monetary remuneration for hired employees. Article 143 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates issues related to the tariff system for calculating wages. It is the most common. In addition, there is special terminology and a number of nuances that distinguish this method from others. It is useful for accountants, personnel officers and simply workers to know the defining points.
Article 143 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: tariff system
Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 143 defines the basic concepts and rules of the tariff system of remuneration. Gradation of the level of labor income of employees depending on their professional skills is achieved by introducing a tariff system of payment for work performed at the enterprise.
What is the tariff system of remuneration?
It provides the following main points:
- for working specialties, hourly wage rates are established, which are grouped by specialty and directly depend on the complexity of the work performed;
- engineering and technical personnel receive wages based on monthly salaries (they are also grouped by specialization and increase as the category increases);
- it is allowed to introduce a range of official salaries, when for one specialty and category the employer has the opportunity to set different official salaries;
- You can set a single level of tariff rate (salary), and all other employee salaries can be calculated by multiplying by tariff coefficients provided for by the tariff payment system implemented in the organization.
Typically, the tariff system is established on the basis of the wage fund available at the enterprise, the volume, complexity of the actions performed, taking into account the average state level of payment for work in similar specialties. Typically, the wage fund is calculated based on the company's projected income.
Remember, a properly structured tariff system of labor remuneration will motivate employees to professional growth, and the level of payment above the market average will ensure low turnover of personnel in the main professions.
It is necessary to understand that it is advisable to inflate the level of compensation for labor activity only in relation to acute shortages of highly intelligent specialties. All other employees will feel comfortable if their income level is 10–30% higher than similar specialties in other companies.
How are wages regulated?
According to new developments regarding the spending of the wage fund on various incentive payments, professional state standards are used, according to which the work of each official or employee is assessed taking into account the effectiveness of his activities.
But the problem of inadequate assessment of work remains, since the old distinction between the manager and the employee works, and the professionalism of the latter is not taken into account.
In addition, officials are prone to misuse of funds for other purposes.
How and in what amount a salary advance is paid - read in this article.
Classification according to new standards
Classification in the tariff schedule is based on several components:
- Industry;
- Government and commercial organizations;
- Division within the enterprise.
For example, their categories, base salary and minimum wage take part in the tariffication of payments for medical workers.
In addition, rates are based on:
- A centralized act established by the authorities;
- Contractual basis – collective agreement.
In this case, a new remuneration system is applied, but taking into account the old principles.
Payment categories and coefficients.
Rank coefficients and rates for payment
The coefficients used may vary depending on the industry of application, but for budgetary organizations fixed indicators are used in almost any area.
For example, for budgetary organizations in medicine the following figures are used:
| 1 | 1 | 1 100 |
| 2 | 1,04 | 1 144 |
| 3 | 1,09 | 1 199 |
| 4 | 1,142 | 1 256,2 |
| 5 | 1,268 | 1 394,8 |
| 6 | 1,407 | 1 547,7 |
| 7 | 1,546 | 1 700,6 |
| 8 | 1,699 | 1 868,9 |
| 9 | 1,866 | 2 052,6 |
| 10 | 2,047 | 2 251,7 |
| 11 | 2,242 | 2 466,2 |
| 12 | 2,423 | 2 665,3 |
| 13 | 2,618 | 2 879,8 |
| 14 | 2,813 | 3 094,3 |
| 15 | 3,036 | 3 339,6 |
| 16 | 3,259 | 3 584,9 |
| 17 | 3,510 | 3 861 |
| 18 | 4,500 | 4 950 |
Important: in this case, if an employee works in a rural area, then 25% of the base salary is added to his salary.
If this is a deputy, then his salary is 10 - 20% lower than the manager, taking into account qualifications, degree, honorary title.
If the specialty is not indicated in the inter-industry tariff directory, then such a specialist’s salary is calculated in accordance with the unified tariff and qualification directory.
Examples of payment calculations
If time wages are used, then the number of hours worked is simply multiplied by the rate per hour.
The employee worked 150 hours in a month, his rate per hour is 134 rubles, it follows that he earned:
150 * 134 = 20,100 rubles per month.
Since he fulfilled the plan, according to the collective agreement he is entitled to a bonus in the amount of 20% of his earnings, that is:
- 20,100 * 0.2 = 4,020 rubles premium. Here you will find out the rules by which monthly bonuses are calculated for employees.
- 20,100 + 4,020 = 24,120 rubles earnings.
In addition, he has a 5th category, and this involves using a coefficient of 1.268, which indicates the employee’s earnings in a given month are 30,584.16 rubles.
Important: if an employee does not fulfill the plan, the employer has the right to deprive him of the bonus.
Tariff category
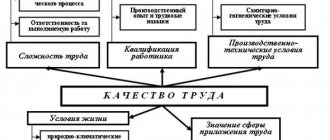
The minimum unit for determining the basic level of employee income is the tariff category. It serves to establish a fixed level of payment (rate, salary) for work performed.
The tariff category is determined by the level of knowledge, experience and qualifications of the employee
The tariff category is formed based on the following criteria:
- complexity of the actions performed;
- having prior work experience in similar conditions;
- the level of available special training;
- a list of works available to be performed by a specific employee.
The basic document for forming a category and assigning it to a specific worker is the tariff and qualification directory, which contains all the necessary key information for the employer. The assignment of a specific category to a certain level of payment for fully completed work is carried out by the employer together with trade unions. As a result, all this should be reflected in the collective agreement (company agreement).
Remember, employees with the same ranks, but in different specialties, may belong to different pay groups. Here everything will depend on the complexity, responsibility of the actions performed, as well as their role in the overall technological process of the company.
To establish a higher rank during the employment of an employee, the latter must document that his experience, qualifications, and level of knowledge are sufficient to perform the entire list of work provided for such rank. In the future, the employer can initiate a commission check of the employee’s compliance with the rank assigned to him.
Labor pricing is a concept that covers the pricing of both work and workers.
The tariffing of work means the establishment of a rank for each type of work or its assignment to one or another pay group, depending on the conditions in which it occurs, the characteristics of the given production and the qualifications required of the employee. Tariffication of workers consists of assigning them ranks depending on their qualifications and the degree of complexity of the work performed, corresponding to the requirements of ETK.S. The procedure and rules for charging workers are set out in the ETKS. [p.18] In health care facilities, special qualification commissions are created to carry out tariff ratings for workers, headed by deputy heads of health care facilities. These commissions include leading specialists and mentors from among highly qualified workers. [p.18] ETKS consists of 69 issues. At enterprises transporting and storing oil, petroleum products and gas, issue 36 is mainly used. Tariffing of workers in cross-cutting professions, in particular electric welders, workers in mechanical workshops, electrical and heating networks, and drivers, is carried out according to the corresponding issues of ETKS. [p.92]
For the tariffication of working technological installations, a tariff and qualification reference book for workers employed at oil and gas processing enterprises is used. [p.83]
The establishment of a worker's tariff category and the assignment of work to one or another category of the tariff schedule (i.e., tariffication of workers and work) is carried out on the basis of a tariff-qualification reference book. The directory contains production characteristics of all types of work, with established tariff categories for them, qualification characteristics of workers, which contain a list of duties of a worker of a certain profession, indicating what he should know, be able to do, and for which he is responsible. [p.179]
ET provides for payment differentiation across 18 categories. Tariffication of workers is carried out according to 8 categories. This corresponds to the current Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Work and Professions of Workers (UTKS). At the same time, for highly qualified workers employed in important and responsible jobs, as well as in particularly important and particularly responsible jobs, salaries can be set based on 9-10 categories of ET payment according to the lists approved by ministries and departments of the Russian Federation, and from 11-12 categories ET payments - according to lists approved by the Russian Ministry of Labor. This measure is provided in order to strengthen material incentives for the most complex and skilled labor of workers.
Tariffication of workers is carried out according to eight categories, which corresponds to the current Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Work and Professions of Workers (UTKS). For highly qualified workers employed in important and responsible jobs, as well as in particularly important and particularly responsible jobs, it is allowed to set salaries based on 9-10 categories of ET wages according to lists approved by ministries and departments of the Russian Federation, and from 11-12 categories of the ET system —according to lists approved by the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation. [p.491]
The assessment of the qualifications of an electrical installation worker and the assignment of a certain category to him (worker tariffication) are carried out on the basis of a tariff and qualification directory of works and professions of workers engaged in construction and repair and construction work (TCS). [p.260]
Tariffication of workers (assignment or increase in rank) is carried out on the basis of a tariff reference book. The worker must answer all the questions provided under the heading Must know, and perform at least three types of work specified in the section of the reference book Examples of work, while fulfilling the current production standards while observing the quality of work provided for by the technical conditions. [p.262]
Tariffing of workplaces. [p.284]
Main sections of the collective agreement scope of action goals admission, probationary period, dismissal, working conditions benefits for individual categories regulation of working time temporary disability and breaks in work payment of travel allowances composition of labor costs forms of remuneration certification of workers work evaluation system pricing of workers, employees and workplaces additional payments bonuses payment for rationalization proposals payroll training and advanced training of personnel labor and life safety social security resolution of labor conflicts principles of interaction between the administration and trade union leadership appendix. [p.334]
The tariff-certification system of remuneration is a combination of rigid tariffication of jobs and a flexible system for establishing personal salaries. The procedure for calculating wages includes four stages [p.355]
To organize wages, it is necessary not only to determine the category of work, but also to carry out the tariff classification of workers, that is, assigning them a certain tariff category depending on their professional knowledge and work skills. For these purposes, the tariff and qualification reference book indicates the necessary requirements (characteristics) that determine the amount of professional knowledge (what a worker should know) and labor skills (characteristics of the work that he should be able to perform) required by a worker of this category. [p.241]
To organize remuneration for labor, it is necessary not only to determine the type of work, but also to rate the workers, that is, assign them depending on the level of professional knowledge and work skills. divided digit. Currently, tariffs for work and workers are carried out in industry on the basis of the Unified Tariff and Qualification Reference Book (UTKS). If the ETKS does not contain a characteristic for any of the work (operations) being performed, then its category is determined by analogy with a similar work. The ETKS is periodically revised so that it reflects the achieved level of technology, labor organization and production and contains examples of truly characteristic and typical work. Only if these conditions are met is the correct tariffication of work and workers and payment for their labor guaranteed. [p.157]
In conditions of tariffing of workers on the basis of a single six-category grid, a tariff-qualification category can be used to build a qualification structure. However, assessing changes in the qualifications of workers according to their tariff categories with a certain degree of approximation is permissible only if the tariff and qualification reference books are constant during the analyzed and planned periods, as well as the unity of the criterion for assigning workers to categories of the tariff schedule. Otherwise, the indicator of the worker’s tariff category is not commensurate with the degree of complexity of the work and the actual level of qualifications. [p.460]
Details about the tariffs for workers and certification of managers, specialists and employees (see paragraphs 2.2.2 and 2.3 of this handbook). [p.136]
When organizing labor remuneration, not only the tariffication of work is carried out, i.e., the assignment of work to a certain tariff category, but also the tariffication of workers, i.e., the assignment of tariff categories to workers corresponding to their qualifications. The main criterion for assigning a certain tariff category to a particular worker is whether he or she has the professional knowledge and labor skills necessary to perform work assigned to a given tariff category. This work is carried out by special qualification commissions, which include representatives of the administration and trade union organization (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the RSFSR). When deciding on the establishment of tariff categories for workers of a particular production site, the qualification commission also includes foremen, and, if necessary, qualified workers of this profession and other specialists. [p.63]
Establish that, pending the revision of the current Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Work and Professions of Workers, the mandatory requirement for specialized secondary education when grading workers for the range of professions and tariff categories provided for in the List is determined by the ministries and departments of the USSR and the Councils of Ministers of the Union Republics in agreement with the relevant committees trade unions. [p.16]
Tariffication of workers (assignment or increase in rank) is carried out on the basis of a tariff reference book. The worker must answer all questions provided - [p.193]
The practice of charging workers should be based on the need to match their qualifications to the complexity of the work performed. [p.27]
Constant improvement of the technical base of production and labor organization of workers is accompanied by progressive changes in the content of their work, the composition of the labor functions performed in the direction of growth of the functions of mental labor associated with the management, regulation and control of the progress of technological (working) processes. Under these conditions, the knowledge acquired by workers both in preparation for work and in the process of on-the-job training acquires decisive importance among qualification factors. Therefore, knowledge requirements should become an important factor in the pricing of workers and be appropriately reflected in the Unified Tariff and Qualification Handbook. [p.27]
In this case, one should be guided by a unified inter-industry List of professions for higher-level workers whose qualification level requires secondary specialized education, approved by Resolution of the State Committee of the USSR Council of Ministers for Labor and Social Issues of September 2, 1977 No. 288. The resolution stipulates the conditions for tariffication of workers by professions included in the specified List. [p.28]
When charging workers, production characteristics are used, the contents of which are set out in the tariff and qualification reference book. For each profession and qualification, this reference book provides a comprehensive description of the work and a list of the necessary knowledge and skills of the worker. The worker's tariff category is established and assigned by the tariff and qualification commission, headed by the shop manager, with the participation of a representative of the trade union organization, engineers, highly qualified workers and craftsmen. The commission checks the worker’s theoretical knowledge in the field of product manufacturing technology, design and control of the machine or [p.101]
This method allows for a fair distribution of collective earnings with timely and correct tariffication of the team’s workers, the correspondence of the categories of workers to the categories of work, and the conscientious attitude of all workers to the performance of their duties. However, in practice, violations of these conditions are possible. To more fully take into account the individual contribution of each worker to the results of the work of the team, with the consent of its members, labor participation coefficients (LPCs) can be applied. They represent a generalized quantitative assessment of the labor contribution of each participant in the work. [p.245]
In addition, when pricing a worker, his economic training on the following basic issues must be taken into account: the most important indicators of the production plans of the site and the role of the worker in their implementation, production efficiency (basic concepts) and means of increasing it, ways to increase labor productivity and the quality of products, basic concepts about production costs , profit and economic accounting, basic concepts of labor organization and requirements for labor organization in a team and at the workplace, forms and systems of wages, etc. [p.124]
The Unified Tariff and Qualification Guide is intended for the tariffication of workers engaged in construction, installation, repair and construction work, in ancillary production and other farms on the balance sheet of construction, repair and construction organizations (construction sites), as well as those working in repair - construction shops of enterprises. [p.288]
S.t.r. depends on the distribution of workers according to the categories of the tariff structure; the greater the number of workers will be charged according to the middle and highest categories, the higher it is in the enterprise as a whole. Data on S. t.r. workers and jobs make it possible to judge the degree to which workers’ qualifications correspond to the complexity of the work they perform. If S. t.r. workers significantly exceeds the average level of work performed, then the tariffs for workers are overestimated if the S. t.r. below the average level of work, then the tariffs for workers are underestimated. [p.75]
ET provides for payment differentiation across 18 categories. The specific level of remuneration for each employee is established based on the results of tariffication of workers and certification of employees. [p.359]
Tariffication of workers is carried out according to eight categories (from 1st to 8th). This corresponds to the current Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Work and Professions of Workers (UTKS). At the same time, in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 14, 1992 No. 785, in institutions, organizations and enterprises that are financed by the budget, highly qualified workers employed in important and responsible work and in particularly important and particularly responsible work may be set salaries based on 9-10 categories of ET payment according to lists approved in the prescribed manner by ministries and departments of the Russian Federation, and from 11-12 categories of ET payment - according to lists approved by the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation. This measure is provided in order to strengthen material incentives for the most complex and skilled labor of workers. [p.359]
The categories for remuneration of workers are established by the head of the enterprise, a separate structural unit of the main activity of the railways, based on the results of tariffication of workers and certification of managers, specialists and employees. [p.404]
LABOR TARIFFICATION is a concept that includes both the tariffication of work and the individual tariffication of workers. Tariffing of work means determining the degree of complexity of its implementation and assigning it to one or another category of the tariff scale (see Analytical assessment of the complexity of labor). Individual tariffication of employees consists of assigning an employee, depending on his qualifications, one or another category in accordance with the requirements of the tariff and qualification reference book. Tariffication of workers acquired special significance and urgency [p.375]
Time standards for work performed by production site foremen [5] are intended for calculating aggregated time standards, establishing standardized tasks, developing or adjusting industry standards for the number of foremen, as well as planning their number at production enterprises. They contain operational time costs by type of work depending on the influencing factors (Table 8.18). When calculating the standard number of production site foremen, in addition to the labor intensity of standardized work, calculated according to time standards, the labor intensity of work not provided for by the standards is also taken into account, established on the basis of photographic observations, the numerical value of which should not exceed 10% of the labor intensity of standardized work (participation in the development of regulations on bonuses , in commissions for the tariffs of workers, in the organization of public reviews on labor organization, etc.). [p.301]
The use of Methodological Guidelines in the development of tariff and qualification reference books for workers is aimed at ensuring uniformity in the tariffication of work of equal complexity both within branches of production and between industries, as well as unity in the tariffication of workers of equal qualifications. [p.3]
This method makes it possible to produce a generally fair distribution of collective earnings with timely and correct tariffication of the workers of the team, the correspondence of the categories of workers to the categories [p.292]
ETKS serves to determine the categories of work and workers. In most industries, work is divided into six categories, in some industries - into eight. With the help of ETKS, the most difficult task of comparing (comparing) various types of work according to the degree of their complexity, and, consequently, according to the level of qualifications, is solved. Tariffing of workers, i.e. assignment to them, depending on the level of professional knowledge and labor skills of a certain category, is carried out by the commission on the basis of the current ETKS, which includes more than 70 issues for professions common in all sectors of the national economy, as well as industry issues and is mandatory for use in state enterprises and advisory for enterprises of other forms of ownership. [p.186]
Tariffication of piece workers is carried out in accordance with the tariffication of the work they perform. When dealing with various operations, the grade of work performed may be higher or lower than the grade assigned to the worker, but the deviation should not be more than one grade. When this deviation in individual jobs is more than one grade, then the worker, in accordance with current legislation, is paid the difference between grades, if it is stipulated in the collective agreement. [p.143]
Tariffication of works
In order to correctly determine the relationship between the list of actions performed and the employee’s ability to do it at a high professional level, all work is charged. Tariffing refers to the sorting of specific actions that an employee with a certain level of qualifications must be able to perform. The set of such actions increases in proportion to the level of increase in the level of work assigned to the employee.
It is important to take into account the following nuances:
- The minimum set of requirements falls into the first category.
- For each subsequent rank, an increase in the skills required to perform is provided. At the same time, the expansion of skills is carried out without reducing the list of skills at lower levels.
- To gain skills in certain types of work, special training and education may be required, followed by passing tests or exams.
Based on a correctly completed work tariff, the employer has the opportunity to assign the employee the correct rank, clearly covering the level of his qualifications, past training, and existing experience in performing similar actions. Accordingly, a fair ranking of pay for work performed is established, and motivation appears for other workers to develop in order to move to the next level in rank, and therefore in pay.
Remember, the pricing of work is also taken into account in the process of developing and approving labor standards, prices for piecework, and determining the coefficients of individual labor participation if the work of ordinary workers is carried out collectively.
Tariff and non-tariff wage system
Unlike the tariff system described above, in the non-tariff system (BSOT) there are no base rates and no fixed salaries. There is a unified wage fund (payroll) and a matrix of conditions that, in the opinion of the employer, are important for the organization to achieve the expected results.
Such conditions may be:
- the volume of services provided by each employee (for example, he may be paid a percentage of the volume of services);
- the amount of profit received;
- employee qualification level coefficient (EQL);
- participation rate.
BSOT example.
LLC "Snezhinka" Payroll for April 2021 - 300,000. CGC of the director - 3; chief accountant - 1.5; sales manager - 1.3; cleaners - 1.
Sum of odds: 3 + 1.5 + 1.3 + 1 = 6.8.
Director's salary = 300,000 / 6.8 × 3 = 132,353 rubles.
Accountant's salary = 300,000 / 6.8 × 1.5 = 66,176 rubles.
Salary of a sales manager = 300,000 / 6.8 × 1.3 = 57,353 rubles.
Cleaner's salary = 300,000 / 6.8 × 1 = 44,118 rubles.
However, such a system is quite exotic, labor-intensive and rarely used.
Advantages and disadvantages
The tariff system has its advantages and even some disadvantages. Among the positive and negative aspects of this method of stimulating highly productive labor, the following points should be highlighted:
| Advantages | Flaws |
| there is a clear gradation of the level of payment for a specific amount of work; | in order to receive the next rank or category, you must pass a test by a special commission (or undergo training); |
| it is possible to divide employees based on their qualifications; | to move from one category to another you need to wait a certain time; |
| each employee understands what he is paid for, or can be paid wages; | in some cases, the basis for assigning a category is the presence of a certain education. Therefore, young students with minimal work experience may be more likely to advance in their careers than older, experienced employees with no education; |
| there is always motivation for development in order to move up the career ladder; | The existing monetary gap between ranks (categories) does not always correspond to the level of necessary labor costs that are required from the worker. |
| the gap between the pay of highly skilled workers and low-skilled workers significantly reduces staff turnover. |
Remember, the introduction of a tariff system of remuneration, even with some of its shortcomings, ultimately has a positive effect for the company as a whole. Especially if the company is aimed at long-term existence and active development.
What is she?
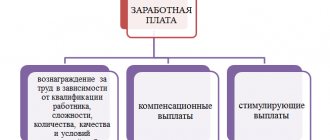
The tariff schedule is a set of qualification categories and coefficients that determine wages .
This form of payment is designed to take into account the nature of the work (harmful and dangerous conditions), intensity, weather conditions in which employees work, and their professional level. Grids are formed based on:
- Labor intensity.
- Hazards (normal, difficult, dangerous working conditions).
- Length of time worked at the enterprise or position.
- Industry principle of formation of the remuneration system (different types of industry have their own categories).
The wage scale is based on hourly wages. For some workers or employees, accrual is made based on the volume produced, for example, in various industries. The planned volume is then broken down by the number of hours in a shift or working day. In this way, the employee’s hourly rate is calculated regardless of his type of activity.
The enterprise may assign rates outside the categories or higher salaries.
The tariff schedule contains a certain number of ranges - on average, a 6-bit grid is used. If there is a need, a system with a large number of digits is created, usually due to the complexity of production. The second component of the system is the coefficient. Knowing them, you can calculate how much the employee will receive.
The differences between this system and the grade system are discussed in the following video:
State regulation of tariff mechanisms
Tariff and qualification requirements for employees are determined through the Employee Qualification Directory (QDS).
Mechanisms in wage regulation in modern market conditions should be based solely on the mutual combination of contractual and government interaction. The system in the field of wage control is decisive in the formation of appropriate tariffs.
One of the main tasks of state regulation is, first of all, to clearly establish the minimum wage, tariff rates of the leading category, as well as the necessary coefficients. The contractual nature involves the use of tariff, general and sectoral agreements, as well as collective and labor documents.