Modern forms and types of remuneration
Forms and systems of remuneration change over time. The employer’s task is to choose one or another monetary remuneration option that encourages the employee to improve their work performance and improve their skills. In the new labor legislation, the forms and methods of payment differ fundamentally in characteristics.
There are two types of salary:
- main;
- additional.
The basic salary is paid in a certain amount at a standardized rate, based on the principle of time worked, additional payments include payments for time not worked, for example, as vacation pay.
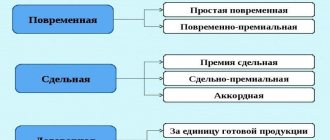
There are two main forms:
- piecework;
- time-based.
The concept of “piece-rate form of remuneration” is used when payments to employees are made based on various changing quantities of products produced by the employee and standardized tariffs. Piece payment options are available:
- The piece-bonus form, in addition to the salary according to the tariff and other payments, provides for the payment of a bonus by the organization. The piecework-bonus form is effective for stimulating staff to improve the work process and eliminate shortcomings in work.
- The amount of progressive piecework wages from the minimum and above varies depending on the amount of products that the employee produced in the organization for a certain period.
- Indirect piecework wages are typical for workers in auxiliary production or service industries and are calculated based on the total amounts at the wage rates of employees of the enterprise they serve.
- The chord or brigade form of remuneration is included in the concept of “collective forms of remuneration” and is one of the types of collective payments. The concept of “chord system” is used in cases where it is necessary to complete a set of works within a specific period. Usually the work is performed by a team (team) of workers. With the lump-sum system, the organization calculates the amount of monetary remuneration on a collective basis - to the entire team, and then the amount is divided among the employees. For the purpose of incentives, if work is completed ahead of schedule and the work process is effectively improved, the lump-sum system allows for the payment of bonuses to employees in accordance with the standardized tariff schedule. The chord system is effectively used in construction, shipbuilding, and large-scale repairs of large equipment.
- The essence of the simple piecework payment method involves payment in an amount calculated on the basis of prices and tariffs adopted at the enterprise and units of production.
Time payment is possible in the following options:
- with a simple time wage, its amount from the minimum is calculated and changed based on the standard time actually worked by the employee, taking into account his qualifications and established tariffs.
- In the case of time-based bonus payment, an incentive bonus is included in the employee’s salary.
- Time-based payment with a standardized task implies the fulfillment of a certain plan.
- The time-piece form is mixed, and includes both signs of time-based and signs of piecework payment.
A separate type of payment methods should include the concept of “commission wages”, which, in turn, is divided into two more types: commission-bonus and commission-piecework. Such a system is a good incentive for staff to improve their skills and effectively perform their duties.
The essence and peculiarity of the commission system is the payment of sums of money to staff depending on the benefits that they bring to the organization. The concept of the system under consideration is well characterized by paying an employee a percentage of the quantity of goods sold, which stimulates his productivity.
Such an approach to payroll has a stimulating effect on the professional contribution of staff to the organization’s activities.
Analysis of the forms and systems of remuneration allows us to conclude: in modern, changing social conditions, the management of an enterprise or organization and the employee are given a wide field of opportunities to improve and choose the most acceptable and convenient method of remuneration, being within the framework of the norms and principles of the law.
Types of wages
It is worth at least somehow distinguishing between the concepts of type of salary and form. Because there are two main types. But from them there is already a division into various forms, of which there are much more.
Basic salary. It is calculated according to the salary agreed upon and specified in the employee’s employment contract. Different positions have their own salaries, based on their complexity, amount of work and required qualifications. Accordingly, on the basis of the salary, taking into account the hours worked, the cost of labor is paid.
The second type of salary is piecework. Here, labor is assessed not according to skills, experience and professional skills, but according to the type of work performed by the hired employee. That is, there is no salary, there is the amount of work done and paid.
Piece wages are of the following types:
- Direct piecework.
- Piece-progressive.
- Piece-premium.
- Indirect piecework.
- Chord.
- Collective.
And time wages, which is the first type, described above, are divided into types:
- Simple time payment.
- Time-based bonus.
Time wages
Exists in enterprises where work standards are either not possible or simply not necessary. A simple example. A factory employee, if he is given the conditions that he will receive a certain amount of money for a certain number of parts produced on a machine, will try to do it faster, but will not do it better. And quality is very much required, because we are talking about a technical product that requires high precision. That is why he is not provided with such conditions, and payment is made for time. Then the plant employee will not be in a hurry. It will be easier for him to do his job efficiently, although it will take longer. Another thing is that this will have to be monitored so that there are no employees who would spend “working time” in idleness.
This scheme, which is based on time, allows employees to be paid by the hour, rather than by the speed. And even if on one day the employee does less than on another, this will not affect the money paid. On the part of the plant management, there will be no opportunity to increase the level of production of working personnel. But it will be possible to save on wages by increasing production capacity.
If we consider the subspecies, we can identify the main difference. A simple time-based wage means only a salary, without bonuses. The size does not change with the same operating time. If there are salary conditions for a month, and a person spent all the required days of his shift at work that month, he receives a salary in the amount of the established salary.
The time-bonus method of remuneration implies that a bonus part can be added to the basic salary. The company's management and responsible persons themselves regulate the amount of bonuses, but determine the percentage based on specific indicators of the company's profit in a given month. But sometimes there is an option when the amount of bonuses, as well as the salary, is a fixed amount depending on the conditions.
Important! If in your enterprise it is not quantity that is important, but quality, then a time-based form of payment of wages will be the optimal solution. Because the employee will not strive to do more in the same period of time.
Cash form for payment of labor
The Labor Code determines what unified monetary form of wages will be the main type of settlement between the employer and the employee. This legal requirement is due to the changing meaning of money in a market economy.
It is receiving money that stimulates the employee to perform his duties efficiently and improve his skills.
Salaries are paid at established rates in monetary units that have legal circulation in the state. In the Russian Federation, payments are made in the form of cash or non-cash payments in rubles, although labor legislation does not contain a direct ban on payments in foreign currency.
Nevertheless, payment of wages in foreign currency may be regarded as a violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. When the foreign currency exchange rate changes downwards, the amount of payments to the employee is minimized, which will negatively affect his financial situation.
Forms of payment
What forms of remuneration are there? There are only two main forms:
- monetary (cash or non-cash payment);
- in kind (products or any material assets), but not more than 15% of the total salary.
The natural form, although provided for by Russian legislation, is extremely rare in practice. The dominant option is the monetary form with a predominance of non-cash payments. Remunerating employees by transferring funds to an employee’s bank card is currently the most convenient option for employers. It relieves them of the need to work with a cash register, receive money for salaries at the bank, and monitor their safety.
At the same time, individual entrepreneurs with a small staff most often prefer to use cash and pay workers from the proceeds. The law does not oblige employers to strictly adhere to any of the forms. Everyone has the right to choose the one that is convenient at a particular stage of business development.
The employer can choose one of the payment systems: give money to employees in cash or transfer to a bank card
Pay in kind
An employer may enter into an agreement with an employee to pay wages in kind (non-cash). However, the law imposes a requirement on this type of payment: the part paid in kind should not exceed 20% of the total salary; this socially protects the employee.
The concept of “in-kind form of remuneration”, in essence, involves the provision to the employee of the products that the organization or enterprise produces or purchases, as part of the salary. Payment in kind is established by the employment contract with the employee. Before concluding an agreement that approves a non-monetary form of remuneration, the employee writes a statement establishing the form in question for remuneration.
Salary and its types
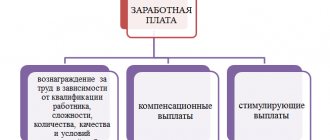
The concept of “wages” (also known as “wages”) and its types are established by Section 6 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This part of labor legislation defines the term as compensation for labor depending on the complexity of processes, operating conditions, and the number of tasks. Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the inclusion in the structure of the concept of compensation and incentive payments.
The types of salaries can be different not only depending on the institution, but also within the structure, since financial motivation depends on what skills, abilities, and qualifications the employee has and in what conditions he works.
In the structure of monetary motivation, there are various types of wages and forms of remuneration:
- Nominal salary is the money an employee receives for his work. Typically includes two parts:
- basic (permanent) salary - from the employee’s tariff income;
- additional (variable) - from incentive additional payments, bonuses for increased performance.
- Real salary is the totality of goods and services that an employee is able to purchase for a nominal salary. Depends on size:
- nominal salary (more money - more services);
- taxes paid (the higher the income tax rate, the lower the real income);
- prices (higher price - lower value).
Article 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation classifies wages into two more types:
- Monetary, in which work is paid in rubles or currency (in cases established by current legislation.).
- Non-monetary (except for payment in bonds, coupons, receipts, alcohol, drugs, toxic substances, weapons).
Using the second type, the employer must comply with the following provisions:
- obtain the employee’s consent to non-monetary payment in writing;
- pay in this format no more than 20 percent of the amount due;
- the fact of payment in kind is common for the field of activity;
- the prices of goods that compensate for part of the labor are reasonable.
Partial payment in kind
Payments to staff using partial payment for labor in products are enshrined in labor law, and are, in essence, an additional option for remuneration. This type of settlement involves, along with the payment of funds calculated at special tariffs, the issuance of products produced by the enterprise or purchased by the enterprise.
The transition of wages from cash to partial payment of products must be due to compelling reasons. As a rule, the employer resorts to a similar unified scheme of settlements with the employee in a situation of difficult financial situation of the enterprise.
Partial payment of labor in products prevents the disadvantages of the unstable economic situation of the organization.
It is important for the employer to obtain consent (written application) from personnel to partially pay for labor with products. When making payments, the employer must be guided by the principles of fairness and reasonableness and assess the cost of products not higher than the market value in a particular economic sector. As wages, the employer can only issue products that are in free circulation.
Remuneration with different types of piecework system
There are several options to solve the problem.
| Types of piecework system | Description |
| Straight variety | The number of units of output is paid directly. |
| Progressive | For each unit of goods above the established plan, the reward is increased. |
| Premium | There is not only a salary paid according to a direct piece-rate system, but also a bonus. Savings on material consumption, absence of defects and tight deadlines, fulfilled plans are some of the determining factors. |
| Indirect | Related to support staff remuneration. The amount of payment is measured as a percentage of the salaries of other employees. |
| Chord | It takes into account the extent to which the plan was completed overall. It doesn't matter what the unit of output was. Such varieties can be individual or collective. |
Cases of payment of wages in kind
The form of remuneration under consideration is used at enterprises whose products the employee can regularly and effectively use. For example, quite often at enterprises in the agricultural sector of the economy, in conditions of an unstable situation of the organization, it is practiced to pay part of wages in food products.
Products issued as wages must be suitable for use. As a general rule, the organization makes payments in kind in the form of consumer goods. Wages in kind are given to personnel taking into account qualifications, quality of work, number of hours worked, and can be used as an incentive measure.
Author of the article
Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Basic concepts and definitions
The commented article defines the basic concepts used in Chap. 20 and TK.
Remuneration for labor (performing a labor function in accordance with the concluded employment contract), according to the definition given in the commented article, consists of three parts: tariff (tariff), compensation and incentive.
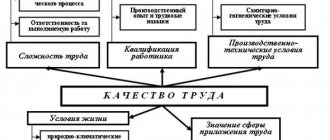
The main part of the salary, sometimes called the tariff, is calculated on the basis of the criteria established by the Labor Code: the qualifications of the employee; complexity, quantity, quality and conditions of the work performed.
Wages are paid to the employee for fulfilling labor standards established in accordance with the law (Articles 159 - 162 of the Labor Code). Labor standards essentially determine the amount of labor a worker must provide to the employer. The universal measure of the quantity of labor is working time, although other quantitative characteristics, such as daily output, can also be used.
Paying for labor according to quantity means that the employee is paid for all the labor he provides. For example, if an employee was involved in overtime work during the month, he is paid not only for work within the normal working hours, but also for additional (overtime) work. On the contrary, if the employee was absent from work, only the time actually worked is paid.
The quality of work—the second most important criterion for determining wages—characterizes its complexity, responsibility, intensity, heaviness, and independence.
The opinion that has spread in recent years that mention of the quality of labor means the absence of defects in the work (the conscientious performance by the employee of his work duties) is not consistent with the economic doctrine that introduced this term into circulation. The quality of work, in contrast to quantity, is a characteristic of its content. It is taken into account when setting wages even before a particular employee starts working and does not reflect the employee’s attitude towards the performance of his duties.
The quality of work is manifested primarily in its complexity - the level of tasks performed by the employee. The complexity of work can be judged by the name of the specialty or position: there are specialties for which the performance of work requires initial, secondary or higher professional training; positions can be characterized by the presence of categories (doctor of category I, highest category, etc.) or by an indication of the degree of responsibility and independence of the work performed (junior researcher, researcher, senior researcher, etc.).
The complexity of the work corresponds to the qualifications of the employee required to perform the relevant work. Thus, the remuneration criteria identified by the legislator to a certain extent duplicate each other. It is important to remember that an employee’s qualifications are taken into account only when they are necessary to perform the work assigned to him. For example, when a highly qualified worker enters into an employment contract to perform unskilled work, the amount of his salary is determined by the complexity of the work he performs, and not by his qualifications, which in this case does not matter.
In addition, both the complexity of the work and the qualifications of the worker are elements that characterize the quality of work. Taking into account the fact that the quality of labor is also indicated as a criterion for determining remuneration, it would be sufficient to provide that remuneration for labor is established in accordance with its quantity and quality.
The final criterion for determining the basic part of wages is the conditions of the work performed by the legislator. This is a really important criterion, but it is more important for the second - compensatory - part of wages, since tariff rates and salaries are relatively rarely set taking into account working conditions.
Basic state guarantees for workers' compensation
Whatever types of remuneration the employer applies, he is obliged to respect the rights of employees in any case. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes a number of fundamental requirements for the timing of payment of wages and the procedure for their calculation.
15 requirements for an employer to pay staff
- Each employee has an employment contract, which specifies the salary.
- Payments are made at least twice a month, and the interval between them does not exceed 15 calendar days.
- The enterprise regularly indexes wages in relation to the real increase in consumer prices for goods and services.
- When paying wages, the employee receives a payslip, which lists all the components of the amount paid and the deductions made.
- Vacation pay is paid no later than three days before the start of the vacation.
- Deductions from wages are made only legally and are limited to 20% (in cases provided for by law - 50% or 70%) of the payment due to the employee.
- If the payday falls on a weekend or non-working holiday, it is paid the day before.
- Work overtime, at night, on weekends and holidays, as well as in harmful, dangerous or special climatic conditions is paid at an increased rate.
- Downtime caused by the employer is paid in the amount of at least 2/3 of the average salary, and for reasons beyond the control of the parties - in the amount of at least 2/3 of the tariff rate or official salary.
- Manufacturing defects that occur through no fault of the employee are paid in full - on an equal basis with suitable products.
- When an employee performs work of varying qualifications under a time-based system, he is paid at the rates established for higher qualifications; under a piece-rate system, he is paid at the rates for the specific work being performed.
- The monthly salary of an employee performing the work standard is not less than the current regional minimum wage.
- If the enterprise has a trade union body, all local acts establishing the procedure for remuneration are adopted taking into account its opinion;
- On the day of dismissal, a full payroll is made to each employee.
- When developing the tariff schedule, the provisions of labor and collective agreements, industry agreements, professional standards and tariff and qualification reference books were taken into account.
The law obliges the employer to provide equal pay for work of equal value (Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the organization uses a salary system, set the same salaries for employees occupying the same position, having the same qualifications and performing similar duties. At the same time, the final salary may vary due to compensation, allowances, bonuses and other additional payments.
| Important! Non-transparent bonus criteria or unjustified refusal to pay bonuses, salary variations for the same position, non-payment of advances, salaries below the minimum wage, non-issuance of pay slips - all this leads to conflicts with employees, litigation, unscheduled inspections and thousands of fines. . |
Organization of remuneration: how to choose a convenient and effective system
Each of the currently existing forms of remuneration has certain advantages and disadvantages. For example, under “piece-work” conditions, an employee is interested in increasing output and is ready to work with maximum productivity, but the pursuit of the quantity of products produced can negatively affect its quality. Conversely, time-based payment reduces the costs of product quality control, but at the same time reduces labor productivity, and wages become more difficult to link with the final result. For both the employee and the employer, not only the final amount of earnings matters, but also the procedure for its formation.
To decide on the scheme by which the company’s employees will be paid, and to choose the most profitable option, take a two-day master class from experts in the field of personnel accounting and personnel work. You will learn exactly how remuneration systems differ from each other (briefly and clearly), how to optimize the salary fund and minimize costs, what opportunities the summarized recording of working hours opens up for the employer, and what difficulties may be encountered in the process of transition to a new accounting regime.
| Advice Specify the chosen method of settlements with personnel in local regulations: regulations on wages and bonuses, internal labor regulations, collective agreement. |
It is very important that the organization of remuneration at an enterprise is based on principles that are as transparent and understandable to staff as possible. Only in this case will each employee know what exactly he must do to achieve the required result, and will be able to determine the final amount of his salary. If the system used by the employer is too complex and confusing, and the criteria by which labor costs are assessed are not clearly defined, staff motivation will be low, as will labor productivity.