Salary. remuneration established for the employee determines how correctly he will use his working time and what productivity he will show. This issue also affects the organization’s budget, the specifics of reporting to the tax service, and compliance with legal requirements in the field of labor legislation.
- Basic salary
- Time wages
- Piecework wages - Expert commentary
There are different and quite dissimilar types of monetary remuneration, for example, piecework wages or time-based wages. The use of one or another option depends on the wishes, requirements of the employee, proposals from the employer, the availability of tax benefits, etc. Let's consider the basic concepts from this area of activity.
What does salary consist of?
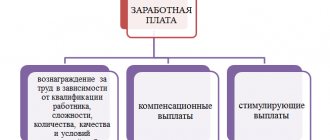
Monetary remuneration for an employee who performs the tasks assigned to him by the employer is called salary. It consists of three key parts: remuneration for labor, compensation and incentive payments. Let's look at each of these components.
Remuneration for work
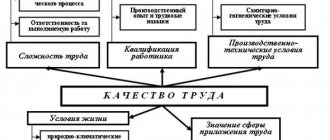
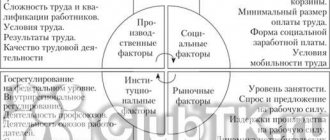
The key factors that influence the amount of remuneration a person receives for the work he performs are:
Skill level. The minimum wage is guaranteed by Russian legislation to all people working full time, but if a citizen has qualifications in his profession, that is, a decent level of knowledge and experience, confirmed by documents, he has the right to claim a higher salary. The qualification consists of:
- Theoretical knowledge;
- Practical specific skills;
- Work experience in a similar position to which the person is applying.
The better the situation in each specified point, the more claims the employee can make regarding wages.
Important! Article 195 of the Russian Labor Code defines the vertical and horizontal components of qualifications. The first concerns the level of complexity of the work entrusted to a person, the second - his profession for which he is hired.
Compensation payments
The second component of remuneration according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which is variable in terms of the entire size and regularity of payment. Depends on what actions the employee performed during the past reporting period in the performance of official duties. Compensation may include payment for one of the following:
- Pay for work at night, considered from 22:00 pm to 6 am the next day;
- Working overtime, that is, when the amount of time spent on performing duties is higher than the established working day;
- Performing official duties on holidays or weekends;
- If a person is forced to be in dangerous conditions that are harmful to health, an additional payment is also due for this.
Another reason to receive a compensation payment is performing duties beyond those established by the profession. Each specified point obliges the employer to pay more; for example, wages on weekends and holidays can even be paid at a double rate.
Incentive payments
By order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development, number 818, so-called incentive payments are provided for budgetary organizations, designed to increase the labor efficiency of hired employees, their level of consciousness in the workplace, etc. Such incentives include:
- Payments that can be issued for high performance in performing the duties assigned to a person;
- Additional payments for the quality of work, when a person shows desire and his work brings better results;
- A percentage of the salary is provided for length of service - the amount of work experience in one place with continuous work.
Incentives also include bonuses for hard work, issued both for fulfilling a specific volume of obligations and, say, at the end of the calendar year.
Incentive payments are set so that they can be quantified according to certain criteria. In order to avoid disputes and ambiguities in the case of incentive remuneration for teaching staff of educational institutions, as well as remuneration for medical workers, other employees of the institution may be involved in the discussion of the legality and validity of such a step on the part of the management, so that the decision is made of a collegial nature.
Interesting: Increase in salaries for public sector employees. Which categories of public sector employees will have their salaries increased?
Employee benefits
The reward system that exists in any organization consists of three main elements. First of all, this is the basic payment for labor. This is considered the basic salary. The other two elements are additional payments (bonuses, bonuses, etc.) and social incentives.
Remuneration for labor is a permanent part of cash payments for the employee. It is calculated for the performance of permanent duties provided for in the job description. Remuneration for work in terms of basic salary consists of the official salary provided for in the staffing table and various allowances. In this case, the size of the official salary depends on the position held or tariff category. Allowances are introduced to take into account the individual contribution of the employee to the production process. They are usually calculated as a percentage of the existing salary. Bonuses can be established for length of service and for knowledge of any foreign language, as well as for performance efficiency, etc.
Main types of remuneration
The legislation provides for the division of the amount of remuneration into the basic salary, as well as various additional payments issued depending on the situation.
Basic salary
This is a payment, the size of which depends on the factors already mentioned: the amount of time worked at the workplace, the quality of the work performed, the conditions applied in accordance with the tariff schedule, and the employee’s skill level. The size of the salary may be affected by bonuses, compensation for downtime in labor activities that were not the fault of the workers themselves, going to work at night, etc. This also includes various bonuses.
Interesting: Is the bonus included in the calculation of average earnings? How to take into account bonuses when calculating an employee’s average earnings.
Additional salary
This includes numerous payments that represent a person not for the time worked, but for his special position before the law. Examples:
- Vacation pay, to which every officially employed person in the country is entitled by law;
- Maternity leave for young mothers who temporarily left work to care for newborns;
- Benefits for working as minors.
This also includes monetary compensation for unused vacation, paid, among other things, upon dismissal of an employee from his place of work.
Maternity leave and salary
The law says that any woman can count on leave equal to 70 days before giving birth, as well as 70 days after. The main thing is the total number of 140 days. But in each case, you can divide this time into other parts. You can expect an increase of several days if the birth is complicated.
Going on maternity leave
During maternity leave, the employee receives an average salary. Or an average stipend if the employee is studying somewhere.
Even the unemployed are eligible to receive a scholarship. But only if they are registered with the employment service. After all, the payment comes from the capital in the Social Fund. insurance. If, before registration, the workplace was absent for two years or more, then the benefit will be minimal. There are also government payments, but they deserve a separate discussion.
When calculating wages in an incomplete month, it is important to find out what exact rate is used: daily, hourly, or monthly.
In the case of an hourly rate, the hourly rate is multiplied by the time worked. If necessary, the bonus is multiplied by the norm per unit of time. The result is then divided by the hours actually worked.
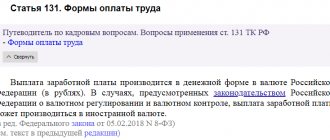
Salary may or may not be monetary. In the latter case, they do not rely on the basis for payment, but on the way in which they pay the employee. The monetary form is currently the most widely used. But the law does not prohibit the execution of employment agreements, which state that payment is made in a different form.
So, there are several types of payroll. It is important to accurately understand this issue in order to avoid errors in calculations.
Top
Write your question in the form below
Forms
The Labor Code stipulates various forms of remuneration, trying to take into account all the abundance of types of employer-employee relationships. The following options are worth considering.
Forms of remuneration. Photo: en.ppt-online.org
Time wages
The most common payment option for work in post-Soviet countries, including the Russian Federation. This can be either an hourly wage or monthly payments. First, it is calculated how many hours/days a person has worked, then this indicator is multiplied by the current rate and the amount required for payment is obtained. Its size may be affected by bonuses that are either issued on the initiative of management or are provided for in the employment contract when it is drawn up and when a person is hired.
Interesting fact! It is common to use a salary - the amount specified in the employment contract, which is guaranteed to be paid monthly. In practice, the salary often does not depend on the actual amount of time worked, but here the initiative is entirely on the side of the authorities and depends on the relationships established in fact between specific people.
Piece wages
The definition of piecework payment is more complex than in the previous case; there are the following varieties:
- Direct piecework wages . In this case, the employer sets certain prices per unit of actions performed, parts produced, etc. employee. Accordingly, the hired worker receives a certain final amount based on the amount of work performed. With this form of relationship, the person’s qualification level is taken into account;
- Piece-bonus wages. A more complex version of the previous type of payment, which, in addition to the payment of funds for each useful action, also provides for the receipt of a bonus issued for exceeding the established production plan;
- Piece-progressive wages. This provides for gradual progress, including increased pay depending on output. Any work above the norm is paid additionally;
- Indirect piecework wages. It is used to calculate payments to employees involved in servicing workplaces, for example, adjusters, assemblers, etc. Since the success of the workers’ activities depends on their work, the salary is calculated by multiplying the indirect piece rate by labor productivity, that is, the amount of work actually performed by the workers on the equipment.
Formula: Piecework wages.
Photo: infourok.ru There are also other options:
- time-based bonus wages,
- chord,
- mixed forms of payment.
The latter is the most common, as it allows management to approach the payment of salaries in the most flexible manner, taking into account as much as possible the wishes and characteristics of the work activity of each employee.
Remuneration for work, its component part
As we see from the legislative definition of wages, it contains certain concepts that actually constitute remuneration for work, that is, wages.
In fact, wages consist of two parts: the main part and the additional one. The main part of the salary includes the tariff rate, which includes the official salary. Labor legislation has definitions of parts of the basic salary.
Tariff rate is a fixed amount of remuneration for an employee for performing a standard of work of a certain complexity (qualification) per unit of time, without taking into account compensation, incentives and social payments. [3]
Salary (official salary) is a fixed amount of remuneration for an employee for the performance of labor (official) duties of a certain complexity for a calendar month. The salary also does not include compensation, incentives and social payments.
In the Labor Code in the same article there is such a thing as a basic salary, a basic wage rate, which means the minimum wage rate for an employee engaged in professional activities, both workers and employees who are included in a certain qualification group. The basic salary also does not take into account compensation, incentives and social payments.
ATTENTION! Methods of collecting compensation from an employer for delayed wages.
The main part of wages, as a rule, in all countries with developed economies is formed by the influence of the state, since this part is a guarantee of wages. That is, remuneration for work is guaranteed by the state.
As for the additional (above-tariff) part of wages, it is formed on the initiative of society itself, that is, workers and employers.
As a rule, the above-tariff part of wages is regulated by collective agreements, agreements, as well as at the individual level, that is, by including provisions in the employment contract for the payment of compensation, incentives and social benefits.
Minimum wage
The minimum wage, which is abbreviated as the minimum wage, sets the minimum salary that every officially employed person must receive. The concept of minimum wage is widely used not only when calculating wages, but also when calculating the amount of various benefits, the amount of assistance during pregnancy, incapacity of persons, etc. The law allows the constituent entities of the Federation to establish on their territory a different level of minimum wage from the general one, but it must be no less than that specified throughout the country.
At the moment, the legislation of the Russian Federation has established the following minimum wage values:
- The minimum wage in Russia reached 12,130 rubles for the period of 2020;
- The minimum wage in Moscow is 20,195 rubles.
The Russian government plans to increase the minimum wage in the country from the current 12 thousand rubles to a small 14 thousand, but to do this in stages, until 2023.
Interesting fact: The minimum wage in the United States at the moment, that is, at the end of 2021, is officially $7.25 per hour, which equals about 560 rubles at the rate of 77.1 rubles per dollar.
Reasons for encouraging employees
Personnel who regularly perform their official duties and do not violate internal regulations and labor legislation are subject to encouragement.
Experts recommend using this measure of team motivation whenever an individual employee demonstrates positive activity. In addition, do not forget about stimulating the entire staff as a whole (this can be done through corporate events, etc.).
Effective promotion must meet the following criteria:
- to be significant;
- carried out in a short time (no longer than a week);
- be affordable (remuneration should be intended for both strong workers and weaker ones);
- be fair (in other words, appointed for real merit);
- be transparent (that is, be officially announced in front of all personnel, which allows you to increase the prestige of one employee and increase the motivation of others).
Reasons for rewarding individual employees or the entire team may be exemplary performance of official duties, helping to improve the competitiveness of products or services, exceeding planned targets, long-term work in the enterprise, proposing innovative ideas, or improving a person’s qualifications.
Hourly
In the Russian Federation and the post-Soviet space, it is traditional to work at a rate, or for the salary specified in the contract. Salary wages are convenient for both the employer and especially the hired worker, since in fact the amount of time worked is secondary for him, and he usually receives a full salary. But entering hourly wages on the part of the employer is not difficult, since the hours worked by a person are recorded in any case, even when the salary is given for a rate.
Depending on the agreement between employees and the organization, the hourly wage may be as follows: regular, bonus, standardized.
Accounting entries for dividend payments
In accounting, dividend payments are recorded by postings on the date when the participants’ decision to pay them was made.
The recipient and the payer have accounting entries reflected in different accounts.
Accounting of transactions for recipients is documented by the date of the decision - Dt76 Kt91, and upon payment - Dt51 Kt76.
The payer's postings are indicated depending on whether the recipient has an employment relationship with the company, and whether NP or personal income tax is due.
Calculation of dividends in 1C:Accounting 8
To enter information about dividends into the 1C: Accounting 8 program, a basis is required. This is the decision of the founders adopted at the general meeting or the sole decision of the sole participant.
Postings from the payer are made on different accounts based on the status of the founder:
- for a participant who is not in an employment relationship with the company - Dt84 Kt75;
- for an employee – Dt84 Kt70.
Accordingly, depending on whether the recipient works for the payer or not, the postings are also broken down.
For accrued and withheld taxes: Dt75 Kt68 - for non-working shareholders and Dt70 Kt68 - for employees.
For the listed dividends: for non-workers - Dt75 Kt51, for employees - Dt70 Kt51.
Paid taxes are indicated on Dt68 and Kt51.
How to record the accrual and payment of dividends in accounting
To reflect accruals in 1C, on the “Operations” tab, select “Accrual of dividends”, where they indicate all the information about the operation being carried out:
- date;
- name of the payer and recipient;
- accrual period;
- sum;
- necessary explanations.
To reflect the transaction in accounting, all you have to do is select “Record” and “Post”.
The payment is reflected using the same operation. To create a payment document, you must click “Create based on” and select the appropriate method: “Cash withdrawal” or “Payment order”.
How can a tax agent calculate personal income tax at a rate of 13 percent?
The rate of 13% applies to individuals – residents of Russia. The calculation of personal income tax is influenced by whether the tax agent himself received income from participation in the activities of another legal entity. If not, then the tax is calculated as dividends accrued to an individual × 13 percent.
If the tax agent received income from participation in the activities of another organization in the past or present year, then it is necessary to establish whether such income was taken into account when making payments to its founders. If yes, then personal income tax is calculated as in the first paragraph.
Otherwise, first calculate the personal income tax deduction using the formula:
Resident dividends / Total amount of dividends for all participants × Payments received by the payer
Now the tax is calculated at a rate of 13%:
(resident dividends – deduction) × 13%.
How can a tax agent calculate personal income tax at a rate of 15 percent?
The personal income tax rate of 15% is established for non-residents of the Russian Federation, unless otherwise approved by an international treaty (clause 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, the tax for non-residents is calculated using the same formula as for residents of Russia, only with a corresponding coefficient of 15%.
When must a tax agent withhold and transfer personal income tax?
For each type of organizational form of a company, tax legislation establishes different terms for withholding and transferring personal income tax:
- If the payer is a joint-stock company, then personal income tax must be transferred within one month after the payment of dividends (subclause 3 of clause 9 of Article 226.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- If it is an LLC, then the deadline for transferring the tax is one day, not counting the day when dividends are paid (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Chord payment
Sometimes in employee-employer relations the concept of lump sum payment is encountered. In this case, issues such as the amount of work, deadlines, and the amount of remuneration are agreed upon in advance when drawing up the contract. This option gives the parties to the transaction a clear understanding of their rights and obligations and encourages employees to work hard for results.
Chord work can be offered to either one person or a whole team. The agreement on it must indicate:
• Name and list of planned works; • Prices for all types of work; • The price of performing the specified amount of work.
The optimal areas for using this payment option are construction and industry.
Piecework wages – Expert commentary
QBF Vice President Maxim Fedorov comments.
Vice President of QBF Maxim Fedorov
“The remuneration system adopted by the employer shows how remuneration to employees is calculated. According to labor legislation, two main types are established - piecework and time-based wages. Both of them can be combined with the premium system.
Time-based wages depend directly on the time worked and the tariff rate, and piece-rate wages depend directly on the result, on the number of products manufactured, work done, etc.
The piecework wage system is:
- collective (team), in which payment depends on the results of the work of the team as a whole;
- lump sum, where the final salary is calculated based on the completed volume of a complex task or order (individual types or stages of work may “cost” differently);
- piece-progressive, in which production up to a certain standard is calculated at one rate, and if the established standard is exceeded, higher prices are used.
Thus, the piecework wage system is one of the types of piecework payment. The chord system is used when it is necessary to evaluate the result of the work of a group of people (although there are cases with a single employee) performing different types, stages, stages of work for a period specified by the employer (customer).
The chord remuneration system is distinguished by the following features:
- the final result of the work is predetermined;
- there are clear deadlines for completing a set of works to obtain a clear result;
- The approximate cost of the work package is also known in advance.
This payment system is common in certain industries - construction, development, design work, where a group of employees makes efforts to achieve results. At the same time, there are many stages and types of work in construction, for which it is difficult to establish separate tariff rates, and it is difficult to estimate in money the contribution of each employee, who sometimes differ greatly in qualifications.
In general, lump sum payment is not very common. The employer can establish such a reward system for solving specific tasks.
For example, when force majeure, emergency, emergency circumstances occur, and it is necessary to involve a group of employees in order to complete a certain amount of work by a certain date. In this case, it is difficult to calculate the number of hours spent by each employee, setting the tariff is also problematic (and sometimes there is simply no time), so the accord system will help out the employer, and the employees will understand what payment they will receive if the team copes with the task.
Another example of the possible use of the chord system is commissioning work (they are not regular, daily for production, they require the participation of different specialists, it is impossible to schedule all types and stages of work in advance and at the same time there is a clear final result - working equipment by a certain date).”
What is a prize called?
First of all, let's understand the very concept of a bonus. Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation includes a bonus in the employee remuneration system, along with salaries, rates, additional payments and allowances of a compensatory and incentive nature. It must be said that the boundaries of these specified concepts are outlined in the legislation as a whole. In practice, incentive bonuses in the LNA are sometimes called bonuses, since both payments are of an incentive nature. Along with the term “bonus,” the term “bonus” is used as a synonym in business literature. A bonus, if we talk about it as a bonus, would rather mean a bonus of an irregular nature.
Is it possible to apply a disciplinary sanction to an employee in the form of deprivation of bonuses ?
At the same time, labor legislation does not prohibit bonus incentives that are not directly related to labor results. They are appointed, as a rule, selectively, by decision of management and serve as an incentive for conscientious work in general. An example of such incentive payments could be bonuses for a professional holiday or anniversary. The whole variety of bonus incentive payments and the features of their application are reflected in the “Regulations on bonuses” of the company or other similar LNA.
Question: For violation of labor discipline, an employee was brought to disciplinary liability in the form of a reprimand. However, the employer subsequently deprived this employee of his bonus due to disciplinary action, citing the provisions of the collective agreement. Is it legal to deprive an employee of a bonus? Isn't this a repeated punishment for the same violation? View answer
Salary
Salary is a form of time-based payment for work performed, while its other name is fixed payment. The most common option for us to interact with an employer is when a person receives a monthly amount specified in the contract. Its size can be influenced both positively and negatively. Bonuses, additional payments, taking unpaid leave or days off, sick leave - all this affects the amount that the employee will receive at the end of the month.
This is a kind of time-based wage, the formula of which is calculated simply - the specialist’s hourly rate scale is multiplied by the number of hours he worked. Additional payments are required by law for overtime.
Formula: Time-based wages. Photo: infourok.ru
Remuneration for minors
All workers under 18 years of age are subject to the rules on remuneration for minors. In general, cooperation with such persons is characterized by the presence of a shortened working day, taking into account production, the time actually spent on work. If the employer wishes, persons under 18 years of age may receive additional payments and bonuses, even when working part-time. Any questions regarding remuneration for work in conditions deviating from normal ones are considered on an individual basis, but as a rule, children are not allowed to take up such work options due to lack of experience and qualifications.
These are the main points regarding the issue of remuneration in various situations. Cooperation with subordinates in compliance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is the guarantee that a business will not have trouble during inspections by the competent authorities.