Modern types of remuneration and wage systems
Accounting, payment and labor regulation are responsibilities that every employer must fulfill. You can pay for work performed in different ways, but one way or another, each enterprise establishes certain rules according to which the work of personnel is taken into account, charged and rewarded. To understand exactly how material remuneration is paid, let’s briefly consider the main forms and systems of remuneration.
| Valentina Mitrofanova will tell you what's new in labor legislation this week. Watch the new episode of Personnel Review. |
There are three salary systems:
- Tariff.
- Tariff free.
- Mixed.
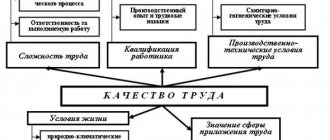
The most common today is the tariff system of remuneration, the types of which (“piecework” and time-based wages) are used by most employers. Under the tariff system, the salaries of workers of different categories are differentiated based on a number of conditions: the type and degree of complexity of the work performed, the intensity and nature of the work, natural and climatic conditions, etc. Non-tariff forms and systems of remuneration tie earnings not to clear tariffs, but to the final results of the work of the entire enterprise or structural unit in which the employee is registered, and the total amount of funds allocated by the employer to the wage fund. For each employee, their own coefficient of labor participation in the results of the team’s activities is established. Taking into account this coefficient, the individual salary is subsequently calculated.
Mixed remuneration has the characteristics of two other systems - non-tariff and tariff. On the one hand, the employer does not completely abandon tariff setting; on the other hand, it adjusts tariffs depending on the results of staff work and applies the labor participation coefficient when calculating individual salaries. In the modern economy, you can find different forms of remuneration related to the mixed system, in particular, “floating” salaries, dealership and commission payments.
Piece and time-based forms of remuneration: briefly about the main thing
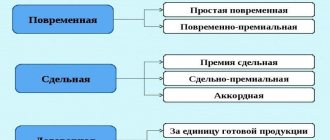
The main forms of remuneration within the tariff system are piecework and time-based. The difference between them lies in the method of accounting for labor costs: with the piecework system, the amount of products produced by the employee is taken into account, with the time-based system, the time worked. When setting a time-based salary for an employee, the employer primarily takes into account two factors: the qualifications of the specialist and the amount of time worked. This calculation scheme is most relevant when it comes to office, creative, research, scientific and any other work that is very difficult to standardize.
Time payment can be:
- Simple . Time worked is paid regardless of the amount of work performed.
- Time-based bonus . In addition to payment according to the tariff, the employee receives bonuses for the quality and efficiency of work.
- Salary . Depending on the qualifications of the employee and the category of work performed, a fixed salary is established.
| Advice To calculate wages without errors with a time-based form of remuneration, fill out a time sheet daily, noting employee attendance and absence, the number of hours and days worked, lateness and overtime. |
“Piecework” is used when the employer has a real opportunity to keep records of the products produced. In order to standardize the labor of personnel in a piecework system, output volumes are established.
6 types of piecework wages
- Straight . Fixed piece rates are used, and the employee’s salary directly depends on the volume of work performed or the number of products manufactured.
- Piece-premium . Bonuses are provided for exceeding production standards and the absence of defects in products;
- Piece-progressive . The results of labor within the established norm are paid at regular rates, and products produced in excess of the norm are paid at increased rates, but not more than double the rate;
- Collective piecework . Salaries are set for the entire team (team, department, group of specialists), and then redistributed among employees by decision of the team members;
- Indirect piecework . It is used mainly when calculating wages for employees servicing production equipment and main workplaces, and depends on the productivity of personnel working at the serviced workplaces;
- Chord . The complex of different works performed by employees is assessed, indicating the deadline for their completion.
Another common version of “piecework” is a salary set as a percentage of revenue received. Often used in retail and wholesale trade. The more products the company sells, the more the employee will earn.
Piecework
This payment option depends on the amount of work the employee has performed in his position. This option is used in those industries of production or service where the quantitative characteristics of performing a particular job are important.
In order for piecework wages to be used as efficiently as possible, special standards can be established, based on the results of which the employee receives increased pay for exceeding the established standards. The salary part, as in time-based wages, is not provided for in the piecework mechanism.
Piecework remuneration is a mechanism that allows you to achieve good quantitative results, since it is aimed at directly stimulating the employee due to the fact that the level of wages depends directly on the quantitative indicator of the work performed.
Basic state guarantees for workers' compensation
Whatever types of remuneration the employer applies, he is obliged to respect the rights of employees in any case. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes a number of fundamental requirements for the timing of payment of wages and the procedure for their calculation.
15 requirements for an employer to pay staff
- Each employee has an employment contract, which specifies the salary.
- Payments are made at least twice a month, and the interval between them does not exceed 15 calendar days.
- The enterprise regularly indexes wages in relation to the real increase in consumer prices for goods and services.
- When paying wages, the employee receives a payslip, which lists all the components of the amount paid and the deductions made.
- Vacation pay is paid no later than three days before the start of the vacation.
- Deductions from wages are made only legally and are limited to 20% (in cases provided for by law - 50% or 70%) of the payment due to the employee.
- If the payday falls on a weekend or non-working holiday, it is paid the day before.
- Work overtime, at night, on weekends and holidays, as well as in harmful, dangerous or special climatic conditions is paid at an increased rate.
- Downtime caused by the employer is paid in the amount of at least 2/3 of the average salary, and for reasons beyond the control of the parties - in the amount of at least 2/3 of the tariff rate or official salary.
- Manufacturing defects that occur through no fault of the employee are paid in full - on an equal basis with suitable products.
- When an employee performs work of varying qualifications under a time-based system, he is paid at the rates established for higher qualifications; under a piece-rate system, he is paid at the rates for the specific work being performed.
- The monthly salary of an employee performing the work standard is not less than the current regional minimum wage.
- If the enterprise has a trade union body, all local acts establishing the procedure for remuneration are adopted taking into account its opinion;
- On the day of dismissal, a full payroll is made to each employee.
- When developing the tariff schedule, the provisions of labor and collective agreements, industry agreements, professional standards and tariff and qualification reference books were taken into account.
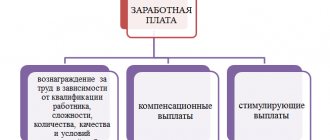
The law obliges the employer to provide equal pay for work of equal value (Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the organization uses a salary system, set the same salaries for employees occupying the same position, having the same qualifications and performing similar duties. At the same time, the final salary may vary due to compensation, allowances, bonuses and other additional payments.
| Important! Non-transparent bonus criteria or unjustified refusal to pay bonuses, salary variations for the same position, non-payment of advances, salaries below the minimum wage, non-issuance of pay slips - all this leads to conflicts with employees, litigation, unscheduled inspections and thousands of fines. . |
Time-bonus method
When analyzing modern remuneration systems, you should consider them in comparison. Thus, the time-bonus system is distinguished by the presence of an incentive bonus. In this case, there is a certain rate, tariff. But they add extra encouragement to it. It can be monthly or quarterly. Some companies pay such a bonus every six months or a year.
The bonus is calculated as a percentage of the established salary. Sometimes fixed, fixed amounts of money are used. The choice depends on the characteristics of the company’s activities and the motivation policy of its personnel.
Bonuses can be given for achieving the required quantitative or qualitative indicators.
So, you can consider the calculation method of a simple and time-based bonus system. For example, an employee’s salary is 12 thousand rubles. Out of 22 working days in a month, he worked only 20 days. His salary will be as follows:
Salary = 12000: 22 * 20 = 10909 rub.
In the same situation, with a time-based bonus payment system, the calculation would be different. In this case, the employee could have a monthly bonus of 25% of his salary. If an employee, for a good reason, did not go to work for 2 days in a month, but fulfilled the set standard (for quality or quantity of products), his salary will be as follows:
Salary = (12000: 22 * 20) + (12000 * 25%) = 13909 rub.
It is more important for the company that the employee fulfills the requirements set for him regarding the quality of his work. At the same time, he may not go to work for 2 days (for a good reason) and receive more money than with a simple time-based payment system.
Organization of remuneration: how to choose a convenient and effective system
Each of the currently existing forms of remuneration has certain advantages and disadvantages. For example, under “piece-work” conditions, an employee is interested in increasing output and is ready to work with maximum productivity, but the pursuit of the quantity of products produced can negatively affect its quality. Conversely, time-based payment reduces the costs of product quality control, but at the same time reduces labor productivity, and wages become more difficult to link with the final result. For both the employee and the employer, not only the final amount of earnings matters, but also the procedure for its formation.
To decide on the scheme by which the company’s employees will be paid, and to choose the most profitable option, take a two-day master class from experts in the field of personnel accounting and personnel work. You will learn exactly how remuneration systems differ from each other (briefly and clearly), how to optimize the salary fund and minimize costs, what opportunities the summarized recording of working hours opens up for the employer, and what difficulties may be encountered in the process of transition to a new accounting regime.
| Advice Specify the chosen method of settlements with personnel in local regulations: regulations on wages and bonuses, internal labor regulations, collective agreement. |
It is very important that the organization of remuneration at an enterprise is based on principles that are as transparent and understandable to staff as possible. Only in this case will each employee know what exactly he must do to achieve the required result, and will be able to determine the final amount of his salary. If the system used by the employer is too complex and confusing, and the criteria by which labor costs are assessed are not clearly defined, staff motivation will be low, as will labor productivity.
Tariff methodology
Modern remuneration systems in an organization can be based on a tariff approach. For this purpose, tariff rates, tariff schedules and coefficients, as well as official salaries are developed. These categories are an integral part of the presented approach.
The tariff schedule is formed by a list of positions or professions that are assessed in terms of complexity of work and qualifications. For this, appropriate coefficients are used.
The tariff category is a value that reflects the complexity of the employee’s work and the level of his professional training. In contrast to this indicator, the qualification category is a value that reflects the level of qualifications of the employee. It is received at the educational institution after a training course.
Tariffication of work is the process of comparing the type of work and the tariff or qualification category. This allows you to assess the complexity of the employee’s activities. This procedure is carried out under the influence of the Unified Qualification Directory.
Modern remuneration systems (including the tariff approach) are stipulated in contracts, local agreements, and organizational regulations. Different approaches to remuneration are used for managers and subordinate personnel. This is explained by the peculiarities of their motivation.