04.09.2019
0
119
4 min.
Quite often, a situation arises when employees occupy another position in parallel with their main job. In the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), such workers are called part-time workers. They are both internal and external. Article 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates an additional basis for the dismissal of this category of citizens at the initiative of the employer. In order to get acquainted with general concepts, types of part-time work, conditions and procedure for terminating the contract, read this article.
Form of notice of dismissal of a part-time worker
There is no unified form for this document. The notification is drawn up in free form indicating:
- name of the organization (or full name of the individual entrepreneur);
- title of the document;
- reasons for dismissal;
- date of termination of the employment contract (last day of work);
- date of document preparation;
- Full name and signature of the head of the organization (IP).
Let's sum it up
- Notify the part-time worker of dismissal under Art. 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is required 2 weeks before termination of the employment contract.
- The notice can be delivered in person or sent by registered mail with a list of attachments.
- There is no unified form of notification; it is drawn up in free form.
- Missing the deadline for notifying a part-time employee of dismissal is a violation of labor law. For this, the employer may be held liable under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Often, an employer has positions for which it is necessary to hire an employee from another organization who will work part-time. There can be many reasons for hiring a part-time worker, each of which influences the decision to hire an external or internal part-time worker.
If an employer hires a permanent employee for a specific position, there is no need to have a part-time employee.
Dear readers! To solve your specific problem, call the hotline or visit the website. It's free.
The procedure for dismissing an external part-time worker at the initiative of the employer
The dismissal of an external part-time worker is no different from the dismissal of employees working in the main position, since the termination of the employment contract in this case occurs only on the basis of the provisions of the Labor Code.
Except for cases where termination of an employment contract occurs on the grounds provided for in Chapter 13 of the Labor Code, the grounds should also include the hiring of an employee for this position for whom the specific work will be the main one.
If this is the reason for dismissing a part-time worker, the employer must be guided by Article 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in carrying out the dismissal procedure.
Otherwise, the dismissal procedure is no different from the dismissal of an employee working in the main position:
- after giving the employee a written notice, the employer is given at least two weeks to prepare all the necessary documents, including those that will reflect the work of the part-time worker from his professional point of view and will be able to confirm his work experience;
- during the time established as necessary for notice of dismissal and subsequent work as a part-time worker, the employer is obliged to make all necessary payments to the employee;
- the employee, in turn, must completely transfer all matters to the person accepted as the main employee.
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
The order to dismiss a part-time worker is signed on the day indicated as the last day of work of the part-time worker in the notice handed to him.
Types of part-time workers
A part-time worker is an employee who regularly works during his free time from his main job. These employees work part-time.
There are two types of part-time work:
- Internal - a specialist is assigned to different positions at one enterprise.
- External - the employee performs work duties for different employers.
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, a person can have several additional positions, but only within reason. Each of his work must be official, regardless of which organization provides it.
The procedure for dismissing an internal part-time worker
How to fire an internal part-time employee? An internal part-time worker is an employee who occupies two positions within one organization, one of which is the main one, and he performs the duties of the second in his free time from the first job. In this case, payment is made both for the main job and for part-time work.
If an employee quits his main job and does not get another job, then part-time work becomes the primary place of work. It is unacceptable to dismiss an internal part-time employee due to the hiring of a new specialist for this position, since the part-time employee is already the main employee, even if he works part-time.
Also, the law does not prohibit terminating a part-time contract for absenteeism or other disciplinary offenses.
Free consultation
8 800 511-39-66Ask a question
Nuances of the procedure
Any employee working part-time has the right to terminate their employment relationship at their own request. But dismissal is also possible at the initiative of the employer.
Such termination of an employment contract is regulated by Article 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. But it should be noted that if the employee is a person who has benefits in accordance with Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which, in the event of termination of the employment contract, provides guarantees to pregnant women and persons with family responsibilities, then the employer does not have the right to dismiss them at will.
In addition, it is prohibited to interrupt the employment relationship with an employee who is on annual leave or sick leave. It should be noted that if a part-time specialist quits his main job, then the additional work will become his main job.
In this regard, it will no longer be possible to terminate the employment contract with a part-time worker due to the hiring of another person for his position.
An employer who decides to terminate an employment relationship with a part-time employee must take into account the legal specifics of the employee’s position. This will allow you to avoid serious mistakes, as well as violations of the law.
If the employer does not pay enough attention to this issue, then conflict situations may arise that will have to be resolved in court.
The dismissal of a specialist working part-time is carried out in accordance with Article 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If the contract is open-ended, then the employer can terminate it if a person is hired for a part-time position for whom this position will become the main job.
The manager must notify the part-time employee of this in writing fourteen days before the date of dismissal.
If a fixed-term contract has been concluded with a specialist, the employer cannot terminate it before the end of the contract term. Exceptions are possible only in connection with violation of labor discipline by an employee, as well as during the liquidation of the organization.
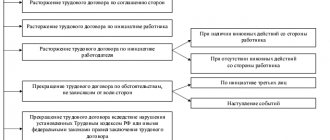
Grounds for dismissal
The grounds for terminating an agreement with a part-time worker may be such things as the personal initiative of the employee, the decision of the employer , or the mutual consent of both parties.
Also, the termination of a part-time business partnership occurs if the main employee leaves the place. The procedure for dismissing a part-time worker is specified in Art. 288 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, it is possible to terminate a working relationship if the contract with a part-time partner is signed for an indefinite period . If the document has a specific validity period , this action will be prohibited . This rule is prescribed by Art. 59 part 2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
If the contract between the employer and the worker is concluded for an indefinite period, and the main employee comes to work, then the employer will need to notify the temporary worker in writing 2 weeks before terminating the contract. Calculation occurs as standard - on the last day of work. At the same time, an entry is made in the work book about leaving work in connection with the return to work of the main employee.
Termination of an employment contract with a part-time worker at the initiative of the employer
The process of how to fire a part-time employee at the initiative of the employer is similar to the principles of terminating a contract with the main working personnel. Termination of labor relations is regulated by Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This can happen for the following reasons:
- Liquidation of a company.
- Reduction of working personnel. Here the employer undertakes to notify subordinates of the decision made 2 months before the termination of the partnership. This rule is regulated by Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If the employee is employed on a seasonal job , the notice period is reduced to one week .
- Disciplinary violations by hired personnel. This may include frequent absenteeism, drunkenness at work, and loss of confidence. To terminate a business partnership with a citizen who has stumbled, the employer must prove his unlawful behavior, which contradicts the regulations src=»https://tkrf1.ru/faq/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/uvolnenie-po-sovmestitelstvu-1.png "class="aligncenter" width="600″ height="562″[/img]
Important! An employer cannot fire a female part-time worker if she is in a position. The exception in this case is the complete liquidation of the company. Termination of business relations at the initiative of the employer with a pregnant woman is possible if the employee repeatedly violates the disciplinary requirements put forward by the company.
It is prohibited to fire employees who are on vacation , maternity leave or sick . However, under such circumstances, the hired workers themselves can write an application to terminate the employment contract. Then a standard two-week work period . In this case, its terms will be calculated depending on the date of writing the application.
At your own request
According to Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a part-time worker has the right to terminate cooperation with the employer on his own initiative. At the same time, he must notify his superiors of his decision 2 weeks before leaving. Sometimes management can accommodate you and shorten the notice period for a decision to leave the workplace.
submit a written to the head of the company. There he must write about terminating the business relationship on his own initiative. The countdown of days to work begins the day after the application is submitted. On the last day of work, the company must pay the citizen in full and pay him all due payments - salary, severance pay, compensation for vacation that was not used.
If we are talking about internal part-time work , then the employer makes a corresponding entry in the employee’s work book . If an external part-time worker is dismissed , the procedure for terminating cooperation becomes a little more complicated:
- The employee must make a copy of the dismissal order.
- Have the document certified by the company with which the employment relationship is being terminated.
- Provide the document to your superiors at the main place of employment .
Reference! An entry in the work book is made in the main company where the employee works. In this case, a note must be made about the former part-time job with reference to Article 77, paragraph 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If a citizen terminates business relations with both employers, then two separate entries are made in the book.
For other reasons
Termination of the contract between the part-time worker and the employer can occur by agreement of both parties. The procedure for carrying out the procedure is regulated by Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. An offer to terminate cooperation can come from both the employer and the employee. Most often, the employer is the initiator if he has no claims against the employee. Both parties sign a document indicating the mutual termination of cooperation. A two-week period may not be required.
The settlement procedure for “leaving” a job by mutual agreement of the parties follows the same principle as when terminating a contract by a personal decision of a part-time worker. On the last day of work, the employee receives all payments that are due - salary , compensation for unused vacation , severance pay.
Attention! It is worth considering that if there is a unanimous decision to end cooperation, those resigning are deprived of the opportunity to withdraw their resignation letter within 2 weeks from the date of signing it.
When laying off a part-time employee, the employer must notify the other party of the decision. On a general basis, this is done 2 months before the reduction. If a part-time worker is employed for a season , the employer warns him about the layoff 7 working days in . If the parties’ business relations are under a fixed-term agreement (for a period of up to 2 months), notification is given 3 business days before termination of the agreement.
Grounds for termination of the contract
Most grounds for termination of employment are the same for all employees. This means that, according to the law, it is quite possible to fire a part-time employee without his desire. In particular, the legislation provides for the following cases of termination of a contract at the initiative of the employer:
- Liquidation or termination of the work of an organization or its division, if it and the head office are located in different localities.
- Reduction of staff.
- Insufficient qualifications of the employee, revealed after his certification.
- More than one instance of failure by an employee to perform official duties, provided that there is a valid disciplinary penalty.
- The co-worker lost trust due to the guilty actions he committed.
- The employee provided incorrect information about his income, conflict of interest, etc., if this is imposed on him by legislative acts.
- The specialist has committed an offense that is contrary to moral standards and is therefore incompatible with continuing to work in the organization.
It is also worth noting such grounds as gross violation by an official of his labor duties. Such violations include:
- absenteeism;
- presence at the workplace under the influence of alcohol or drugs;
- disclosure of personal data of enterprise employees or trade secrets that were known in connection with production activities;
- theft committed by a part-time employee at the enterprise;
- violation of safety regulations that could lead or has already led to serious consequences;
- providing documents with false information when applying for a job.
Thus, Russian legislation recognizes the legal termination of employment relations with external and internal part-time workers at the initiative of the employer. But for this, their dismissal must be carried out for one of the reasons specified in the regulations.
Process order
Since an employee engaged in labor activity is considered a full-fledged employee, his dismissal is carried out in accordance with the established procedure. Moreover, the basis for this process must be provided for by labor legislation.
In the event of termination of an employment contract due to staff reduction, the employer is obliged to notify the employee who combines various duties two months before the date of termination of the relationship. At the same time, he needs to issue an order that changes will be made to the structure of the organization, expressed in the reduction of some positions.
Then the employer must offer the released specialist other vacancies in the same organization. If a person does not want to take one of the vacant positions, then he is fired with a severance pay equal to average earnings over the next two months.
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
The employer should keep in mind that the following categories of employees cannot be dismissed due to staff reduction:
- women who are pregnant and have a child under three years of age;
- sole breadwinners in a family with dependents;
- trade union members whose work in the organization is related to trade union activities.
If the termination of the employment relationship with a part-time employee occurs due to the hiring of a main employee, then the dismissal is made either on a general basis or in connection with an additional reason. The second option applies only to those part-time workers with whom an open-ended contract has been concluded.
On the last working day, you should make a full payment with a specialist. In addition, he needs to be given a work book and all the necessary documents.
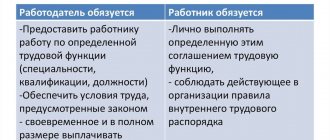
Article 284. Duration of working hours when working part-time
The duration of working hours when working part-time should not exceed four hours a day. On days when the employee is free from performing work duties at his main place of work, he can work part-time full time (shift). During one month (another accounting period), the duration of working time when working part-time should not exceed half of the monthly standard working time (standard working time for another accounting period) established for the corresponding category of employees.
The restrictions on the duration of working hours when working part-time, established by part one of this article, do not apply in cases where the employee has suspended work at his main place of work in accordance with part two of Article 142 of this Code or has been suspended from work in accordance with parts two or four of Article 73 of this Code.
back to contents
Employee Notification
If the employer intends to terminate the employment relationship with a part-time employee for any valid reason, then, in accordance with the procedure established by legal acts, he is obliged to notify the employee in writing fourteen days in advance. According to the accepted rules, he must give the specialist a notice indicating the reason and date of the upcoming dismissal.
Such a document is issued against signature. If an employee refuses to receive a notification, then a statement of refusal must be drawn up and registered in the appropriate journal.
Practice shows that disputes between an employer and an employee often arise due to the content of the document notifying the termination of the employment contract. For example, it does not indicate the date of dismissal or its reason.
If a part-time worker who has received such a notice applies to the court to protect his rights, the decision will be made in his favor. This is due to the fact that he will be able to confirm his claims with reliable facts by providing an incorrectly executed document.
The employer also needs to be confident in the legality of his actions, that is, in the decision made and the sufficiency of the grounds for terminating the employment relationship if the initiative to dismiss the employee comes from him.
Drawing up an order
Termination of an employment contract with a part-time employee should be formalized accordingly, that is, in accordance with regulatory legal acts. To do this, the organization needs to issue an order to dismiss the specialist.
The document must indicate the following information:
- surname, name, patronymic of the employee;
- the position he holds;
- the date of his dismissal;
- grounds for termination of the contract;
- due payments.
The document must be signed by the manager and the dismissed employee, who must put a mark confirming familiarization with the order. This procedure is the same when terminating an employment contract for both internal and external part-time workers.
Difference in registration of dismissal
Despite the fact that the process of ending an employment relationship is basically the same, there are some differences in the systems for dismissing different types of part-time workers. In particular, they relate to the reflection of the fact of cooperation in a person’s work record.
Thus, in the document of an employee who has a main job at another enterprise, there is no need to enter information about dismissal, because his work book remains with the main employer. If the employee needs confirmation of these relationships, then he can ask to provide all the necessary copies and extracts.
If an internal part-time worker is fired, the employer is obliged to make an entry in the work book, since it is kept by him and, accordingly, it is the employer who is responsible for filling it out. The same applies to situations when a part-time worker quits his main job.
Dismissal rules
The procedure for terminating a business relationship may vary slightly depending on whether the part-time relationship was external or internal. Depending on the grounds for the day of termination of the employment relationship, the procedure may be regulated by Articles 80, 78, 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation . If we are talking about internal part-time work, then articles 73, 286 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation .
With external part-time
Depending on whether the dismissal of an external part-time worker occurs at the initiative of the employer or his personal desire, an order must be issued or an application must be submitted by the employee himself. If the employee's departure occurs as a result of the main worker returning to work, the employer sends the part-time worker a written notice , which he must sign. Next, a dismissal order .
Important! The very principle of terminating a business relationship is similar to the dismissal of an internal part-time employee. The only difference is in creating an entry in the work book. When external, the document is stored in the company of the main employer. Therefore, it is he who must make the appropriate entry in the work book.
The column in the work book contains information that the employee was dismissed from his part-time job. To do this, the worker must make a written request to the primary employer. First, he will need to prepare a copy of the order of dismissal from another place of work, certified by the former employer .
With internal
Depending on the reason for the termination of the business partnership, an appropriate dismissal order If the termination of a business partnership occurs at the initiative of the employer , he undertakes to notify the employee of this by written notice. The same rule applies if a key employee takes over. If leaving the company is personal desire , then he submits a corresponding application to the employer. Further procedure for dismissing an internal part-time worker:
- An order to terminate cooperation is issued.
- The employer makes a note about the termination of the business relationship in the employee’s personal card.
- A corresponding entry is made in the work book.
Reference! The documentation states that dismissal occurs from a part-time job.
Allowed compensation
An employee working part-time is entitled to annual leave, despite the fact that he performs his duties only at half the rate. This is indicated in the Labor Code.
In this regard, upon dismissal of such an employee, compensation should be calculated for those days off that he did not use for some reason. If he rested more days than he was entitled to at the end of the cooperation, the amount of vacation pay paid earlier is withheld from the specialist.
According to the law, a part-time worker must receive leave from work at an additional job at the same time as he receives days off from his main job. But you need to keep in mind that an employee can, at his discretion, take a vacation earlier than set in the schedule.
In addition, the employer must pay the dismissed part-time worker severance pay , if this is stated in the organization’s labor or collective agreement. Compensations are issued on the employee’s last working day.
The employer needs to understand that a part-time employee has all the rights and obligations established by the Labor Code. This means that it is possible to fire a part-time employee, both external and internal, without the consent, but all the nuances of the procedure must be observed.
If the employer, terminating the employment relationship, commits violations, then the dismissal will be considered illegal. In this case, the dismissed person can turn to the courts to protect their rights.
Issues of terminating an employment contract with a part-time worker usually do not cause controversy if the employment relationship is terminated on general grounds. But if a part-time worker is fired due to the hiring of an employee for whom this work will become the main one (Art.
288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the emergence of a labor dispute is almost inevitable. In the article, using examples of court decisions, we will show what violations are committed by employers when dismissing a part-time worker on this basis.
Documentation and procedure
The procedure for terminating an employment contract depends on who initiated the dismissal.
The main document is an order issued by the management of an organization or enterprise.
The basis for issuing this document is a notification application received from the employee, or documents documenting violations on his part. And if a permanent employee has been found, a notification is sent to the employee by the employer himself.
At the same time, making a corresponding entry in the work book has its own characteristic features. The entry is made by a personnel service employee at the place of main work on the basis of a copy of the order or certificate issued at the additional workplace. There is no stamp!
In case of recorded violations
- The employer asks the offender to write an explanatory note. In case of refusal, an act is drawn up recording the violation.
- Based on the explanatory note, an internal memorandum is drawn up. At this stage, the employer has the right to limit himself only to disciplinary action. It should be noted that two punishments at once - disciplinary (for example, a reprimand) and dismissal are not applied according to labor legislation.
- If a decision is nevertheless made to dismiss, a corresponding order is issued, which is signed by the employee (in the T-8 form). If a refusal is received from the employee, it is recorded in an act with two witnesses. The act is then filed in the offender’s personal file.
- Based on the order, notes are made in the personal file and work book.
- The payments due to the employee are calculated and the final payment is made.
An order to fill out when dismissing a part-time worker can be found here.
When hiring a permanent employee
Regulated by Article 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- Management sends a written notice to the part-time worker, informing him of the date of termination of the contract. The document is sent two weeks before dismissal. At this stage, the employee may quit his permanent job, preferring a part-time position. In this case, the employer can no longer hire a new employee for the same position.
- An order is issued within two weeks. The employee can sign it or refuse to sign. Refusal requires drawing up an act in front of two witnesses.
- Then entries are made in the work book and personal file. And on the last working day the final payment is made.
Read more about the procedure for terminating an employment contract with a part-time worker at the initiative of the employer in other cases here.
When leaving at the initiative of an employee
- The employee himself sends a notification to management. The document indicates the day of dismissal and the reasons for leaving. For fixed-term contracts, this document is drawn up three days before termination. Open-ended contracts require two weeks' notice.
- The notification received serves as the basis for issuing an order. The employee is familiarized with the order, and he puts his signature on it.
- After that, entries are made in the work book and personal file. Compensation payments are accrued in the form of wages and funds for unused vacation days. Payments are made on the last working day.
- Also, the law allows the signing of a document by agreement of two parties. On its basis, an order is issued and a calculation is made. The employee can independently set the date of termination of the contract and agree on additional compensation payments.
In case of disability
If the first disability group is assigned, the part-time worker has the right to terminate the employment contract urgently.
To do this, you must contact management with a statement and documentary evidence of a valid reason. In this case, the employee has the right to request immediate dismissal , citing the impossibility of continuing to work.
Further paperwork takes place according to the generally accepted procedure. An order is issued, notes are made in the personal file and work book, payments are calculated and calculations are made.
Dismissal of a part-time worker.
Termination of an employment contract with a part-time worker in the event of hiring an employee.
The dismissal of a part-time worker in the event of hiring an employee for whom this work will be the main one occurs as follows: the employer warns the dismissed person in writing at least two weeks before the termination of the employment contract.
Let us consider the court decision from a generalization of the practice of considering civil cases arising from labor relations for 2009 of the Kaa-Khemsky District Court of the Republic of Tyva.
K. filed a lawsuit against MDOU “Kindergarten No. 5 “Rodnichok” for reinstatement at work, recovery of wages for the period of forced absence and compensation for moral damage, indicating that since 09/01/2008 she worked as a part-time music director in the kindergarten.
By order of September 1, 2009, she was dismissed as a temporary employee; she considers the dismissal illegal.
When considering the case, the court found that the plaintiff, having a permanent job as a teacher at the Children's Art School, was hired part-time at the Rodnichok kindergarten as a music director at 0.5 rates, allocated from the rate of the main employee B., at indefinite term.
Later, B. approached the head of the kindergarten with a request to grant her again 0.5 times the salary of a music director, since she has two minor children and is a widow. In connection with the satisfaction of her request, K. was dismissed as a temporary employee.
In accordance with Art. 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in addition to the grounds provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws, an employment contract concluded for an indefinite period with a person working part-time may be terminated in the event of hiring an employee for whom this work will be the main one, about which the employer in writing form warns the specified person at least two weeks before termination of the employment contract.
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
Since the main employee was already working, but a part-time worker was hired at his 0.5 rate for an indefinite period, the employer was still obliged to warn him at least two weeks before terminating the employment contract.
Dismissal of a part-time employee during vacation or illness.
Dismissal of a part-time worker during vacation or a period of temporary disability at the initiative of the employer, including under Art. 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, illegal.
On 04/08/2010, the Sovetsky District Court of the city of Tomsk considered the case regarding G.’s claim against the LLC for reinstatement at work, recovery of wages, vacation pay, average earnings for the period of forced absence, and compensation for moral damage.
G. filed a lawsuit against the LLC for reinstatement at work and, in support of her claims, indicated that she was hired by the defendant to work part-time for an indefinite period. On 02/08/2010, she received a letter from the defendant at her home address stating that on 02/14/2010 she would be dismissed in connection with the hiring of an employee on a permanent basis for her position. At the time of receiving the letter, she was on vacation (from 02/08/2010 to 02/20/2010) and was undergoing treatment. On February 27, 2010, she received another letter stating that her employment relationship had been terminated.
At the court hearing, the defendant’s representative did not admit the claim and explained that on 02/03/2010 a notice of dismissal from his position was sent to the plaintiff. The dismissal order was issued on February 17, 2010; G. refused to familiarize herself with it.
After listening to the explanations of the parties, examining and evaluating the evidence presented, the court considered that the claim should be partially satisfied on the following grounds.
According to the employment contract, G. was hired by the LLC on a part-time basis for the period from 11/01/2006 to 01/31/2010. From G.’s testimony it is clear that she actually began performing the work, but the employment contract was signed only on 01/01/2007 and for an indefinite period. The defendant's representative admitted this fact.
In this regard, when deciding on the dismissal of the plaintiff, the employer was obliged to take into account the provisions of Art. 288 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Paragraph 23 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2 “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” establishes that when considering a case on the reinstatement of a person whose employment contract was terminated at the initiative of the employer, the obligation to prove the existence of a legal basis dismissals and compliance with the dismissal procedure are the responsibility of the employer.
As follows from the order, from 02/01/2010, V. was hired on a permanent basis to work in the LLC for the position held by part-time worker G.. A record of hiring is available in V.’s work book. The fact of his employment was confirmed by witnesses. Taking into account the above, the court considers that V.’s employment with the LLC on a permanent basis from 02/01/2010 was confirmed. This means that the employer had a legal basis for dismissing the plaintiff. At the same time, the procedure for dismissing a part-time worker was not followed, which is confirmed by a number of circumstances.
The employee must be notified in writing of the date of the upcoming dismissal of the part-time employee, which cannot occur earlier than two weeks after the notification. The notice dated 02/03/2010 addressed to G. indicated that the employment contract with her would be terminated on 02/14/2010. When dismissing the plaintiff on 02/17/2010, the employer was obliged to warn him in writing about the upcoming dismissal no later than 02/03/2010. Thus, initially the notification of the upcoming dismissal did not comply with the requirements of the law, and therefore cannot be recognized as proper as containing false information about the date of dismissal of the part-time worker.
In addition, according to the provisions of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is not allowed to dismiss an employee at the initiative of the employer (except in the case of liquidation of an organization or termination of activities by an individual entrepreneur) during the period of his temporary disability and while on vacation. Dismissal of a part-time worker under Art. 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is dismissal at the initiative of the employer. By terminating the employment relationship on the 17th, that is, before the end of the vacation on February 20, the LLC significantly violated the norms of labor legislation and the procedure for dismissal. Under such circumstances, even if there are grounds for dismissing the plaintiff, the court cannot recognize the dismissal as legal. G. was reinstated to her previous job at the LLC as of February 17, 2010.
Dismissal of a part-time worker under Art. 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is dismissal at the initiative of the employer.
The Arkhangelsk Regional Court considered case No. 44-G-385 on Sh.’s complaint against earlier court decisions to reinstate her at work.
Sh. worked as a urologist in a hospital (hereinafter referred to as the MUZ) part-time at 0.5 times the salary. Subsequently, she was fired due to the hiring of another employee, for whom this work was the main one (Article 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Disagreeing with the part-time dismissal, Sh. appealed to the Oktyabrsky District Court.
Arkhangelsk with a claim against the Ministry of Health for reinstatement at work, changing the wording of the legal regime of the work performed, recovery of maternity benefits, recovery of monetary compensation for moral damage. In support of the claims, she indicated that the defendant incorrectly defined the type of employment contract concluded with her as part-time work, since the work of a urologist was her only and permanent place of work.
Moreover, the defendant could not fire her on his own initiative, since on the date of her part-time dismissal she had a disabled child under the age of three and was pregnant. By the decision of the Oktyabrsky District Court in satisfying the claims of Sh.
denied. The cassation court left this decision unchanged.
The regional court, having checked the case materials, noted that the courts, making a decision not in favor of the plaintiff, rejected her argument that working for the defendant was the main (only) place of work, and considered Sh.’s work as a urologist to be a part-time job.
To substantiate this conclusion, the courts referred to the application and order for part-time employment. However, their opinion is wrong.
And that's why.
In themselves, the application and order for part-time employment are not indisputable evidence of the plaintiff’s part-time work. When deciding on the terms of the employment contract, one should proceed from the compliance of the order with the requirements of the current legislation and the actual conditions of the employment contract.
According to Art. 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, part-time work is the performance by an employee of other regular paid work under the terms of an employment contract in his free time from his main job. From the content of this provision of the law it follows that work under an employment contract is part-time if:
- the employment contract was concluded with an employee who is already in an employment relationship with the same or another employer;
- under this contract, other work is performed in addition to the main one;
- The work performed under another employment contract is regular and paid.
Thus, part-time work requires the employee to have another (main) permanent and paid place of work.
From the case materials it follows that neither on the date of concluding the employment contract with the defendant, nor on the day of dismissal, Sh. had another permanent place of work.
Since the conclusion of an employment contract on a part-time basis reduces the level of rights and guarantees of the employee, in particular, it allows him to be fired in connection with the hiring of another person, the court had to assess the legality of the condition in the employment contract concluded with the plaintiff on part-time work.
The Arkhangelsk Regional Court indicated that the resolution of the dispute regarding the dismissal procedure also depends on the conclusions regarding the legality of Sh.’s work on a part-time basis.
Moreover, the regional court declared the previous decisions unlawful in terms of the Ministry of Health's compliance with the dismissal procedure for Sh., since she has a disabled child under the age of three and was pregnant at the date of dismissal.
The courts of the first and second instances came to the conclusion that dismissal under Art. 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not constitute dismissal at the initiative of the administration, and therefore the guarantees established by law regarding the prohibition of dismissal at the initiative of the employer of pregnant women and women with children under three years of age do not apply to Sh.
However, the guarantees established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for pregnant women and women with children under three years of age apply to any grounds for dismissal if it occurs on the initiative of the administration. When making decisions, the courts should have taken into account that upon dismissal under Art.
288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation unilaterally expresses the will of the employer to replace a part-time worker with another employee for whom this place of work will be the main one. The initiative or consent of the part-time employee for dismissal was not required.
The legislator in the Labor Code established certain benefits for women upon dismissal, regardless of whether they work at their main place of work or part-time (Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer with pregnant women, as well as women with children under three years of age, single mothers raising a disabled child under 18 years of age, is not allowed, except in cases of liquidation of the organization.
Based on the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the regional court overturned the previous court decisions and reinstated Sh. at work.
Features of the work of a part-time worker and his dismissal when the main employee leaves
Part-time work is a type of labor relationship between an employee and an organization (legal entity), as well as an individual entrepreneur who employs individuals.
According to Article 60.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, people can enter into an unlimited number of employment contracts to perform work in their free time from their main job. Remuneration is based on divided in half . The law does not limit the amount of bonuses and additional payments.
The norms of Article 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulate that an enterprise has the absolute right to hire an unlimited number of part-time workers. It is clear that certain restrictions are set by the size of the company's salary fund.
Labor relations are concluded between the parties in a written form of an employment contract :
- For a certain period. Norms Art. 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows the conclusion of such a contract to perform certain work, when applying for work abroad and when forming a team of seasonal workers. The work period is strictly regulated by specific dates.
- No specific validity period specified .
In practice, there are two types of part-time work . By external we mean hiring a citizen who is not registered with a given organization at his main place of work. Internal part-time work is a situation when a company employee is officially hired for one more position, but no more than 0.5 times the salary . Registration of additional labor relations is carried out by a separate personnel order .
Important! To understand how to fire a part-time worker at the initiative of the employer, you need to know the norm of Article 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It states that the employer has every right to terminate the employment relationship with a part-time worker if the opportunity arises to take on a person who will work full-time (the main job).
The motivating advantages of such a solution are as follows:
- the efficiency of the staff will increase;
- the working time of a unit at the enterprise will increase;
- there will be no difficulty in regulating vacation time , which for a part-time worker should coincide with vacation at the main place of work.