30.08.2019
0
99
3 min.
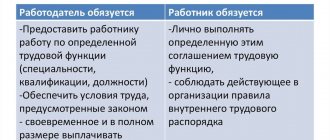
An employment contract is a key document that regulates the relationship between an employer and an employee of an enterprise. It is concluded by mutual decision, after agreements have been reached related to the amount of wages and the responsibilities of a citizen. If a period is not specified, the document is considered unlimited. Termination is possible upon dismissal or in court, but Article 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for other grounds for termination of the contract.
Failure to comply with what other restrictions may cause termination of the employment contract?
For some groups of workers, the legislator has established restrictions on the use of their labor in certain types of work. Thus, in particular, women are prohibited from working by manually lifting weights in excess of the norms permissible for them (Article 253 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In order to teach, teachers must have no criminal record or criminal record. Minors under 15 years of age are required to have permission from their parents and guardianship authorities when applying for work.
For other features of the work of minors, see the article “What benefits are provided for minor workers.”
There are other cases.
For all of these employees, the following is true: if, when signing an employment contract, any of the listed conditions and restrictions were not met, then the employment contract must be terminated under Art. 84 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Violations in the employment contract
The main reason for breaking a contract signed between an employer and a hired employee is the presence of violations of the code or other federal regulations. The first part of Article 84 contains a list of such violations .
They concern:
- Failure to comply with the provisions of a court verdict limiting the employee’s right to hold a position or carry out activities that were determined by the court.
- Contraindications to performing the work specified in the contract. If the inability to perform official duties is caused by health conditions or medical recommendations, this fact must be confirmed in the form of a medical document of the established form, issued by a special commission.
- Lack of confirmed qualifications and knowledge necessary for the job. Citizens hired for positions of advisers, specialists, and managers are required to have professional education and appropriate qualifications.
- Suspension from work or other administrative sanction that precludes the employee from performing his duties listed in the employment contract. Such restrictions are valid only if they were issued by the court, as well as by bodies and employees empowered to consider administrative cases. The employer can detect the fact of disqualification of a hired employee or removal from certain activities in a special database. Such a database was created by the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs and regional departments of internal affairs. The procedure for obtaining information from this database is determined by the relevant Manual and instructions.
- Prohibitions and restrictions regarding the involvement in work of citizens who were previously dismissed from municipal and state positions. These requirements are reflected in the Federal Law of the Russian Federation.
- Failure to comply with the provisions of regulatory documents containing information on restrictions on a certain type of activity.
If any of the listed inconsistencies with established legislation are identified, Article 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation comes into force, obliging the concluded contract to be terminated. Violations of other types not reflected in the first paragraph of this article are subject to Federal Law.
Results
Dismissal on the basis of Art.
84 of the Labor Code is carried out in the case when an employment contract is concluded in violation of the rules for its conclusion. If the fault lies with the employer, he is obliged to offer the employee other vacancies and pay severance pay. If the employee is at fault, for example, did not provide a document on education, and the work requires special knowledge, then the benefit is not paid and other work is not offered. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Article 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Article 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the issue of termination of an agreement due to violation of the rules for signing it, which were relevant at the time of its preparation. An employee has the right not to continue working at the enterprise if the document was drawn up or signed in violation of the regulations established by law.
These may include:
- Hiring a person under 18 years of age.
- Incapacity of a person.
- The presence of a psychiatric illness that does not allow a person to account for his actions.
- Lack of a diploma or certificate confirming education.
It is important to know! Article 84 is rarely used for dismissal, but if violations were committed through no fault of the employee, he has the right to receive severance pay in the amount of a month’s salary. When the personnel service refuses to indicate this reason in the work book, the citizen protects his rights by appealing to the state inspectorate or court.
Termination of an employment contract
Dismissal on the basis of Art. 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is permissible if, at the time of concluding the contract, serious violations of the provisions of the current legislation were committed. The situations are clearly described in the first part of the article. The following are considered significant circumstances:
- There is a court decision prohibiting a specialist from performing certain activities for a specific period of time (or at all).
- The citizen has officially certified medical contraindications to engage in the work specified in the employment contract.
- The HR department was not provided with a document that would confirm the declared education or qualifications for admission to a specific job.
- The regulatory authorities issued a resolution providing for administrative penalties and prohibiting them from working anywhere under an employment contract.
- The Labor Code or regional regulations prohibit the involvement of a specific category of citizens in certain types of work.
- In other cases provided for by federal legislation.
A person may receive official contraindications to engage in certain activities before the device is installed. If he does not inform the employer about this and the agreement is signed, the company has the right to subsequently terminate it unilaterally, not pay severance pay and not look for a position to replace the one for which the citizen applied.
Procedure for terminating an employment contract
Part 1 of Article 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation applies only if there is a violation of the rules for signing an agreement. After identifying it, the employer is obliged to follow a certain procedure, which is as follows:
- Draw up an order in a unified form No. T-8a. It indicates the reason for termination of the agreement.
- The employee is introduced to the document upon signature. If this is impossible for objective reasons, then a corresponding act is drawn up about this.
- Preparation of certificates of earnings for the last months of work at the enterprise.
- Issuance of full payment and work book.
The day of termination of the employment contract is considered the last day of work of the employee. If he was not actually in his place, then the day of settlement. It is not allowed to send basic documents by mail without the consent of the citizen. The entry is made in accordance with the accepted wording, in particular in Part 1 of Art. 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, indicates “termination of an employment contract due to violation of the established rules of conclusion.”
Attention! The law does not provide clear deadlines for an employee to become familiar with the dismissal order. Therefore, the absence of a signature on the second copy is not a violation of existing requirements.
Contents of the comment
Commentary 2021 to the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on termination of the contract between employer and employee is a very important addition. It contains information regarding the procedure for filling out and providing documents to a dismissed employee:
- He receives a work book only upon dismissal. If on the day of signing the relevant order it is not possible to issue it, the employer must send the former employee a notice of the need to obtain the book or send it by mail to the residence address. From the moment the notice is sent, the employer is relieved of the responsibility provided for the untimely issuance of the document (including material, prescribed in Article 234).
- When entering information about dismissal into the book, authorized persons are guided by the wording of the Labor Code or other law and must indicate the article that served as the basis and its individual sections.
The procedure for filling out a work book does not provide clear templates in accordance with which the entry should be formulated. The main thing is that it is assigned a serial number, the date and reason for the termination of the contract are present, and the number of the law and order applied in each specific case is indicated.
It is mandatory that the information about dismissal entered must be certified by the signature of the employer or responsible employee, the seal of the company (its personnel department) and the signature of the owner of the record book.
There are several recommendations indicating which grounds for dismissal cannot be applied to an employee and are indicated in his work book. First of all, these are circumstances of a general civil nature that discriminate against one of the parties to the contract (for example, membership in a party or refusal to join it).
Payment of severance pay
When professional interaction is terminated prematurely, in most cases the person is provided with financial support in the form of severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings.
It should be noted that the worker can count on such a payment only if the violation was not committed by himself.
If the worker has committed an offense himself, then financial assistance will not be provided to him. This also applies to translation. In such a situation, the manager is not obliged to offer alternative options.
Change of position and place of work
In accordance with Article 84 Labor Code, the contract must be suspended if the employer refuses to comply with the employee’s wishes regarding his transfer to another position. A subordinate has the right to make a written request for transfer to:
- job vacancy;
- lower position;
- work requiring similar qualifications;
- lower paid activities.
The law obliges the employer to offer those vacancies that meet the wishes of the employee and imply work at his place of residence.
However, if a violation of the law is revealed in the employee’s actions (providing false documents, violating court decisions, etc.), the employer is exempt from the need to notify about vacancies. Transfer to another region or region is allowed only when it is previously agreed upon by the parties and is fixed in an employment contract or additional agreement. In any case, the desire to change the place of work (and therefore the place of residence) must come from the employee. Coercion from superiors is excluded.
The general procedure for registering the termination of an employment contract provides for the payment of a monetary benefit to a dismissed employee in the amount of his monthly salary only if he did not violate the law or other rules during his work activity.