We are all accustomed to the fact that in order to find a job we need to contact various legal entities: enterprises, individual entrepreneurs, organizations. But at the same time, there are many ways to find employment, and the classic agreement concluded between an enterprise and a citizen is not the only option for official earnings. Not everyone knows, but there is also an agreement that is concluded between two individuals.
Such an agreement has a number of features, since the work under it is slightly different in structure. In this article we will look at the rules for drawing it up, the nuances of signing and actions.
Labor relations
Employment agreements between individual entrepreneurs and employees are not uncommon. However, labor relations between two individuals not engaged in entrepreneurial activities, although widespread, are rarely documented.
Thus, well-known examples of labor relations between individuals who are not entrepreneurs and the employees they hire may be:
- caring for sick and elderly family members (nurses);
- supervision and care of children (nannies, teachers);
- housekeeping (maids, cooks, gardeners);
- driving a family vehicle as a family chauffeur, etc.
In these cases, the mutual reluctance of the employer and employee to draw up an employment contract is quite understandable. So:
- it is not beneficial for the employer to declare himself as an employer, since this imposes on him a number of obligations related to the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, for example, making mandatory insurance payments for the employee, paying for sick leave, providing paid leave, etc.;
- For various reasons, it is not beneficial for an employee to declare himself as an employed person, since official employment can lead to undesirable consequences for him, for example, the need to pay personal income tax, a reduction in the amount of social benefits, loss of unemployed status or the cancellation of existing benefits.
Tax and labor authorities are not able to track the entire variety of labor relations arising between individuals, therefore the question of concluding an employment contract or refusing to conclude it remains entirely at the discretion of these individuals.
For our part, we can only state that for both the employee and the employer there are many advantages in formalizing an employment relationship.
Which individuals can hire
The following citizens can become employers:
- officially registered as individual entrepreneurs;
- working as lawyers and notaries;
- hiring people to provide services in their personal household (cleaners, nannies, butlers, etc.).
There is an important condition: hiring employees is only available to adults.
Individual entrepreneurs
In this regard, individual entrepreneurs are practically no different from legal entities. The rules for maintaining personnel documentation at individual enterprises allow their owners to:
- draw up rental agreements;
- fill out personnel work books;
- determine the conditions and requirements of the organization’s internal regulations.
The main difference between individual entrepreneurs and legal entities in the matter of hiring employees is that the former do not necessarily need to register concluded contracts with the municipality of the locality.
ATTENTION! A citizen registered as an entrepreneur is not deprived of his right to act as an employer of individuals to receive services in his personal household as an individual.
Lawyers and notaries
Lawyers or notaries are registered as a lawyer's office or a notary office, respectively. The algorithm for hiring citizens for permanent employment is similar to hiring employees as personal assistants.
Employers of personal assistants and domestic staff
Individuals who are not registered as entrepreneurs have the right to hire citizens for their own needs. For example:
- driving a personal vehicle;
- property protection;
- management of the estate;
- creative activity;
- help around the house, etc.
According to the provisions of the Civil Code, a person, when hiring an employee for personal needs, is obliged to make pension contributions in respect of his employee. To do this, he must register with the Pension Fund as an employer within a thirty-day period from the date of execution of the contract.
What the law says
In accordance with Article 20 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an individual can act as an employer if he meets one or more criteria, namely:
- is an individual entrepreneur with the right to hire workers to perform work related to his legal business activities;
- is an individual entrepreneur under a license (notaries and lawyers) with the right to hire workers to perform work related to advocacy or notarial activities;
- is an adult;
- is legally competent.
The last two points apply to individuals who do not have the status of an individual entrepreneur and have the right to hire workers to perform functions in the employer’s household.
Employment contract between individuals
Any citizen can hire another person and register his work officially, without being an individual entrepreneur. The rules for drawing up such an employment contract and the working conditions under it are regulated separately by the Labor Code.
All details regarding the execution of a rental agreement between two citizens, neither of whom is registered as an individual entrepreneur, are regulated by legislative acts:
- Chapter 48 of the Labor Code - determines the basic procedure for formalizing and implementing business relations with an employer who is an individual;
- Article 303 of the Labor Code – regulates the conditions for registering a job with an individual.
ATTENTION! In the matter described, the term “employment contract”, as well as the conditions and rules for its execution, do not differ from standard situations. The legal aspects of this issue are also determined by the provisions of Article 56 of the Labor Code.
Advantages of the agreement
Any contract, including an employment contract, establishes the rights and obligations of counterparties. The absence of a written contract makes it impossible to file claims related to non-fulfillment of the agreed terms. For example:
- accidental or intentional destruction of the employer's property by an employee will not entail compensation for damage, since the fact of the employee's access to this property will not be confirmed by anything;
- the dismissal of an employee cannot be appealed due to the absence of an employment contract;
- dismissal of an employee will not be accompanied by payment of severance pay;
- an employee working without a contract is not entitled to paid leave, etc.
That is, neither the employer nor the employee will have access to the procedure for protecting their rights related to labor relations. But, in our case, the lack of opportunities to protect rights is fully compensated by the lack of responsibilities, which means that we can hardly expect a boom in the conclusion of employment contracts between individuals in the near future.
If you decide to enter into an agreement
The legislation does not impose any special requirements for an employment contract between individuals, which means that it will include a standard set of structural elements characteristic of any employment contract.
So, the main structural elements will include:
- date and place of conclusion of the contract;
- Full name, addresses and passport details of counterparties;
- the subject of the contract, that is, the actual fact of establishing labor relations between the employer and the employee;
- the employee’s place of work, that is, the address of the premises (area) in which he will perform his functions;
- work start date;
- information about the employee’s functions, that is, the job for which he is employed. For example, child care, care for the elderly, gardening, etc. There can be many options, the main thing is that they do not include even a hint of the employer’s entrepreneurial activity. Thus, an employee can take care of the garden and pick flowers, but the employer has no right to oblige him to sell these flowers at the market;
- information about the employee’s qualifications. This may be required when the employer requires education or relevant experience. For example, the contract must stipulate that the employee has a driver’s license, a certificate of completion of massage therapist courses, or a diploma in pedagogical education;
- work schedule and rest schedule;
- duration of the contract, conditions of the probationary period;
- salary amount, method and procedure of payment;
- other conditions that the parties may agree on. For example, an additional condition may include the employer’s obligation to provide the employee with a place to live at the place of work;
- signatures of counterparties.
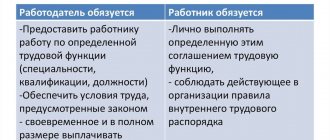
We have already said above that by concluding an employment contract as an employer, an individual assumes the obligation to comply with the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in relations with an employee. Thus, the employer is obliged:
- provide the employee with annual paid leave of at least 28 days;
- provide the employee with weekly uninterrupted rest of at least 48 hours;
- do not exceed the 40-hour working week;
- pay all statutory insurance premiums for the employee.
An individual employer is obliged to transfer personal income tax from the employee’s income only if he is an individual entrepreneur. Individuals who are not entrepreneurs are required to pay only mandatory insurance contributions for their employees.
An employer who is not an entrepreneur must register an employment contract concluded with an employee with local executive authorities.
Payment of taxes and contributions under such an agreement
The employer is obliged to pay his employee wages at least twice a month (advance payment and the basic amount of remuneration). From these funds he must pay taxes and insurance premiums for the employee in the amount of:
- personal income tax – 13%;
- to the federal budget – 20%;
- social insurance – 2.9%;
- medical insurance - 3.1% (2% - to the territorial body, 1.1% - to the federal body);
- pension contributions - 14% (8% - insurance part, 6% - funded).
All specified contributions, with the exception of personal income tax, are paid from the personal funds of the employer. Only 13% income tax is withheld from the employee’s remuneration.
The provisions of Article 243 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allow individual employers to reduce contributions under the Unified Social Tax by the amount of contributions to the employee’s pension insurance by issuing a tax deduction.
A sample employment contract with an individual can be downloaded from this link.
What to do with a work book
The importance of a work record book is largely overestimated and it is possible that in the near future it will be forgotten as a phenomenon. An employment contract is sufficient to confirm the fact of an employment relationship.
However, for now the obligation to maintain an employee’s work book is established by law, but only for business entities - individual entrepreneurs and legal entities, as well as public and government organizations and enterprises.
Individuals who do not have the status of an entrepreneur are not only not required to make entries in the employee’s work book, but do not even have the right. This means that the fact of employment relations will be confirmed exclusively by the contract.
List of documents
An employment contract concluded between individuals is subject to the same conditions and rules as a document drawn up between a legal entity and an employee.
List of documents for registration:
- passport or residence permit (for foreign citizens);
- insurance certificate;
- tax number;
- military ID for military personnel;
- work book (only for drawing up an agreement with an individual entrepreneur);
- other documents at the request of the employer (medical record, police clearance certificate).