Events happen in life when it becomes necessary to terminate an employment relationship. At the same time, the conclusion of an employment agreement does not always end with a statement “on one’s own.” In the article we will consider in detail the general grounds for termination, and also give their various classifications.
Classification of bases
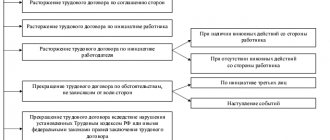
Termination of an employment contract is a fairly common action in the relationship between an employer and an employee. There are many reasons for this, which are described in detail in labor legislation. The grounds for termination of an employment contract are numerous, therefore labor legislation contains as many as 3 concepts related to this issue, which differ from each other in essence.
In addition to “termination of the contract”, there is also “termination of the employment contract” and “dismissal” of the employee.
The broadest meaning of these terms is given to the “termination” of the contract, since it includes cases of completion of the labor process by mutual agreement of the parties, the activity of the employee or employer.
“Termination” of an employment contract refers to those situations in which the employment relationship is changed by the activity of the parties to the contract. According to the laws of logic, such a name can be used in relation to all grounds, except those that are not subject to the will of the parties. The term “dismissal” is identical to the concept of “termination”.
MY RIGHTS: HOW TO PROTECT YOUR RIGHTS
Labor legislation on the grounds for termination of employment relations
Labor Law Standards:
- Article 75 “Labor relations when changing the owner of the organization’s property, changing the jurisdiction of the organization, its reorganization, changing the type of state or municipal institution” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (as amended on 02/05/2018);
- Article 77 “General grounds for termination of an employment contract” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 78 “Termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 79 “Termination of a fixed-term employment contract” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 80 “Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employee (at his own request)” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 81 “Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 83 “Termination of an employment contract due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 84 “Termination of an employment contract due to violation of the rules for concluding an employment contract established by this Code or other federal law” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 84.1 “General procedure for formalizing the termination of an employment contract” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The general grounds for termination of employment relations are reflected in Article 77 “General grounds for termination of an employment contract” of the Labor Code.
Ground 1 for termination of employment relations: termination of the employment contract by agreement of the parties.
This basis reflects the contractual nature of labor and labor relations between workers. They arise and terminate by agreement of the parties to the employment contract. If the parties to the employment contract have reached an agreement to terminate the employment contract, the employment contract is terminated at any time within the period determined by the parties.
Article 78 “Termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties” of the Labor Code
Ground 2 for termination of employment: termination of a fixed-term employment contract.
The expiration of an employment contract is a legal fact that gives rise to the termination of the employment contract regardless of the will of the employee or employer. At the same time, the employer is obliged to warn the employee about the termination of the employment contract at least 3 calendar days before dismissal.
Article 79 “Termination of a fixed-term employment contract” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Ground 3 for termination of employment relations: termination of the employment contract at the initiative of the employee.
An employee has the right to terminate an employment contract by notifying the employer in writing no later than 2 weeks in advance, unless a different period is established by the Labor Code or other federal law. The specified period begins the next day after the employer receives the employee’s resignation letter.
By agreement between the employee and the employer, the employment contract can be terminated even before the expiration of the notice period for dismissal.
Upon expiration of the notice period for dismissal, the employee has the right to stop working. On the last day of work, the employer is obliged to issue the employee a work book and other documents related to the work, upon the employee’s written application, and make a final payment to him.
Article 80 “Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employee (at his own request)” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Ground 4 for termination of employment relations: termination of the employment contract at the initiative of the employer.
An exhaustive list of cases when an employment contract can be terminated by the employer is given in Article 81 “Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer” of the Labor Code.
Also, if the test result is unsatisfactory, the employer has the right to terminate the employment contract with the employee before the expiration of the test period, warning him about this in writing no later than three days in advance, indicating the reasons that served as the basis for recognizing this employee as having failed the test. The employee has the right to appeal the employer's decision in court.
Article 71 “Result of the test when applying for a job” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Ground 5 for termination of employment relations: transfer of the employee, at his request or with his consent, to work for another employer or transfer to an elective job (position).
Such a transfer is made when the employee has received a written invitation from another employer to join him for work. In order for such dismissal to become possible, a joint expression of the will of 3 persons is necessary. Otherwise, the employee can leave only of his own free will.
Article 80 “Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employee (at his own request)” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
To apply such a basis as transfer to an elective position, an act of election of an employee to an elective position exempt from production work is required. Therefore, the dismissal order and the employee’s work book must not only indicate clause 5 of Article 77 “General grounds for termination of an employment contract” of the Labor Code, but specify on which of these two grounds the employee is dismissed.
Ground 6 for termination of labor relations: the employee’s refusal to continue working due to a change in the owner of the organization’s property, a change in the jurisdiction (subordination) of the organization or its reorganization.
In accordance with Article 75 “Labor relations when changing the owner of the organization’s property, changing the jurisdiction of the organization, its reorganization, changing the type of state or municipal institution” of the Labor Code, when changing the owner of the organization, the new owner has the right to terminate the employment contract with the head of the organization and no later than 3 months from the date of his ownership of the organization’s property.
The new owner has the right, at his discretion, to change the officials included in the “management team”, in particular the head of the organization, his deputies and the chief accountant, i.e. terminate the employment contract with any of them.
Ground 7 for termination of employment: the employee’s refusal to continue working due to a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties.
As a general rule, the terms of an employment contract can be changed only by agreement of the parties and in writing.
In paragraph 21 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2, the courts are explained the need to take into account Article 56 “Obligation of Proof” of the Civil Procedure Code, according to which the employer is obliged, in particular, to provide evidence confirming that a change in the conditions determined by the parties the employment contract was a consequence of changes in organizational or technological working conditions, for example, changes in equipment and production technology, improvement of jobs based on their certification, structural reorganization of production, and did not worsen the employee’s position in comparison with the terms of the collective agreement or agreement.
Ground 8 for termination of employment: refusal of the employee to be transferred to another job,
necessary for him in accordance with a medical report issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, or the employer does not have the relevant work.
The employer is obliged to transfer the employee, with his written consent, to another available job that is not contraindicated for the employee due to health reasons.
There may be cases when an employee refuses to be transferred to the offered job or when the employer does not have such a job. In this case, the employment contract is terminated on the basis of clause 8 of Article 77 “General grounds for termination of an employment contract” of the Employment Contract.
Ground 9 for termination of employment: refusal of the employee to be transferred to work in another location together with the employer.
The employee’s refusal to be transferred to work in another location together with the employer is grounds for termination of the employment contract (clause 9 of Article 77 of the Employment Contract).
To terminate an employment contract on this basis, it is necessary that the employee and the employer are actually transferred to another location. In this case, the employee must be given notice of the employer's transfer to another location. The notice is given against signature.
If the employee refuses to receive notice of refusal, a corresponding act is drawn up.
Ground 10 for termination of employment relations: circumstances beyond the control of the parties.
The article “Termination of an employment contract due to circumstances beyond the will of the parties” of the Labor Code establishes the grounds for termination of an employment contract due to circumstances beyond the will of the parties.
The peculiarity of this article is the combination of grounds for termination of an employment contract, which are legal facts - actions or events that do not depend on the will of the parties.
Ground 11 for termination of employment relations: violation of the rules for concluding an employment contract established by the Labor Code or other federal law, if this violation precludes the possibility of continuing work.
Labor legislation provides for employees subject to dismissal under Part I of Article 84 “Termination of an employment contract due to violation of the rules for concluding an employment contract established by this Code or other federal law” of the Labor Code, an additional guarantee of their right to work, obliging the employer to attempt their internal employment, that is, offer the employee a transfer with his written consent to another job available to him in the given area.
In all considered cases of termination of employment relations:
- termination of the employment contract and dismissal of the employee is formalized by order (instruction) of the employer. The employee must be familiarized with the order (instruction) of the employer to terminate the employment contract against signature;
- at the request of the employee, the employer is obliged to provide him with a duly certified copy of the specified order (instruction). In the event that an order (instruction) to terminate an employment contract cannot be brought to the attention of the employee or the employee refuses to familiarize himself with it against signature, a corresponding entry is made on the order (instruction);
- The day of dismissal of an employee is the last day of work. On this day, the final settlement must be made with the employee and a work book must be issued, and upon the employee’s written application, other documents related to the work must be issued;
- in the event that on the day of termination of the employment contract it is impossible to issue a work book to the employee due to his absence or refusal to receive it, the employer is obliged to send the employee a notice of the need to appear for the work book or agree to send it by mail. From the date of sending this notification, the employer is released from liability for the delay in issuing the work book.
Part 6 of Article 84.1 “General procedure for formalizing the termination of an employment contract” of the Labor Code
If you have any questions about the violation of your rights, or you find yourself in a difficult life situation, then an online duty lawyer is ready to advise you on this issue for free.
TERMINATION OF THE EMPLOYMENT CONTRACT. DISMISSAL
Termination of an employment contract by mutual will of the parties
Article 77 of the Labor Code in 11 paragraphs lists the general grounds for termination of an employment contract, including a change in the validity of the agreement at the will of the parties, the employee or the employer, due to objective circumstances independent of the will of persons, and others.
Clause 1 of Article 77 provides for agreement of the parties as one of the grounds. For this reason, it is possible to terminate both a contract for an indefinite period and a fixed-term employment contract. The peculiarity of the contract is that the wishes of only one party are not enough to terminate the legal relationship, regardless of who initiated the termination.
Termination of the contract on the grounds under consideration occurs exactly within the period agreed upon by the parties.
If the parties do not agree on the end time of the employment contract, then termination on this basis is not permitted. In cases where the date of termination of the contract is agreed upon by the parties, but the employee does not terminate his labor function and the employer does not issue a dismissal order, the existing employment relationship continues.
Advantages of dismissal “by agreement of the parties”
It is clear that labor relations are a bilateral agreement, where both parties have their own status and weight, while termination of labor obligations can be initiated by one or the other party, or another option is possible: to agree and make a collegial decision that is beneficial to both.
The first, perhaps the most compromise form of terminating the relationship between an employee and an employer, is an agreement of the parties (Section No. 78 of the Code). Using this article, it is necessary to take into account that this compromise can only be applied in situations where the will of one party is not enough to terminate the contract, that is, the desire of only the employee or only the employer is not enough. A bilateral expression of will is required to sever the labor relationship.
As a rule, under article seventy-eight, a fixed-term contract is terminated before the end of its term. Or when, with a standard employment contract, both the employer and the employee have a desire to end the relationship. But the employer does not see any other way of dismissal (there is simply no reason to terminate the contract), and the person is ready to leave, but wants to receive additional compensation.
This procedure becomes optimal when it is necessary to fire an employee, but you do not want to spoil the relationship and his reputation. In this option, both parties go in the same direction when terminating their employment obligations.
In this option, the separation procedure follows the standard algorithm:
- A person submits a letter of resignation; it should be noted here that in this option this is not necessary. But if a person has determined for himself the amount of “compensation” and wants to declare this to the employer, this must be done so as not to be surprised later when he sees the final calculation note or the figure in the order to terminate the contract.
Even if the employee does not write a standard statement, he has the right to inform the employer about his claims upon dismissal “by agreement of the parties”
- A bilateral agreement is signed to complete the labor obligations. It is prepared in two copies, it states the date of departure, as well as the amount of compensation, the sequence and periods of compensation payments.
The termination agreement by agreement of the parties specifies all the necessary conditions: the period of dismissal, the amount and period of payments
- An order is being prepared, where the wording of the basis does not indicate section No. 78 of the Code, as it seems to be according to the logic of things. The correct wording looks like this: “Termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties, clause 1, art. No. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation." The justification must include the number and date of the document signed by the parties.
- The necessary papers are prepared for the person being dismissed, calculations are made, and the following documentation is issued:
- employment history;
- order to terminate obligations;
- all documents and certificates requested by the dismissed person regarding his activities (the request for provision must be made in writing, all certificates must be issued within three days, this can be done even several years after leaving);
- standard payments - salary and payments for vacations not taken;
- additional compensation (by agreement).
The advantages of this option for the employer are:
- You can fire any employee in one day;
- In this option, the employee does not have the right to file a lawsuit for wrongful dismissal;
- guarantees that the employee does not have any material claims;
- the employee can be assigned (and he will do this efficiently) with the responsibilities for the correct transfer of affairs to the appointed responsible persons;
- All categories of workers can be fired (including mothers with children under three years of age, minors and pregnant women).
In this option, the employee receives:
- in addition to all the required payments, additional compensation - a compensation bonus (most often, this is a salary for 1-3 months);
- the opportunity to go on paid leave before dismissal;
- the right to register with the employment service and receive benefits.
We emphasize: it is possible to cancel an agreement “by agreement” (as in the case of concluding an agreement) only if both parties agree (comments can be found in paragraph No. 20 of the decision of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 2 of March 17, 2004).
Video: the perfect dismissal
Termination of an employment contract due to the employee’s refusal to continue the employment relationship
An employee may refuse to fulfill personal labor obligations as a result of a radical change in contractual terms previously agreed upon by the parties. If such a change is due to the initiative of the employer, then he is obliged to notify the employee in writing 2 months before making changes to the text of the employment contract.
If the employee does not agree to work under other conditions, the employer is obliged to provide him with another job suitable for his conditions and state of health or transfer him to a vacant lower-paid position.
An employee has the right to refuse to resume work if the owner of the organization changes, the jurisdiction (subordination) of the organization changes, or its reorganization occurs.
The agreement can be terminated by the employee’s refusal in various cases of a significant deterioration in the terms of the contract, for example, in the case of a necessary relocation of the organization to another location, since in this case unnecessary inconveniences for the employee not provided for in the contract may arise.
Payments
For unpaid days, wages should be accrued with all due bonuses, allowances and other payments in accordance with the administrative documents of the enterprise.
During illness, benefits are accrued on the basis of a certificate of incapacity for work.
vacation days due to him in full , then he should be accrued compensation, which is also accrued for previous years, taking into account additional vacation days.
In certain cases, a severance (one-time) benefit equal to the average monthly earnings is accrued. Benefits are accrued if there is a reduction in staff or headcount, as well as during the liquidation and reorganization of an enterprise.
Under the same circumstances, a one-time benefit is paid to citizens employed in seasonal work in the amount of average earnings for 2 weeks.
A one-time benefit in the amount of average monthly earnings is provided to individuals who are fired due to improper registration by the personnel department of their hiring.
In case of liquidation of an organization , reduction of staff or number without warning the employee 2 months in advance and upon his application, one-time assistance is paid for 2 months.
When replacing the owner of an enterprise , which is accompanied by a change in management, one-time assistance is accrued to such employees for 3 months.
One-time assistance for 2 weeks is accrued in cases of dismissal:
- associated with deteriorating health that does not allow you to perform your duties;
- in case of conscription into the army;
- in connection with the reinstatement of the former employee;
- refusal to move to another area associated with the transfer of an enterprise.
Termination of the contract at the initiative of one of the parties
Termination of labor agreements is permitted by active actions of either party - the employer or the employee (Articles 71, 80, 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The termination of contractual agreements by the personal will of the employee is otherwise called dismissal. The employee has the unconditional right to unilaterally refuse the employment relationship. This fully applies to the constitutional principle of freedom of labor.
The only condition established by law is the procedure according to which the employee must notify the administration in writing of his dismissal.
The employer has the right to pay the employee only on the grounds contained in the law or contract. An employer, unlike an employee who resigns at his own request, is limited in his right to freely decide on the refusal of the employee’s services.
It is possible to dismiss an employee if the dismissal:
- motivated;
- is carried out in accordance with the established procedural order;
- accompanied by the issuance of severance pay;
- applies to persons for whom there is no prohibition on dismissal at the initiative of the employer (for example, pregnant women).
Guarantees
If an employee is sick or on legal vacation, an administrative document for dismissal is not drawn up.
The issue of dismissal at the initiative of the employer is considered by the trade union committee
A pregnant woman is in a privileged position relative to others.
Mothers who raise children without a father, women with children under three years of age, or with disabled children also have more rights.
An employer can initiate the dismissal of a minor citizen with the permission of the state labor inspectorate or other government body.
Grounds excluding the possibility of continuing the contract
Facts that arise against the will of the parties include, for example, conscription into military service, the sentencing of an employee to punishment, the loss of the employee’s ability to work, the elimination of an employee’s access to state secrets, if such access is necessary for a specific job.
The terms of the contract may be violated, in particular, by concluding a contract contrary to a court decision to prohibit engaging in a certain type of activity or hiring an employee who has health contraindications. The Labor Code, when considering cases of termination of a contract, also regulates, among others, a number of grounds that exclude the validity of an employment contract.
The law lists them as:
- termination of the agreement;
- the presence of circumstances that arose not by the will of the parties;
- violation of the accepted conditions for concluding an employment agreement (Articles 79, 83, 84 of the Labor Code).
Both the employee and the employer can declare that the contract has expired. Moreover, if none of these parties has received a demand to terminate the agreement, and the employee is still doing his job, then the fixed-term nature of the contract loses force and it is renegotiated for an indefinite future.
Other grounds for termination of the contract
There are specific operating conditions for different employees. For example, standards of behavior that cannot be violated are clearly established for teachers. Pedagogical activity is incompatible with the use of incorrect educational measures and immoral behavior.
Strict conditions are provided for civil servants and other categories of employees.
Also, the contract is terminated if the conclusion procedure is violated. For example, a person who does not have a higher education was hired for the position of court secretary. This position requires a graduate degree in law.
Registration of the contract termination procedure
The description of the grounds for termination of an employment contract will not be entirely complete if we do not consider the documentary procedure established for cases of its termination.
The contract is terminated by an order from the employer, with the obligatory indication of the grounds for dismissal, the date, and a link to the article of the Labor Code. The order is issued to the employee for review against signature. Then he is given a work book with information entered into it using the legal formulations of the Labor Code and other laws.
Any entries made in the work book during work in the organization must be certified by the employer or other official, the seal of the organization and directly the personal signature of the employee himself.
Author of the article
The employer is the initiator of the break
One of the grounds for dismissal is termination of the employment contract at the initiative of the employer. Types of dismissals at the request of an organization (individual entrepreneur) are as follows (Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- staff or headcount reduction (for more information, see “Staff reduction procedure: step-by-step instructions”);
- liquidation of the organization (for more information, see “Notice of dismissal in connection with the liquidation of the organization (sample)”;
- the employee's inadequacy for the position confirmed by the results of certification;
- dismissal of the manager, deputy managers, chief accountant due to a change in the owner of the organization’s property;
- repeated failure by an employee to fulfill job duties (for more details, see “Procedure for applying disciplinary sanctions (step-by-step instructions”);
- a one-time gross violation of labor duties (for more details, see “Dismissal: a type of disciplinary sanction”);
- loss of trust;
- committing an immoral act;
- making an unjustified decision by the manager or chief accountant that resulted in damage to the company’s property;
- unsatisfactory results of completing the probationary period (for more information, see “Dismissing an employee who has not completed the probationary period”);
- provision by an employee of false documents when concluding an employment contract.
These are the main options for terminating an employment contract provided for by labor legislation.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.