According to the law, a citizen has the right to stop working at any time. Dismissal at will is provided for in Article 77, paragraph 3, part 1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but the procedure requires compliance with a number of rules. The employee is obliged to notify the employer in advance of the upcoming dismissal. However, the parties may agree and not comply with the established rules. We will talk further about how to proceed to quit, the rules for entering information into the work book, as well as the liability that an employer who violates the rights of an employee may be held liable for.
How to terminate a contract with an employee
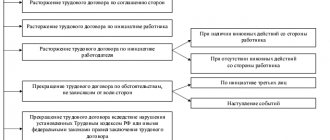
If a person, of his own free will, decides to stop working in an organization, the provisions of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Article 80 come into force. These reflect the rules that must be followed without fail.
Keep the following points in mind:
- An employee may terminate the employment relationship if he notifies the employer at least 14 days before the expected date of departure by writing a statement. In some cases, the notification period may change if the relevant rules are enshrined in the current legislation.
- If the dismissal occurs for reasons beyond the employee’s control or is associated with unlawful actions of the employer, the employee independently decides how many days before leaving he writes a statement.
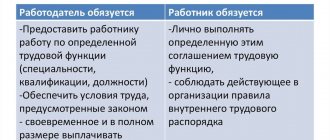
- At the time of completion of the activity, a full financial settlement with the employee occurs. Additionally, he is provided with a work book and other documents reflected in the legislation.
- A person has the right to withdraw a resignation letter before the end of the service period, with the exception of situations where a new specialist has already been invited to the position.
- If the employee no longer wishes to terminate the contract, the agreement continues to apply.
St77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation In New Edition With Comments 2021
Termination of an employment contract in connection with the employee’s refusal to continue work due to a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties. The procedure for terminating an employment contract in connection with the employee’s refusal to continue work due to a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties is determined by Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the content of which we discussed earlier .
The structure distinguishes between simple and complex legal facts and legal compositions. Labor legislation provides for both types of such facts.
For example, most cases of termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer presuppose the need for a legal structure: as a rule, the employer’s will alone is not enough to terminate the employment relationship; a reason is required, which determined the emergence of the corresponding right for the employer.
Stages of voluntary dismissal
If an employee independently wants to stop working for the company, this is the simplest situation. It is regulated by the Labor Code, or Labor Code. Usually, the parties independently agree on all the nuances of terminating legal relations, and conflicts do not arise.
It is important! Sometimes unscrupulous employers require you to write a statement of your own free will, while dismissing you for other reasons. In this situation, you can challenge the legality of the dismissal by going to court.
Today, experts have developed a clear scheme that must be followed in order to resign at your own request.
Video
To complete the procedure you will need to:
- Prepare an application and submit it to the employer. Please note that the date of dismissal is considered the final day of employment in the organization.
- Wait until the working period ends. The standard period is two weeks. If a person holding a managerial position is dismissed, the period is extended to 1 month. At the mutual request of the parties, the working period may be terminated earlier. The employer cannot insist that the period be reduced without the employee's wishes.
- A dismissal order is issued. The corresponding document is drawn up on the final day of work. The documents are provided to the employee for review. If necessary, the employee can obtain a copy of the order.
- The employee is provided with a salary certificate for the last two years. If issuing a document at the time of dismissal is not possible, it can be provided within 3 days from the receipt of the relevant application.
- The employer notifies the Pension Fund of dismissal.
- A record of termination of employment is made in the employee’s personal card.
- Draw up a settlement note. The document records information about the employee, information about termination of activity, information about accruals and payments received upon dismissal.
- Perform a full calculation. All funds must be provided by the last day. If the person was not present at work at this moment, the money is transferred the next day after receiving the corresponding request.
- An appropriate entry is made in the employee’s work book and the documents are issued to the owner.
- Provide a copy of the documentation that was presented at the time of hiring.
Video
We take into account the nuances when terminating a fixed-term employment contract
Document flow / We complete it step by step
Is it necessary to notify the employee about the expiration of the employment contract?
— Yes, it is necessary, unless the contract is concluded for the duration of the duties of the absent employee.
What can be negotiated upon early termination of an employment contract?
— On the period of termination of employment relations and the amount of monetary compensation.
Is it always necessary to refer to Article 77 of the Labor Code in the work book upon dismissal?
- No not always.
The dismissal of your employee will be legal if, when terminating a fixed-term employment contract with him, you follow three rules: - dismiss the employee on the grounds provided for by law;
— follow the dismissal procedure established for the selected reason1;
— draw up a document on termination of the employment contract (dismissal order).
Step 1. Determine the grounds for dismissal
Many employers believe that the only basis for terminating a fixed-term employment contract is the expiration of its validity period (Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, the law allows it to be terminated early and for other reasons.
It is important on what basis you terminate or terminate a fixed-term employment contract with an employee. The procedure for completing your personnel documents depends on the grounds for dismissal. First of all, let’s look at the difference between the concepts of “termination” and “termination” of an employment contract (see.
scheme). The Labor Code in Article 77 combines these concepts into one - “termination of an employment contract”.
However, there are differences between them: to terminate an employment contract, a volitional sign is important (the initiative of one of the parties, its request, its consent), while termination occurs as a result of negotiations (agreements) or reasons (events) independent of the wishes of the parties.
Step 2. Follow the dismissal procedure
As already said, the procedure for dismissal depends on the grounds. Let's look at the most common grounds for dismissal.
Expiration of the employment contract (Clause 2, Part 1, Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
As a general rule, a fixed-term employment contract is terminated due to the expiration of its term (Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Be sure to notify your employee about this in writing at least three calendar days before the date of termination of the contract (Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Such notification should not be considered a formality: if neither party demands termination of the employment contract and the employee continues to work, the contract will be considered concluded for an indefinite period (Article 58 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The form for notifying an employee of the termination of a fixed-term employment contract is not established by law, so it can be drawn up, for example, as shown in the sample.
Employer's initiative (Clause 4, Part 1, Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
An employment contract may be terminated early at the initiative of the employer in the cases specified in Article 81 of the Labor Code. You must notify the employee of your decision in writing.
For example, notify each employee personally about the termination of the employment contract due to the liquidation of the organization, against signature, at least two months before dismissal (Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, employees who have entered into an employment contract for a period of up to two months must be notified of the upcoming dismissal at least three calendar days in advance (Art.
292 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), and seasonal workers - no less than seven calendar days (Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Employee initiative (Clause 3, Part 1, Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
An employee has the right to terminate an employment contract with an employer before its expiration on his own initiative (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). To do this, he must submit a resignation letter to the employer (see sample below) in compliance with the deadlines established by law (see table below).
Deadlines for an employee to submit a resignation letter of his own free will
SituationDeadline for filing an applicationGrounds
| Early termination of an employment contract concluded for a period of more than two months | Within 14 calendar days | Part one art. 80 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Early termination of an employment contract concluded for a period of up to two months | In three calendar days | Part one art. 292 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Early termination of an employment contract by an employee engaged in seasonal work | In three calendar days | Part one art. 296 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Early termination of an employment contract with the head of the organization | No later than one month | Article 280 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Termination of an employment contract with an athlete or coach (except for cases where the employment contract was concluded for a period of less than four months) | No later than one month | Part one art. 34812 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| The inability of an employee to continue his work (for example, upon enrollment in an educational institution, retirement and for other reasons), as well as the employer’s violation of the law, the terms of a collective agreement, agreement or employment contract | Within the period specified in the employee’s application | Part three of Art. 80 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
Agreement of the parties (Clause 1, Part 1, Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
According to Article 78 of the Labor Code, an employment contract (including a fixed-term one) can be terminated at any time by agreement of the parties (see diagram below). When terminating a fixed-term employment contract by agreement of the parties, the parties sign a corresponding agreement (see sample below).
| Error | How to do it right |
| Many employers agree to pay their employees who worked for them under a fixed-term employment contract and fell ill within 30 days after dismissal, temporary disability benefits only for 75 days of their illness, referring to Part 4 of Article 6 of Law No. 255-FZ. They fear that the Russian Social Insurance Fund will not accept the amounts paid to these workers as offset. | Such employees must be paid for all days of their illness (Part 2 of Article 5 of Law No. 255-FZ). Part 4 of Article 6 of Law No. 255-FZ refers to employees who work under a fixed-term employment contract concluded for a period of up to six months and become ill during work, and not about all employees under a fixed-term employment contract, and especially not about those who fall ill after dismissal. |
What happens if…
As a result of the inspection of the State Labor Inspectorate, the employer will be obliged to provide the employee with benefits for the days of his illness and pay a fine of up to 50,000 rubles (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
If the employer assigns benefits to the resigned employee, and the Federal Social Insurance Fund of Russia does not accept the paid amounts as offset, the employer will be able to successfully claim them through the court.
The FSS of Russia did not reimburse such expenses before the adoption of Law No. 255-FZ, and not after (Resolution of the FAS of the North-Western District of November 28, 2005 No. A56-13502/05).
Step 3. Issue a dismissal order
Termination of a fixed-term employment contract is formalized by order of the employer (Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employee must be familiarized with the order to terminate the employment contract against signature. It is drawn up in accordance with the unified form No. T-82.
Step 4. Make an entry in the work book
As a rule, upon dismissal, an entry is made in the employee’s work book with reference to the grounds specified in Article 77 of the Labor Code.
It is important to remember that the entry in the labor contract upon termination of a fixed-term employment contract with certain categories of workers may have a reference to other norms of the Labor Code. Thus, the employment contract with a scientific and pedagogical worker is terminated due to the expiration of the period for election by competition under paragraph 4 of part one of Article 336 of the Labor Code (see.
sample). And if the employee is not elected to the position, the employment contract with him should be terminated in accordance with paragraph 3 of part one of Article 83 of the Labor Code.
If it turns out that the employee submitted a false education document during employment, the employment contract with him will be terminated early under paragraph 11 of part one of Article 81 of the Labor Code.
Remember the main thing
Note the experts who took part in the preparation of the material:
Evgenia SIMAKOVA, lawyer, expert at the Personnel Business magazine:
— An employment contract can be terminated either due to the expiration of its validity period or on other grounds provided for by law.
. The procedure for processing documents when terminating an employment relationship with him depends on the grounds for dismissal of an employee.
Alena LACHUGINA, document specialist at the municipal educational institution of additional education for children “Station of Young Technicians” (Biysk):
— Termination of a fixed-term employment contract by agreement of the parties allows the employee and employer to agree on its terms themselves
: for example, about the payment of monetary compensation to the employee and the period for termination of the employment relationship.
Yulia SAFINA, Group lawyer (Moscow):
— The employee must be notified in writing of the termination of the employment contract due to its expiration at least three calendar days in advance.
. If neither party has requested termination of a fixed-term employment contract due to the expiration of its validity period, it is recognized as indefinite.
Galina MEREZHKINA, payroll accountant, Municipal Unitary Enterprise "Krasnoyarsk Housing and Communal Services" (urban settlement "Krasny Yar", Volgograd region):
— After termination of a fixed-term employment contract, the employee has the right to receive temporary disability benefits if he falls ill within 30 days from the date of dismissal
. This right belongs to him regardless of the duration of the employment contract.
Related documents
Document Will Help You
| Articles 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 83, 336 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Establish the grounds on which a fixed-term employment contract may be terminated |
| Article 58 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Find out in what cases a fixed-term employment contract can become indefinite |
| Articles 180, 292, 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Familiarize yourself with the procedure for notifying employees of their dismissal in connection with the liquidation of the organization |
| Articles 80, 280, 292, 296, 34812 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Determine how long in advance the employee is obliged to notify the employer of termination of the employment contract with him on his own initiative |
| Articles 291, 295 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Calculate the amount of annual paid leave that should be provided or compensated to the employee upon his dismissal |
| Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 255-FZ) | Clarify the period of payment of temporary disability benefits to which the employee is entitled to claim after his dismissal |
Source: https://e.kdelo.ru/260886
Preparing a resignation letter
Clause 3, Part 1, Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation reflects all the features of voluntary dismissal. However, information about the application form is not provided here. The form of the document is also absent in other regulatory legal acts. Therefore, the employer has no right to reject the application due to non-compliance with the established form. However, the HR department usually has ready-made samples on the basis of which the employee must prepare his application.
Additionally, the form contains a list of mandatory information:
- Full name and position of the head of the company;
- the reason for termination of work - it is enough to indicate the presence of your own desire;
- reference to the norms of current legislation - Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- last day of work;
- Full name of the person terminating the employment contract;
- date, signature and its decoding.
What to do if they don’t sign
The manager is not always ready to let go of a valuable employee, so problems may arise with signing the resignation letter. If such a situation does arise, you should always remember that in this matter the legislation is always on the side of the employee. The employer has no right to keep him at work longer than required.
In fact, management’s signature on the application is not a prerequisite for dismissal.
If the employer refuses to accept the application, then all the same, the employee, from the next day, after writing it and warning the manager about his intentions, begins the required work, and after two weeks must be free.
If, after 14 days, the employee has not been paid the salary due to him and the work book with all the required entries has not been returned, such an action will be considered a gross violation of the law, and in double the amount.
In such a situation, you can sue the organization, which will definitely be on the side of the employee.
Also, do not be afraid of threats from your superiors that dismissal will be made on the basis of an article for violation. If there were no misconduct on the part of the employee or the statute of limitations has expired, he does not have the right to do so, which is also punishable.
Preparation of an order
In order to formalize the dismissal of an employee under clause 3, part 1, article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to draw up an order on the day the citizen ceases to work in the selected organization. Once the document is signed, the employee is considered dismissed.
Video
There are several forms of order. So, if one employee quits, a T8 document is drawn up. When you need to fire several employees at once, use form T-8a. The legislation does not reflect that it is necessary to use the above format.
It is enough that the document contains mandatory information, the list of which includes the following information:
- information about the organization;
- date of preparation of the order and its registration number;
- information about the contract on the basis of which the person was hired;
- moment of dismissal;
- information about the employee;
- grounds for termination of an employment contract;
- documentary evidence of the employee’s initiative to terminate the agreement at his own request;
- signature of the employee and employer.
Commentary on Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The article under comment provides for general grounds for termination of an employment contract, i.e. grounds that apply to all employees regardless of their category. The norms contained in this article are in some cases of a reference nature. This means that, for example, upon termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties, upon dismissal of an employee at his own request or at the initiative of the employer, Art. Art. 78 - 80 or 71, 81 Labor Code (see Art. 71, 78 - 81 Labor Code and commentary to them).
According to clause 2 of the commented article, fixed-term employment contracts are terminated upon expiration of the term of the employment contract (clause 2 of Article 58, Article 79 of the Labor Code and commentary thereto), except in cases where the employment relationship actually continues and neither party has demanded their termination. Article 79 of the Labor Code (see commentary to it) provides for the procedure for terminating a fixed-term employment contract, and also specifies the circumstances under which a fixed-term employment contract is subject to termination (for example, the completion of a certain job, the expiration of a certain season). An entry in the work book about the dismissal of an employee upon expiration of a fixed-term employment contract must be with reference to clause 2 of the commented article.
If, at the end of the term of a fixed-term employment contract, the employee continues to work and neither party to the contract has demanded its termination, such a contract is transformed into a contract concluded for an indefinite period. The legislator emphasized that the requirement to terminate the employment relationship must come from either the employee or the employer before the end of the fixed-term employment contract. Such an agreement can be terminated only when there are other grounds for this.
When terminating an employment contract in connection with the transfer of an employee, at his request or with his consent, to work for another employer (see Article 72.1 of the Labor Code and commentary to it), clause 5 of the commented article applies. The same paragraph contains another basis for termination of an employment contract - transfer to an elective position. To apply this basis, an act of election of this employee to the appropriate elective position is required. Since the commented article contains two independent grounds for dismissal, the employee’s work book must contain a reference to paragraph 5 of this article, but with the obligatory clarification of the wording of the reason for dismissal.
Paragraph 6 of the commented article provides for three grounds for refusal to work in connection with a change in the owner of the organization’s (enterprise’s) property, a change in the jurisdiction (subordination) of the organization (enterprise), or reorganization of the organization (enterprise) (see Article 75 of the Labor Code and the commentary thereto). When dismissing an employee on this basis, the entry in the work book should not simply refer to paragraph 6 of this article, but should clarify the reason for such refusal (change of owner of the organization’s (enterprise’s) property, change of jurisdiction, reorganization).
If an employee refuses to continue working due to a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties (see Article 74 of the Labor Code and the commentary to it), dismissal is possible only if the employee was offered the appropriate work, and he refused it, or if such work did not have. However, if there was another job, but was not offered to the employee, then such dismissal may be declared illegal by the court.
Resolving cases of reinstatement of persons whose employment contract was terminated under clause 7 of Art. 77 of the Labor Code (refusal to continue work in connection with a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties), or on the recognition as illegal of a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties when the employee continues to work without changing the labor function (Article 74 of the Labor Code), it must be taken into account that, based on Art. . 56 of the Code of Civil Procedure, the employer is obliged, in particular, to provide evidence confirming that the change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties was a consequence of changes in the organization of labor or in the organization of production, for example, changes in equipment and production technology, improvement of jobs based on their certification, structural reorganization of production , and did not worsen the employee’s position in comparison with the terms of the collective agreement or agreement. In the absence of such evidence, termination of the employment contract under clause 7 of Art. 77 of the Labor Code or a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties cannot be recognized as legal.
Paragraph 8 of the commented article has been supplemented with a new basis for termination of an employment contract - the absence of relevant work in the organization if the employee, in accordance with medical indications, needs to be transferred. At the same time from Art. 81 Labor Code (see commentary to it) subsection excluded. “a” clause 3, which provided for termination of the employment contract at the initiative of the employer in cases of inconsistency of the employee with the position held or the work performed due to health reasons. At the same time, the issue of payment of severance pay has been resolved.
If the employee refuses to be transferred due to the employer's relocation to another area (see Part 1 of Article 72.1 of the Labor Code and commentary thereto), the employee is paid severance pay in the amount of two weeks' average earnings (see Article 178 of the Labor Code and commentary to it). her).
Paragraphs 10 and 11 of the commented article are of a reference nature. Therefore, when dismissing an employee, references to these norms are never made either in the order or in the work book. Termination of the employment contract occurs according to Art. Art. 83 and 84 Labor Code (see commentary to them).
In accordance with Part 2 of the commented article, an employment contract may be terminated on other grounds provided for by the Labor Code and other federal laws. Additional grounds for terminating the employment contract of certain categories of employees are given in Section. XII TC. For specifics of labor regulation for certain categories of workers, see Art. Art. 278, 288, 307, 312, 336, 341 and 347 Labor Code and commentary. to them. In addition, there are additional grounds for dismissal of federal civil servants, judges and prosecutors provided for by federal laws.
Entering data into documentation
Initially, the information is recorded in a personal card. It is drawn up in form T-2. The entry is certified by the signature of the personnel officer. The completed document is provided to the employee for review. The person confirms the information by signing.
Video
Additionally, the accounting department draws up a calculation note. It is drawn up according to the T-61 form. The document reflects information about payments due to the employee. Then the work book is filled out. It reflects the fact that a person works in a certain organization and records information about dismissal.
You need to write:
- Company name;
- the moment the employee was hired and his position;
- information about the contract and other grounds for employment;
- date of dismissal and reasons for termination;
- seal impression and signature of the HR employee;
- citizen's signature.
When filling out documents, use correct wording.
Entry in the work book
According to established standards, a work book is issued on the day the dismissal order comes into force.
It contains the following information:
- The date and number of the entry entered.
- The article under which the contract was terminated.
- The date the order was issued and its number.
In some cases, a former employee cannot come to pick up his work book on the day the document is signed. You can pick it up on another day, in addition, the employer can send the document by registered mail. When issuing a work book, a corresponding entry must be made in the personnel department. This eliminates the possibility of problems arising in the event that a former employee makes a claim about its loss or non-issuance.
Payment to the employee
Article 77, paragraph 3, prescribes a full settlement on the day the person completes his activities in the organization. At this moment, a work book is also provided. If the relevant procedure is violated, a person may consider his interests violated and demand compensation for all types of damage. For missing the deadline for providing funds, interest is charged. Additionally, there are penalties for late payment. They can be charged against the company itself and its management.
Video
An employee may qualify for the following payments:
- accrued but not provided wages;
- amounts due under a certificate of incapacity for work;
- compensation for unused vacation;
- funds provided for by law and internal regulations of the company.
Funds are provided on the last day of work. The only exception is payments for sick leave. By law, funds may be accrued not on the day of dismissal, but later. In such a situation, the amount is provided on the day of payment of wages or received after dismissal. The rule applies if the period between the provision of sick leave and the day of payment of wages exceeds 10 days.
Please note: By law, the employer is required to pay for sick leave that was provided by the employee within a month from the date of termination of official employment. The rule applies if a person has not managed to get a job in another organization.
If a person does not show up for work on the day of payment, payments are made the next day after the corresponding request is made. In this case, the work book can be sent by mail.
Video
Article 83. Termination of an employment contract due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties
The employment contract is subject to termination due to the following circumstances beyond the control of the parties:
1) conscription of an employee for military service or sending him to an alternative civilian service that replaces it;
2) reinstatement of an employee who previously performed this work, by decision of the state labor inspectorate or court;
3) not being elected to office;
4) sentencing of an employee to a punishment that precludes the continuation of previous work, in accordance with a court verdict that has entered into legal force;
5) recognition of the employee as completely incapable of working in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
6) death of an employee or employer - an individual, as well as recognition by a court of an employee or employer - an individual as deceased or missing;
7) the occurrence of emergency circumstances that impede the continuation of labor relations (military action, catastrophe, natural disaster, major accident, epidemic and other emergency circumstances), if this circumstance is recognized by a decision of the Government of the Russian Federation or a government body of the relevant subject of the Russian Federation;
 disqualification or other administrative punishment that precludes the employee from fulfilling his duties under the employment contract;
disqualification or other administrative punishment that precludes the employee from fulfilling his duties under the employment contract;
(Clause 8 introduced by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
9) expiration, suspension of validity for a period of more than two months or deprivation of an employee of a special right (license, right to drive a vehicle, right to carry a weapon, other special right) in accordance with federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, if this entails the impossibility of the employee fulfilling his duties under the employment contract;
(Clause 9 introduced by Federal Law dated June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ)
10) termination of access to state secrets if the work performed requires such access;
(Clause 10 introduced by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
11) reversal of a court decision or cancellation (declare illegal) of the decision of the state labor inspectorate to reinstate the employee at work;
(Clause 11 introduced by Federal Law dated June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ)
12) bringing the total number of employees who are foreign citizens or stateless persons in accordance with the permissible share of such employees established by the Government of the Russian Federation for employers carrying out certain types of economic activities on the territory of the Russian Federation;
(Clause 12 introduced by Federal Law dated December 30, 2006 N 271-FZ)
Is it possible to avoid processing
As a general rule, a citizen is required to work for 2 weeks. However, in some cases it is permissible to shorten the period.
This is possible in the following situations:
- the employee was on a probationary period - activities can be terminated within three days;
- the person was called up for military service;
- the employer neglected the law, which resulted in a violation of the employee’s interests - the person decides how many days in advance to notify the employer;
- the employee moves to another area with a spouse for whom a long-term order has been prepared;
- both parties to the legal relationship are interested in reducing the working period;
- the employee is sick and has sick leave - dismissal without work is permissible;
- the person entered the full-time department of a university and cannot continue working in the organization;
- the person has become disabled or has disabled children in their care who need care. It will be necessary to confirm that the condition has worsened and he cannot work as before.
Article 81. Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer
Guides to personnel issues and labor disputes. Questions of application of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
An employment contract can be terminated by the employer in the following cases:
1) liquidation of an organization or termination of activities by an individual entrepreneur;
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
(see text in the previous edition)
2) reduction in the number or staff of employees of an organization or individual entrepreneur;
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
3) the employee’s inconsistency with the position held or the work performed due to insufficient qualifications confirmed by certification results;
4) change of owner of the organization’s property (in relation to the head of the organization, his deputies and the chief accountant);
5) repeated failure by an employee to perform labor duties without good reason, if he has a disciplinary sanction;
6) a single gross violation by an employee of labor duties:
a) absenteeism, that is, absence from the workplace without good reason throughout the entire working day (shift), regardless of its duration, as well as in the case of absence from the workplace without good reason for more than four hours in a row during the working day ( shifts);
b) the appearance of an employee at work (at his workplace or on the territory of an organization - employer or facility where, on behalf of the employer, the employee must perform a labor function) in a state of alcohol, narcotic or other toxic intoxication;
(clause “b” as amended by Federal Law dated June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ)
(see text in the previous edition)
c) disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, commercial, official and other) that became known to the employee in connection with the performance of his job duties, including disclosure of personal data of another employee;
d) committing at the place of work theft (including small) of someone else's property, embezzlement, intentional destruction or damage, established by a court verdict that has entered into legal force or a decision of a judge, body, official authorized to consider cases of administrative offenses;
e) a violation by an employee of labor safety requirements established by the labor safety commission or the labor safety commissioner, if this violation entailed serious consequences (industrial accident, breakdown, catastrophe) or knowingly created a real threat of such consequences;
7) commission of guilty actions by an employee directly servicing monetary or commodity assets, if these actions give rise to a loss of confidence in him by the employer;
7.1) the employee’s failure to take measures to prevent or resolve a conflict of interest to which he is a party, failure to provide or provide incomplete or unreliable information about his income, expenses, property and property-related liabilities, or failure to provide or provide knowingly incomplete or unreliable information about income, expenses, on the property and obligations of a property nature of their spouse and minor children, opening (availability) of accounts (deposits), storing cash and valuables in foreign banks located outside the territory of the Russian Federation, ownership and (or) use of foreign financial instruments an employee, his spouse and minor children in cases provided for by this Code, other federal laws, regulatory legal acts of the President of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Russian Federation, if these actions give rise to a loss of confidence in the employee on the part of the employer;
(clause 7.1 introduced by Federal Law dated December 3, 2012 N 231-FZ, as amended by Federal Laws dated December 29, 2012 N 280-FZ, dated May 7, 2013 N 102-FZ)
 the commission by an employee performing educational functions of an immoral offense incompatible with the continuation of this work;
the commission by an employee performing educational functions of an immoral offense incompatible with the continuation of this work;
9) making an unjustified decision by the head of the organization (branch, representative office), his deputies and the chief accountant, which entailed a violation of the safety of property, its unlawful use or other damage to the property of the organization;
10) a single gross violation by the head of the organization (branch, representative office), his deputies of their labor duties;
11) the employee submits false documents to the employer when concluding an employment contract;
12) has become invalid. — Federal Law of June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ;
13) provided for in the employment contract with the head of the organization, members of the collegial executive body of the organization;
14) in other cases established by this Code and other federal laws.
The procedure for certification (clause 3 of part one of this article) is established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, local regulations adopted taking into account the opinion of the representative body of workers.
(Part two as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
Dismissal on the grounds provided for in paragraph 2 or 3 of part one of this article is permitted if it is impossible to transfer the employee with his written consent to another job available to the employer (both a vacant position or work corresponding to the employee’s qualifications, and a vacant lower position or lower-paid job) which the employee can perform taking into account his state of health. In this case, the employer is obliged to offer the employee all vacancies available in the given area that meet the specified requirements. The employer is obliged to offer vacancies in other localities if this is provided for by the collective agreement, agreements, or employment contract.
In the event of termination of the activities of a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of an organization located in another locality, termination of employment contracts with employees of this unit is carried out according to the rules provided for cases of liquidation of the organization.
Dismissal of an employee on the grounds provided for in paragraph 7 or 8 of part one of this article, in cases where guilty actions giving grounds for loss of confidence, or, accordingly, an immoral offense were committed by the employee outside the place of work or at the place of work, but not in connection with the performance of his labor duties, is not allowed later than one year from the date of discovery of the misconduct by the employer.
(Part five was introduced by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
It is not allowed to dismiss an employee at the initiative of the employer (except in the case of liquidation of an organization or termination of activities by an individual entrepreneur) during the period of his temporary incapacity for work and while on vacation.
(Part six introduced by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
If a pensioner resigns
Having reached a certain age, a person can count on financial support from the budget. In this case, termination of work is permissible. The dismissal procedure is no different from the classic scheme. All you have to do is write a statement and submit it to your employer.
Video
However, exceptions are provided for working off. A person reports that he is stopping work due to retirement; he has the right to leave at any convenient time, even if the work has not been completed. However, if the person subsequently re-enters the workforce, he or she can no longer use this benefit.