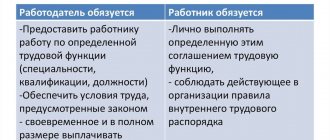
The employment contract is concluded in writing, drawn up in two copies, each of which is signed by the parties. One copy of the employment contract is given to the employee, the other is kept by the employer. The employee’s receipt of a copy of the employment contract must be confirmed by the employee’s signature on the copy of the employment contract kept by the employer.
(as amended by the Federal Law
dated June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ)
ConsultantPlus: note.
On identifying the constitutional and legal meaning of Part 2 of Art. 67 see Resolution
Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated 04.02.2020 N 7-P.
An employment contract that is not formalized in writing is considered concluded if the employee began work with the knowledge or on behalf of the employer or his authorized representative
. When an employee is actually admitted to work, the employer is obliged to draw up an employment contract with him in writing no later than three working days from the date of the employee’s actual admission to work, and if relations related to the use of personal labor arose on the basis of a civil law contract, but were subsequently recognized as labor relations - no later than three working days from the date of recognition of these relations as labor relations, unless otherwise established by the court.
(as amended by Federal Laws dated June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ
, dated December 28, 2013
N 421-FZ
)
When concluding employment contracts with certain categories of workers, labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms may provide for the need to agree on the possibility of concluding employment contracts or their terms with the relevant persons or bodies that are not employers under these contracts, or to draw up employment contracts in more copies.
(as amended by the Federal Law
dated June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ)
Is an employment contract canceled if an employee is unable to start work due to illness?
An employment contract concluded in the written form established by law can be canceled if the employee does not begin to perform his official duties on the start date of work specified in the contract. A canceled contract is equivalent to an unconcluded one.
The possibility of canceling employment contracts relieves both employees and employers from unnecessary paperwork. An employee, without any negative consequences, can refuse a planned return to work, and the employer has the opportunity to quickly change the personnel situation by recognizing the contract with such an employee as not concluded.
According to labor law, the employer is not obliged to find out the reason for the employee’s absence from the workplace on the day when, according to the employment contract, he is supposed to start work. The employee’s illness is not a circumstance preventing the cancellation of the contract.
However, the employer remains obligated to pay disability benefits to the employee whose contract was canceled if he provides sick leave. The opening date of the sick leave is very important - benefits will be paid only if the employee falls ill before the day the employment contract is cancelled.
Despite the fact that illness, also confirmed by a sick leave certificate, is a valid reason for absence from work, the employer by law has the right to cancel the contract with an employee who does not show up for work on the first day. Each employer decides independently whether to restore employment relations with such an employee after the cancellation of the employment contract. If it is decided to rehire a sick employee, his relationship with the employer is formalized again in the standard form of an employment contract.
Labor collective and employment contract
The employer enters into an agreement with the employee and prepares related documents.
The written form is drawn up in two copies; it is advisable to have signatures of the parties on each sheet and all attachments. We recommend you study! Follow the link:
How to take sick leave to care for a sick relative
In many institutions, the employment contract or related documents will have several signatures of the heads of important structural divisions of the enterprise. This does not mean that they will all be the employee's supervisors.
Such institutions include the following:
- government;
- military;
- medical;
- performing special work, etc.
The list is not buried, as many organizations fit the description.
Each employee has his own manager and work team. An employment contract will not be used in the work process. A job description will appear, but the labor process that characterizes a specific enterprise will always prevail in all areas.
Any deviation from the established labor process or failure to comply with the manager’s order, failure to take into account the opinion of another manager, ignoring the director’s plans, or offense inflicted on a client, partner, or tax inspector will cause interest in the job description and employment contract.
Essentially, the form of employment contract is the foundation of a relationship that works when the normal course of the work process experiences unexpected fluctuations, achievements or problems. Any deviation from the norm is an employment contract, job description or current legislation.
Refusal of official employment
Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the employer’s obligation to conclude a written agreement with the employee. contract within 3 days from the date of commencement of work duties. For non-compliance with this norm, a fine is provided (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). For legal entities persons, the fine is at least 50 thousand rubles. Two copies of the work are printed. contracts, one of which is transferred to the employee (Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The absence of a signed employment contract does not mean that the employee is deprived of all the rights granted to him by the Labor Code. The contract is considered concluded by default if the employee began to perform his work duties at the direction of the employer (the head of the company or his representative). But in this case, the right to officially be considered an employee of a particular organization must be proven. If an employee begins to work without signing a contract, and the employer refuses to conclude it after three days, then the first possible action should be an attempt to convince management to formalize the employment relationship. You can notify the director in writing about the obligation to formalize the work. agreement upon actual admission to work, referring to Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and demand familiarization with the order for employment. If the employer refuses to enter into an agreement even under pressure, you need to be ready to confirm the fact of working in the organization. To do this, you need to collect evidence of the existence of an employment relationship and the performance of assigned job functions. It is important to confirm the fact that the employee was allowed to perform duties by the employer himself, or his representative who has the right to do so. Otherwise, the employer may claim that the employee decided to work on his own and no one entrusted him with the work. So, having evidence, an employee can protect his rights at work. inspection or in court. If it is proven that he was actually allowed to perform his duties, the organization will pay a fine and compulsorily formalize the work. relationship. At the same time, even in the absence of an employment contract in which the amount of the employee’s salary should be specified, it is the employer who will have to prove in court that he has no debts to the employee. What can serve as proof of admission to work? This:
- any documents dated and related to the work (orders, instructions, acts, receipts, copies of reports, etc.);
- a certificate of the amount of salary and insurance contributions (the employer must issue such a certificate upon application);
- the fact of receiving a salary, sick leave, vacation, etc.;
- audio and video recordings confirming the fact of work;
- testimony of witnesses (colleagues, clients);
- availability of uniform, building pass, access to corporate mail, etc.
So, citizens can protect their labor rights and prove their right to official employment by all legal means - this opportunity is given by the Constitution and Article 352 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If it is not possible to resolve the conflict due to refusal of employment peacefully, then it is resolved in court.
Commentary on Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
One of the guarantees of the legal status of an employee is the requirement enshrined in the commented article to conclude an employment contract in writing. Until September 25, 1992, the parties to the employment contract themselves determined the form of the employment contract (oral or written).
The written employment contract is drawn up in two copies, and both are signed by both parties. One copy of the agreement is kept by the employer, the other is given to the employee. A written form of an employment contract is mandatory for both a contract concluded for an indefinite period and a fixed-term employment contract.
Clause 12 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 N 2 states that an employment contract is concluded in writing, drawn up in two copies (unless the law or other regulatory legal act provides for the drawing up of employment contracts in a larger number of copies), each of which signed by the parties (Parts 1, 3 of the commentary article). Hiring is formalized by order (instruction) of the employer, the contents of which must comply with the terms of the concluded employment contract (Part 1 of Article 68 of the Labor Code). The employer's order (instruction) on hiring must be announced to the employee against signature within three days from the date of signing the employment contract (Part 2 of Article 68 of the Labor Code).
Current legislation does not provide for a general standard form of a written employment contract, so it is determined by the parties themselves. However, when concluding an employment contract, it is necessary to strictly comply with the provisions provided for in Art. 57 Labor Code (see commentary to it).
It should be noted that Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated March 2, 2005 N 49 approved a Model employment contract with the head of a federal state unitary enterprise <1>.
——————————— <1> BNA. 2005. N 23.
At the same time, in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated March 16, 2000 N 234 (as amended on June 20, 2011) <1> heads of federal executive authorities, when concluding an employment contract with the head of a federal state unitary enterprise, may provide in the employment contract the following grounds for its termination in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 278 TK:
——————————— <1> NW RF. 2000. N 13. Art. 1373; 2001. N 31. Art. 3281; 2002. N 41. Art. 3986; 2006. N 13. Art. 1408; N 47. Art. 4897; 2008. N 11 (part 1). Art. 1030; 2010. N 2. Art. 234; 2011. N 28. Art. 4203.
a) failure by a unitary enterprise to fulfill the indicators of economic efficiency of its activities approved in the established manner;
b) failure by the head of a unitary enterprise to comply with decisions of the Government of the Russian Federation and federal executive authorities adopted in relation to the unitary enterprise in accordance with their competence;
c) making transactions with property that is under the economic control of a unitary enterprise, in violation of the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation and its special legal capacity determined by the charter of the unitary enterprise;
d) the presence at a unitary enterprise, through the fault of its director, of more than three months of wage arrears;
e) failure to ensure the use of the property of a unitary enterprise for its intended purpose in accordance with the types of its activities established by the charter of the enterprise, as well as failure to use budgetary and extra-budgetary funds allocated to it for its intended purpose for more than three months;
f) violation by the head of a unitary enterprise of the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as the charter of the unitary enterprise regarding the communication of information about the presence of interest in making transactions, including among affiliated persons;
g) violation by the head of a unitary enterprise of the ban on carrying out certain types of activities established by the legislation of the Russian Federation and the employment contract;
h) failure, through the fault of the head of a unitary enterprise, to fulfill the duties established by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation or the charter of the unitary enterprise related to conducting an audit of the unitary enterprise.
In order to provide methodological assistance to federal budgetary institutions in concluding an employment contract and an additional agreement to the employment contract with an employee on changing the terms of remuneration in connection with the transition to a new remuneration system, Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated August 14, 2008 N 424n approved Recommendations for concluding an employment contract with employee of a federal budgetary institution and its approximate form <1>.
——————————— <1> Bulletin of labor and social legislation of the Russian Federation. 2008. N 10.
In accordance with Part 2 of the commented article, an employment contract that is not properly drawn up is considered concluded if the employee actually began work with the knowledge or on behalf of the employer or his representative. This is an important legal guarantee when hiring an employee. When an employee is actually admitted to work, the employer is obliged to draw up an employment contract with the employee in writing no later than three days from the date of the employee’s actual admission to work.
The above Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation emphasizes that if the employment contract was not properly drawn up, but the employee began work with the knowledge or on behalf of the employer or his authorized representative, then the employment contract is considered concluded and the employer or his authorized representative is obliged no later than three days from the date of actual admission to work, draw up an employment contract in writing (Part 2 of the commentary article). It should be borne in mind that the representative of the employer in this case is a person who, in accordance with the law, other regulatory legal acts, constituent documents of a legal entity (organization) or local regulations, or by virtue of an employment contract concluded with this person, is empowered to hiring workers, since it is in this case that when an employee is actually admitted to work with the knowledge or on behalf of such a person, an employment relationship arises (Article 16 of the Labor Code) and the employer may be obligated to formalize an employment contract with this employee in a proper manner.
The conclusion of employment contracts or their terms with certain categories of employees in cases provided for by laws and other regulatory legal acts may be made dependent on their agreement with the relevant persons or bodies. Coordination is also necessary when drawing up employment contracts in a large number of copies.
Responsibility for compliance with the procedure for concluding an employment contract rests with the employer.
Opportunity to work without an employment contract for an individual entrepreneur - a family member
This possibility is not permissible from a legal point of view. Members of the entrepreneur's family must be officially registered for work - by labor. contracts. Family ties do not play a role in this case. Labor relations imply the subordination of employees to work rules, certain conditions, and the performance by them of a certain list of duties for a fee. If family members of an individual entrepreneur are subject to a certain regime, perform work assigned by the entrepreneur and receive payment for it, then they have an employment relationship with him. Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, part 1, establishes the mandatory written form of labor. agreement. But at the same time, unregistered employment relationships are also valid if the employee, with the knowledge of the employer, begins to carry out his instructions and proves this in court. Having admitted an employee to work, the employer is obliged to conclude an agreement with him within three days (Part 2, Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, the law does not allow exceptions for relatives. Regardless of whether the employee is a family member, the individual entrepreneur is obliged to conclude an employment contract with him after allowing him to perform his duties. Failure to comply with this requirement of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation entails liability:
- fine from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles for legal entities. persons;
- fine from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles. for persons conducting business activities without legal education. persons (Clause 3, Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).