Reduced working hours are established: for workers under the age of sixteen - no more than 24 hours per week; for workers aged sixteen to eighteen years - no more than 35 hours per week; for employees who are disabled people of group 1 or 2 - no more than 35 hours per week; for workers whose working conditions at their workplaces, based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, are classified as hazardous working conditions of the 3rd or 4th degree or hazardous working conditions - no more than 36 hours per week.
The length of working time for a particular employee is established by an employment contract on the basis of an industry (inter-industry) agreement and a collective agreement, taking into account the results of a special assessment of working conditions.
On the basis of an industry (inter-industry) agreement and a collective agreement, as well as the written consent of the employee, formalized by concluding an additional agreement to the employment contract, the working hours specified in paragraph five of part one of this article may be increased, but not more than 40 hours per week with payment to the employee of a separately established monetary compensation in the manner, amount and on the terms established by industry (inter-industry) agreements and collective agreements.
The length of working time of students of educational organizations carrying out educational activities, under the age of eighteen, working during the academic year in their free time from receiving education, cannot exceed half of the norms established by part one of this article for persons of the corresponding age.
This Code and other federal laws may establish reduced working hours for other categories of workers (teaching, medical and other workers).
Reduced time by law
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not define in detail what a shortened working day is. Article 92 speaks of a reduced duration in the context of the time allocated for work, introducing restrictions per week depending on the categories of workers.
The duration is not related to the will or agreement of the employer and hired personnel and is determined by the maximum limitation of hours per week for the following persons:
- those under 16 years old “according to a passport” – 24, when combining work with study – 12 (half);
- age category from 16 to 18 years and disabled people of groups 1 and 2 - 35, when combined with study - 17.5;
- workers in dangerous or harmful conditions of the 3rd and 4th degrees - 36;
- medical personnel – 39;
- teaching staff – 36;
- women working in rural areas and northern regions – 36.
Limits can be established by special laws regulating activities and intersectoral agreements that are binding on business entities in cases where the duration is reduced compared to the internal local acts of the organization.
The specific duration is determined by the employer by labor regulations. Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes a reduced working time regime in relation to daily work shifts exclusively for the above categories.
The reduction of the working day is provided for to the maximum permissible hours of work for persons:
- For students of secondary general education and vocational educational institutions working temporarily during the holidays:
- 14-15 years old – 4;
- 15-16 years old – 5;
- 16-18 years old – 7.
- For students of the above institutions when combining study and work during the semester:
- 14-16 years old – 2.5;
- 16-18 years old – 4.
- For disabled people who have a reduced working day by decision of a medical and social examination, the amount of permissible time interval of work during the day is prescribed in rehabilitation measures that have the force of law for the employer.
- For those working in harmful and dangerous conditions, where a reduced working time regime is established:
- with a 36-hour week – 8 (standard);
- at 30 hours – 6.
- External part-time work: features of work under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Restrictions regarding the reduction of working days and reduction of working hours during a shift are provided for in Article 284 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for external part-time workers. If at the main place of work a part-time worker is exempt from performing work duties on a specific day, then the part-time worker can work full time. On days of employment, the employer whose citizen is registered as a part-time worker is obliged to reduce the working day to a maximum of 4 hours.
How is work paid during a shortened working week?
Many citizens have no idea how earnings are calculated during a shortened working week. However, in reality there is nothing complicated in such a calculation.
Remuneration for work done by a citizen during reduced working hours is accrued in the same amount as employees are entitled to during a normal work schedule.
However, this is not always the case.
Employees whose remuneration follows different rules:
- minors (their work is paid in proportion to the time worked or depending on output);
- students on part-time or evening courses (during their release from work, they are paid half the average salary at their main place of work, but not less than the minimum wage);
- disabled people of groups I and II (their work will be paid in proportion to the time worked if they work less than the norm established for this category).
Let's consider the procedure for paying teenagers. The salary and bonuses of such employees will depend on the form of remuneration used in the organization, but taking into account the reduced time standard. Moreover, the maximum amount of remuneration is unlimited.
For example, consider a situation where a time-based wage system with normal working hours has been introduced at the place of employment of a minor. What remuneration is due to a 15-year-old employee if his weekly work is 24 hours? Accountants use the following formula: tariff rate per hour of labor x time worked (24 hours). The result obtained will be the teenager’s salary. However, income tax (13%) must still be deducted from the “net” remuneration.
Short-time working hours, with some exceptions, are paid in the same way as normal working hours.
The main feature of this length of work is that workers are not deprived of social guarantees and benefits provided to employees who have a regular work schedule.
List of basic social guarantees according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- payment of sick leave;
- payment for the next vacation;
- compulsory social insurance (contributions to the Pension Fund, etc.);
- payment for travel allowances (Articles 167, 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- reimbursement of transportation expenses for employees when working on a traveling basis (Article 168.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- Art. 170, 172 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contain a number of guarantees provided by the employer to the employee when he performs state or public duties, for example, donation, participation in court proceedings as a juror or witness.
Employees performing their duties on a short-time basis are entitled not only to general social guarantees and benefits, but also to others designed specifically for them.
Social guarantees for teachers:
- periodic receipt of additional professional pedagogical education;
- extended annual basic leave and once every 10 years leave lasting up to 12 months;
- early assignment of an old-age pension;
- providing those in need with social or specialized (rented) housing;
- other measures legally established in the Russian Federation and its regions.
Social guarantees for medical workers:
- the possibility of retraining at the expense of the employer if it is impossible to perform one’s job due to health conditions or due to the downsizing (liquidation) of the organization;
- periodic certification for the qualification category and taking into account its results when setting salaries;
- creation of non-profit organizations with a professional orientation;
- professional liability insurance;
- additional guarantees established in the Russian Federation and regions.
Minors enjoy the following benefits:
- do not work at night;
- they are not entrusted with more than what is stated in the employment contract;
- do not work on a rotational basis and do not go on business trips;
- do not work on holidays and weekends (even if other workers are involved).
Employees who are under 18 years of age enjoy privileges during their holidays. For example, they have access to vacation equal to 31 calendar days. At the same time, they can independently choose when it is best for them to rest.
Leave is granted to a minor even if he has not worked for the employer for even six months.
If we talk about those who have to work in dangerous or even harmful conditions, they are entitled to additional leave every year.
This applies to citizens working:
- in underground and open-pit mining in open pits and quarries;
- in areas of radioactive contamination;
- in other jobs associated with adverse effects on human health from harmful physical, chemical, biological and other factors.
For disabled people of groups I and II, not only social guarantees and benefits are provided (30-day leave, monthly cash payments, pensions, etc.), but also tax benefits (tax deduction for personal income tax, exemption from paying property tax for individuals, etc. ).
Part-time work at will
When applying for employment or in the process of performing official duties, by mutual agreement of the parties, on the basis of Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee is established with a part-time employment regime, which presupposes:
- part-time shift during the working day;
- shortened work week;
- combination of short working hours and part-time work.
The part-time employment regime can be applied on an indefinite basis or with the establishment of a specific period with the possibility of further review and extension. In addition to mutual agreement, there are situations when the employer is obliged to establish a part-time regime if the employee wishes, expressed by submitting an appropriate application.
Convenient working hours for the applicant are established on the basis of a written expressed desire:
- a pregnant woman for the entire period of pregnancy, if the fact is confirmed by an antenatal clinic, regardless of the timing;
- one of the parents or a substitute person, guardian, trustee in the presence of a child under 14 years of age or a disabled person under 18 years of age;
- caring for a sick relative, subject to the need for care, confirmed by the appropriate conclusion of a medical institution.
Part-time work does not contain restrictions regarding work experience for a given period, which is considered similar to full-time work. Wages are calculated in proportion to the time spent on the labor process. The number of days of annual leave is not limited, but vacation pay is automatically reduced in size due to the inclusion of reduced wages during the year.
Taking into account the specifics of the enterprise’s activities, the employer can initiate the use of a reduced work time regime. Hired personnel must be notified of the changes being made 2 months before the innovations. With expressed consent, changes in essential conditions are considered normal and do not require compensation payments.
Employees entitled to work on reduced hours
The duration of shortened working hours for different categories of workers was established by the Government of the Russian Federation, taking into account the opinion of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations. A reduced working week compared to the normal length is provided as a protective measure for workers under the age of majority, workers working in dangerous and harmful conditions, and having health limitations.
Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges the employer to provide work on reduced working hours to the following categories of workers:
- persons under 16 years of age are entitled to a working week of no more than 24 hours;
- persons from 16 to 18 years old - they are guaranteed a working week of 35 hours;
- disabled people of groups 1 and 2 - they are also guaranteed a 35-hour work week;
- workers whose work is carried out in places with hazard class 3 or 4 - they are entitled to a working week of no more than 36 hours. The hazard class indicator of a workplace is determined based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, the procedure and purpose of which are specified in Art. 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ.
In addition, federal regulations may also establish such an obligation.
Pre-holiday days
- Remuneration for work on holidays and weekends
A reduction of the working day by 1 hour is provided for in Article 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation during the work shift preceding a holiday. If the organization has established a 6-day work week, then the shortened day according to the Labor Code on the eve of the holiday cannot be more than five hours.
If it is impossible to reduce the working day due to the continuity of the production process and when performing a certain type of work, the time worked is included in overtime with subsequent compensation based on the employee’s choice:
- providing additional rest time (time off);
- remuneration according to the standards provided for overtime work.
Payment in an increased amount is allowed if the norm is approved in internal documents. Holidays before which the standard duration of work is shortened are determined by Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
A short working day for categories of citizens not employed in continuous production is paid in the same way as full-time employment. With a time-based form of payment, wage adjustments are not made to absolutely all employees involved on the pre-holiday day.
Minor workers and students
The minimum age for employment established by law is 16 years, with the consent of parents or adoptive parents - 14 years. At the same time, the law does not prohibit persons studying in educational institutions from working in light work during their free time from study.
For employees under the age of 18 who are receiving general or secondary vocational education, the employer is obliged to establish a working week, the duration of which cannot exceed half of the working week established by this article for employees of this age category.
The length of a work shift/day cannot exceed:
- for workers under 15 years of age - five hours;
- for workers aged 16 to 18 years - 7 hours;
- for students in general education institutions and persons combining study and work aged 14 to 16 years - 2.5 hours;
- for students in general education institutions and persons combining study and work aged 16-18 years - 4 hours.
During the academic year, workers studying in evening general education institutions must have either a working week shortened by one day or a work shift (working day) shortened by this number of hours.
Procedure for registering a shortened working day
The regime of a specific person, different from the general regime of the company, requires individual registration. How to formalize a part-time work week or a shortened working day depends on the legislative establishment of restrictions or an agreement reached by the parties.
If the initiator of the regime is the legislator, then information about limited employment must be written down in a separate paragraph upon admission with reference to the regulatory legal act.
If the initiative belongs to the employee, then an additional agreement is drawn up based on the application.
The final stage is the publication of an order for the enterprise reflecting:
- grounds for part-time or reduced working hours;
- work schedule indicating the beginning and end of the work shift and technical and lunch breaks;
- establishing days off;
- period of limited employment;
- links to the document and copies of attachments (passports of minors, certificates of disabled people, an act of a specialized commission confirming the degree of harmfulness of conditions, an employee’s statement, etc.).
If the shortened day, according to the Labor Code, is a pre-holiday day, then no additional documents need to be completed.
Women
For women working in rural areas, the Decree of the Supreme Council of the RSFSR dated November 1, 1990 “On urgent measures to improve the situation of women, families, maternal and child health in rural areas” established a working week of 36 hours.
A similar length of the working week is established for women working in the Far North and equivalent areas (Article 320 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This condition must be specified in the employment contract.
Salary
Wages are calculated depending on the limiting party in the general case. If the basis for reducing the working day or week contains a federal law or other regulatory act, then the time limit is considered the norm for an employee of a particular category, therefore, he must be paid according to the established standard for the fully worked period. However, there are nuances and exceptions to the rules on the issue of how a shortened day of work is paid.
Minors
An exception to the standard rule regarding remuneration for working and studying minors is imposed by Article 271 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Wages are calculated in proportion to the time worked, despite the fact that a shortened working day and a shortened working week are established by the Labor Code (Article 92), and not by the desire of the minor or management.
According to the legislator, a decrease in the level of wages reduces guarantees for young specialists, but attracts the attention of a promising employer to the use of minors, since the absence of the need for additional payment makes them more attractive for joining the labor process. If you wish to finance from your own sources, there are no legal restrictions on additional payments to the standard regime.
Working disabled people
The right to a shortened work week is provided for working disabled people of groups 1 and 2. If a medical certificate stipulates part-time work, then the case is mandatory for the employer when a reduced working day is required by law.
The work schedule established by a medical institution must be paid in the same way as the time of the full labor process in accordance with Article 23 of Law No. 181-FZ, which regulates issues of social protection of people with disabilities.
On its own initiative, the employer can make additional payments before working for a full period under any employment regime for a disabled person of groups 1 and 2, however, a prerequisite is payment for a 35-hour week before the standard 40-hour regime.
Commentary on Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. According to Art. 91 of the Labor Code, the normal working hours in organizations cannot exceed 40 hours per week. The Code assumes that normal working hours may be less than 40 hours. Art. is dedicated to this. 92 of the Labor Code, regulating issues of reduced working hours.
Shortened working hours are characterized by the following main features:
1) reduced working hours are the full norm for certain categories of workers;
2) factors determining the need to introduce shorter working hours are working conditions, the special nature of work, physiological or age-related characteristics of the workers themselves;
3) reduced working hours are introduced for the purpose of increased protection and labor safety of these workers;
4) the wages of employees for whom reduced working hours are established are not reduced in proportion to the time worked. An exception is established only for minor workers. Thus, the wages of workers under 18 years of age with a reduced duration of daily work in accordance with Art. 271 TC is paid taking into account the reduced duration of work. The employer may, at his own expense, make additional payments to them up to the level of wages for employees of the corresponding categories for the full duration of daily work.
The commented article lists the categories of workers for whom reduced working hours are established:
- no more than 24 hours a week - for workers under 16 years of age;
- no more than 35 hours per week - for employees who are disabled people of groups I and II;
- no more than 35 hours per week - for workers aged 16 to 18 years.
The working hours are set to no more than 36 hours per week for workers employed in jobs with hazardous working conditions of the 3rd or 4th degree or hazardous working conditions.
In this case, the working hours of a particular employee are established by an employment contract on the basis of an industry (inter-industry) agreement and a collective agreement, taking into account the results of a special assessment of working conditions. In other words, the employment contract with a specific employee must necessarily reflect the results of a special assessment of working conditions that will affect the length of working hours of this employee. In the absence of an industry agreement and a collective agreement, the employment contract will be the only document establishing the duration of working hours.
The length of working time for students of educational institutions under the age of 18, who work during the academic year in their free time from school, cannot exceed half of the norms established by Part 1 of the article in question for persons of the corresponding age (12 and 17.5 hours per week).
2. For disabled people of groups I and II in accordance with Art. 23 of the Law on the Protection of Persons with Disabilities establishes reduced working hours - no more than 35 hours per week while maintaining full pay. However, if a disabled person works, for example, 30 hours, then he receives wages in proportion to the time worked, i.e. as for part-time work.
3. Federal law may establish reduced working hours for other categories of workers (teaching, medical, etc.).
The basis for reducing working hours in these cases are special regulations relating to each category separately.
Thus, Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 2075 established that the working time (standard hours of teaching work per wage rate) for teaching staff is established on the basis of a reduced working time of no more than 36 hours per week.
The following standards are established for teaching staff, depending on their position and (or) specialty, taking into account the characteristics of their work.
Working hours:
36 hours per week:
— employees from among the teaching staff of educational institutions of higher professional education and educational institutions of additional professional education (advanced training) specialists;
— senior teachers of preschool educational institutions, educational institutions of additional education for children and children's homes;
— educational psychologists, social educators, teacher-organizers, industrial training masters, senior counselors, labor instructors;
— methodologists, senior methodologists of educational institutions;
— tutors of educational institutions (with the exception of tutors engaged in the field of higher and additional professional education);
— heads of physical education of educational institutions implementing educational programs of primary vocational and secondary vocational education;
— teachers-organizers of the basics of life safety, pre-conscription training;
— instructors-methodologists, senior instructors-methodologists of educational institutions of additional education for children in sports;
30 hours per week - for senior teachers of educational institutions (except for preschool educational institutions and educational institutions for additional education of children).
Standard hours of teaching work per wage rate (standardized part of teaching work):
18 hours per week:
- teachers of grades 1 - 11 (12) of educational institutions implementing general education programs (including special (correctional) educational programs for students and pupils with disabilities);
- teachers of educational institutions implementing educational programs of secondary vocational education with a pedagogical orientation (with the exception of teachers of such educational institutions for whom the standard hours of teaching work have been established for a salary rate of 720 hours per year);
- teachers of special disciplines 1 - 11 (12) classes of music and art general education institutions;
- teachers of 3 - 5 classes of schools of general music, art, choreographic education with a five-year period of study, 5 - 7 classes of art schools with a seven-year period of study (children's music, art, choreography and other schools), 1 - 4 classes of children's art schools and schools general art education with a four-year period of study;
— teachers of additional education, senior teachers of additional education;
— trainers-teachers, senior trainers-teachers of educational institutions of additional education for children in sports;
— foreign language teachers of preschool educational institutions;
— speech therapists of healthcare and social service institutions;
24 hours a week - teachers of 1st - 2nd grades of schools of general music, art, choreographic education with a five-year period of study, 1st - 4th grades of children's music, art, choreography schools and art schools with a seven-year term of study;
720 hours per year - teachers of educational institutions implementing educational programs of primary vocational and secondary vocational education.
Standard hours of teaching work per wage rate:
20 hours a week - for speech pathologists, speech therapists, speech therapists;
24 hours a week - music directors and accompanists;
25 hours a week - for educators working directly in groups with students (pupils, children) with disabilities;
30 hours per week:
— physical education instructors;
- educators in boarding schools, orphanages, after-school groups, boarding schools at general educational institutions (boarding schools), special educational institutions for children and adolescents with deviant behavior, preschool educational institutions (groups) for children with tuberculosis intoxication, health care institutions and social services;
36 hours per week - for teachers in preschool educational institutions, preschool groups of general education institutions and educational institutions for children of preschool and primary school age, in educational institutions for additional education of children, in dormitories of educational institutions implementing educational programs of primary vocational and secondary vocational education, and other institutions and organizations.
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 14, 2003 N 101 “On the working hours of medical workers depending on their position and (or) specialty” established the working hours of medical workers depending on their position and (or) specialty.
Three lists of categories of medical workers have been approved.
The first list includes positions and (or) specialties of medical workers, organizations, as well as departments, wards, offices and working conditions, work in which gives the right to a shortened 36-hour work week.
The second is the positions and (or) specialties of medical workers, the organization, as well as departments, wards, offices and working conditions, work in which gives the right to a shortened 33-hour work week.
The third - positions and (or) specialties of medical workers, organizations, as well as departments, wards, offices and working conditions, work in which gives the right to a shortened 30-hour work week.
Each list indicates the position and (or) specialty of the employee, as well as the nature and conditions of his work.
For example, doctors, paramedical and junior medical personnel have the right to a reduced 36-hour work week when working with open radioactive sources. The nature and working conditions include work directly related to open radioactive substances (production, processing, storage, packaging, research, application and other types of work), the activity of which in the workplace corresponds to class III, II and I work; work directly on the preparation and maintenance of natural and artificial radon baths (see also Article 350 of the Labor Code).
4. The working hours of a particular employee are established by an employment contract on the basis of an industry (inter-industry) agreement and a collective agreement, taking into account the results of a special assessment of working conditions.
In accordance with Federal Law dated December 28, 2013 N 426-FZ “On special assessment of working conditions,” a special assessment of working conditions is a single set of consistently implemented measures to identify harmful and (or) dangerous factors in the working environment and the labor process (hereinafter also referred to as harmful and (or) hazardous production factors) and assessing the level of their impact on the employee, taking into account the deviation of their actual values from the standards (hygienic standards) established by the federal executive body authorized by the Government of the Russian Federation for working conditions and the use of individual and collective protective equipment for workers.
In accordance with Art. 14 of the Law under consideration, working conditions according to the degree of harmfulness and (or) danger are divided into four classes - optimal, acceptable, harmful and dangerous working conditions.
Optimal working conditions (class 1) are working conditions in which there is no exposure to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors on the employee or the levels of exposure of which do not exceed the levels established by standards (hygienic standards) of working conditions and accepted as safe for humans, and prerequisites are created to maintain a high level of employee performance.
Acceptable working conditions (class 2) are working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which do not exceed the levels established by the standards (hygienic standards) of working conditions, and the altered functional state of the employee’s body is restored during regulated rest or by the beginning of the next working day (shift).
Harmful working conditions (class 3) are working conditions under which the levels of exposure to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors exceed the levels established by the standards (hygienic standards) of working conditions, including:
1) subclass 3.1 (harmful working conditions of the 1st degree) - working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, after exposure to which the altered functional state of the employee’s body is restored, as a rule, in a longer period than before the next working day (shift), the cessation of exposure to these factors, and the risk of health damage increases;
2) subclass 3.2 (harmful working conditions of the 2nd degree) - working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can cause persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the appearance and development of initial forms of occupational diseases or occupational diseases of mild severity (without loss of professional ability) arising after prolonged exposure (15 years or more);
3) subclass 3.3 (harmful working conditions of the 3rd degree) - working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can cause persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the appearance and development of occupational diseases of mild and moderate severity (with loss of professional ability to work) during the period of working activity;
4) subclass 3.4 (harmful working conditions of the 4th degree) - working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can lead to the emergence and development of severe forms of occupational diseases (with loss of general working capacity) during the period labor activity.
Hazardous working conditions (class 4) are working conditions in which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which during the entire working day (shift) or part of it can create a threat to the life of the employee, and the consequences of exposure to these factors cause a high risk of developing an acute occupational disease during work.
If workers employed in workplaces with hazardous working conditions use effective personal protective equipment that has undergone mandatory certification in the manner established by the relevant technical regulations, the class (subclass) of working conditions may be reduced by a commission based on the conclusion of an expert from an organization conducting a special assessment of conditions labor, by one degree in accordance with the methodology approved by the federal executive body, which carries out the functions of developing and implementing state policy and legal regulation in the field of labor, in agreement with the federal executive body, which carries out the functions of organizing and implementing the federal state sanitary -epidemiological surveillance, and taking into account the opinion of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations.
In agreement with the territorial body of the federal executive body exercising the functions of organizing and implementing federal state sanitary and epidemiological supervision, at the location of the relevant workplaces, it is allowed to reduce the class (subclass) of working conditions by more than one degree in accordance with the methodology specified in Part 6 tbsp. 14 of the Law on special assessment of working conditions.
With regard to workplaces in organizations carrying out certain types of activities, a reduction in the class (subclass) of working conditions can be carried out in accordance with industry specifics approved by the federal executive body exercising the functions of developing and implementing state policy and legal regulation in the field of labor, in agreement with the federal executive body exercising the functions of organizing and implementing federal state sanitary and epidemiological supervision, and taking into account the opinion of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations.
The criteria for classifying working conditions in the workplace are established as provided for in Part 3 of Art. 8 of the Federal Law “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” with a methodology for conducting a special assessment of working conditions.
5. Article 15 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 N 421-FZ “On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation in Connection with the Adoption of the Federal Law “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” provides that when implemented in accordance with the provisions of the Labor Code (as amended . Federal Law N 421-FZ) in relation to workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, compensation measures aimed at reducing the negative impact on their health of harmful and (or) dangerous factors of the working environment and the labor process (abbreviated duration of working hours, annual additional paid leave or monetary compensation for them, as well as increased wages), the procedure and conditions for the implementation of such measures cannot be worsened, and the amounts reduced in comparison with the procedure, conditions and amounts of compensation actually implemented in relation to these employees measures as of the date of entry into force of the said Federal Law, subject to the preservation of the appropriate working conditions in the workplace, which were the basis for the appointment of the implemented compensatory measures.
Since 2014, the legislator has decided on the possibility of increasing the weekly working hours of persons employed in jobs with harmful and dangerous working conditions. This duration can be increased to 40 hours per week if three prerequisites are met:
1) such a possibility must be provided for by an industry (inter-industry) agreement;
2) such a possibility must be provided for by the collective agreement;
3) the written consent of the employee must be obtained, drawn up in the form of a separate agreement to the employment contract.
Let us repeat: only the presence of all three conditions makes it possible to increase the weekly working hours of workers engaged in work with harmful and dangerous working conditions to 40 hours a week.
The legislator does not classify work in excess of the established 30 or 36 hours a week as overtime work, but determines that such work must be compensated by separately established monetary compensation. The procedure, amounts and conditions for the payment of such compensation must be established by industry (inter-industry) agreements and collective agreements.
6. The Law on Social Protection of Citizens Working with Chemical Weapons establishes that persons working with chemical weapons also enjoy the right to a shortened working day. Depending on the type of work performed and categories of workers, working hours are set at no more than 24 and 36 hours per week (Article 5).
7. The basis for reducing working hours in the cases specified in the last part of Art. 92 of the Labor Code, there are special regulations relating to each category separately.
The reduction of working hours for employees at risk of contracting the human immunodeficiency virus while performing their official duties to 36 hours a week is provided for by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 3, 1996 N 391 “On the procedure for providing benefits to employees at risk of contracting the human immunodeficiency virus while performing their official duties.” responsibilities."
8. For women working in rural areas, a 36-hour working week is established, unless a shorter working week is provided for them by other legislative acts (see paragraph 1.3 of Article 1 of the Resolution of the Supreme Council of the RSFSR dated November 1, 1990 “On urgent measures to improve the situation of women, families, maternal and child health in rural areas”).
Shortened working hours are established not only for those women who work in agricultural production, but also for those who work in the workshops (sites) of industrial enterprises located in rural areas, in construction organizations, military units (civil personnel), oil and gas fields, as well as at all other enterprises and their structural divisions located in rural areas.
9. Except for the cases provided for by the Code and other federal laws, reduced working hours may be established by a collective agreement and local regulations of the organization at the expense of the organization’s own funds.
Disabled people
Standards of working time for disabled people are established taking into account the requirements of the Federal Law of November 24, 1995 No. 181-FZ “On the social protection of disabled people in the Russian Federation” and on the basis of a medical report on the state of health of a particular person (Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In order to implement the provisions of the Federal Law, organizations with more than 30 employees are required to establish a quota for hiring people with disabilities. The quota is defined as a percentage of the organization’s average headcount and is no more than 4% (but not less than two employees).
If it is not possible to accept a disabled person into an organization, it is obliged to pay a fee to the regional budget for each disabled person in accordance with the quota.
If an employee becomes disabled due to the fault of the employer, the employer is obliged to create a special workplace for him. Regardless of the organizational and legal form, the employer is obliged to create the necessary working conditions for the employee in accordance with the IPRA - an individual rehabilitation and habilitation program. At the same time, the employment contract concluded with a disabled employee should not contain conditions that worsen the employee’s position in comparison with those stipulated in the Labor Code and other regulations of the Russian Federation.
Harmful and dangerous working conditions
Federal laws establish the following types of work, obliging the employer to establish a shortened working week for employees employed in them:
- work with chemical weapons (Federal Law of November 7, 2000 No. 136-FZ “On the social protection of citizens engaged in work with chemical weapons”). These workers have a 24- or 36-hour work week. In addition, they are entitled to compensation and benefits established at the federal and regional levels;
- work in medical institutions (Article 350 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For health workers, the established working hours are 39 hours per week. Depending on the position (specialty) and working conditions, the duration of the working week can be reduced to 36 hours, 33 hours or 30 hours (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 14, 2003 No. 101 “On the length of working hours of medical workers depending on their position and (or) specialty";
- work in medical institutions related to the direct conduct of X-ray therapy and X-ray irradiation with drugs in radiology rooms and laboratories. For these workers, the working week is set to 24 hours;
- work in medical institutions, veterinary institutions, involving interaction with people or animals with tuberculosis, or the production and storage of animal products. For these workers, a working week of 30 hours is established (Federal Law of June 18, 2001 N 77-FZ “On preventing the spread of tuberculosis in the Russian Federation”);
- work in healthcare institutions that involves carrying out diagnostic and therapeutic measures for HIV-infected patients or working with HIV-infected biomaterials. They are entitled to a shortened working week of 36 hours (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 3, 1996 No. 391);
- work in educational institutions associated with increased intellectual and nervous stress. For such workers, a 36-hour work week is established; depending on the position/specialty, taking into account the characteristics of the work, the duration of their working time (standard hours of teaching work per wage rate) is established by the Government of the Russian Federation (Article 333 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- flight work as crew members of civil aviation aircraft. For these categories of workers, a maximum duration is established;
- working week equal to 36 hours (Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated July 12, 1999 No. 22).
The list of professions and positions with hazardous working conditions, in the presence of which the employer is obliged to establish reduced working hours for workers employed in them, is given in the list approved by the Resolution of the State Committee of the USSR Council of Ministers on Labor and Wages and the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated October 25, 1974. No. 298/P-22) in accordance with:
- The Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Work and Professions of Workers;
- Qualification directory of professions of workers, communication workers and junior service personnel not included in the Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Work and Professions of Workers;
- A unified nomenclature of employee positions.
The duration of the shortened working day in this case will be determined as follows:
- 8 hours - with a 36-hour work week;
- 6 hours - with a 30-hour work week;
- 6 hours - with a shorter working week.
Moreover, if the profession or position occupied by the employee is not in the above list, but on some days the employee performed work in harmful or dangerous working conditions, then on the corresponding dates the duration of his working day should not exceed that established for employees performing this work. work constantly.
If employees performed various types of work, including, but not limited to, work in harmful and dangerous working conditions, and spent more than half of the working day in these conditions, then it cannot last more than six hours. The law gives the employer the right to independently expand the list of positions and professions of employees who are entitled to reduced working hours if, in his opinion, working conditions are harmful or dangerous.
Legal privileges for other categories of citizens
Management can also shorten their working hours for employees who initially performed their professional duties in accordance with generally accepted rules, but due to certain life circumstances are forced to switch to a reduced schedule:
- during pregnancy;
- when raising a child under 14 years of age;
- while caring for a sick relative.
In this case, the employee submits an application addressed to the head of the organization (company, institution), which he is obliged to endorse, and then satisfy the request specified in it. If the above reasons exist, the director has no right to refuse the employee. In other cases, changing the work schedule remains at his discretion.
Workers in the medical industry also fall into the category of people in need of part-time work. Subject to the provisions of Art. 350 TK the maximum amount of time allotted for work is 39 hours. If there are difficult conditions, which characterize a number of medical institutions, an employment period of 36, 33, 30 hours is formed, respectively. This applies to psychiatric clinics, tuberculosis clinics, and institutions for HIV-infected people.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other by-laws provide for partially limited employment for citizens belonging to the following categories:
- persons dealing with chemical weapons, conducting experiments with chemicals – 24 hours;
- pilots and flight crew – 36 hours;
- women working in rural areas, northern regions – 36 hours.
It is important to know! A shortened schedule is offered to women workers in agricultural production, in industrial workshops, in enterprises located in villages, villages, towns, as well as those working in the construction industry and military units.
Article 333 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows teachers to use a reduced working period. According to Order of the Ministry of Education and Science No. 1601, additional conditions apply to certain categories of the educational sphere. For them, work hours per week can be 36-20 hours.
Payment to employees during a shortened work week by force of law
Payment to such categories of employees differs from the payment procedure for employees whose working week has been reduced by agreement with the employer. If an employee’s working hours are reduced by force of law, then pay wages as for full working hours: the establishment of shortened working hours does not entail a reduction in wages.
An exception is workers under 18 years of age. As a rule, they are paid wages for the time actually worked or depending on output. However, it is important to check industry agreements as they may include an obligation to make additional payments up to full salary. For example, full payment is provided for minor employees of housing and communal services organizations (clause 6.8.4 of the Industry Tariff Agreement in Housing and Communal Services, approved by the All-Russian Industry Association of Employers on December 8, 2016).
Is it possible to establish a part-time working week during non-working days due to coronavirus?
Reduce working hours in accordance with Art. 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is possible only for certain categories of workers. But establishing part-time working hours by agreeing with employees is quite acceptable. The basis for establishing such a regime is the decrees of the President of the Russian Federation on non-working days due to the spread of coronavirus.
If part-time work is established due to coronavirus, it is also necessary to conclude additional agreements with employees to employment contracts and draw up an order on part-time working hours. In the preamble to the order, refer to the Presidential Decree and/or the requirements of Rospotrebnadzor.
Since each region independently determines the date of resumption of work after quarantine, the end of the period of part-time work both in the order and in the additional agreement can be indicated by the wording “... until the introduction of the regime of daily activities.” This approach will allow you not to re-issue all the documentation.
Increasing the number of working hours, according to Art. 92
By law, a person is required to work no more than forty hours a week. How to correctly determine the norm of employment for the required period (month, quarter or year), taking into account its fixed duration, is described in the paragraphs of the Federal Law and is regulated by special bodies.
To avoid problems, every manager should mark the time worked by subordinates. In some situations, the administration can increase the working day by several hours without breaking the law. These actions are provided for in Art. 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - “Overtime work”, therefore they require payment at a different rate. Personnel can be involved if they have their written consent and instructions from their superiors. The reasons for this are the following.
- We urgently need to finish the work we started.
- Damaged equipment must be repaired and restored.
- It is necessary to take measures to prevent a disaster, accident, or eliminate their consequences.
- Carry out activities related to the introduction of a state of emergency or martial law.
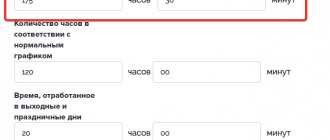
Advice! The duration of work performed above the norm should not exceed two hours a day. You are allowed to work no more than 120 hours of overtime per year.
Increasing working hours
The working hours of each employee are determined in his employment contract, which, in turn, is drawn up on the basis of a collective agreement and industry regulations. In some cases, subject to the employee's written consent, the employer may increase the employee's working hours to a normal 40-hour work week.
The formalization of such an agreement between the employee and the employer occurs by drawing up an additional agreement to the employment contract. In this case, the employer is obliged to pay the employee monetary compensation, the amount of which is determined by industry regulations and the collective agreement of a particular organization.
What is the difference between short-time and part-time work?
Short-time and part-time work are different concepts and should not be confused. They have a number of serious differences:
- In situations established by law, a reduction in the working week is permissible, but only for certain categories of citizens. The main working time is reduced by reducing working hours daily or introducing an additional day off. Part-time work can be set for any employee, by mutual agreement with the employer.
- In case of part-time working hours, the enterprise, by agreement with the employee, has the right to let him go for any number of hours (days), and in case of reduced working hours, the reduction in the number of hours (days) worked is fixed by law.
- The duration of types of shortened working hours is regulated and determined by the relevant normative act.
- The rules for calculating pay for employees working in a shortened and part-time work week are different. In case of a shortened working month (week), wages are paid as for fully worked hours. And if it is incomplete, the salary is calculated according to the time worked or the volume of products, goods, and products produced.
A shortened work week is paid differently than a part-time work week. There are certain features that are worth considering.
Features of payment for time worked
Remuneration for workers with reduced working hours is made taking into account the actual time worked/volume of work. The employer, regardless of the remuneration system adopted by him, can make additional payments to such employees from his own funds (Article 271 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Remuneration for workers engaged in heavy work, work with harmful and dangerous working conditions is established at an increased rate (Article 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Employees combining work and study are paid 50% of the average earnings at their main place of work, but not less than the minimum wage (Part 3 of Article 176 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).