Working hours and rest time according to the law
The provisions of the Labor Code contain such concepts as “working time” and “rest time”.
Working time is a time period equal to several hours. And during these hours the citizen fulfills his professional duties.
It is considered normal if a person works no more than 40 hours a week. If a subordinate works 5 days a week, his working day is 8 hours. With a 6-day work week, the working day is reduced to 7 hours (with the day before the weekend being 5 hours). This rule applies to most employees of organizations. The minority includes those categories for which a reduction in working hours is provided. This is done to protect their health.
Rest time is a period used by a citizen at his own discretion (i.e., time when he may not work).
Rest time is considered:
- breaks during the working day (shift);
- daily (between shifts) rest;
- weekend;
- holidays;
- vacation.
What is included in working hours
Working time includes the following:
- time to perform work duties, including: receiving work orders;
- proper preparation of materials;
- studying technical documentation;
- preparing and cleaning workplaces, etc.;
Saturday work is not considered part of working time. If there is still a need to involve employees in the cleanup, this is done only with their written consent.
Exceptions are the following situations:
- preventing the consequences of a disaster or accident;
- implementation of duties extended to a subordinate in connection with the introduction of a state of emergency.
In these exceptional cases, employed people are required to go to work even on weekends.
Medical examinations must be carried out during working hours. If an employee does not agree to undergo a medical examination on his day off, the employer does not have the right to insist on this.
Anything that does not relate to the employee’s duties under the employment contract should not be done during working hours. Each organization may have its own prohibitions, but they should not contradict labor legislation.
Working hours for a certain group of workers
Less than 40 hours per week can be worked by:
- minors;
- disabled people of groups I and II;
- working in conditions that are harmful to health or life threatening;
- teachers;
- medical staff.
In these cases, the permissible duration of work is determined by law. There are options when a limit is not set, but the employee has the right to work less (for example, this applies to pregnant women). It is also possible to adjust working hours by agreement between the employee and the employer.
Table: working hours for a certain group of people
| Category of workers | Duration of work |
| Minors | For those who do not study or work during the holidays:
For students working during the academic year in their free time:
|
| Persons with reduced ability to work | For disabled people of groups I and II - no more than 35 hours per week |
| Workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions | No more than 36 hours per week |
| Teachers | No more than 36 hours per week |
| Medical staff | No more than 39 hours per week |
| Students in part-time and part-time forms of education | For a period of 10 academic months before the start of a diploma project (work) or passing state exams, a working week shortened by 7 hours is established at will. During the period of release from work, these employees are paid 50% of the average earnings at their main place of work, but not less than the minimum wage. |
Work on holidays
Before the holidays, the shift of subordinates is reduced by one hour. If a person had a rest on the day before the holiday, then the schedule does not change.
If it is not possible to interrupt the work of the organization and release subordinates earlier without damaging the process, management has the right to compensate for the “extra” hour of labor with remuneration for overtime or time off.
On holidays, the employer reduces the working day by one hour
Breaks during an 8-hour workday
During the day, the organization’s personnel can count on certain breaks in the work process. They are necessary to restore the strength of subordinates and increase their performance. Only a portion of these breaks are counted as working time and paid.
According to the law, the manager must provide employees with the following breaks:
- special breaks for heating and rest;
- periods intended for feeding the child (every 3 hours for 30 minutes);
- breaks due to the nature of the work (for example, for professional computer users).
The lunch break is not part of the working time, so no payment is made for this period. It is understood that the employee is free to use such a pause in the work process at his own discretion.
If the specifics of production do not allow time for lunch, such a break is included in working hours.
Breaks during an 8-hour working day in total should not exceed 2 hours. The employer has the right to independently decide when exactly the employee can take a break. All the nuances of suspending the work process are recorded in the internal documents of the organization.
What are the working hours?
There are several types of working time, namely:
- normal;
- abbreviated;
- incomplete.
Subordinates may also be subject to special work regimes while maintaining the same general time. For example, their workday may be fragmented or flexible.
Normal working hours
The norm is 40 hours of work per week. This duration applies to employees who do not belong to preferential categories in most organizations with normal working conditions.
Working on a reduced schedule
Reducing working hours leads to a decrease in its duration compared to the norm. However, remuneration for the work of a subordinate is accrued in the same amount. The exception is for employees whose remuneration will depend on output.
Those who are permitted by law can work on a reduced schedule. However, they must provide documentary evidence of the justification for introducing reduced working hours.
Partial working hours
In practice, part-time work days or weeks are often established. The remuneration in this case is directly dependent on the hours worked. If management and employee agree to the upcoming changes, the work schedule changes. For certain categories of employees, the duration of part-time work is not standardized. The general rule is that a working day should not be less than 4 hours, and a week should not be less than 20 hours.
The obligation to transfer to a similar regime lies with the employer if such a request comes from:
- pregnant employee;
- mother (father) of a child under 14 years of age;
- mother (father) of a child with a disability under 18 years of age;
- an employee caring for a sick family member in accordance with a medical report.
Underemployment may occur if there is a threat of mass layoffs.
For example, an organization has introduced a 5-day work week with an 8-hour work day (40-hour week). At the request of a subordinate, he may be assigned not an eight-hour, but a six-hour working day (i.e., a 30-hour working week). This will be part time. If a 17-year-old employee gets a job at this company, by law he can work no more than 35 hours a week - 5 days for 7 hours. This is a shortened mode. But a teenager also has the right to part-time work; he can negotiate with management for the same 30-hour week.
Video: Irregular working hours
Dividing the working day into parts
The head of the organization, with the consent of the employees, can apply a fragmented work schedule. This innovation is justified if it is necessary to increase productivity. Sometimes the working day is divided into parts for another reason, for example, if the load distribution during the day occurs with unequal intensity. At the same time, the total working time should not exceed that specified in the Labor Code.
As a rule, the day is divided into two parts. Between these parts there is a break, the duration of which is more than two hours.
Flexible working hours
Flexible work schedule is regulated by Art. 102 of the Labor Code. In this case, the start and end times of work are established by agreement between the employee and his supervisor. However, no one is canceling the standard hours required for work.
Flexible schedules include:
- fixed time (during which the employee is required to remain at the workplace);
- variable (flexible) time at the beginning and end of the working day, which the employee has the right to distribute himself;
- break for food and rest (not included in working hours);
- the duration of the accounting period (during which the employee must work the standard working hours established for this category of persons).
Such a work regime is necessary in the following cases:
- If the work is related to creativity. Creative people are known to try to avoid standard work schedules.
- If the organization needs to distribute work due to uneven workload, the influence of external conditions.
- If the employee is bound by obligations outside of work, and the time of his presence at the workplace is not important.
For example, an accountant needs to take a child to educational activities several times a week. A woman can do her work at any time. She can set a flexible schedule according to the following scheme: the accounting period is a week, during which time she must work 40 hours. From 10:00 to 13:00, the accountant must be present in the office to coordinate the reporting and submit documents for signature. She plans the rest of her hours on her own. Lunch break - 1 hour without a fixed time.
Persons working in this regime are entitled to the same guarantees as other subordinates, namely:
- equal pay for work of equal value;
- provision of benefits in accordance with medical and other indications;
- inclusion of this work in the insurance period, etc.
During a business trip, flexible working hours are not applied, and accounting is carried out as during normal work hours.
Article 91. Concept of working time. Normal working hours
Working time is the time during which an employee, in accordance with internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties, as well as other periods of time that, in accordance with this Code, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, relate to working hours.
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week.
The procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain calendar periods (month, quarter, year), depending on the established duration of working time per week, is determined by the federal executive body exercising the functions of developing state policy and legal regulation in the field of labor.
(Part three introduced by Federal Law dated July 22, 2008 N 157-FZ)
The employer is required to keep records of the time actually worked by each employee.
Methods for studying working time
In organizations, using various methods, the time spent on work by each subordinate is analyzed and studied. This is done so that labor productivity not only does not fall, but, on the contrary, grows.
Observations can be carried out in the following ways:
- visual (using clocks and stopwatches);
- using semi-automatic technology, i.e. individual time expenditures are recorded by instruments under the control of an observer;
- using automatic devices (industrial television, film and video).
One of the methods for studying the labor process is timing
Table: methods for studying working time
| Method name | Character traits |
| Photography of working hours | This method is used if there is a need to analyze time spent on labor within the working day. To do this, a sheet is prepared that reflects the results of observations. Photography of the labor process is used for the following purposes:
Research can be of three types:
The most commonly used is individual photography of the labor process, i.e., one subordinate is taken as the object of observation. If surveillance is carried out on several workers, such actions will be considered a group photograph. |
| Timing | It is used to analyze and measure individual elements of the labor process, and not to study the working day. The time of the operation is measured using a watch or stopwatch. |
| Photochronometry | This method combines the study of labor process costs during a shift using the two previous methods. |
Postponement of 2021 holidays
If a non-working holiday falls on Saturday or Sunday, then the day off is transferred to the next working day (Part 1 of Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
| Where | Where | |
| January 4 (Saturday) | —> | May 4 (Monday) |
| January 5 (Sunday) | —> | May 5 (Tuesday) |
| February 23 (Sunday) | —> | February 24 (Monday) |
| March 8 (Sunday) | —> | March 9 (Monday) |
| May 9 (Saturday) | —> | May 11 (Monday) |
Planning, organizing and controlling the work process
If the management of an organization wants to increase the efficiency of the production process, it must competently plan and organize the working time of each employee.
Planning your working time allows you to do the following:
- increase the level of operational efficiency:
- optimize your work schedule;
- improve time use techniques;
- weed out ineffective activities;
- Clearly separate work and personal time.
Time planning is divided into types according to various criteria:
- by scope (general and specific);
- by content (strategic, operational and current);
- by objects (personnel, production, financial);
- by periods (short-term, medium-term, long-term);
- if possible, changes (rigid and flexible).
Work process planning is always reflected on paper. In recent years, electronic planning has become popular.
Any plan must be recorded in writing
Features of working time planning:
- No matter how perfect a plan is, adjustments are always made to it.
- All actions recorded in the plan are divided by time into short-, medium- and long-term.
- The plan must be realistic, that is, you should not plan difficult things to accomplish.
- It is necessary to record not only goals, but also expected results.
- The plan must reflect the deadlines for completing the assigned tasks.
- It is necessary to appoint responsible persons for certain actions, i.e. delegate authority.
In my opinion, any work requires proper planning. A formalized plan helps distribute the amount of work during the working day and determine primary goals and objectives. Based on personal experience, I can note that the most important things are best done in the morning, when performance is at its maximum. It is especially important for freelancers to have a written or electronic plan on hand, since careful planning is what helps you be disciplined.
For example, the working day of an advertising agent will include several blocks: cold calls, preparation of commercial proposals, negotiations, travel to conclude an agreement. If you can set aside a certain time during the working day for calls, then other activities require flexible planning. Therefore, it is difficult to control them.
Organization of the working time of any employee includes:
- Preparation of a work schedule.
- Selecting working hours for subordinates.
These points are recorded in the internal labor regulations, in employment contracts and additional agreements to them, in shift and vacation schedules.
Any organization must create a work schedule for each employee.
Related to the concept of regime is the issue of accounting. To do this, a time sheet is kept, where information is entered about employees going to work, reasons for absence and the number of hours worked. This document is mandatory, and in addition to it, the company can use other forms of accounting.
To record the actual time worked, a special time sheet is used, which records all attendances and absences for work of each employee, the number of hours spent on performing duties
Control allows you not only to record the time of arrival and departure of employees, but also to evaluate the efficiency of using working time. It is necessary to maintain labor discipline and to fairly remunerate subordinates. Various means are used for control:
- Logbook.
- Regular employee reports.
- Computer technologies (special applications that track time and monitor telephone calls, etc.).
- SLUD. Access control and management systems make it possible not only to provide employees with the ability to access certain premises and objects, but also to establish how long the employee remained within the organization’s territory.
- CCTV.
- A program for tracking employees' working hours at work computers.
How to calculate working time fund
The working time fund must be taken into account by the management of the organization. If you don't do this, it will be difficult to determine how many employees will be needed to complete the job and how long it will take. The fund is used to balance working hours.
The working time fund is the planned time allocated for the work of each employee.
When planning the working time fund, actual information is taken as a basis, which is compared with predicted indicators, and downtime in the labor process is also taken into account.
The working time fund includes the following indicators:
- Calendar fund (represents the total period for which the fund is determined).
- Nominal fund (this is the number of days in a year remaining after deducting all weekends and holidays).
- Maximum probable fund (the maximum number of days per year during which the employee performs his functions).
- Attendance fund (involves accounting for actual time worked).
The basis of this fund is the calendar period during which calculations are made. These may be the following periods:
- Year (relevant if you need to conduct a full-fledged study of employee productivity).
- Quarter (needed for cumulative time tracking).
- Month (the indicator is used when calculating salaries, determining the ratio of actual workdays to the production rate).
When calculating the nominal fund, you must use the following formula: calendar fund - holidays - weekends.
The maximum probable fund is calculated as follows: nominal fund - vacation (28 days). The result obtained using this formula will be considered the general production standard. This indicator is important for determining the optimal number of workers in an organization.
To calculate the turnout fund, the following formula is used: the maximum probable fund is the number of days missed. In this case, all working days missed for objective reasons will be taken into account, namely:
- maternity and child care leave;
- sick leave;
- leave due to training;
- time off by agreement with the employer;
- additional paid leave.
Management should make a comparison between the actual work hours of workers and production needs. The resulting ratios allow us to determine how many workers need to be involved in the work process.
How to balance working hours
To increase labor productivity in an organization, it is necessary to identify existing reserves. For this purpose, a balance is drawn up for the use of working time.
The balance includes two sections:
- working time resources (working time fund and absence from work due to holidays or vacations);
- use of working time (this includes indicators that allow us to characterize the structure of the fund).
Working time balance is a table that reflects the distribution of calendar days and hours and their use by the organization’s employees. The calculation of the indicator is carried out for one employee or for a group of workers. In the latter case, workers should share similar working conditions and the same length of vacation.
Working time balance is calculated as a comparison of plan and actual indicators
Stages of drawing up a balance sheet:
- The predicted indicator is calculated according to the calendar, taking into account standard labor time, as well as data on vacations and other absences.
- The periods of downtime expected by the employer and the possible incapacity of the employee are taken into account.
- The average indicator is determined, i.e. the duration of the shift is multiplied by the standard days of work, after which the result is divided by the number of employees.
- Forecasted standards are compared with actual ones. Based on the differences, the measures that are necessary to improve labor efficiency are calculated.
Exceeding the norm: overtime and irregular working hours
Art. 99 of the Labor Code qualifies overtime work as work performed on the direct instructions of the employer outside the normal working hours. If we are talking about daily accounting, then such work will be considered work after the end of the working day or shift. If we are talking about summarized accounting, then such work is considered to be work that lasts more than the standard number of hours during the accounting period.
One of the mandatory conditions is that the employer’s instructions to work overtime must be in writing. Overtime work may be required subject to certain restrictions. The permissible limits depend on the type of work that must be performed overtime, the categories of workers involved, and finally, on the duration of overtime work.
Employee consent to overtime work is required to solve the following problems:
- to complete the work begun, which for objective reasons was not completed during the working day, provided that failure to complete this work will result in irreversible damage to property and create a threat to the life and health of people;
- to carry out repair work when a malfunction prevents the further work of a large number of workers;
- to replace a replacement worker who did not show up.
There are reasons why employees may be required to work overtime without their consent. These reasons are related to the need for action to prevent disasters or to carry out work to normalize the functioning of life support systems for the population during liquidation of the consequences of emergency situations.
In other cases, overtime work is possible with the consent of the employee, taking into account the opinion of the trade union organization. However, the procedure for taking into account the opinion of the trade union organization is not explained by the code (Article 371 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), and in practice, it is enough for the employer to notify the trade union (if there is one) of its decision related to overtime work.
The law prohibits overtime work for pregnant women and adolescents under 18 years of age. If there is consent and there are no medical contraindications, then it is allowed to involve women with children under 3 years of age and disabled people in work beyond the normal length. However, in such circumstances, a special licensing procedure applies: the specified employees confirm in writing that they are aware of their legal right not to work overtime.
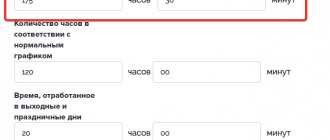
The amount of overtime work for its performer should not exceed 4 hours for 2 consecutive days and for 120 hours per year. Overtime work should be paid in an increased amount (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
An irregular working day is considered to be a work schedule in which the duration of working hours differs significantly from the duration of work established by legislative acts. With such a schedule, workers may sometimes be required to work outside the normal working hours. The presence of an irregular working day is an essential condition of the labor function, and therefore it must be necessarily reflected in the employment agreement.
Procedure and rules for registering working hours
The main document of the enterprise that records the working regime is the internal labor regulations (ILR). They regulate:
- procedure for hiring and dismissing workers;
- rights and obligations of subordinates;
- working hours established for certain positions;
- reasons and rules for changing the work schedule;
- time allotted for rest;
- sanctions threatening an employee for violation of labor discipline, etc.
The internal labor regulations must describe in what mode a subordinate must work
The presence of PVTR is mandatory in any organization. They are requested by the labor inspectorate during inspections.
The document is developed independently, taking into account the specifics of the organization’s economic activities, but its provisions should not contradict the Labor Code. All employees must be familiarized with the rules and signed.
Order on approval of the working day schedule
In order for the internal labor regulations to come into effect, they must be agreed upon with the trade union (if there is one) and approved by the appropriate order. It is compiled in free form and should contain the following components:
- Name of the organization.
- Order number, date and name of the locality.
- The name of the document is “Order on approval of internal labor regulations.”
- Legal grounds (Article 190 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The content part is the approval of the attached rules.
- Procedure for informing employees.
- Indication of the application - PVTR details.
- Signatures of the manager and responsible officials.
Internal labor regulations are approved by order
Application for time on weekdays
If an employee needs to leave work, he must fill out a corresponding application. It doesn’t matter whether he wants to be absent for a few hours or the entire working day.
The application for leave shall include the following information:
- Full name and position of the person to whom the application is addressed (this is the employee’s immediate superior or director);
- name of company;
- Full name and position of the applicant;
- name of the document (application);
- main text with the request and explanation of the reason (the date of the leave is indicated).
The application for a day of rest provides the rationale for the employee’s request.
If the boss agrees to provide such time, he puts a visa, signature and date on the document. In this case, the absence of the employee will not be regarded as a violation of labor regulations.
The employer is not obliged to provide employees with time off, however, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for exceptions. The following categories of workers have the right to an unscheduled day off:
- old age pensioners;
- disabled people;
- WWII participants;
- parents or relatives of military personnel who died in service.
There are good reasons that do not allow an employer to ignore an employee’s request:
- donating blood for donation;
- death of close relatives;
- marriage;
- birth of a child.
The employee negotiates the date and number of days off directly with his superiors.
Certificate of employee working time
The working time certificate records the number of hours worked by the employee for a certain period. The certificate can be provided by the management of the organization at the request of the worker or at the request of various authorities. There is no unified form of the document, so it is drawn up in any form.
An employee’s working time certificate usually contains the following data:
- information about the employee (his full name, position);
- accounting period;
- amount of time worked.
The certificate is signed by the head of the organization.
A certificate of employee working time is drawn up in free form
Time log
A working time log is necessary to record the time of arrival and departure of subordinates. It is used for the following purposes:
- records of tardiness and leaving work early;
- tracking the working hours of employees with flexible working hours;
- taking into account the involvement of employees in overtime work.
There is no unified form of the document. The content of the magazine depends on the goals of the employer.
The log book must be distinguished from the time sheet. The latter is a document that is filled out according to standard requirements and is required for reporting. A journal is an internal document of an enterprise that an employer can maintain at its discretion. Both of them can be used as arguments in case of disagreement between the parties to the employment relationship regarding the number of hours worked, i.e. as evidence for legal proceedings.
As a rule, the working time log contains:
- Full name and position of the employee;
- structural subdivision;
- time of arrival at the workplace;
- employee's signature upon arrival;
- signature of the responsible person;
- care time;
- number of hours worked;
- a note about deviation from the work schedule (lateness, delay for valid reasons, overtime);
- employee's signature upon leaving;
- signature of the responsible person.
The time log records the time employees arrive and leave work
This document is formatted as follows:
- all sheets are numbered and stitched;
- on the last page there is a seal containing information about the number of sheets;
- the signature of the responsible person or manager is placed (on the same seal).
Recording working hours according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2021
Employers, regardless of their organizational and legal form, are required to keep a timesheet of working time worked by each employee for a certain period of time (Article 91 of the Labor Code). Accounting means recording the duration of hours actually spent on the performance of labor functions, as well as periods of rest and other distractions.
For these purposes, responsible persons appointed by the head of the organization maintain time sheets. Only with proper and complete documentation is it possible to avoid claims and disputes from employees and regulatory structures.
The timesheet is the basis for calculating wages for each employee.
Changing the operating mode
Often the working hours in an organization undergo changes. If this happens at the request of the boss, an order is issued. With its help, the following is conveyed to subordinates:
- start and completion dates of changes, if they are temporary;
- an indication of changes in such elements of the labor regime as the working day, week, etc.;
- a list of all planned breaks in the labor process;
- positions affected by the innovation.
The order to change working hours is communicated to employees two months before the upcoming changes
Employees are familiarized with the order against receipt. The next step is to draw up an additional agreement to the employment contract. Here it is necessary to describe the new working conditions of the employee. If the PVTR do not contain references to the possibility of such changes in the operating mode, it is necessary to issue an annex to them.
If the initiator of the changes is a subordinate, he must submit an application with a request to transfer him to a different work regime.
The application will be considered correctly completed if it contains the following:
- the date from which the employee would like to work under the new regime;
- characteristics of the current regime;
- indication of desired hours of work;
- written evidence of the validity of the request.
If the manager does not object, he puts his visa on the application, then an order and an additional agreement to the employment contract are drawn up.
An application for changing working hours must contain an explanation of the request for transfer to a new work schedule
Working time tracking - we identify the norm and excess
Control over whether the duration of labor time complies with existing standards is carried out in the process of recording working time. The process of organizing labor at different enterprises can be organized on different principles. In particular, labor time can be recorded for various time periods, and, as a rule, enterprises choose from three options: day, week or summarized accounting.
Daily recording of working time is advisable for those employers whose work schedule assumes that the duration of work is the same on any day. In circumstances where the actual daily working hours exceed the standard, the difference is not compensated for by shortfalls in subsequent days, but is classified as overtime work.
Weekly recording of working hours is required in circumstances where, within the normal limits of weekly work, the length of working days may actually fluctuate from day to day. Weekly accounting is appropriate, for example, when work is carried out on a flexible schedule (Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Summarized accounting of working time is most necessary for such labor regimes as shift work (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) or rotational work (Article 300 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The principle of this type of accounting is as follows: the time of work is counted not as a week, but as another period (three weeks, a month, two months, etc.). The use of a different duration of interval for calculating working time is due to the fact that for objective reasons, for example due to the specifics of the enterprise, it is not possible to strictly adhere to the established, standardized duration of weekly or daily work. The time period taken by the employer for the purpose of standardization for calculating the number of working hours is called the accounting period. The total duration of work during this time cannot be more than the normal weekly, multiplied by the number of weeks. With all this, for the length of this period Art. 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines a maximum of one year.
For more information on calculating the standard hours for a shift schedule, see the material “Normal hours for a shift work schedule according to the Labor Code.”
It is the employer's responsibility to record the time worked by employees. Moreover, it is necessary to take into account time both within the normal duration and in cases where working time standards are exceeded due to overtime work or work in irregular working hours. These two concepts characterize the employment of an employee in excess of the established norm and, therefore, require separate legal regulation.
Efficient use of working time
The employer must be able to determine how effectively working time is used by each subordinate. For this purpose, it would be useful to use mathematical methods.
For example, the coefficient of extensive time use is calculated. Calculation formula: Ke = (total time fund - breaks in work)/total time fund. The ideal is taken to be equal to one. If Ke differs significantly from the ideal indicator, it means that labor time is not being used effectively.
In the same way, loss and time coefficients are calculated. In this case, the numerator will be the desired value (in minutes), and the denominator will still be the total amount of time. The dependence in this case will be the opposite - the proximity of the obtained value to unity will indicate that working time is spent ineffectively.