What is "working time"
The definition of this concept is contained in Art. 91 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to this standard, this is the period of the day during which the employee performs his immediate job duties in accordance with the established internal labor regulations and the conditions specified in the contract.
The length of the working day according to the Labor Code (2020) is limited only by the upper limit - this is also stated in Art. 91 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Normal work hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week. This rule applies to all employees, regardless of how many days their work week lasts: 5 or 6. And anything beyond the norm is overtime.
Maximum duration of daily work for certain categories of citizens
Separate time limits are established for one shift. Special legislative acts may establish the maximum permissible duration of daily work for certain categories of workers.
An example is the Order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation, according to which the daily working hours for crew members should in no case exceed the established maximum limit of 40 hours per week.
In general, it can be concluded that, in accordance with this Order, the normal duration of one shift should in no case exceed eight hours and should take place from Monday to Friday. Moreover, with such a minimum work schedule, the employee must be given two days off - Saturday and Sunday.
This order separately identifies women workers in the Far North, as well as workers who have not yet reached the legally established age of 18 years.
For such employees, managers must establish a 36-hour work week. Consequently, the duration of one shift for such workers is shorter and amounts to 7.2 hours.
Separately, it is worth noting that the maximum duration of work duties by crew members, which includes keeping watches and performing any additional work, should not exceed 12 hours in one day. For such employees, the head of the organization must establish a special two-shift schedule, according to which each employee will work 12 hours for two days in a row.
Work for 12 hours in a row should not exceed 30 days in a row.
If we are talking about employees with limited terms of performance of labor duties, working on a two-shift schedule of 12 hours a day, then their standard working hours should not exceed three months in a row, including on the eve of night shifts.
The establishment of a working schedule of 12 hours a day and on the eve of night shifts is established by the direct employer, taking into account the opinion of the trade union body of the enterprise. The duration of shifts on the eve of night shifts in this mode of operation cannot be reduced.
Who is entitled to reduced working hours?
For some categories of workers, the legislation has determined a different length of working time - reduced (Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- for teenagers under 16 years of age - no more than 24 hours a week;
- for workers aged 16 to 18 years - 35 hours per week;
- for disabled people of group I or II - no more than 35 hours per week;
- specialists working in enterprises with harmful and dangerous working conditions are required to work no more than 36 hours a week. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the results of the SOUT;
- doctors should work no more than 36 hours a week;
- teachers - no more than 36 hours per week;
- employees working in the Far North and equivalent areas and in rural areas are allocated to work no more than 36 hours a week.
Separate regulations may establish other indicators for certain categories of citizens or representatives of certain professions. There are no legal requirements for minimum hours worked.
Special cases when working time control is ineffective
Monitoring the work day is necessary to maintain discipline, maintain momentum and for a reward system. Creative, technical professions and related projects are not always controllable; it can be difficult to fit employee productivity into a clear time period. There are thousands of examples when prolonged reflection and seeming idleness end in insight. CrocoTime will note the result achieved and the efforts spent to achieve it.
And a specialist does not always need a full 8-hour day to complete the assigned tasks. With high productivity, it can be completed in shorter periods of 7 or even 6 hours. It is no coincidence that disputes arise about the duration of a continuous working day.
Western scientists defend the opinion that when the 8-hour working day is shortened, the KPI increases, that today it takes much less time to do one’s job well. The accounting and control program will reflect human activity. Perhaps his achievements cannot be measured by the amount of time spent on them, they are valuable as a fact.
So in each specific case you will have to decide how to control what goals to achieve as a result of personnel monitoring. But the main thing is to do it openly and honestly.
In what cases can the working day be reduced?
How long a particular employee must work is indicated in his employment contract. Thus, by agreement between the parties, it can be issued for a partial period of time (Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the boss does not have the right to refuse a request to establish a shortened working day or a short week for the following categories of workers:
- pregnant employees;
- a parent (guardian, trustee) raising a child under 14 years of age (or a disabled child under 18 years of age);
- employees caring for a sick family member (this need will have to be confirmed by a medical certificate).
In this case, part-time work is established for a period convenient for the worker, but not more than for the period of existence of circumstances. When determining the schedule of work time and rest time, the wishes of the employee are taken into account. It is worth knowing that such measures will not affect the citizen’s labor rights, in particular, the length of leave and length of service. Only for money.
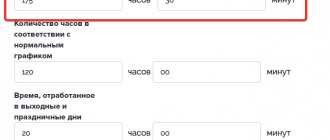
Every boss must keep records of the time worked by employees. For example, an employer may need to find out the average working hours during a working day.
The average working day is a parameter that shows how many hours of work per employee per day.
How is it calculated? Average working day - formula:
SPr = OKCHChr / KD,
Where:
- SPr - average length of day;
- OKChChr - the total number of man-hours worked;
- CD - number of days in the accounting period.
To determine the average for all employees, another formula is used:
SP = OKCH / KR,
Where:
- SP - average duration;
- OKCH - the total number of man-hours worked at the enterprise;
- KR - number of employees.
Why keep track of working hours?
Do you know what the most delicious coffee is? The kind you can drink in the office. It is no coincidence that during this ritual, which can go from morning to lunch, a significant part of the time flies by, which could and should be spent on performing immediate duties. Employees spend up to 30% of their working hours on distractions: entertaining reading on the Internet, solving personal queries, unimportant conversations with colleagues.
You shouldn’t even hope that these activities can be completely eliminated from your life. They are also necessary for relaxation and for greater efficiency. It's a matter of spending time wisely. The manager, perhaps more than ordinary employees, feels its value. The success of an enterprise, projects, and plans depends on the real output and passion of people. That’s why it’s so important to introduce mindfulness in relation to your activities as one of the company’s rules. Controlling the radioactivity and informing people that it is being carried out will allow:
- increase discipline;
- understand where time is lost and find its reserves;
- optimize business processes;
- improve performance, productivity, set up a responsible attitude towards responsibilities.
Losses from unproductive surfing on the Internet during the working period bring billions of losses, experts from the FBK Institute for Strategic Analysis say. In 2021 in Russia, this figure averaged 300 billion rubles. Therefore, employee control will remain with us for a long time.
Working hours for teaching staff
Article 333 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states: for teaching staff, a reduced working time is established - no more than 36 hours per week.
The length of teachers’ working hours is determined individually and depends on factors such as:
- job title;
- standard hours per rate;
- contract teaching load;
- upper limit of teaching load (2 rates).
Detailed information about the accepted standards for the length of working time for teachers is presented in Order of the Ministry of Education and Science dated December 22, 2014 No. 1601.
Ways to control working time
Delays are combated through access control systems. They are installed in almost every building, block the entrance of unauthorized persons and monitor movements around the territory. ACS is often integrated with video surveillance. It not only detects tardiness and other distractions, but also prevents theft attempts.
To track mobile workers whose activities involve constant movement around the city and neighboring regions, GLONASS, GPS, GPS beacons or a GPS tracker in smartphones are used. Sales managers, forwarders, couriers, merchandisers themselves choose a router that shows the trajectory of movements, stops, delays and at the same time allows them to have the necessary corporate documents at hand, use the intranet and extranet.
Understanding the quality and volume of employment of office and remote specialists is provided by automatic time tracking programs. Some employers do not consider it shameful to install spy systems to scan web pages on a PC, connect to web cameras, and take screenshots.
Let us remind you that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation prohibits hidden tracking of a person as violating his rights. Then the question arises, what goal does the boss pursue when using automated radioactive waste accounting programs? Catch a subordinate doing inappropriate activities and punish him? Or should we use them to establish interaction between the two parties and strengthen the position of the enterprise in the competitive world?
Work on weekends
Provisions of Art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation applies to all groups of employees. The pre-holiday day should be shortened by at least 1 hour. This is due to the fact that a person must be given the opportunity to prepare for rest. These rules apply to all hired employees.
There are not only federal, but also local holidays. They affect the length of the working week. An exception to the rules are events that are related to professional activities. For example, metallurgists celebrate their holiday in July. But this event is not considered a day off.
Employers are not required to reduce working hours due to professional events. Sometimes a specialist is needed on a day off. In this case, the employer is obliged to pay the employee overtime at higher rates. This need may be due to the nature of the work performed.
Overtime work
Work performed by an employee on the initiative of the administration is overtime. The employer must take into account the provisions of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Management does not have the right to force a specialist to work after the end of the working day. He must give voluntary consent. The administration arranges overtime hours in accordance with the order. Accounting records overtime hours separately.
The administration is obliged to pay the overtime spent by the specialist at increased rates. Such a need may arise, the workshop does not have time to fulfill the plan. The presence of an employee may be required if it is necessary to prevent property damage.
Important! Urgent labor is not only paid at higher rates. It is impossible without the consent of the employee. The administration is obliged to issue a written order.
For schoolchildren
The length of the working day (shift), as we have already found out, is established to one degree or another for certain categories of persons. In the case of the media, everything is clear - there, basically, the employer himself dictates his own rules, but taking into account the established weekly labor norm. But what if we are talking about minors?
In this case, the maximum allotted to the employee is 5 hours a day. But this is only for workers under 16 years of age. After this restriction, you can work a maximum of 7 hours a day until you reach adulthood. By the way, it is important to understand here that the employee does not have to be trained. Otherwise, during the study period, they can work in shifts of 2.5 and 3.5 hours per day, respectively. This is exactly what a working day (duration) can be. The Technical Regulations of the Russian Federation indicate that no one has the right to leave minor employees to work part-time, even overtime. In any case, while studying in educational institutions.
Commentary on Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Working time consists of the time actually worked during the day. It may be less or more than the duration of work established for the employee. Working hours also include other periods within the normal working hours when work was not actually performed. For example, paid breaks during the working day (shift), idle time not through the fault of the employee.
The duration of working hours is usually established by fixing the weekly standard of working time.
The maximum limit on the duration of working hours is established by law, thereby limiting the duration of working hours. Article 37 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, enshrining in paragraph 5 the right to rest, indicates that a person working under an employment contract is guaranteed the working hours established by federal law.
The Labor Code allocated working time to Section IV, consisting of two chapters (15 and 16).
Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines working time.
Working time is the time during which an employee, in accordance with the internal labor regulations of the organization and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties, as well as other periods of time that, in accordance with laws and other regulatory legal acts, relate to working time. Based on this, the parties to labor relations have the right to determine the boundaries of working time, establish the beginning of the working day, its end, the time for a lunch break, as well as the working time regime, through which the working hours established by current legislation are ensured.
The Code emphasizes that normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week. This maximum working time applies to the vast majority of workers and is therefore legally considered a universal labor measure.
The significance of the legal limitation of working hours is that:
1) ensures the protection of the employee’s health from excessive fatigue and contributes to the longevity of his professional working capacity and life;
2) for the working hours established by law, society and production receive from each employee the necessary certain measure of labor;
3) allows the employee to study on the job, improve his qualifications, cultural and technical level (develop personality), which, in turn, contributes to the growth of the employee’s labor productivity and the reproduction of a qualified workforce.
The time during which the employee, although he does not perform his job duties, but performs other actions, includes periods of time that are recognized as working time, for example, downtime through no fault of the employee. So, for example, in accordance with Article 109 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, working hours include special breaks for heating and rest provided to workers working in the open air in the cold season (for example, construction workers, installers, etc.) or in closed, unheated rooms, as well as for loaders engaged in loading and unloading operations. The temperature and wind strength at which this type of break must be provided are determined by executive authorities. The specific duration of such breaks is determined by the employer in agreement with the elected trade union body.
Breaks for industrial gymnastics must be provided to those categories of workers who, due to the specific nature of their work, need active rest and a special set of gymnastic exercises. For example, drivers are entitled to such breaks 1 - 2 hours after the start of the shift (up to 20 minutes) and 2 hours after the lunch break. In relation to any other categories of employees, the issue of providing them with such breaks is resolved in the internal regulations.
According to Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, working hours include additional breaks for feeding the child (children), provided to working women with children under the age of one and a half years, no less than every three hours of continuous work, lasting at least 30 minutes each. Breaks for feeding children are included in working hours and are subject to payment in the amount of average earnings.
As a rule, working hours include periods for performing basic and preparatory and final activities (preparing the workplace, receiving work orders, receiving and preparing materials, tools, familiarizing with technical documentation, preparing and cleaning the workplace, handing over finished products, etc.) provided for by technology and labor organization, and does not include the time spent on the road from the checkpoint to the workplace, changing clothes and washing before and after the end of the working day, and lunch break.
In conditions of continuous production, the acceptance and transfer of shifts is the responsibility of shift personnel, provided for by the instructions, norms and rules in force in organizations. The acceptance and handover of a shift is due to the need for the employee accepting the shift to familiarize himself with the operational documentation, the condition of the equipment and the progress of the technological process, to accept oral and written information from the employee handing over the shift to continue conducting the technological process and servicing the equipment. The specific duration of shift reception and transfer time depends on the complexity of the technology and equipment.
At the same time, taking into account that Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives the parties to labor relations the right to determine the principles of regulation of working time themselves, the issues of including the above time periods in working hours must be resolved by them independently. The decision made is enshrined in the internal labor regulations approved in accordance with the established procedure.
Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week in either a five or six day work week. This is the standard working time established by law (Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), which must be observed by the parties to the employment contract (employee and employer) throughout the Russian Federation, regardless of the organizational and legal form of the enterprise, type of work, and length of the working week. Normal working hours are a general rule and apply if the work is performed under normal working conditions and the persons performing it do not need special labor protection measures; applies to physical and mental workers. Normal working hours must be of such duration as to preserve the ability to live and work. Its duration depends on the level of development of production forces.
It should also be taken into account that the normal working hours established by Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation apply equally to both permanent and temporary seasonal workers, and to employees hired for the duration of certain work (Articles 58, 59 Labor Code of the Russian Federation), etc.
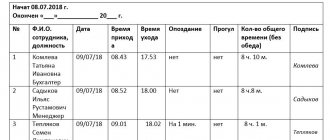
The legislator provides for the obligation of the employer to keep records of the time actually worked by each employee. The main document confirming such accounting is a working time sheet, which reflects all work: daytime, evening, night hours of work, hours of work on weekends and holidays, overtime hours of work, hours of reduced work against the established duration of the working day in cases provided for legislation, downtime through no fault of the employee, etc.
It is necessary to distinguish between the duration of working hours during the day and the norms of working hours. The length of the working week is calculated from seven hours of the working day; the length of working time during the day may vary.
In addition to normal working hours, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates issues of reduced working hours, part-time work, irregular working hours, overtime, etc.
Part-time work
The need to reduce working hours may be due to family circumstances. Most often, the initiator of such a decision is the employee himself. The head of the enterprise cannot refuse the following categories of employees:
- pregnant women;
- guardians raising a disabled child;
- the need to change your work schedule may be due to a serious illness of a close relative.
The employee receives a salary based on the hours worked. A person chooses the schedule according to which he wants to work. The approval of the employer is required for its approval. Part-time work can be established by the employer himself.
This need may be associated with the re-equipment of production. The administration may introduce a part-time working week due to the difficult financial situation. A part-time work regime introduced at the initiative of the employer cannot last more than 6 months. At the same time, the employee’s income decreases sharply. In the long term, the company risks losing qualified specialists who will be forced to look for another job.