Working hours according to the Labor Code are an ambiguous concept. According to the legislative norms in force in the Russian Federation, it includes basic elements that can be presented in various variations. The employer, having the basic requirements of labor legislation, uses local acts to form a regime, as a result of which two established formats appear - within a separate organization and for specific staff units. The first is included in the collective agreement, the second is prescribed in the employment contract with the individual contractor. This material presents the basic concepts and features of establishing a working regime within the framework of current legislation.
Working hours according to the labor code
What does working time consist of?
Legal acts that are related to the subject of the working regime reveal the following concepts that make up its elements:
- The number of working days an employee works per week.
- Duration of work shifts and their rotation within the work schedule.
- Start and completion of work within one shift.
- The duration of the break, its beginning and end within the shift.
- Other indicators that may affect working hours.
The labor regime is formed from individual components prescribed in the Code
If we consider the operating regime in more detail, it is established within the framework of Art. 100 Labor Code:
- According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, an employee can be present during the performance of official duties in the format of a five-day week with two days off, or a six-day week with one day off. Options with a sliding weekend schedule are possible.
- The content of the internal regulations and shift schedule also records the duration of the working day, as well as its time period, the specifics of establishing a break, and the total number of shifts during the day.
- The change of working days and days off is also prescribed in the collective agreement or internal documents of the enterprise.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation Article 100. Working hours
Local acts on the labor regime and its features must comply with the Labor Code. You also need to ensure that they are drawn up in accordance with other federal laws governing labor relations, as well as collective agreements adopted at the level of a particular organization.
The concept of working hours
Working hours - distribution of working hours during a specific calendar period - day, week, year.
The working hours must provide (Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- length of the working week (five-day with two days off, six-day with one day off, working week with days off on a rotating schedule, part-time work week);
- work with irregular working hours for certain categories of workers;
- duration of daily work (shift), start and end times of work, time of breaks in work, number of shifts per day, alternation of working and non-working days, which are established by a collective agreement or the internal labor regulations of the organization in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws, and a collective agreement , agreements.
Features of the working hours and rest time for transport, communications and other workers with a special nature of work are determined in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Thus, the working time schedule is its distribution per day, week, beginning and end of work. The regime also includes the structure of the week, shift schedules, as well as intra-shift and inter-shift breaks in work, the beginning and end of the working day, shift, week. The regime also includes a shift work method, flexible, rotating schedules.
A working day, a working shift and a working week are measures of working time that also reflect its mode.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation distinguishes the following working hours:
- normal operating mode (single shift) - Art. 100 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- irregular working hours (special) - art. 101 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- flexible working time regime - Art. 102 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- shift work mode - art. 103 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- mode of working time divided into parts (fragmented working day) - Art. 105 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
A working day is the working time established by law during the day. The duration of daily work, its beginning and end, breaks during the working day are provided for by the internal labor regulations, and in the case of shift work - also by shift schedules, including the rotation method.
Shift work is work in two, three or four shifts. Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the procedure for its introduction. Working two shifts in a row is prohibited.
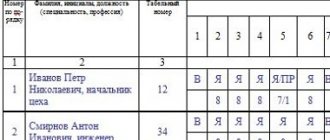
A work shift is the duration of working hours established by the shift schedule for a group of workers and its alternation with other shifts during the week or month. Shift schedules are drawn up by the employer taking into account the opinion of the trade union committee and are attached to the collective agreement; as a rule, they are brought to the attention of employees no later than a month before they come into effect.
Shift schedules can be: two shifts, three shifts, and in continuously operating production - four shifts, when three shifts are working and the fourth is resting. The duration of the shifts according to the schedule is set so that each employee, during a calendar week or month, works the standard working hours (normal or shortened) established for him. The duration of the night shift is set by a schedule shorter than the day and evening shifts by 1 hour. When working in shifts, shifts with night working hours (from 10 pm to 6 am) do not include workers who are not allowed to work at night: pregnant women and workers under 18 years of age. Women with children under 3 years of age may be involved with their written consent (Article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Disabled people may be involved in night work only if this work is not prohibited for them by medical recommendations and with their written consent.
Working week – duration and distribution of working time during a calendar week. The length of a working week can be
- normal,
- abbreviated
- part-time (for example, 2-3 days a week).
The structure of a working week can be:
- five days with two days off in a row;
- six days with one day off, which is determined by the organizations themselves.
When working in flexible working hours, the beginning, end or total duration of the working day (shift) is determined by agreement of the parties. The employer ensures that the employee works the total number of working hours during the relevant accounting periods (working day, week, month and others).
Sliding or flexible work schedules are established in the interests of the employee by agreement of the parties to the employment contract. Such schedules can be established by a collective agreement or internal regulations for certain categories of employees (pregnant women, women with children of preschool and primary school age, disabled people). In the middle of the day, an employee with such a schedule is required to be at work (this is the so-called fixed time, as opposed to variable time). The beginning and end of work are determined by agreement of the parties.
A split working day is possible for some workers, for example for livestock breeders (hours of cleaning, feeding animals, milking cows - the rest of the time is free from work) or for drivers of buses, trolleybuses, trams (the day can be divided according to peak hours on public transport) . But even under this regime, the employee must work the required number of working hours per week or month.
Such a division of the working day into parts is allowed by the employer on the basis of a local regulatory act adopted by him taking into account the opinion of the trade union committee of the organization (Article 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The rotational method of work is the work of a rotational shift (shift) in an area significantly remote from the permanent place of residence (20-40 km). The shift (shift) goes out for 2–3 weeks, and sometimes more, lives in a rotation camp (for example, at the oil fields), and the work shift can last 12 hours straight every day. The shift time, including both working time and rest time, can be up to 1 month. A shift cannot leave until another shift arrives. Then she rests at her place of residence for up to 1 month. Travel time to and from the shift is also included in the shift. In exceptional cases, taking into account the opinion of the trade union committee, the duration of the shift can be increased to three months (Article 299 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Minor workers, pregnant women and women with children under three years of age are not involved in this work (Article 298 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Special working hours
Irregular working hours , according to Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is a special work regime, according to which individual employees may, by order of the employer, if necessary, be occasionally involved in the performance of their labor functions outside the normal working hours. The list of positions of employees with irregular working hours is established by a collective agreement, agreement or internal labor regulations of the organization (the employee agrees to the establishment of an irregular working day for him upon entering work).
Difference from overtime work:
- overtime - paid at an increased rate depending on the number of hours worked in excess of the norm;
- work on irregular working hours is compensated to the employee by additional leave (provided regardless of the number of hours worked in excess of normal working hours. The right to it arises even if the employee was not involved in work outside the established working hours).
The use of irregular working hours is allowed only from time to time when there is a production need for it. If such work is systematic or permanent, this will indicate a violation of Art. 101 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Employees may be involved in work with irregular working hours only to perform their labor functions, which they must perform under an employment contract. An employee cannot be obligated to perform any other types of work, including outside the normal working hours.
Irregular working hours may apply:
- for management, technical and business personnel;
- workers whose work cannot be accurately recorded in time;
- workers who allocate time at their own discretion;
- persons whose working time, due to the nature of the work, is divided into parts of indefinite duration.
0
5
Types of operating modes
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, the following work formats can be used:
- A work regime consisting of a sequence of shifts - the schedule may include two, three, four shifts in a row. Introduced in conditions of increased business activity. The employee must learn about the establishment of a shift schedule no later than 30 days before the start of this format. It is spelled out in the collective agreement and, as a rule, takes into account the opinion of employees represented by a representative body.
- A work regime with a flexible schedule, when the only performance criterion is the total number of working hours in a month, year or calendar day (these indicators refer to so-called accounting periods).
- Work regime with the division of the day into several parts according to the intensity of workload.
The law reveals aspects related to the formation of a working regime
There is also the concept of irregular working hours, when some workers can be periodically involved in performing work if there is a need for this on the part of management. Moreover, the length of the working day will be outside the normal range. The list of those positions that have similar characteristics can be found in the text of the collective agreement, agreement or in the rules by which the internal work schedule of the company is organized.
Irregular working hours
The mode refers to a special mode of operation, which is regulated by Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and involves the performance of labor functions by an employee outside the duration of the current working time schedule. The main distinctive feature of this work mode is that the employee, subject to the general work mode, can be engaged by the employer to carry out his work duties before the start or at the end of the work shift.
It is important to note that working with irregular working hours involves the employee performing, in additional time, only his job duties as specified in the employment contract. The employer does not have the right to require the employee to perform work that does not comply with the employment contract (Article 60 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The list of positions that may correspond to irregular working hours is determined by a collective agreement or the internal labor regulations of the enterprise. The irregular working hours regime can be applied to persons:
- managerial, administrative, business or technical personnel;
- working without working hours;
- working according to a schedule with splitting working hours into parts of indefinite duration.
An employee working on an established irregular working day may be involved in performing his work outside of the schedule without his consent only occasionally, thereby excluding systematic overtime. At the same time, the employee does not have the right to refuse to perform such work outside the established standard working hours. Employees whose working hours are irregular receive annual paid leave (at least 3 calendar days), while they use weekends and holidays on a general basis. Also, on the basis of Art. 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, overtime beyond the normal working hours can be compensated with the written consent of the employee himself, as overtime work.
Work week
In the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the working week is the main measure of working time. This term appeared back in the Soviet years, when the five-day week was introduced everywhere.
Currently, laws in the Russian Federation do not unambiguously interpret the number of hours in a work week, but they are introducing a limit on the maximum number of hours within the framework of the industry-wide standard.
With this standard, an employee with two days off works for five days, and is free for rest and personal time on Saturday and Sunday. There is a law in force that was adopted in 1991 - this norm is additionally prescribed in the Labor Code and the Labor Code.
The specified norm, equal to 40 hours, is relevant for all workers in the Russian Federation, including permanent, temporary and seasonal labor. It also does not depend on the schedule.
The six-day work week is established in those areas where the use of a five-day working week reduces labor efficiency. In particular, they can work for 6 days in a row in communications, trade, transport companies, and 24-hour pharmacies.
It is not possible to work within the standard 5-day period in every industry.
The law only limits the length of the working day under this regime - it cannot be more than seven hours if the work week is standardized at 40 hours, does not exceed six hours if the work schedule is 36 hours, and does not exceed four hours if the work schedule is standardized based on a 24-hour working week.
Under certain circumstances, the employer is obliged to approve not 40-hour work weeks in the work schedule, but 32- and 36-hour ones.
In order to comply with restrictions in case of deviations from the standard scheme, the employer uses shift work and prescribes a certain number of working hours in the accounting period.
The maximum long period for which the average number of hours should not exceed standard indicators, within the framework of the Labor Code, is taken at the rate of 12 calendar months.
The regime is prescribed for each full-time employee, regardless of status
Duration of daily work (shift) for certain categories of workers
The legislator has determined the maximum amount of time that certain categories of employed people can spend at work.
Young people aged 15 to 16 years and from 16 to 18 years old cannot have a work shift of more than 5 and 7 hours, respectively. Teenagers who are students, as well as those whose age is between 14 and 16 years old - no more than 2.5 hours, and students whose age is 16-18 years old - no more than 4 hours. The duration of the shift for disabled people is determined by a medical report.
The harmfulness or danger of work is a reason to reduce working hours to 8 hours per shift, with 36 working hours per week, and to 6 hours per shift, with 30 working hours per week.
Certain features also exist regarding the work of creative teams. Such persons carry out their work under the conditions established by local acts, collective and labor agreements.
Restrictions that apply to the operating mode
There is a difference between the concepts of “reduced” work time and “part-time” working mode. Shortened working hours are being introduced for a certain part of employees whose activities fall under preferential categories. It is spelled out in the Code and standardized for each type.
Legislation introduces shortened working weeks for certain categories of persons.
Table 1. Working week - exceptions to the rule
| Category | Number of working hours |
| Child under 16 years of age | 24 hours a week |
| Citizen of the Russian Federation who has reached the age of 16-18 years | 35 hours per week |
| Disabled people of groups 1 and 2 | They also work no more than 35 hours a week |
| Workers in hazardous industries | Limit – 36 hours |
Harmful production conditions lead to a reduction in work
Thus, a reduction in working hours is the norm for those citizens who, due to age, health conditions and special working conditions, cannot work within the normal 40-hour regime. According to the requirements of the law, the employer shortens the working week for such persons.
As for the approval of part-time work in an organization, there may be enough reasons for this. Moreover, this regime depends entirely on the agreement of the parties.
Regardless of what kind of regime is present at the workplace, an entry about shortened and part-time regimes is not made in the work book.
Part-time work is established by agreement
In the table below you can see the comparative characteristics.
Table 2. Comparative analysis of formats
| Criterion | Abbreviated | Incomplete |
| Type of workers | 1. A child under 16 years of age. 2. A citizen of the Russian Federation who has reached the age of 16-18 years. 3. Disabled people of groups 1 and 2. 4. Workers in hazardous industries. | All types of employees, including persons who have the right to work on a short-time basis. |
| Employer's obligation | If an employee’s activities fall under a legislative provision that obliges the use of a shortened working week, then preventing this is not permitted on a legislative basis. | Similar working conditions are formed at the request of any of the parties (boss, performer), on a mutual basis. There are also exceptions in this category when it is not possible to refuse to implement part-time work and is considered a gross violation of the Code. This applies to women bearing children, guardians and trustees who have taken care of persons under the age of 14, or children with disabilities who have not reached the age of majority. This format of work cannot be denied to employees who care for people who need special care for health reasons and who have a specialist’s opinion in their hands. |
| Number of days in a working week and other indicators | They are prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other legislative acts. | Various options are possible by agreement of the parties with varying durations. Participants in labor relations can agree on a part-time workday, fit the workweek into this format, or use a combination of these elements. |
| When and for how long is it relevant? | It begins from the moment an employee is hired and continues until the end of the employment agreement (if we are talking about minors, then this format is relevant until they reach the age of 18). | They are introduced at the stage of signing the agreement with the employee, and can also be introduced later at the initiative of either party. The period is specified in the text. There is a six-month limit when management takes the initiative. |
| Formal basis | Code on relations between employees and managers, and other rules of law that reveal aspects of their interaction. Sometimes the basis is a labor agreement or a collective agreement with the rules enshrined in it that apply at a particular enterprise. | The basis is an additional agreement, which can be found in the annex to the employment agreement; it is drawn up after the corresponding order is issued. |
| Payments | Wages are paid in the amount corresponding to full employment. Workers who have not received the status of adult citizens can count on wages taking into account a reduced work schedule. | Wages are paid within the hours worked according to the schedule or in the context of the work performed. |
Pregnant women have the right to a part-time work schedule
Types of working hours
The provisions of the Labor Code define the types of working time used:
- usual - depending on the system by which work time is recorded. Most often it is reflected in a 5 or 6-day work week.
- Irregular – established for certain categories of workers, by order of the manager. This type cannot be installed on a permanent basis.
- Flexible - allowed in individual teams and departments, on the basis of self-regulation. The flexible working time regime should not contradict the legislative principles on the total number of hours worked. Flexible working hours may be temporary.
- Shift work is a working time regime in which employees can work in several shifts and in an equal number of hours.
- Shift work is a regime and recording of working hours of a special type, which is typical for performing work outside the place of primary residence, which means it is impossible to return to the place of residence every day.
- Divisible – characteristic of work with different types of intensity.
Part-time working hours can be established at the request of the employee. Pregnant women, parents of children (under 14 years of age) and persons caring for sick relatives can petition management and ask for a part-time working schedule.
The introduction of a part-time working regime falls within the competence of the company’s management, which is formalized by order. An order to change working hours, based on an exclusive decision of management, may have signs of a change in significant working conditions.
Incomplete workflow schedule
There are several possibilities for using the partial chart format:
- The first of these concerns part-time shift work with a daily schedule. For a five-day shift from 9.00 to 18.00, this regime means that with the same number of days of the working week, the shift may become shorter. For example, an employee must be at work not the standard number of hours, but from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. every working day, etc.
- It is also possible to reduce working days in the work week while maintaining the standard schedule. An example would be the introduction of a 3-day workday instead of a 5-day format while maintaining an eight-hour working day.
- The third option presents a synthesis of the first and second, implemented by agreement between the manager and the employee.
The employee notifies his superiors of his desire to follow the new regime by means of a statement
Documentation, when the initiative comes from a team member, consists of drawing up the text of the statement, signing and submitting it to management for consideration. It indicates that they would like to go to a part-time schedule - a week, a working day, or start working duties, reducing both points. The application also contains information about how many hours a day the employee would like to go to work (or days a week).
Sample application for transfer to part-time work
At the next stage, management draws up an additional agreement, which contains the conditions agreed upon verbally with the employee. Here the above parameters are specifically stated, as well as the period during which this agreement is valid, and the terms of payment, which will directly depend on the amount of work or hours spent at the workplace.
The additional agreement to the contract is valid for a certain period of time
When the additional agreement ceases to be relevant, the employee will automatically switch to full-time work. If there is no specific date in the text of the document, such a transition can take place at the initiative of one party and by mutual agreement with the manager at any time.
The specified format of part-time work does not affect the duration and payment of vacation, which is provided every year, the accrual of work experience, and payment of sick leave, including cases of pregnancy and childbirth.
Payment depends on the format of the working mode
Example
The employee was hired and was promised 20 thousand rubles for a month of work. A standard work schedule of 40 hours was established. From September 1 last year, the employee began to work part-time, with a 25-hour work week. According to the new schedule, he is on duty during the day for 5 years. Thus, in September the salary will be 12.5 thousand rubles.
The management's initiative concerns only the cases presented in the text of the Labor Code. In particular, Article 74 describes cases of organizational changes, technological changes in the composition of work, which may be followed by the dismissal of workers. In practice, this happens when new equipment is introduced, a production line technology is changed, when the staff turns out to be too bloated and unclaimed units have to be cut.
There must be a compelling reason for downsizing
All specified changes must be justified. For example, financial situation may not be an obvious reason for establishing part-time work. But if the financial situation forces us to make adjustments to the production process and pay increased attention to commissioning, it will inevitably lead to a reduction in units of labor. Each employee must have access to official information confirming temporary factors in the decline in business activity of the enterprise.
To save jobs, a corresponding order is issued in any form. For such a document there is no clear form and strict sequence of sections. Its content remains at the discretion of management, which can reduce the working hours and use the new format for a limited time - up to six months.
Employees must be notified of changes to work schedules
Employees must receive timely information about all changes in the terms of employment agreements in the form of notifications indicating specific reasons, or personal familiarization with the order. The deadline for obtaining information is at least 2 months before the expected date of transition to part-time work.
In the case of individual notifications in writing, employees have more time to review. But at the same time, their consent to implement part-time work and/or a week is not required - confirmation of receipt of information and a personal signature is sufficient for this. Refusal requires personal written participation - the employee must prepare a text in which he indicates the reasons why he cannot accept the new routine.
An employee may refuse to participate in schedule changes by handwriting the document
Table 2. Information on the basis of which the employee receives notification of transfer to a new labor regime
| Information | Approximate content |
| 1. Validity period of the new operating mode. 2. The reasons that prompted management to come to the decision on part-time work. 3. The text records which elements are classified as incomplete - a day, a week, or both (in a mixed version). 4. Terms of payment of wages. 5. The text contains information about maintaining the benefits of full-time work during a part-time period. 6. Consequences of refusing to go to work part-time. | When setting up a new production line, a partial shift schedule is being introduced and will last through November of this year. At work - the presence of the following regime: a five-day working day (Mon-Fri), the duration of the working day is 4 hours, lunch is 1 hour. Rights regarding the provision of vacation, sick leave and length of service are not violated. Wages are paid according to hours worked. The decision must be confirmed in a written response. If the answer is negative, the employment contract will be terminated in accordance with the requirements of labor legislation (format by agreement of the parties) in the absence of other vacant positions. |
Employees do not always agree with the new work regime
What is working time
The basic state law establishes the right of citizens to work, as well as the specifics of working hours and rest. At the same time, this right involves limiting the time that applies to a worker, as well as allowing workers to use weekends and holidays for rest.
The definition of “working hours” is reflected in Art. 91 of the Labor Code, it means the period of time during which the employee has the authority to perform labor duties determined by the internal labor regulations and the employment contract that forms the basis of the legal relationship that has arisen. Such time may also include other time periods that are established as such by legislative norms.
Other working periods may include the time employees are idle, the time of a paid break provided during work, the period of business trips, rest periods between shifts, etc.
Legislative regulation of working time aims to achieve:
- productive use of the time period for carrying out work;
- protecting the health and performance of workers hired under employment contracts;
- increasing the professionalism of performers engaged in joint hired labor.
Night duty of employees
With a certain schedule, employees are forced to work not only during the day, but also in the dark, which is usually called night mode - the period between 10 pm and 6 am is special, since at this time the body must rest and not cope with work responsibilities.
Night work is also regulated by the Code
Employees are subject to certain conditions that apply to them if they work at night:
- At night a person has the right to work 1 hour less.
- A night shift becomes equivalent to a day shift if the performance of work duties at night is necessary for the functioning of the enterprise, as well as with a shift schedule and a six-day work week.
- Pregnant women and minors cannot go to work at night (with the exception of the creative and entertainment industries).
- Some categories of employees can go to work at night if they have written consent with them. Such employees include the category of women raising a child 0-3 years old, persons with disabilities who will not be harmed by night work. In addition, employees who are parents of disabled children, caring for sick relatives, single mothers and single fathers with a child under five years old can submit a request for night duty on their own initiative. The application will need to be accompanied by a doctor’s opinion stating that the potential employee has no contraindications for staying awake at night. This is especially true for disabled people who are registered with doctors - they are required to hand over to the employer all documents from which one can clearly judge their current health status.
- The work of creative teams and mass media teams is regulated by agreement within the team, while the need to work at night is approved by a special procedure - passing a triple commission.
In order to start working at night, you need to notify management of your desire.
The consent to work at night usually states:
- Information about the manager/management team.
- Information about the employee.
- Actually agree with the night operating mode.
- They put a date and signature.
Next, the application goes to the manager and is reviewed by him personally, or by employees of the HR department, he forms the appropriate order.
Not everyone has the right to work at night
The Labor Code does not allow working more than 7-8 hours - this is the standard working time at night. Specifically, the formation of the night shift range occurs in accordance with working conditions and basic benefits associated with work activity.
As part of the work schedule, an employee may be partially affected by night shifts - for example, if he works in the evening and leaves work at one in the morning. In this case we are talking about the so-called partial night time.
If an employee was on shift in the evening and turned it in at 4 am, then the employee who replaced him will no longer be assigned night duty. A night shift is considered when at least half of the time was spent in the dark.
The shift preceding the night work period is called the evening shift. For an hour of work at night, the premium will be 20%.
Night work is an additional burden on the body
In general, the duration of night working hours is contained in local documents, collective and individual acts and agreements. You can find the following elements in them:
- The beginning and end of the night working period, as well as the duration of the working day that follows the night shift.
- Payment for night time.
- Responsibilities that must be performed when working at night.
A reduction in the night work period is not implied for those citizens who meet the following categories:
- Having a reduced schedule during the day.
- Initially hired as part of the night regime - watchman, security guard, etc.
For all other employees who, due to their duties, do not have to go to work at night, the Code prescribes a certain number of night shifts - they are prohibited from visiting the workplace at night for more than 2 days in a row.
Night wage units are higher than day ones
How are night shifts paid?
Staying at the workplace at night is subject to additional monetary payments. Government surcharges in the form of various coefficients have floating values. The Labor Code also does not specifically indicate the amount of the premium. Partial recommendations for payment for night work can be found in the table.
Table 3. Night work - how it is encouraged
| Field/specialties | Promotion | Appointed by whom/what |
| 1. Military. 2. Fire department employees. 3. Watchmen, security guards. | 35% of payment for a daily unit of labor | Decree of the State Customs Committee of the USSR of 1990 |
| Medical workers | 50% of payment for a daily unit of labor | By order of the Ministry of Education - 1999 |
| 1. GUFSIN employees. 2. Employees of internal affairs bodies. | 35% of payment for a daily unit of labor | By order of the Ministry of Justice in 2000 |
Some employees are entitled to benefits for night work
In general, by studying statistical and reporting data in the business environment, we can conclude that each unit of labor will be paid more for working at night, with the additional amount ranging from twenty to forty percent. At the level of the Government of the Russian Federation, a minimum bonus for such work has been approved in the amount of 20 percent.
Overtime mode
Overtime work may be performed outside the basic schedule. Of course, there must be objective reasons for this. The manager’s mere desire to involve a person in performing work overtime is clearly not enough. The classic case when there is a need for increased loads is associated with the onset of emergencies, industrial emergencies, problems with water, gas and heat supply at the enterprise, interruptions in transport, communications, and electricity supply.
In the situations presented above, the employee’s signature and consent are not required. The work is being carried out under emergency conditions or martial law, so measures to resuscitate the enterprise’s activities will be required from all employees, without exception.
Overtime activities have time limits
If the situation is less urgent, the employee must personally sign a document expressing his desire to work overtime. Moreover, he has every right to refuse to work under such conditions.
It is prohibited to involve pregnant women and minors, as well as disabled people, women with children under 3 years old in overtime work without appropriate consent and a medical certificate allowing them to attend work on overtime conditions.
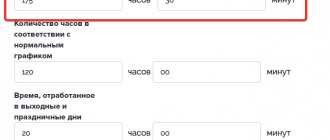
For overtime work, no more than 120 units of working time are allowed, which are cumulatively added up over one year. An additional legal restriction is that overtime work should not be performed for more than two days in a row in the amount of 4 hours. All hours of work exceeding the normal level are strictly taken into account by the employer. Payment points are clearly presented in the text of the Labor Code. If the first 2 hours are paid at one and a half equivalent, then the next 2 hours of overtime are paid at double the equivalent. Also, allowances are regulated by local production acts.
Reducing overtime pay is not permitted. In this case, the employee chooses what to do with this compensation - receive a payment, or subsequently exchange overtime hours for additional days of rest.
Opening hours on weekends
There are not many holidays in the Russian Federation during which workers stay at home and rest. They are associated with the New Year holidays, men's and women's international holidays, May holidays and days of unity and independence. Weekends can be either Saturday and Sunday, or one Sunday with a six-day work week. Locally, Monday may also be designated as a day off. There is no clear regulation that an employee has two days off in a row, but such a recommendation can be traced at the legislative level.
The legislation of the Russian Federation establishes the format of holidays and weekends
Working on holidays and weekends means violating the procedure established by the legislation of the Russian Federation. But here there are exceptions to the rule:
- Emergency prevention, industrial accidents and/or liquidation of consequences.
- Under martial law.
- Prevention of property damage in an organization or at the state level, as well as in the event of the risk and occurrence of accidents.
Work on weekends is paid at least 2 times higher than the regular tariff rates within the shift. In other words, piecework workers will receive double payment for the order, hourly employees will receive double payment for the period worked, and for salaried persons a remuneration is expected in an amount equivalent to the payment of one working day.
Instead of money, you can use the benefit differently and ask for future compensation for work on well-deserved days of rest in the form of additional vacation periods. In this case, payment for time off will not be made.
The above standards do not apply to certain areas related to entertainment and spectacle - representatives of creative professions, including workers in cinema, circus shows, drama and opera houses, receive payment in accordance with local acts signed within the team.
Breaks during working hours
Of the breaks accepted in the organization, the following categories can be distinguished:
- Pauses for eating and rest from work duties.
- Pauses for feeding infants.
Work breaks are subject to clear systematization and payment
If the child has not reached the age of 1.5 years, feeding the child is allowed at least once every 3 hours. The break is at least half an hour. Such breaks are included in working hours and are subject to recording and subsequent payment. The employee herself has the right to add the indicated periods to the lunch period, transfer them in total to the end or beginning of the working day, varying the regime at her own request.
A manager has no right to deny a woman the right to breastfeed, just as she has no right to refuse employees to go to lunch and spend their breaks completely with personal matters. In the case when management insists on working during lunch, in fact we are talking about free labor, since this time is not included in the tariff schedule.
If such cases with bans on breaks are observed in the organization, you must immediately contact the labor inspectorate with a statement. If the outcome is positive, the employer will face not only a court hearing and payment of a fine, but also compensation in the form of double salary in favor of each representative of the work team.