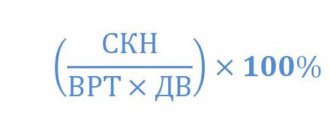Wages are the main type of income for most citizens, and for many even the only one. Therefore, this is a very important economic factor and a serious indicator not only of the cost of labor, but also of the country’s financial resource. In addition, this is the most real motivation for an employee’s work, a regulator of supply and demand in the labor market and a sign of professional status.
Let's consider the difference between the two main types of wages - real and nominal.
How is real wage ?
Scope of this concept
The types of wages are not specified in the Labor and Tax Codes, they are not distinguished in accounting, and are not used in reporting and working documentation. These terms are general economic terms and also relate to statistical information.
The general definition of wages relates to the reward for work. Looking at it from different points of view, one can define salary as:
- compensation for labor in cash;
- part of the total product in financial equivalent, which becomes the property of the worker depending on the quantity and quality of his labor costs;
- the cost of labor resources used in the production process;
- part of the expenses of a manufacturer or entrepreneur intended to pay for hired labor.
The state guarantees workers wages not lower than the minimum allowable amount established by law ( minimum wage ).
What is the minimum wage (minimum wage) ?
Factors of influence
In conclusion, I would like to mention what affects wages in general. For convenience, we present the diagram:
The diagram clearly gives an idea of how nominal wages differ from real wages and what factors influence them:
- Fixed wage rate.
- Price level. The higher the prices, the lower the purchasing power of the population and the wages.
- Number of taxes and tax rates. The more deductions are made from an employee’s salary, the less money he has left to meet his needs, i.e. the wages decrease.
- In addition to taxes, other deductions may be made from employee salaries (union dues, etc.), which negatively affects the wages.
Nominal salary
The nominal value of wages denotes its numerical expression. This is the amount of money that is intended to be paid for the work of an employee in a given period.
Properties of nominal wages:
- reflected in special documents in the form of digital values (in the staffing table, payroll, etc.);
- has an absolute expression;
- includes not only the amount given to the employee in person, but also mandatory deductions in the form of taxes and contributions to social funds.
REFERENCE! The amount exempt from required deductions, which the employee receives as a result, is called “net” wages.
Forms of nominal salary
- Remuneration accrued specifically for work, depending on the time spent, the amount of work performed and its quality characteristics.
- Payment based on labor results:
- by the number of its products (piecework);
- at established rates;
- according to time worked.
- Compensation for special working conditions:
- additional payments for harmfulness and severity;
- overtime;
- business trips;
- overpayment for night work;
- bonuses for leadership work;
- payment for forced absences and/or downtime, etc.
- Payments for non-working hours:
- vacation pay;
- sick leave;
- additional payments provided for by internal regulations, for example, health benefits, etc.
- Incentive payments:
- bonuses;
- bonuses;
- monetary awards;
- 13 salary, etc.
How to register non-payment of bonus to an employee ?
The concept of nominal wages
Nominal wage is the payment for the employee’s labor activity without taking into account taxes and fees, accrued insurance premiums and expenses for clothing and food. According to another definition, this is the totality of all accruals in favor of the employee for a certain time period or for the amount of work performed. This is the amount that is specified in the employment contract concluded with the employee, that is, before personal income tax is deducted from it.
The nominal salary includes:
- Salary or tariff rate.
- Premium.
- Incentive bonuses and payments.
- Additional payment for difficult working conditions that deviate from normal (for night shifts, working overtime or on holidays).
- One-time additional payments for work performed.
The average nominal salary is determined for a certain period worked by employees: quarter, half-year or year. Typically, the term “average nominal salary” is used only at the state level in official documents; it is not used in ordinary organizations.
Nominal wages are usually expressed in national currency. But within the framework of international studies, it can be reduced to a single currency, which will make the difference between incomes more clear.
Real wages
The money received by a hired worker is the source of his existence. He buys clothes and food with it, spends it on travel, spends it on his family, and, if necessary, on treatment, and also provides for his entertainment and development. Therefore, the amount of wages should reflect the volume of values that can be purchased for it at a given time stage. The purchasing power of the amount received in hand is the real wage .
If prices for goods and services were constant, then there would be no need to distinguish between the concepts of nominal and real wages: a single figure would reflect the well-being of each individual worker, since it would be possible to determine exactly what he could buy with it.
However, the market situation with its constantly changing conditions makes the discrepancy between real and nominal wages inevitable. At different times and under different circumstances, you can live completely differently on the same amount.
What affects real wages:
- market price fluctuations;
- inflation;
- the relationship between supply and demand for goods and services in the consumer market;
- amounts by which the nominal salary is necessarily reduced (taxes, fees, deductions).
Inflation processes for the year
The rate of inflation is determined over annual and monthly periods. There are publications of annual size and broken down by month. The calculation of statistics is based on the consumer price index. The index is calculated as the ratio of the values of the current consumer basket to the base year. Before the start of the annual period, Rosstat makes a forecast that does not always coincide with the result.
| Year | Inflation rate |
| 2016 | 5.4% (forecast 8-8.5%) |
| 2015 | 12.9% (forecast 8%) |
| 2014 | 11.36% (forecast 5.5-6%) |
| 2013 | 6.45% (forecast 5-6%) |
To determine the decrease in real income for the year while nominal wages remain unchanged, the formula is used:
D real = D nominal / (1 + I), where:
- D real – real income;
- D nominal – nominal income;
- I is the amount of annual inflation growth. The impact of inflation on monthly income is calculated in a similar manner.
An example of the impact of inflation on real wages
Employee M. received wages for January 2015 and January 2016 in the amount of 28,000 rubles. Let's calculate the change in real wages due to inflation processes. To simplify the calculation, taxation is not taken into account.
- Let's determine the amount of decrease in real wages for 2015: Z2015 = 28,000 / 1 + 0.129 = 24,800.71 rubles.
- Let us determine the decrease in real wages for 2015: R2015 = 28,000 – 24,800, 71 = 3,199.29 rubles.
- Conclusion: The real cost of wages for employee M., with an equal nominal value, decreased in 2015 by 3,199.29 rubles.
Real wage index
The value characterizing changes in real wages in a particular time period is called the wage index . It is calculated by dividing the actual wage index at par by the consumer price index . The latter is determined by comparing the base price of the consumer basket and its value at the specific time under study. The consumer basket is a set of goods and services established by the state that provides the necessary minimum for citizens.
FOR EXAMPLE. Let's take the nominal salary of 2015 as 100%. Let's say that on average in 2021 it grew by 15%. Then the nominal wage index in 2021 will be equal to 115%. At the same time, the cost of the consumer basket increased by 20%, that is, the consumer price index is 120%. Then the RRP index for the current year compared to the previous year, taken as the base, will be approximately 96%. This means that the purchasing power of citizens has fallen somewhat.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! Indices of nominal and real wages, along with average monthly “nominal” indicators, are components of statistical information that must be provided by all member countries of the Eurasian Union to the Eurasian Economic Commission, according to Decision No. 175, adopted by the Board of this commission in Moscow on December 29, 2015.
Difference and relationship
Similarities
Both nominal and real wages represent the cost of labor power. Both types of wages will have a monetary value and will be calculated in the currency in which the employer makes payments to its employees. Both of these types of salaries cannot have the same amount, since contributions to the state are made at the expense of the employer, and accordingly, he includes these expenses in the wages of his employees.
Difference
How do real wages differ from nominal wages? The fact that the real salary is strictly tied to the existing prices of consumer goods and services, and the nominal one is just a certain amount earned by a specialist without taking into account inflation and taxes, the size of which does not reflect the real economic situation. That is, the first is formed in the form of a set of goods that can be purchased with the amount received, and the second is expressed in the cost of a certain type of work performed or hours worked.
Connection
A simple Phillips curve
In order for a nominal salary to turn into a real one, all tax and pension contributions made by the employer must be subtracted from its value. Accordingly, the amount of nominal wages can often be calculated by the employer based on its own costs of doing business. Since the business owner is forced to make considerable tax contributions to the state, it is quite understandable that he will strive to save on the cost of paying employees. At the same time, the question of whether the employee can comfortably live on the money that is actually paid to him is unlikely to worry the employer.
Codependence of nominal and real wages
It seems that nominal wages always directly reflect real wages. However, this is not the case in cases of economic crisis and currency depreciation, when the increase in the amount of accrued wages “does not keep pace” with the rise in prices for goods and services. For the same amount as yesterday, the consumer cannot afford to purchase the same volume of goods and services. In such a situation, the process of inflation .
NOTE! The experience of developed countries reflects the difference between real and nominal wages over a smaller base time frame. The amount accrued per working hour and its relationship with the number of labor results created during the same time are taken into account.
In Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation talks about the employer’s obligation to promptly and fully provide remuneration to employees for their work. In addition, the employer is required to strive to increase its actual content (Article 134 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Letter from Rostrud No. 1073-6-1 dated April 19, 2010).
What determines the amount of wages?
The amount of wages depends on many factors that also affect production itself. These include:
- Supply and demand. The higher the demand for a certain profession, the higher the chance of receiving an increased salary. Specialists in rare or irrelevant professions are unlikely to count on big money. The so-called “fashionable” professions also fall into the risk group: due to an overabundance of specialists in certain profiles, they have to underestimate the cost of their services.
- Qualification, position and age. High qualifications and sufficient experience allow an employee to apply for a higher position or pay. The best age is considered to be from twenty-four to forty-five years. During these years, an employee is able to bring the greatest benefit to the employer.
- The volume of sales or goods produced , in other words, the revenue of the employer himself, his production costs and the situation on the economic market.
- Place of residence , city, region. It is no secret that guest workers who come from abroad usually earn less than local workers.
- Trade unions and legislation can have some influence , but their intervention is minimal. There are also sometimes differences between the wages of women and men, but these cases are extremely rare.
"Gray denomination"
Since the tax burden is tied to nominal wages, the employer is always tempted to set them as low as possible, down to the minimum wage. To compensate for the resulting gap between nominal and real wages, he pays employees additional funds outside of accounting documents or in another form.
Such schemes cause harm to the state and, if possible, are monitored and suppressed. If the wage fund is suspiciously low, and its nominal values are too far from real ones, the regulatory authorities will definitely become interested in this situation. A tax audit and explanation, and possibly more serious measures, are inevitable.
Relationship between indicators
The lack of connection between parameters leads to “inconsistency” in fundamental values, although labor legislation obliges to ensure the actual maintenance of money.
Article 134 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation puts forward specific measures to ensure that nominal wages correspond to its real level:
- Wage indexation. The procedure refers to methods that make it possible to bring into line the real content of money, which is depreciated in absolute value due to the growth of the consumer price index. The implementation mechanism was provided for by a special federal law, which was repealed before practical application, creating a legal vacuum regarding the procedure. The algorithm must be written in internal local documents reflecting:
- implementation mechanism;
- periodicity;
- list of indexed payments;
- the procedure for determining the indexation threshold (basic consumer price growth index);
Carrying out indexation only for citizens with low incomes or those in need of social guarantees to a greater extent is not considered discrimination in accordance with Article 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, since it is due to the protection of the interests of less protected segments of the population.
- Systematic revision of the minimum wage. An increase in the minimum nominal wage leads to the need to increase the established normative indicators that are below the permissible criterion determined by the state, which helps to increase the real component of the payroll.
Since indexation and salary increases improve the material well-being of workers, personal consent to the implementation of measures from workers is not required.
Additional salary factors
Some states have additional restrictions or incentives regarding the amount of wages for employees. They may be:
- gender – female gender is sometimes discriminated against in terms of salary;
- race – also sometimes unfairly and unreasonably reduces the salary;
- age – working pensioners and young professionals may find themselves in a different salary situation than the majority of employees;
- certain preferences - the owner of the company can, although this is unlawful, set higher salaries for positions occupied, for example, by his relatives, etc.