The right to paid leave under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Every year, every officially working citizen receives the right to complete rest at the expense of the employer. This norm is enshrined in Art. 122 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Employees who have worked for more than six months can receive such rest.
It should be noted that the legislator has introduced several exceptions regarding the provision of leave before the expiration of six full months of work. The exceptions included:
- pregnant women (before childbirth), or immediately after leaving maternity leave;
- minors who are under 18 years of age on the day of application;
- employees who decided to adopt a baby under 3 months old;
- other cases provided for by federal laws.
It should be borne in mind that the six-month standard is valid only in the first year of an employee’s work. In other periods, leave can be granted at any time agreed with the employer. Typically, such agreement is fixed in the vacation schedule.
The minimum duration of annual rest for all categories of workers cannot be less than 28 days. This norm may be increased by special laws. At the same time, depending on working conditions, the worker receives the right to additional leave according to the law (harmfulness, danger, difficult and specific working conditions), as well as under a collective agreement.
Remember, the employer’s obligation to provide the worker with rest, to retain his job for this period, as well as the average salary, is enshrined in law. Violation of this norm entails legal liability (administrative, criminal).
If an employee decides to quit
The opposite situation is also possible, when an employee, going on leave in connection with labor and labor, did not use the rest days allotted to her this year. Then, in the event of her dismissal on her own initiative after maternity leave, the organization will be obliged to compensate her for the days she did not take off in material form. In other cases, the replacement of regular leave for pregnant employees with money is not provided for by law.
According to the rules of Art. 121 of the Labor Code, the time when the employee was not actually at the workplace is included in the time count for calculating the next paid leave, but it (the workplace) was retained by the employee. This includes the period of leave, including for pregnancy and childbirth, that is, maternity leave, which is regulated by the same article.
But maternity leave is not included in this count; this period is not taken into account when calculating the time worked by the employee.
Maternity leave before maternity leave
The employer's obligation to satisfy a pregnant woman's request to provide her with additional annual paid rest is enshrined in Art. 260 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Based on this, several practical nuances should be highlighted:
- a woman who has officially confirmed her pregnancy has the opportunity to take leave, regardless of her length of service with a particular employer;
- the presence of a vacation schedule with a different period of its provision at this moment cannot be the basis for refusing a pregnant woman a vacation;
- the worker has the right to take part of the vacation in proportion to the time worked, or to take in advance the entire vacation period for a specific year. The second norm applies only to the main rest period of 28 days and must be agreed upon by the employer.
To go on vacation, the expectant mother needs to check with the HR department about the number of unused days, check the rest of the vacation until the end of the year, write and submit a corresponding application addressed to the employer through the office.
Registration and payment of vacation pay in this case is carried out in the usual manner. The administration can refuse to provide this type of vacation for money only if the employee has previously used the allotted part of the vacation. Then the woman has every right to take a vacation without payment. And they have no right to refuse her this.
Remember, pregnant ladies enjoy additional privileges. They can take full advantage of their annual leave before sick leave begins.
Labor Code on Pregnant Women
Refusal to conclude an employment contract can be appealed in court Here's what the Criminal Code says about this: Article 145. Unreasonable refusal to hire or unjustified dismissal of a woman on the grounds of her pregnancy, as well as unjustified refusal to hire or unjustified dismissal from work of a woman who has children under three years of age for these reasons is punishable by a fine in the amount of two hundred to five hundred times the minimum wage, or in the amount of the wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of two to five months, or by compulsory labor for a term of one hundred. twenty to one hundred and eighty hours The employer is obliged to establish a part-time working day or part-time working week at the request of a pregnant woman or one of the parents (guardian, trustee)
Providing leave to pregnant women in advance
Pregnant employees enjoy certain privileges. The vacation schedule is suspended for them. At the request of such a lady, she will be able to take an additional paid break at any time convenient for her. At the same time, if we are talking about previously deserved rest, no problems will arise. You just need to write a statement.
It’s another matter if a worker decides to take a vacation in advance (in advance). Here she will have to negotiate with the employer. The law does not prohibit providing the expectant mother with an advance break at the expense of the company. But it does not oblige the manager to pay for periods that have not yet occurred. The employer's concerns boil down to the following points:
- vacation pay is calculated for the current year of work. The expectant mother simply will not work it out completely, because after the sick leave she will go on leave to look after the baby;
- in the event of an employee’s early dismissal, it will be impossible to withhold anything from her salary;
- You can wait over 3 years for the advance payment to be processed. It is during this period that a woman can inspect her baby. The company is obliged to keep her place of work.
Remember, a pregnant woman has the legal right to use the accumulated vacation days before the start of prenatal sick leave in full. Everything above is only in agreement with the employer.
Let's sum it up
- Extension of leave under Birth and Labor is allowed only if the birth was accompanied by complications.
- To extend maternity leave, a woman must provide her employer with an application and sick leave issued by the medical institution where the birth took place.
- The application is drawn up in free form, indicating who is submitting it, to whom it is addressed, the request to extend the vacation and the reasons for the extension.
- Based on the application and sick leave, the employee’s labor and employment leave is extended and additional benefits are paid.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Duration of leave before maternity leave
Now about the duration of paid rest, which is due before maternity leave. The legislator determined that the duration of the main vacation cannot be less than 28 days. At the same time, it can increase by special laws. For example, for teachers this period is set at 52 days.
The legislative framework
The right to annual leave for an employee is guaranteed by the constitution (Article 37), and these issues are directly regulated by Chapter 19. Labor Code.
123rd Art. The Labor Code establishes that leaves are granted according to priority .
The employer draws up a schedule , which is a local legal act of the organization, mandatory after it comes into force.
Expert opinion
Polyakov Pyotr Borisovich
Lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. More than 3 years of experience in drafting contracts.
Humane law makes a number of exceptions . Citizens of these categories have special rights, are not bound by priority and can choose their time. This:
- Pregnant women and women with small children (Article 260).
- Persons raising disabled children (Article 262.1).
- Minor employees (Article 267).
- Part-time workers (Article 286).
- A man whose wife is on maternity leave (4th paragraph of Article 123).
- Law enforcement officers (342nd Federal Law), military personnel, donors (125th Federal Law), veterans (5th Federal Law), holders of orders, liquidators of the Chernobyl disaster and some others.
Postponement of vacation outside the schedule is allowed by Article 124. Labor Code, with another period determined by the employer and employee jointly (1st paragraph). This is mandatory if the employee:
- temporarily disabled;
- performed government duties during vacation;
- did not receive payment (Article 136), or was not notified of the start time two weeks in advance, as required by paragraph 3. 123rd Art.;
- in other cases established by law and local regulations.
At the initiative of the employer and with the consent of the employee, the vacation is transferred to the next year if it is urgently required by production needs.
There are a number of restrictions :
- It must be used no later than one year.
- It is prohibited not to provide it for two years in a row.
- This rule does not apply to minors and workers in harmful or dangerous conditions (Article 124).
Transfer is also possible in optional cases by agreement of the parties to the labor relationship , if this does not violate the law.
Application example
To ensure that the employer does not refuse to provide additional rest to a pregnant woman outside the approved schedule, the application must be completed in a slightly different form from the standard one. Such an application must necessarily contain the following details:
- Full name and full name of the employer.
- The name of the unit, position and decrypted full name of the applicant.
- Title of the document (application).
- The pleading part. Here it is important to start with a reference to Art. 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which provides a pregnant woman with the opportunity to rest at any time convenient for her. Next, you should indicate the number of days of vacation, as well as the start date. Counted in calendar days. Please check with your HR department in advance for the duration of the required rest period. You can also indicate the need to pay financial assistance for recovery, as well as other payments due under the collective agreement.
- Add date and personal signature.
You can write such a statement by hand, or by typing and printing on a computer. The applicant’s signature must be “living”. The application must be registered through the office.
Please keep in mind that it takes some time to review the application, prepare and sign leave orders, calculate and pay entitlements. Therefore, such a document should be written in advance (at least three days before the start of the vacation).
Remember, mentioning Article 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation when writing an application for the vacation period of a pregnant woman is mandatory. This will make it possible to avoid forgetfulness of the administration and formal denial of a legal additional break from work.
conclusions
Annual rest within 28 calendar days before maternity leave is the right of any pregnant woman officially employed by the company.
An employee must be provided with rest time regardless of her length of service and unused vacation days.
Each vacation day is paid in the general manner - based on average earnings for the last 12 months.
Annual leave must immediately precede maternity leave; there should be no return to work between these two periods, otherwise the employer has the right to refuse the employee.
Leave is granted only if the woman herself wishes, based on her application. Management does not have the right to refuse or force someone to take a break.
What to do if they don’t sign the application
In practice, there are often cases when employers simply evade their direct obligations provided for by law. In particular, a pregnant employee may not be allowed to sign her application for additional paid time off outside of the schedule. To avoid any misunderstandings, it is advisable to perform the following actions:
- Receive a certificate from the HR department regarding the remainder of your vacation. Submit your medical document confirming your pregnancy registration there.
- The application must necessarily contain a reference to Art. 260 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- The document must be registered in the office. Have a registration number and date. It is advisable to keep a copy with your registration details.
- The application must be submitted in advance. It is optimal if this is a period that applies to all employees at the enterprise. For example, two weeks before the start date of the vacation.
- Usually the signed order is transferred to personnel and accounting 3 days before the start of the vacation. If it is not yet available on this date, it is advisable to submit a written application to the trade union and inform about the problem. You can also write to the labor inspectorate or prosecutor's office. But this should be done after the holiday has begun, if there is no order by that time.
Guarantees and benefits for pregnant employees
The Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, in a Resolution dated January 28, 2014, identified a number of issues that regulate the labor activities of women who are pregnant, as well as minor citizens. Explanations were given in order for employers to take into account judicial practice. Recommendations were made to follow these provisions, as they relate to the guarantees of women and adolescents working in enterprises and companies.
What was determined:
- Situation: the boss did not know that his subordinate was pregnant. He fired her. Since the law prohibits termination of employment relations with a pregnant woman, the woman can subsequently demand reinstatement at work. The employer is obliged to do this.
- If the end of the employment relationship occurs while an employee of the enterprise is pregnant, it is necessary to extend the contract with her until the birth. In this situation, the birth of a baby is indicated for dismissal on the last day of the BIR.
- When applying for a job, there is no probationary period for women who are pregnant. If the employer has specified it in the agreement, dismissal if the test is not passed is considered unlawful.
- In Art. 64, 70 establish clear guarantees for pregnant women:
- she cannot be denied employment if the woman is pregnant;
- It is prohibited to establish a test for pregnant women.
If an employment contract is concluded with a lady, then she “in a position” has the right to expect:
- Part-time work schedule: this concept includes a shortened shift time, respectively, a week.
- Combination of part-time working hours: it is possible to reduce the number of hours of work per shift and simultaneously reduce the number of days of work per week.
A subordinate can come and contact her boss and ask her to set part-time working hours. According to Art. 93 clause 1, the boss is obliged to meet her halfway.
Special labor status for women who are pregnant:
- Pregnant women should not be involved in work activities on Saturday and Sunday, as well as on holidays.
- Pregnant women do not work shifts.
IMPORTANT: if there is a medical report, then pregnant women can be transferred to lower production rates and easier work.
Providing additional leave before maternity leave
In addition to the main leave, certain categories of workers are also entitled to additional leave. It is important to take into account that before pregnancy, a woman can work for a certain time (within a one-year period) in conditions that allow her to receive additional rest. The list of such conditions by law includes:
- the presence of harmful and dangerous factors;
- irregular working hours;
- special working conditions;
- location in the Far North (regions equivalent to them);
- other reasons specified in federal laws.
In addition, the employer’s local documents, as well as the enterprise’s collective agreement, may provide for other types of additional leave.
Typically, this type of rest is calculated in proportion to the time worked. We must not forget that the calculation of such periods is carried out separately for each category. Then they can be summed up. Having calculated the required number of days, the employee can arrange a work break for herself, similar to the main vacation.
Remember, days of additional leave are counted separately from the main one and are provided in excess of the required 28 days (or the calculated proportion of this period).
Accruals for maternity leave
In 2021, calculation of maternity leave is carried out by analogy with previous years. The Labor Code establishes a payment mechanism.
The calculation of maternity leave is carried out by the accounting department of the enterprise where the woman works. When calculating, the following indicators are taken into account:
- A woman’s earnings for the last two years in total terms. Two years precede the start of maternity leave. Accordingly, if a lady in BIR left in 2021, 2021, 2021 is taken into account.
- Days on which the woman was sick, on vacation, or caring for her child are not counted.
Calculation parameters:
- by the exact number of days in the billing period minus the days that fall out of the calculation;
- Earnings are considered to be the daily average;
- total income for 24 months / for the number of days indicated in the previous paragraph;
- the size of the lump sum payment is indicated;
- To do this, you need the average daily earnings X for the number of days of maternity leave - the last indicator is taken from sick leave.
The amount of the BIR benefit must fit within the established framework.
2018:
| Minimum indicator | Maximum indicator |
| 43615.65 rubles | 282106.70 rubles |
Time off from work and pregnancy
Before you figure out how to take leave before maternity leave, you need to find out what benefits are available to expectant mothers at their workplace.
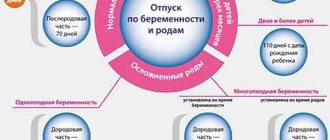
First, pregnant women can count on paid sick leave of at least 140 days (this period includes the time before and after childbirth). Then, every employee who has become a mother has the opportunity to take a vacation, the duration of which can vary from one and a half to three years. At this time, she can completely devote herself to the newborn baby, without thinking about fulfilling her official duties.
Despite the fact that the expectant mother is legally assigned fixed sick leave, the woman may want to leave work earlier and prepare in advance for the birth of the child. How much leave do you have before maternity leave? Let's do the math.
When is it profitable to relax?
Article 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with comments allows a working pregnant woman to take leave before maternity leave or immediately after it. But when is it more profitable to do this? To answer the question, you need to look at what periods vacation pay is calculated for:
- Salary for the year, which was paid until the desired rest.
- If there is no income for the specified period, the previous year is taken.
If the monthly salary during the accounting year before going on maternity leave was unchanged, then the average daily earnings will remain unchanged.
From a financial point of view, going on vacation after maternity leave is beneficial only when, in the last four months before maternity leave, the employee received monthly bonuses, which are included in the calculation of vacation pay. Accordingly, bonuses increase the average daily earnings for the period that is included in vacation pay.
In other cases, it is better for the employee to choose when to go on vacation, based on family circumstances and personal desires.
Pregnant women under protection
The Labor Code contains quite a few articles that guarantee protection for pregnant women and women raising small children.
Specifically, Article 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the ability of working women in a position to choose the time of their next vacation, based on the vacation schedule in the organization.
A woman can rest:
- Right before going on maternity leave.
- After maternity leave.
- During maternity leave. Although this option may exist, it is not preferable, because in this case the woman loses her right to social benefits.
The right of a woman expecting a child to take leave is prescribed by Article 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Annual leave for pregnant women is provided:
- For a permanent employee before going on maternity leave or after, at any time, according to the vacation schedule accepted by the company.
- To an external part-time worker upon presentation of a certificate confirming the provision of such leave at the main place of work. The employee must present a copy of the order or an extract from the vacation schedule.
- An employee working part-time, according to the vacation schedule.
Protect your rights!
It is very important that the rights of pregnant women are respected at work. Most often, this is observed by trade unions and labor inspectorates. However, the expectant mother herself should also be interested in taking advantage of all the benefits of her interesting position in the workplace. Therefore, do not hesitate, bring a certificate from the antenatal clinic confirming your pregnancy, and persistently ask the employer to provide you with the necessary benefits and privileges.
Remember that in addition to maternity leave, you are entitled to official paid sick leave, which is provided to an employee at thirty weeks of pregnancy. Its duration depends on many factors. If the pregnancy proceeded normally, then you will be paid for 140 days of maternity leave; if the birth was difficult (for example, there was a need for a caesarean section), then by law you are required to pay 156 days; if the mother gave birth to two or three children, then another 110 are added to 140 days If a woman’s child died during childbirth, then the state allocated 156 postpartum days for her recovery.