Under what circumstances is shift work permitted?
Labor legislation regulates when it is allowed to establish one or another type of employment, the principles of compliance by the employer with the rights of the employee when establishing a certain type, as well as shift work. The reasons for its introduction are the following factors:
- the duration of the production cycle is significantly higher than the permissible working day established by law;
- achieving maximum effect from the use of equipment, the ultimate goal of which is to increase the volume of products produced, work performed, and services provided.
Shift work is often necessary, for example, in companies where production equipment works non-stop, in convenience stores, as well as in airports, train stations, and hotels.
This regime is characterized by such concepts as a shift schedule and a standard number of hours per month. Certain requirements for the shift schedule are given in Art. 103 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Accounting for hours worked when employed according to a shift schedule
ConsultantPlus has many ready-made solutions, including how to pay for work on a “every three days” schedule. If you don't have access yet, you can get it for free, on a temporary basis! You can also get the current K+ price list.
When conducting work activities on a shift schedule, the method of recording the period worked becomes of particular importance. Due to the fact that during shift work, daily or weekly working time standards may not correspond to the limits established in regulations, a method of recording time worked is necessary in which the legal standard for working hours will be observed at least in a certain working period.
The summarized accounting method meets these conditions (Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The selected reporting period in this case may correspond to a month, quarter, half-year or year, while for workers in harmful or dangerous work the reporting period cannot be more than 3 months. However, a special decision established by an intersectoral agreement and count. agreement, if, when using a quarterly reporting period, it is impossible to comply with legislative standards for working hours, the reporting period for such employees can be extended to a year.
Calculation of the standard duration of work activity for summarized accounting is made based on a certain maximum per week (for example, 40 hours). If summarized accounting is applied to a specialist for whom the Labor Code defines a shortened work week (24, 35, 36, etc. hours), then at the end of the reporting period the amount of hours worked during this time should not exceed the established norms. The procedure for introducing summarized accounting in relation to both the entire workforce and individual staff units is established by the internal documentation of the enterprise, in which it is necessary to indicate the scope of the reporting period.
Shift schedule - what is it for?
A shift schedule or shift schedule is a regulatory document for internal use, developed and adopted at each specific enterprise where it is planned to introduce a shift work schedule. Personnel who will be involved in this regime are familiarized with the schedule in advance - at least one month before its introduction.
A ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus will help answer the most difficult questions about creating a shift schedule. Sign up for a free trial access to the system.
The document should reflect the following points:
- the number of shifts per accounting period (month, quarter, year) and their rotation;
- the start and end time of the shift, as well as its duration;
- breaks provided to employees for rest and eating;
- time allotted for daily and weekly rest.
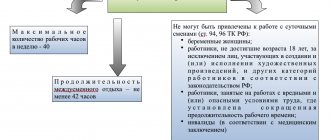
One of the main requirements of the Labor Code for working on a shift schedule is the prohibition of working two shifts in a row. In addition, there is a ban on night work for pregnant employees and persons under the age of majority. Otherwise, employers independently determine work according to a given schedule based on local regulations. Also, when planning, it is allowed to use the standards from the Methodological Recommendations for organizing multi-shift work of production associations (enterprises) of industry, approved by the USSR State Committee for Labor in 1988, to the extent that does not contradict current Russian legislation.
Reasons for defects
For further correct calculation of additional payments for hours of shortcomings, it is especially important to establish the reasons for their occurrence.
They are as follows:
- Due to the employee's fault. Deficiencies discovered at the end of the reporting period may arise due to the employee’s absence from the workplace for valid reasons. This refers to all types of leave - annual, educational, unpaid (“leave at your own expense”), sick leave. There are also disrespectful reasons, namely absenteeism and downtime due to the fault of the worker.
- Due to management's fault. A change in the work schedule that resulted in shortcomings is the fault of the enterprise management. This also includes the initially incorrect drawing up of a schedule, which does not allow the employee to work out the required working hours during the reporting period.
- Due to circumstances beyond the control of the employee and employer. Defects also arise as a result of various force majeure situations, be it natural or man-made disasters, as well as the development of new equipment or technology by employees.
Standard hours for a shift schedule - how to determine
The normal working week is 40 hours. For some categories of workers it may be reduced. This applies to minors or those working in harmful (dangerous) conditions. All this applies to shift work. However, there are nuances here. So, for example, the standard working hours for a shift schedule can be determined in one of the following ways:
- daily - for schedules with the same shift duration;
- weekly - for schedules where shifts vary in length, but workers work a standard number of hours during the week;
- summarized - for schedules where approved shifts differ from each other in duration.
In the first two cases, when paying for the working hours worked by an employee, you should focus on the standard weekly workload - 40 hours or less (for minors or harmful workers). Hours worked in excess of normal (overtime) must be paid at an increased rate.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Yandex.Zen VKontakte Telegram
Difficulties often arise when maintaining summarized records of working time. Let's look at it in more detail.
Calculation of standard working hours
The procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain calendar periods (month, quarter, year) depending on the established duration of working time per week is approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated August 13, 2009 No. 588n .