What laws of the Russian Federation regulate the rights of pregnant women
There are several pieces of legislation that regulate labor relations and various processes related to pregnant women.
The main basis for labor relations is laid down in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Section 12, Part 4 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the list of labor features for different categories of citizens. The work of women and persons who have just given birth is defined in Chapter 41 under the following articles:
- 254 - transfer of pregnant women, as well as persons with a child under 1.5 years of age, to a lighter schedule or work;
- 255 — maternity leave;
- 256 - child care up to 3 years old;
- 258 - break for feeding;
- 259 - a list of guarantees during pregnancy and lactation during business trips, overtime work, night shifts, as well as work on weekends and holidays;
- 260 - guarantees for the priority distribution of annual leave for a woman during pregnancy or childbirth;
- 261 - list of guarantees upon termination of employment relationships;
- 262 (including 262.1) - extraordinary days off and the procedure for granting leave to a parent with a disabled child.
Additionally, there is Federal Law Regulation No. 255-FZ dated December 29, 2006 (social insurance with temporary disability and maternity), which contains Chapter 3, which defines benefits for childbirth or pregnancy, as well as Chapter 4, which establishes the procedure for assigning various payments.
Another important law is Federal Law 05/19/1995 N-FZ, which establishes state benefits for persons with children.
Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Transfer to another job of pregnant women and women with children under the age of one and a half years”
Article 255 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Maternity leave”
Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Parental leave”
Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Breaks for feeding the child”
Article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Guarantees for pregnant women and persons with family responsibilities when sent on business trips, involved in overtime work, work at night, weekends and non-working holidays”
Article 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Guarantees for women in connection with pregnancy and childbirth when establishing the order of provision of annual paid leave”
Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Guarantees for a pregnant woman and persons with family responsibilities upon termination of an employment contract”
Article 262 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Additional days off for persons caring for disabled children and women working in rural areas”
Article 262.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “The order of granting annual paid leave to persons raising disabled children”
Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity”
Federal Law of May 19, 1995 No. 81-FZ “On state benefits for citizens with children”
Rights and guarantees
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, there is an established list of guarantees and rights that apply to women in this situation. Rights and guarantees:
- it is impossible to refuse employment without specifying a reason;
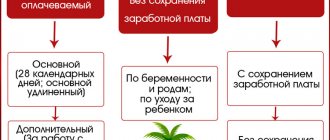
- paid maternity leave;
- dismissal is prohibited;
- annual leave is not provided according to schedule;
- no business trips;
- the work schedule has a shortened version;
- transfer to easier working conditions.
Important! Receiving part-time work can only be done at the initiative of the employee, that is, management does not have the right to establish a light schedule without the consent of the employee.
Among the important points:
- annual leave can be added to maternity leave;
- the article does not provide for a probationary period;
- Any refusal of employment must be accompanied by a written form stating the reasons.
Read also: List of technically complex products
Any employer must take into account all the rights and guarantees of individuals. Otherwise, fines and sanctions may follow both in relation to managers and in relation to the organization. Additionally, inspections by the labor inspectorate will be carried out.
Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Test upon hiring”
Employer Responsibilities
An employer has several responsibilities.
For example, according to the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, he must revise the length of the working day upon the written request of a pregnant employee. It is impossible to refuse a transition to part-time work, even if it is necessary to revise the work schedule of the entire organization. The employer must fulfill all obligations and take into account all rights and guarantees that are provided by law. Forbidden:
- involvement in night work. This is regulated by an article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- it is impossible to call to work on a weekend or holiday in accordance with Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- According to the article, overtime work is not possible;
- Keeping a watch is also prohibited. This is stated in Article 298.
The employer's primary responsibility will be to comply with all rules and regulations. He is not obliged to comply with points not prescribed by law.
Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Part-time work”
Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Night work”
Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Non-working holidays”
Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Overtime work”
Article 298 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Restrictions on work on a rotational basis”
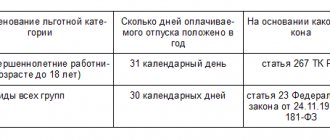
Article 257. Leave for employees who have adopted a child
Employees who have adopted a child are granted leave for the period from the date of adoption until the expiration of 70 calendar days from the date of birth of the adopted child, and in the case of simultaneous adoption of two or more children - 110 calendar days from the date of their birth.
At the request of employees who have adopted a child (children), they are granted leave to care for the child until he (they) reach the age of three years.
In case of adoption of a child (children) by both spouses, these leaves are granted to one of the spouses at their discretion.
Women who have adopted a child, at their request, instead of the leave specified in part one of this article, are granted maternity leave for the period from the date of adoption of the child until the expiration of 70 calendar days, and in case of simultaneous adoption of two or more children - 110 calendar days from their birthday.
The procedure for granting these leaves, ensuring the preservation of the secrecy of adoption, is established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
back to contents
Working hours for pregnant women according to the Labor Code
According to the Labor Code, an employee has the right to contact management with a correctly completed application to switch to a shortened working day. This can be done at any time of the year.
When hiring, part-time work can also be agreed upon immediately.
To switch to a regular schedule, you must contact your manager in the usual manner, that is, write an application requesting a transfer to regular working hours. The authorities cannot refuse this request.
Rights of pregnant women while at work
According to Articles 251-264 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, women during their working life receive a number of rights that can be used if desired. This includes:
- reduction of working hours. It doesn’t matter whether the hours will be reduced from the beginning of the working day or at the end of it. The norm for reduction is 1-2 hours. There may be less, but there is no more;
- vacation pay is paid in full regardless of the time of year and length of service, that is, an employee can work only a few months, but the vacation pay will be full;
- preservation of position and workplace. When an employee goes on maternity leave, this vacancy is assigned, which cannot be assigned full-time to a third party, removed from the staffing table, or reduced. The only legal option would be to transfer the employee to another position, but the consent of the pregnant woman must be obtained;
- There is no probationary period for pregnant women. In a probationary period, an employee can be dismissed only on grounds of unsuitability. In other cases, the position is assigned to a woman;
- the entire dismissal procedure is not standard, since it is impossible to dismiss a woman during pregnancy by decision of the manager. The only legal possibility would be a serious disciplinary offense, that is, dismissal occurs under the article. Another legal option would be a complete reduction in staff as a result of liquidation of the organization. In case of partial reduction of any option, the position remains with the employee.
Important! There is one more important point. If a contract or employment agreement ends during maternity leave, it is automatically extended.
Article 251 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Features of labor regulation”
Read also: How to check if a person has a loan
Article 264 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Guarantees and benefits for persons raising children without a mother”
Time standards and reduction of its duration
Reducing labor time can be expressed in several ways. Options:
- the day or shift is shortened. The number of days themselves does not change, but the length of the working day itself is reduced to two hours. For example, with an 8-hour working day, a 6-hour period is established;
- the work week is shortened. The length of the day remains the same, but the week itself becomes shorter. Example, work from Tuesday to Thursday inclusive instead of Monday to Friday;
- reduce both the day and the week. For example, an employee will work from Monday to Thursday for 6 hours.
There are several options for reduction, but you must follow the rule that the day can be shortened by a maximum of two hours.
Establishment of part-time work
A partial day can only be established using a special procedure. If you just want to, this is impossible, since you will need to complete the required documentation. Procedure:
- obtaining from the antenatal clinic or from the supervising doctor a certificate that fully specifies information about the employee’s pregnancy;
- writing a statement to the employer (immediate supervisor). The document specifies all aspects, including shortening the working day or receiving an additional day off. The duration of such period of work must be indicated;
Sample application for part-time work - the application and certificate are sent to the HR department (in its absence, directly to the manager, including the possibility of sending it by registered mail). The application can be written in two copies so that both versions have a signature. Such a measure may be required to avoid controversial situations;
- familiarization with the order and signature;
- an additional agreement is signed, which is attached to the regular employment agreement or contract. One copy remains in the employee’s hands.
If your boss refuses to shorten the day due to pregnancy, you can contact the labor inspectorate, as well as the prosecutor's office. But you will need evidence, which will be duplicates of documents.
Important! With reduced working hours, wages are calculated according to the hours worked, that is, the salary will be less in proportion to the time worked. This fact must be reflected in the additional agreement, which is drawn up when the time is reduced.
The actual hours worked according to the new schedule, as well as the time of mandatory medical examination, are entered into the timesheet.
When can you go on maternity leave?
According to a number of provisions of Part 1 of Article 255, a pregnant employee, upon application and sick leave, is entitled to leave, which is paid. A certificate of incapacity for work is issued according to the regulations of the Ministry of Health and Social Development, in particular according to Order No. 624n dated June 29, 2011. In accordance with this act, the issuance should be made at 30 weeks in case of a normal pregnancy and at 28 weeks in case of multiple pregnancy.
The maternity period consists of several segments. Before giving birth, the duration of leave is 70 calendar days. An exception is a multiple pregnancy of 84 days. If multiple pregnancy was determined during the birth itself, then the extension is carried out for 54 days.
Time frame after birth:
- 70 days - usual;
- 86 days - with a complication;
- 110 days - birth of two or more children.
The duration of the vacation is total, that is, there is no connection with the days spent before the birth itself.
Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated June 29, 2011 N 624n “On approval of the Procedure for issuing certificates of incapacity for work”
What are the benefits at work?
According to Federal Law No. 255, receiving maternity benefits is possible only if you have insurance. The size of the payment depends on average earnings. From the 30th week of pregnancy, a woman claims the following payments:
- one-time federal assistance in the amount of 613 rubles;
- regional allowance - 600 rubles;
- at the birth of a child - a one-time payment of 16,350 rubles;
- the birth of a second child and subsequent ones - maternity capital in the form of a certificate.
The size of the certificate is 454 thousand. Also, for the second and third child there are additional monthly payments until the child turns 3 years old.
Important! If a woman goes back to work after giving birth, child care benefits are not paid.
The average salary is calculated according to the standard, that is, the amount received for a certain period is divided by the number of calendar days. We receive the amount per day.
Read also: What happens if you don’t pay the loan at all
The billing period does not include vacations, periods of incapacity for work, and temporary release from office.
Duration under the Labor Code
The same 255 regulates the duration of maternity leave. In the standard version it is 140 days. This period increases by 16 days (156 in total) if the birth is difficult, for example, if a caesarean section is performed. At 28 weeks of multiple pregnancy, a woman is given a sick leave certificate for 196 days.
It is believed that out of 140 days, you are supposed to take 70 days off before giving birth and the same period after it. But it is not so. If an employee expresses a desire to work longer, then on the basis of a personal statement she will be given such a chance. That is, the expectant mother has the right to rest only 30 or 40 days before giving birth, and the remaining 100-110 days after.
You can do exactly the opposite, that is, 100 before, and 40 after. A rest period of 196 days can be divided according to the same principle, but it cannot exceed the specified period. If you have 140 days, then no one will allow you to rest for 150.
Rights of a pregnant woman upon dismissal
Dismissal of a pregnant employee is possible only upon liquidation of the organization or closure of the individual entrepreneur.
Important! At her own request, the employee can leave at any time, since there are no restrictions here.
Another option for terminating the employment relationship is dismissal under the article, but there is a nuance here. A disciplinary commission is assembled, which makes a decision that the guilt has been fully proven and the dismissal is justified. For any unjustified dismissal of a pregnant woman or an employee with children under three years of age, the employer is subject to sanctions in the form of fines and various types of liability.
In case of a fixed-term employment contract and its expiration during maternity leave, the period will be extended until the employee returns to work after the expiration of the leave.
If a person works in a temporary position and is pregnant, then after the main employee returns to work, the pregnant woman is provided with all available vacancies for transfer, including lower-level ones. According to Part 3 of Article 261, the list of vacancies that can be offered consists of all positions that are suitable for qualifications, including lower paid and temporary ones.
Law on calculating maternity benefits
Maternity benefits are paid from the funds of the Social Insurance Fund (which in turn are made up of contributions and transfers from workers), but all calculations are made by employers - since they have the necessary information.
Until recently, it was possible to use both old and new rules when calculating benefits, but from January 1, 2013, only new ones.
What does the new law on maternity leave say? The general principles remain unchanged: the benefit is calculated based on the billing period and average earnings. But the principles for determining the billing period have changed.
Billing period
This term means a certain set of fully worked calendar days, on which the full salary was paid, from which all necessary contributions and taxes were deducted.
In the past, the calculation period was taken to be the twelve months preceding maternity leave. The new law on maternity pay states that the last two years worked are taken as the calculation period, and this remains unchanged.
From these two years you need to subtract:
- periods of temporary disability, including being on another maternity leave;
- calendar holidays;
- other days of release from work, in which wages were retained in full or in part, and insurance premiums were not calculated from it.
Thus, it may turn out that out of 730 days only 300 or 450 will be worked - this is the number that will be taken into account.
Average earnings
The law on calculating maternity pay stipulates that each day of maternity leave must be paid from the amount of average daily earnings. How is this amount found? By adding up all material assets paid for the billing period and dividing the final number by the total number of days worked in the billing period. What is taken into account when calculating payments? Following:
- wage;
- bonuses and other incentive funds, if contributions to the Social Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund were deducted from them;
- financial assistance over four thousand rubles;
- regional coefficients;
- bonuses for length of service, scientific publications, etc.;
- any other wage payments, if contributions to the Social Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund have been deducted from them.
Of course, according to the norms of the federal law on maternity leave, the more days worked in the billing period, the higher the average daily earnings will be. But at the same time, the average daily earnings should not exceed the value obtained by dividing the established maximum base for calculating insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for the previous 2 years by 730 days.
So, in 2021, the average daily earnings should not exceed 1901.37 rubles. : (RUB 670,000 for 2015 + RUB 718,000 for 2021) / 730 days. Anything over this number will simply not be taken into account.
Responsibility for violation
For managers who do not respect the rights of employees and pregnant women in particular, liability has been established. It can be of several types:
- if employment is refused without a reason, a maximum fine of 200,000 rubles is imposed. Another option would be the salary for 1.5 years. Compulsory work of up to 360 hours also applies;
- In case of non-payment of wages to an employee, including partial non-payment of labor, the following sanctions may be imposed on the guilty person - a fine of up to 120,000 rubles, a ban on holding a position. In case of complete non-payment, the fine increases to 500,000 rubles;
- dismissal without a valid reason will result in a fine of 200,000 rubles and a ban on holding a position for a period to be determined by the court. In this option, the woman is reinstated to her previous position.
The employer must fully comply with all legislative norms, for example, dismissal of a woman if she is pregnant is possible only in the cases prescribed in the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Failure to comply with legal requirements will result in personal liability, as well as fines and inspections against the organization.
Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer”
Changes in the law for pregnant women
There are several changes to the legislation. For example, the list of persons who can receive maternity payments has been increased. Now foreign citizens and close relatives of the employee can receive these funds. The maximum payment level has increased to 755,000 rubles.
Also among the latest changes:
- the use of female labor in hazardous industries is limited, and therefore pregnant women are transferred to easier work, where there is no danger to the development of the child;
- after 2014, the labor version of the pension was replaced by an insurance one, which led to full enrollment in the maternity period;
- since 2012, if there are small children, 4 additional days off can be provided per month, which are paid at the general rate.
The main changes took place in 2012-2015. At present, there are no plans to introduce various amendments.