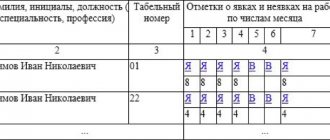
What is a working day
A working day should be considered the time period during which a citizen fulfills the obligations assigned to him by his position. Obligations must be reflected in the employment agreement. The concept under consideration also includes other periods that are reflected in legal acts.
In other words, during the working day a citizen is on duty. In practical activities, problems in this direction are associated with how to correctly calculate the duration of such time.
The management of the organization is responsible for establishing such a duration within the framework reflected in labor legislation. However, not all companies take these rules into account.
Working hours and recording
In the science of labor law, the working time regime refers to the order of distribution of working time within a specific period (daylight hours, evening and night hours, calendar week, month, quarter, etc.).
The working hours are established by a collective agreement or internal regulations of the organization in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, federal laws, collective agreements and agreements. It is possible to establish an individual work schedule for a specific employee by agreement of the parties.
The working hours must include the following elements:
- length of the working week;
- duration of daily work (shift), including part-time work (shift);
- number of shifts per day;
- start and end times of work;
- time of breaks in work, including breaks for rest and meals, determined by specific time frames;
- alternation of working and non-working days;
- work with irregular working hours for certain categories of workers.
Working hours should be distinguished from the operating hours of the organization, since they may not be the same.
Traditionally, the following working hours are distinguished:
- General regime (established for all or most of the employer’s employees. Such regimes, as a rule, are a five-day work week with two days off or a six-day work week with one day off).
- Special regime (established for certain categories of workers. For example, flexible working hours, irregular working hours, etc.).
For employees whose working hours differ from the general rules established by a given employer, these features must be reflected in the employment contract.
Pursuant to Part 2 of Art. 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted Resolution No. 877 of December 10, 2002 “On the peculiarities of the working time and rest time regime of certain categories of workers with a special nature of work,” which established that the peculiarities of the working time and rest time regime of certain categories of workers , having a special nature of work, are determined by the relevant federal executive authorities in agreement with the Ministry of Labor of Russia and the Ministry of Health of Russia, and in the absence of a corresponding federal executive authority - the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation. So, for example, in connection with this, Order No. 15 of the Ministry of Transport of Russia was issued on August 20, 2004, which approved the Regulations on the peculiarities of working hours and rest periods for car drivers.
According to clause 15 of this Regulation, the driver’s working time includes:
a) driving time;
b) time of special breaks for rest from driving on the way and at final destinations;
c) preparatory and final time for performing work before leaving the line and after returning from the line to the organization, and for intercity transportation - for performing work at the turnaround point or on the way (at a parking place) before the start and after the end of the shift;
d) time of medical examination of the driver before leaving the line and after returning from the line;
e) parking time at loading and unloading points, at passenger pick-up and drop-off points, at places where special vehicles are used;
e) downtime not due to the driver’s fault, etc.
Order of the State Fisheries Committee of Russia dated August 8, 2003 N 271 “On approval of the Regulations on the peculiarities of working hours and rest time for certain categories of workers of the fishery complex with a special nature of work” in paragraph 6 it is established that during the operation of fishing vessels and the work of members of fishing brigades (artels) all calendar days of this period (including days of weekly rest, non-working holidays) are working days. Summarized working time recording is introduced. During the operation of fishing vessels, in accordance with the Service Charter on vessels of the fishing fleet of the Russian Federation, a watch service lasting eight hours a day (three shifts) or a two-shift watch is introduced if it is not possible (mainly due to the lack of berths and life-saving equipment) by the established regular crew size work in three shifts.
Let's look at the types of special modes.
An irregular working day as a special mode of work, as a rule, is stipulated when concluding an employment contract and provides for the employee to perform his labor functions, if necessary, outside the established working hours.
This mode was discussed in detail in paragraph 3.1 of the textbook.
The flexible working time regime (Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is a form of organizing working time in which individual employees or teams of organizational units are allowed (within certain limits) self-regulation of the beginning, end and total duration of the working day. When working in this mode, the beginning, end or total duration of the working day is determined by agreement of the parties. The time during which an employee must be present and perform his or her job duties at the workplace may be established. At other times he can start and finish work at his own discretion.
The employer has the obligation to ensure that the employee works the total number of working hours during the relevant accounting periods (working day, week, month and other periods).
One form of flexible working time is a flexible work schedule. This is a mode of work in which the length of time spent at work is fixed, within which workers are allowed to start and finish work at their own discretion.
Shift work (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is introduced in order to more efficiently use equipment, increase the volume of products or services provided, and also in cases where the duration of the production process exceeds the permissible duration of daily work. In this case, a working time regime of one or several shifts is provided. When working in shifts, each group of workers must work within the established working hours in accordance with the shift schedule. Shift schedules are drawn up by the employer taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees and are brought to the attention of employees no later than one month before they come into effect. Working two shifts in a row is prohibited.
Dividing the working day into parts is allowed in accordance with Art. 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in those jobs where this is necessary due to the special nature of the work, as well as in the production of work, the intensity of which is not the same during the working day (shift). In this case, the working day can be divided into parts so that the total working time does not exceed the established duration of daily work. The division of the working day into parts is carried out by the employer on the basis of a local regulatory act adopted taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization. In certain cases, the division of the working day into parts is established by the relevant provisions applicable to workers in certain sectors of the national economy. For example, Order of the Ministry of Communications of Russia dated September 8, 2003 N 112 “On approval of the Regulations on the peculiarities of working time and rest time for communication workers with a special nature of work” approved the List of professions and positions of communication workers for which the employer can establish a divided work schedule day.
Chapter 47 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the specifics of regulating the labor of persons working on a rotational basis, which is defined as a special form of carrying out the labor process outside the place of permanent residence of workers, when their daily return to their place of permanent residence cannot be ensured.
With a shift work method, a summarized accounting of working time is established, and the work and rest regimes within the accounting period are regulated by the shift work schedule. Article 302 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes guarantees and compensation for persons working on a rotational basis.
The working hours, the procedure for providing days off and annual paid leave are established in a number of cases, taking into account the peculiarities of regulating the labor of certain categories of workers (Section XII of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). So, for example, according to Art. 305 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the working hours, the procedure for providing days off and annual paid leave for employees who have entered into an employment contract with an individual employer are determined by agreement between the employee and the individual employer. At the same time, the length of the working week cannot be longer, and the duration of annual paid leave cannot be less than established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Rules and regulations
Initially, it will be necessary to resolve the issue of how long a citizen must perform his duties in the service and how the period worked is recorded. This issue is of particular importance; it is for this reason that the legislation defines specific meanings in this regard. The laws make a reservation that it is permissible to exceed the established values, however, this time must be additionally paid.
It is also worth considering that the duration of work activity can be determined on the basis of a separate law. It sets out the conditions for a group of citizens. In particular, these provisions affect the activities of workers in the medical and educational spheres.
For neither, the duration of the time period under consideration is reflected in individual acts. This means that if working hours are exceeded, this category of persons is not entitled to additional payments.
If we consider these provisions from the point of view of legislation, then in total the specified period cannot be more than 40 hours. This suggests that when establishing a longer working day, this should be considered a violation.
The exception here will be situations when other rules are prescribed by law. If the management of an organization makes attempts to exceed these standards, this indicates a violation of the law.
In such a situation, a citizen has the right to refuse to perform work duties during additional time. In practice, many employees do not go to work in a situation where the established weekly standard has been fulfilled.
Concept and types of working time
Working time concept
For all types of socially useful activities of people, the common measure of the amount of labor expended is working time. Working time, on the one hand, fixes the measure of labor, on the other hand, it provides the employee with time to rest and restore the expended forces. According to academician I.M. Sechenov, for the normal functioning of the body, eight hours of work, eight hours of rest and eight hours of sleep are required.
Working hours are one of the most important working conditions.
The establishment by law of normal working hours makes it possible to: ensure the protection of the employee’s health and promote his longevity at work; obtain from each worker a socially necessary measure of labor; increase the cultural and technical level of the employee, learn on the job, develop one’s personality, which, in turn, helps to increase labor productivity.
Limitation of working hours by law was one of the first requirements that arose at the beginning of the 19th century. labor movement. Under the pressure of the weavers of the Morozov manufactory (Ivanovo), in 1897 the first Law was issued limiting the working day to 11.5 hours, and for women and children - 10 hours. But this Law did not limit overtime work in any way, which negated the limitation of the working day.
Modern labor legislation, when regulating working time, is guided by ILO Convention No. 47 “On the reduction of working time to 40 hours a week” (1935), No. 171 “On night work” (1990), ILO Recommendation No. 116 “ On reducing working hours" (1962).
A person working under an employment contract is guaranteed by the Constitution of the Russian Federation the length of working hours established by federal law, weekends and holidays, and paid annual leave (Part 5 of Article 37). Section is devoted to working time. IV Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Working hours are determined in Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as the time during which an employee, in accordance with the internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties, as well as other periods of time that, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, relate to the worker time.
Thus, we can say that working time consists of two periods.
The first period is the time during which the employee must perform work duties.
The second period is the time when the employee does not actually perform his duties, but in accordance with the law this time is counted as working time.
Such periods, for example, include:
- special breaks determined by the technology and organization of production and labor (breaks for heating and rest of workers working in the open air in cold weather) (Article 109 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
— breaks provided to women with children under the age of one and a half years (Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- breaks for rest and food provided to employees at work where it is impossible to provide breaks used by the employee at his own discretion (Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
— breaks provided to air traffic controllers, downtime not through the fault of the employee (Article 94, Part 1 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), etc.
Separate federal laws and other regulatory legal acts, as a rule, regulating labor relations of certain categories of workers, may provide for other periods that also relate to working time. So, for example, in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia dated March 27, 2006 N 69 “On the peculiarities of working hours and rest time for teaching and other employees of educational institutions”, periods of cancellation of classes (educational process) for students, pupils under sanitary and epidemiological , climatic and other reasons are the working hours of teaching and other employees of an educational institution.
As a rule, working hours include periods for performing basic and preparatory and final activities (preparing the workplace, receiving work orders, receiving and preparing materials, tools, familiarizing with technical documentation, preparing and cleaning the workplace, handing over finished products, etc.) , provided for by technology and labor organization, and does not include the time spent on the road from the checkpoint to the workplace, changing clothes and washing before and after the end of the working day, lunch break, downtime due to the fault of the employee, absenteeism, tardiness, early leaving work.
Types of working time
Depending on the duration, it is customary to distinguish three types of working time: normal, shortened and part-time.
These three types are normalized working hours, i.e. its duration does not exceed the maximum norms established by law. Let's look at each type.
The main type of working time is the so-called normal working time.
The normal working hours are established by Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and amounts to 40 hours per week, which corresponds to international standards based on the provisions of ILO Convention No. 47 “On the reduction of working hours to 40 hours per week” (1935) and ILO Recommendation No. 116 “On the reduction of working hours” (1962).
This norm is the norm for the maximum working time for employees of all organizations, regardless of their organizational and legal forms, as well as regardless of the type of employment contract concluded (for example, a fixed-term employment contract, seasonal work) and the length of the working week (five-day or six-day) adopted by of this employer.
An exception is provided for those workers who, in order to protect their labor, are provided with reduced working hours by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other regulatory legal acts (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The daily duration and working hours are fixed in accordance with the established procedure in the internal labor regulations, collective agreement, and other local regulations while maintaining the prescribed working hours, not exceeding 40 hours per week.
Thus, normal working hours should be understood as the working hours established in the organization in accordance with the internal labor regulations and (or) the employment contract with the employee, not exceeding 40 hours per week.
The second type of working time is shortened working hours.
Shortened working hours mean shorter working hours established for certain categories of workers in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and (or) federal laws compared to normal working hours.
The reduced working time is established depending on the physiological characteristics of the workers’ bodies (age, health), working conditions (dangerous, harmful conditions), characteristics of work activity (increased intellectual activity and emotional stress) and is the maximum allowable working time for these categories of workers. week.
For individual employees entitled to reduced working hours, in addition to its total duration, a maximum working day (shift) is also established.
Shortened working hours may be established by a collective agreement or local regulations in the presence of production and economic conditions.
If an employee has the right to establish reduced working hours for several reasons, then the employer is obliged to establish more preferential conditions. The law does not provide for summation of benefits in this case.
In addition, Art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides that the duration of the working day (shift) immediately preceding a non-working holiday is reduced by one hour. In certain types of work or in continuously operating organizations where such a reduction in work hours is not possible, overtime is compensated by providing additional rest to the employee or, with his consent, payment according to the standards established for payment of overtime work. If a non-working holiday is preceded by a day off, then the working hours are not reduced. For employees who have a six-day work week, the duration of work on the eve of the weekend cannot exceed five hours.
When working at night (from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m.), the duration of work (shift) is reduced by one hour without further work. However, this rule does not apply to employees hired specifically for night work, unless otherwise provided by the collective agreement. At the same time, for some categories of workers, there is either a ban on their involvement in work at night, or a special procedure for attraction (Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Reduced working hours for all the cases listed above is the norm, which, as a rule, does not entail a reduction in wages. The only exception is the payment of minor workers. By virtue of Art. 271 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, with time-based wages, wages of workers under 18 years of age are paid taking into account the reduced working hours. The work of minors under the age of 18 admitted to piecework is paid at established piecework rates. The employer may make additional payments at his own expense.
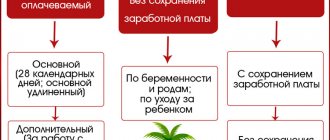
The third type of working time is part-time work. Part-time working time is a duration of working time established by agreement of the parties and fixed in the employment contract with the employee that is less than normal wages in proportion to the time worked.
The concept of part-time work covers both part-time and part-time work, i.e. it is possible to establish:
- part-time work - reducing the duration of daily work (shift) by a certain number of working hours on all days of the working week, which remains five days or six days;
— part-time work week — reducing the number of working days per week while maintaining the normal duration of daily work (shift);
- a combination of part-time work and part-time work week - reducing the duration of daily work (shift) by a certain number of working hours while simultaneously reducing the number of working days per week.
Part-time work does not entail for employees, as established by Art. 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, any restrictions on the duration of annual paid leave and other labor rights and guarantees. Part-time work is included in the content of the employee’s employment contract as one of the mandatory conditions and is reflected in the order (instruction) on hiring, but is not indicated in the work book.
Significant differences between part-time and short-time working hours are presented in Table. 2.
As a general rule, remuneration is not reduced. Remuneration is made in proportion to the time worked or depending on the amount of work performed.
How long should it last
As already indicated, labor legislation specifies the maximum length of the working day. This time is eight hours. It is worth taking into account that the specified period does not include the break provided for lunch.
Several rules apply at this point:
- its duration should be between half an hour and a couple of hours;
- this period is not included in working hours;
- not subject to payment;
- a citizen does not have the opportunity to refuse lunch in order to reduce the length of the workday.
Some companies establish a rule that during lunch you cannot leave the place where a citizen is working. In such a situation, the period in question must be paid and included in the time worked. Special points regarding the concept in question must be reflected in the employment agreement.
Night shifts and part-time jobs
The current legislation establishes rules according to which, before the onset of a day off, the duration of the working period must be reduced. In some cases, citizens have to fulfill obligations to work at night.
Such situations require the use of special rules. Initially, the question needs to be clarified regarding what should be considered night time.
According to the law, this is the period lasting from 22:00 to 06:00. If a citizen's shift falls during this time, it is subject to reduction by an hour if it is followed by a holiday. However, there are also situations when a citizen is hired to perform duties only at night.
In this situation, the list of obligations of the parties is reflected in the employment agreement. It is also worth considering the fact that not all persons have the right to work at the time in question.
For example, you cannot hire:
- a citizen who has lost his ability to work;
- school student;
- a female representative expecting a baby.
If a person belongs to another special category, for example, he has a child under the age of three or a disabled child, then he can be assigned night work. However, the limitation concerns that the specified citizen must agree to such work.
Part-time work
In practice, the duration of the working period may vary. Some restrictions may apply in this case. The company management has the opportunity to determine the duration of the working period in each case.
The 40 hours are distributed randomly. Part-time working hours can only be assigned on the basis of an agreement drawn up between the company management and the citizen.
Not all employees have the right to this opportunity. It is worth considering that payment is made according to the time worked. It is important to take into account that the duration of work does not affect the composition of the social package for the employee. In particular, a person has the right to payment for time while he is on vacation or sick.
You can take advantage of this period:
- women expecting a baby;
- guardians or parents of minor children. The age of the child up to 14 years is taken into account;
- legal representatives of children with disability status. They are entitled to privileges until they reach adulthood;
- persons providing care for a sick relative.
In the latter case, you will need to have documentary evidence of the relative’s status on hand. Otherwise, the company refuses to use the preference.
Where to get positivity from
If the plan is drawn up correctly, then you are likely to experience optimism and cheerfulness. How could it be otherwise, if the plan brings you closer to your goals, if you achieve your goals step by step?.. If this is not so, and you feel that work is taking over your life, which in the meantime is passing by, then something is wrong , and it’s time to either change jobs or find new motivation in it. To do this, you don’t have to run to a specialist - no one has canceled self-coaching. Focus not on problems, but on opportunities, and you will always (or almost always) have a great mood and only successful days!
Weekend
The concept of a working day includes the definition of a day off. In this case, time is subject to redistribution. The law indicates that in the days preceding holidays or non-working periods, the duration of work should be reduced.
These rules are stated in the agreement. If you had to call a person to work on holidays, you will need to pay an increased amount. In this case, the duration of work is established in the contract. It is also possible to reschedule the shift to another day.
Dismissal during vacation or sick leave
Dismissal at the initiative of the employer while the employee is on vacation or sick leave is prohibited. If he wrote a statement of his own free will, there are no legislative obstacles.
The norms of Article 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provide that if an employee was absent during the termination of relations with the employer for a good reason - for example, he was on vacation - then the last working day is determined differently:
- If this date falls on the day when the person fell ill and received a certificate of temporary incapacity for work, and he was fired at the initiative of the employer, this will be the nearest weekday after leaving sick leave. By the way, this is a comprehensive answer to the question: can someone be fired on sick leave? They can’t do it while on sick leave, but immediately after it closes, please. If the employee wrote an application to terminate the contract at his own request or by agreement of the parties, during the termination of the employment relationship he may also be on sick leave.
- If an employee received leave with subsequent dismissal, then the day of dismissal of the employee is the final day of his leave.
About the work of minors
Legislatively defined preferences for citizens who are under age and working. In particular, their working hours are shortened. In such a situation, the rules apply:
- if a person is under 16 years of age, then he can work more than 24 hours a week;
- at the age of 16 to 18 years – the duration increases to 36 hours.
In a situation where a child under 16 years of age is working and studying in an educational institution, the duration of work for him is 18 hours. The daily work norm is no more than five hours. Until adulthood, this figure increases to seven hours.
Working day in the countryside
Currently, innovations are being applied that are included in labor legislation. They are that for female representatives who work in rural areas.
These norms are enshrined in the provisions of the new Article 263.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is worth considering that this idea is not new. Back in Soviet times, this group of citizens received the right to reduced working hours.
The article in question is that women in the village should work no more than 36 hours per week. This guarantee is enshrined in the Labor Law. At the same time, innovation should not affect the amount of wages. It is set equal to that for persons who work 40 hours. This category received the opportunity to use an additional day off.