Breaks and their types
The time of breaks in work is one of the elements of the working time regime, which is established by the internal labor regulations drawn up according to the rules of Art. 189 Labor Code. Breaks during working hours or within shifts are types of rest for workers, fixed by labor legislation, divided depending on:
- specifics of the activity of an organization or enterprise;
- features of the performed labor function;
- categories of workers;
- working conditions, etc.
Among the types of rest allowed by law that are provided to an employee during a working day or work shift, the following are distinguished:
- lunch break;
- special and technological breaks in work;
- rest at work due to special working conditions (in particular, for heating);
- organizational due to the employee’s personal needs (for visiting the toilet, taking medications, etc.);
- additional rest for certain categories of workers (nursing mothers, people with disabilities, etc.).
Let us consider in more detail each of the types, their features, frequency of provision and duration. Moreover, here and further we are talking specifically about pauses in work, and not about daily rest, which, in accordance with Art. 107 TK. The latter includes not only rest after work, but also a break between shifts.
How much rest should you have when working 12 hours?
But there are many productions where the official break, although provided for on paper, is not observed in practice. Workers are forced to drink tea right at their workplace in a hurry. This is a violation of labor laws, but if wages are high, then people remain silent.
According to Art. 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee must be given a break of at least 30 minutes and no more than two hours, which are not counted as working hours.
How much specific time is allocated during a 12-hour work shift at a particular enterprise is regulated by the enterprise itself in the employment agreement, which is signed by the employee when applying for a job at this enterprise.
By signing such an employment agreement, you fully agree with all the working and rest conditions specified in it.
Attention
If fatigue noticeably accumulates already in the first half of the day or shift, this is bad. And one more important point. As the Labor Code says, breaks during the working day are free time, and a person can use it as he pleases.
He can go to the dining room and have lunch, or he can read a book. He has the right to go out for a walk or even go home (if he lives nearby and won’t be late back to work). It follows from this that an employee cannot be limited in the use of precious minutes of rest. If you forbid him to leave the building or leave his workplace, you will be violating labor laws.
This working time standard will be observed in accordance with the relevant rules of the basic labor regime for employees, where a twelve-hour working day will also be established.
If, during all this time, the employee carried out his activities for five days a week for twelve hours, then the working time standard for one week can only be increased in a special form and only by twenty hours.
The same regime of work activity is often established with the further introduction of a general summarized deduction for a certain working period.
Any use of a summarized working day is based only on what is provided for by certain legislation on the duration of the working week, which can also be provided by the main schedule in a standard volume for the entire main accounting period.
Rest time for a 12 hour work shift
But most often such a schedule is in the service sector, and there it is unprofitable to set constant breaks. For example, I work for days, and we go out to smoke/to the toilet/to eat when there are few clients and my partner can handle it alone, and not according to any specific schedule.
- In an organization where a 12-hour working day is established, there should be breaks of no more than 2 hours, but not less than 30 minutes in accordance with Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This time is not included in working hours. When applying for a job, you need to pay attention to what is written in the contract, read it carefully, especially between the lines, and there must be a clause about the rules of the lunch break. Lunch breaks must be specified in the employment contract concluded between the employer and employee. For some types of work, depending on the specialization, there must be additional breaks, for example, rest and heating in accordance with Article 109 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Is it possible to rest at night at work? 12 hour working day. Thank you!
But there must also be breaks during the working day, otherwise the worker will begin to feel like a galley slave. By breaks, the legislator means time that an employee can use for personal purposes - have lunch, have a smoke break, gossip with colleagues.
There are three categories of breaks:
- lunch (for rest and food);
- special – for heating and relaxation;
- for feeding a child.
You need to understand that pauses in the work process are not an annoying waste of time, but a means of preventing employee fatigue and a decrease in productivity.
It is unlikely that you will recruit employees for your company so that they can spend all day working (for such “heroes of labor” a break will no longer help). However, good efficiency is unattainable without quality and regular rest.
And from a purely human point of view: squeezing the last juice out of people is not good.
Rest time for daily work according to the labor code
For 12-hour shifts, the duration of lunch breaks is 1 - 1.5 hours, for daily duty - 2 hours (one hour each in the first and second half of the shift). During this time, the guard must be provided with a replacement so that he can leave his post.
The exact time of the break and its specific duration are established by the internal labor regulations or the employment contract.
If working conditions allow, then a so-called “floating” schedule can be established, in which the employee has the opportunity to take advantage of the time allotted for a lunch break within a specified period, independently determining its start time.
Breaks during the working day: how much rest should employees have?
Only the minimum (30 minutes) and maximum (2 hours) duration of the break, which is not included in working hours, is precisely named. As Art.
108, the duration of rest and breaks “are established by internal labor regulations or by agreement between the employee and the employer.” I myself work 12 hours a day, but we still haven’t agreed on this issue.
You can see the comments here, here and here. As far as I know from the standards I have encountered, for every hour of working time there are five minutes of rest.
Important
More precisely, you work for 55 minutes and rest for 5. Or you work for an hour and fifty, resting for 10 minutes. Plus one hour lunch. That is, 11 working hours.
Article 108 of the Labor Code regulates breaks for an employee during the working day.
Loading page
For example, a person comes at 9 o’clock, works until 1 pm, has lunch between 1 pm and 2 pm (smokes, listens to music, sleeps), and then continues to work until 6 pm. This approach is convenient because all specialists are easy to control.
“So, it’s 14.03, and Ivanov is still chilling somewhere, come on, let’s reprimand him!” However, the effectiveness of this work-leisure model is questionable. The ideal option is to allow employees to decide when and how much to rest.
You simply set the total duration of breaks during the working day (for example, 1 hour), and the employees’ task is to meet this deadline. Alas, this is not always achievable. Unless you have special software that allows people to track the hours they work, it's best to go the standard route.
Rest time for a 12 hour working day
The most common schedules in practice are a day after 2 and a day after 3. With such schedules, the requirement for a 40-hour week is violated, so the employer introduces summarized time tracking provided for in Art.
104 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to Art. 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if it is not possible to comply with daily and weekly working time limits, the employer counts the hours worked for the accounting period and monitors that they do not exceed the established norm for the month/year.
The accounting period can be a month, a quarter, six months, or a year. The law does not allow hours worked to be taken into account for more than a year (for workers in an industry with hazardous conditions, the limit is 3 months).
Thanks to working time tracking, unworked hours can be covered by overworked ones. And in accordance with Article 111 of the Labor Code of Russia, the main day off is only Sunday.
But in such companies, where temporary suspension of activities on weekends is often impracticable, days off will have to be issued on any other day of the week in accordance with the internal work schedule.
In addition, if, in accordance with the contract, it was established for the employee that on Sunday the employee can be involved in activities in accordance with the main schedule of activities, then this day is a working day for him, but payment will be made only in accordance with the usual procedure for this matter. Duration of working time The total rest time for a 12-hour working day, in accordance with Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the main duration of the total working day should not exceed forty hours in one week.
Source: https://11-2.ru/skolko-polozheno-otdyhat-pri-rabote-12-chasov/
Rest and food
The usual name for recreation, the right to which is enshrined in Art. 108 of the Labor Code, common among both employees and employers - lunch break. The law establishes the following rules for granting this pause in work:
- provided for the purpose of food and rest for employees;
- the duration of the break for rest and food is a maximum of 2 hours;
- the minimum duration of a lunch break according to the Labor Code is half an hour;
- is not included in working hours;
- the lunch break can be used by the employee at his own discretion and carried out for any purpose;
- at lunchtime, employees of the organization can leave the workplace;
- A lunch break may not be provided in cases where the employee works no more than 4 hours a day:
- the lunch break has a specific duration established by a local act of the enterprise regulating labor regulations, or the corresponding condition is included in the employment contract;
- It is allowed to avoid a lunch break if, due to the nature of the production process, it is impossible without damage (but in this case, the opportunity to eat and rest during working hours must be provided).
The lunch break is the only one that is not included in working hours.
Breaks during a 12 hour shift
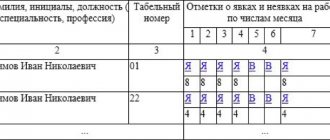
Mikhail [e-mail hidden] Russia, Moscow #6[21783] March 22, 2013, 15:11 Galina, internal labor regulations (ILR) are one of the mandatory personnel documents, every enterprise is obliged to have one, and every employee is obliged to comply with them . They should reflect in detail the work and rest schedule.
You, or even better, your personnel officer, need to draw them up, approve them with the director and put them into effect. I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message, because: A notification is being sent... ARBEIT MACHT FREI #7[21784] March 22, 2013, 15:50 Mikhail wrote: Kanga on the neck wrote: As an option, an additional agreement to the employment contract where the break will be prescribed.
...and you make at least one enemy in the person of the personnel officer. It is enough to make changes to the PVTR.
How many breaks and when should there be during a 12 hour shift?
With the permission of the employer, the time not used for lunch can be used to cover during the day.
- Unfortunately, the duration and number of breaks for rest and eating are not determined in any way by the current Labor Code. Only the minimum (30 minutes) and maximum (2 hours) duration of the break, which is not included in working hours, is precisely named. As Art. 108 the duration of rest and breaks quot; are established by internal labor regulations or by agreement between the employee and the employerquot;. I myself work 12 hours a day, but we still haven’t agreed on this issue.
Kanga on the neck wrote: If it is a shift schedule (2/2 for example), 1 hour is enough for rest. But if you are on a non-shift schedule, and in what cases is one hour not enough? per year no more than 1970 hours with a standard 40-hour week.
From 8 a.m. to 9 p.m., that’s 13 hours at work, minus 1 hour for lunch—12 hours a day according to the report card. Next, simple arithmetic - the rotation method - 2 weeks work, 2 rest. There is 46 hours of overtime per year, this fits into the approved norm, which means we leave a break of 1 hour.
If they worked a month later, they would have to be adjusted.
I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because: A notification is being sent... Mikhail [e-mail hidden] Russia, Moscow #8[21785] March 22, 2013, 07:17 pm Kanga on the neck wrote: in a year no more 1970 hours based on a standard 40 hour week.
Breaks during the working day
What if the shift lasts 24 hours? Why is this question not raised and kept silent? It is not profitable for workers to lift it, since this time is not paid. So everyone is quot; satisfiedquot; one break lasting one hour somewhere in the middle of the shift (you can find out more precisely in the internal rules of your organization) regardless of the length of the shift.
And a couple of breaks to drink tea can be done at the employer’s expense, that’s what they usually do. How many breaks and when should there be during a 12 hour shift? Attention Rest time between shifts according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation during a shift work schedule: how the schedule is drawn up. The work schedule and rest time between shifts during shift work are established taking into account the provisions of Art.
Break during a 12-hour shift
Important So everyone is “satisfied” with one break lasting one hour somewhere in the middle of the shift (you can find out more precisely in the internal rules of your organization) regardless of the duration of the shift.
And a couple of breaks to drink tea can be done at the employer’s expense, that’s what they usually do. the system selected this answer as the best Attention Before maternity leave, I worked 12 hours a day, from 9 am to 9 pm. We had two breaks from 13.
00 to 13.30 and from 18.00 to 18.30.
It turns out that in a 12-hour working day we had two half-hour breaks and twice a working day the bosses let us go for 10 minutes to get some fresh air. Of course, we were happy with such breaks, we were interested in the hours worked, we were paid hourly, piecework.
Vote:
How many mandatory breaks should there be? How many minutes and when (for a 12-hour working day)? tags: employment contract, labor code category: work and career Your work shift is 12 hours. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 108. Breaks for rest and food), during a work shift the employee is given a break for rest and food, which is not included in working hours.
What’s interesting is that the article is called “Breaks” and it talks about one break. In my opinion, this is a flaw in the Labor Code, which for some reason did not interest anyone.
What if the shift lasts 24 hours? Why is this question not raised and kept silent? It is not profitable for workers to lift it, since this time is not paid.
Break between shifts for a 12 hour shift
The new owner should not forget that motivation for work and work schedule are interconnected in a certain way.12 the work schedule implies a schedule like from 8 to 20, or from 9 to 21. You have from 8 to 21! With an 8-hour working day - 8 hours of work and an hour break for lunch.
Actual time at work is 9 hours. Work from 9 to 18. (actually 9 hours, of which 8 are working hours).
Accordingly, with your schedule from 8 to 21 and what is called a 12-hour working day, taking into account that there are two 1-hour breaks for lunch/dinner and in fact the employee works 11 hours.
Then my proportion would be as follows: 8 chrd = 1 hour and 11 chrd = Xchpo, where chrd is X hour working day, and chpo is an hour break for lunch and rest. 8X=11, X = 1.375 hours = 82.5 minutes.
Do I have the right to a lunch break and smoking breaks during work? 12 hour day
Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Breaks for rest and food” prescribes a working break of no more than 2 hours, but not less than half an hour. Accordingly, your break, if you are registered under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, can last from 30 to 120 minutes.
Exactly what time in this period is regulated directly by the enterprise in which you work. Chapter eighteen of Article 108 of the Labor Code defines breaks from thirty minutes to two hours for a working day or shift.
This article does not indicate how to allocate work time and breaks. The schedule, as a rule, is determined by the enterprise itself, and employees sign it as a sign of familiarization and agreement. The article goes like this: Therefore, with a twelve-hour shift, it is quite possible to have one or two breaks lasting from half an hour to two hours.
Labor Code breaks during a 12-hour working day
Only the minimum (30 minutes) and maximum (2 hours) duration of the break, which is not included in working hours, is precisely named. As Art. 108, the duration of rest and breaks “are established by internal labor regulations or by agreement between the employee and the employer.”
I myself work 12 hours a day, but we still haven’t agreed on this issue. You can see the comments here, here and here. As far as I know from the standards I have encountered, for every hour of working time there are five minutes of rest.
More precisely, you work for 55 minutes and rest for 5. Or you work for an hour and fifty, resting for 10 minutes. Plus one hour lunch. That is, 11 working hours.
Article 108 of the Labor Code regulates breaks for an employee during the working day.
Paid breaks during working hours
The duration of regulated breaks for workers of OJSC Bread Factory No. engaged in maintenance and adjustment of equipment, machines and mechanisms, using the example of a repairman: 1.
Characteristics of work: maintenance, adjustment, current and overhaul of equipment, machines and mechanisms; production of non-standard equipment; installation, testing, adjustment and delivery of repaired equipment.
The specified work is carried out directly in the workshop (up to 50% of operational time) and in a specialized room (repair shop).2. Rest time allocated for: 2.1. physical activity (weight of parts and tools – 6-10 kg, load per shift – 6000 – 15000 kgm) – 4 min.
(hereinafter – for an 8-hour shift);2.2.
Usually, the veracity of the statement about the actual presence of the second option can be verified by answering the question of how the dispatcher goes to the toilet.
Ideally, probably, the control panel should be on duty in a shift of not one, but two dispatchers (or three dispatchers for two control panels, etc.
), so that the second one replaces the first one during any breaks (both regulated and not), and the work function should be expanded (not only directly sitting at the console, but also something else, so that it doesn’t turn out that one of them spends more than half of the shift idle).
Something like this. PS I don’t have the slightest idea what ADS is, and what kind of remote control you mean. If there is some specificity that I did not take into account, then don’t blame me.
Source: https://yurburo61.ru/pereryvy-pri-12-chasovoj-smene/
Personal needs
During working hours, an employee may have needs to satisfy personal needs:
- going to the toilet;
- taking medications prescribed by a doctor;
- performing hygiene procedures;
- smoking (for smoking employees), etc.
Labor legislation does not regulate this area directly, but one of the basic principles of labor law in accordance with Art. 2 of the Labor Code is the obligation to provide fair working conditions, which presupposes:
- safe working conditions;
- compliance with occupational hygiene and workers;
- workers' rest.
Consequently, a break from work to satisfy natural personal needs is an inalienable right of an employee, based on the basic principles of labor law. The situation is different with smoking breaks during working hours according to the Labor Code: they are not mandatory, which means they are given only at the personal discretion of the organization’s management.
The intervals of such pauses are difficult to regulate (with the exception of smoking breaks), but they must be specified in the labor regulations or the employee’s employment contract.
Kinds
Every employer knows that he is obliged to provide his employees with a certain number of breaks during the working day. When it comes to a break, a working person immediately thinks of lunch or free time for smoking breaks. But according to the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, there are much more of them.
They are conventionally divided into several groups:
- are common;
- special;
- mandatory;
- recommended;
- paid;
- unpaid.
This classification makes it possible to determine which rest periods can be used by all workers, and which only by representatives of a narrow range of professions.
Common ones include lunch breaks and other types of stopping work for personal needs. Special breaks are used in various industries where employees require additional free time, as well as for certain categories of employees (employees with small children, etc.). If we talk about mandatory and recommended breaks, the former are the responsibility of management, and the latter are provided as necessary and on the basis of internal local regulations. Most periods of rest during the day must be paid, but there are some that are not.
All information about breaks, including their duration, is determined by a large number of documents. These are collective and labor agreements, as well as relevant internal regulations.
Technical
The Labor Code does not contain the concept of a technological break, however, some norms containing the term itself (for example, paragraph 1 of Article 109, Article 351 of the Labor Code) allow us to conclude that it is associated with the characteristics of production activities. They are established by internal regulations. A technical break lasts no more than 15 minutes and is necessary to restore operability or maintain production facilities.
A technical break also includes a break when working at a computer. They are not directly regulated by the Labor Code, but according to the Standard Instructions for Labor Safety when working on a personal computer TOI R-45-084-01, approved by Order of the Ministry of Communications dated July 2, 2001 No. 162, regulated breaks when working on computers must be taken every two hours. This rule is established in clause 3.2, which continues to apply to the present day.
Types of technological breaks
Technological breaks are divided into types depending on what needs they are caused by.
Working at the computer
Technological breaks are regulated in relation to work related to the use of a computer. The organization of work related to PC is established on the basis of SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03, approved on May 30, 2003. The duration of the break, according to Appendix 7 of SanPiN, is 50-140 minutes. The exact duration is determined by the type of activity of the employee and the degree of his workload. Let's take a closer look at the rules:
- Activities with a load level per shift of up to 20,000 characters. Time: 2 hours from the start of the shift and 2 hours after the lunch break. The duration of stops is 15 minutes.
- Load up to 40,000 characters – 2 hours after the start of the working day and 1.5-2 hours after the lunch break. There are 2 stops of 15 minutes or breaks of 10 minutes every hour of activity.
- Load up to 60,000 characters – 1.5-2 hours from the start of the working day and 1.5-2 hours after the lunch break. The duration of stops is 20 minutes. An alternative option is 15-minute stops every hour of operation.
Detailed instructions on organizing recreation are given in the TOI Standard Instruction R-45-084-01, approved on February 2, 2001. These instructions indicate that continuous work at the computer can be no more than 2 hours.
The purpose of the break is to preserve the employee’s health. Rest helps prevent eye strain and fatigue.
12 hour workday
There are Methodological Recommendations MR 2.2.9.2311-07.2.2.9, approved by the Chief Sanitary Doctor on December 18, 2007. A 12-hour shift requires the following periods for employees to rest:
- 2 lunch breaks.
- 4 additional breaks of 10 minutes each.
- Break for a short nap lasting 45-60 minutes.
The last break is given after the first lunch break. It should be noted that this list of rest periods is a recommendation. That is, the employer has the right not to implement this entire list. The Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 181n dated March 1, 2012 does not contain the list in question.
The agreed list of breaks is needed to prevent employee stress, tension and overwork. Short-term periods allow the employee to recover, which leads to increased work efficiency. In addition, they are needed to improve working conditions for workers and ensure their health.
Working in low temperature conditions
Breaks are provided to employees who work under these conditions:
- Cold season and outdoor work.
- Work in closed, unheated spaces.
In this case, rest time is needed for heating. Lack of a break can lead to frostbite and decreased quality of work.
Hard work
Breaks are provided to loaders engaged in loading and unloading operations. This is due to the fact that these employees work with heavy weight. Continuous work can lead to fatigue and injury.
Feeding the baby
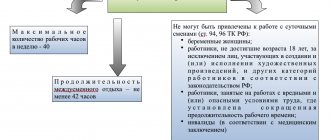
In addition to lunch time, a woman, upon her written application, must be given breaks from work to feed a child under the age of one and a half years, according to the following rules:
- at least 2 times during an 8-hour working day (i.e. at least every 3 hours);
- Duration for feeding 1 child - from half an hour, 2 or more - from 1 hour;
- can be added to lunch or moved to the beginning or end of the day in order to shorten it;
- included during working hours;
- payable (based on the average salary).
This right (additional guarantee) is established by Art. 258 TK.
Unpaid
Not all employees know whether lunch breaks are included in their pay. Oddly enough, a break for rest and food during the working day is not subject to mandatory payment. The employee can spend this time at his own discretion. That is, not only to have lunch or rest, but also to leave work for personal needs.
But there are also exceptions. For example, teachers do not stop working, leaving for personal matters during their vacation. Their lunch time coincides with the students’ lunch, as does its duration. Therefore, they have a paid break for rest and food.
Special
Clause 2 art. 109 provides for the obligation of the employer to provide its employees with time for heating and special premises if the place where they perform their work functions is in the fresh air or in cold rooms that do not have heating. Such special intervals in work have a duration and frequency established by local regulations, and are paid (included in working hours).
Also, internal rules may establish other work, during which special rest time is provided in accordance with the Labor Code. These may include gaps in work after the driver has been behind the wheel for a 12-hour working day and the flight duration is more than 12 hours.
Paragraph 2 clause 10 of the Regulations on the peculiarities of working time and rest time for car drivers, approved by Order of the Ministry of Transport No. 15 of August 20, 2004, obliges in this case to provide the opportunity for rest, including a place equipped for this.
The employer is obliged to comply with all work breaks provided for by legal acts on labor, and the employee has every right to use the time for rest and recuperation. For certain categories of employees and in other cases, at the discretion of the employer, additional labor protection guarantees may be established (including rest periods during the working day).
Types of breaks at work
Legislative acts provide for several types of possible break intervals at work. They depend on the specifics, severity of the work performed, as well as the conditions in which the workers find themselves, when such periods are considered working and must be paid.
Breaks are divided into the following categories:
- lunch and rest;
- rest and recuperation in bad weather conditions;
- time to be able to feed the baby;
- special types.
Break for warmth and rest
It is given to those employees whose working conditions involve heavy physical labor, as well as in adverse weather conditions. Such employees should be given a special work schedule and be provided with adequate space where workers can regain their strength and warm up. It is necessary to take into account that such break time must be counted as working time, entered into the time sheet, and subject to payment.
Workers who are entitled to rest for heating and food include:
- those performing labor functions in the cold or in buildings where there is no heating (builders, janitors);
- loaders with heavy physical exertion, etc.
Baby feeding break
For employees who decide to start working before the child is 1 year and 6 months old, the manager must allocate additional time so that she has the opportunity to feed the baby. The same opportunity should be given to single fathers or guardians.
Many employers are not very willing to agree to such breaks; the majority of them first try to find some reasons for refusal and not allocate another break; they ask questions about feeding, whether the child is fed breast milk or artificial formula.
If a woman for some reason cannot breastfeed her child and gives him artificial formula, on this basis the employer sometimes tries to refuse to allocate additional rest time; this is regarded as a direct violation of the labor legislation of the Russian Federation on the part of the employer.
The time to be able to feed the baby should be as follows:
- the family is raising a single newborn under the age of 1 year and 6 months, the opportunity to feed the child should be within 30 minutes after every three hours of labor;
- If there are two children or more under the age of 1.5 years in a family, then the opportunity to feed takes from one hour.
Such a break must be included in the time sheet and paid according to average earnings.
At the request of the worker, she can submit an application with clarifying points regarding the breaks provided:
- ask to combine an extra break and your lunch time;
- combine and assign breaks with the opportunity to feed the child to the beginning or end of the working day, shortening it.
To properly secure such a break, the employee must submit to the HR department:
- statement;
- a copy of the child's certificate.
An order must be issued for the employee to allocate time for the opportunity to feed the child, taking into account all additional nuances at the request of the employee.
Special breaks
Personal breaks
Breaks to go to the toilet, smoke, chat with a colleague over a cup of coffee or tea are not established by the legislator, but in all kinds of methodological recommendations, in order to reduce the level of employee fatigue and increase productivity, it is necessary to give such breaks for 10–20 minutes. Such rest time can be reflected in the company’s internal regulations. Some companies go further and equip a special room in the office space where their employees will fully rest and replenish their strength.
Technical break
Necessary for workers working with all kinds of equipment. These can be either workers who perform duties at the computer for a long time, or employees who work in production, and most of the time they are behind the conveyor belt. The employer must allow a break of 10–15 minutes, and the total rest time per day should be 50–90 minutes.
A technical break is also necessary:
- air traffic controller, he must interrupt his activities for 20 minutes. after two hours of labor;
- for a driver on intercity flights, he must stop for 15 minutes en route. 3 hours from the starting point and after two hours on the road;
- workers involved in the production of alcohol, juice, yeast;
- workers working with fire-resistant coatings are given the opportunity to rest for a period of ten minutes every working hour;
- whose work involves transporting goods on railway tracks and using respiratory protection equipment, rest must be at least 15 minutes at a remote distance from a place where it is possible to remove the protective equipment;
- employees of postal offices and cadastral chambers who receive citizens and provide consultations.
The above list is not exhaustive; the manager has the right to establish by internal act other positions that provide for a mandatory break to maintain health, efficiency and uninterrupted performance of work functions.
Whether such rest time will be counted as working time and whether it will be paid is up to management to decide.
Changing the duration of the lunch break
The duration of the lunch break varies within acceptable limits:
- For all employees (management initiative): an order is issued to change the PVTR, familiarization is carried out 2 months before the changes enter into force (Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If necessary, the terms of employment contracts are adjusted.
- On an individual basis: the employee’s application is accepted, an administrative document is issued, and an additional agreement is concluded.
According to a similar scheme, the employer has the right to set a variable lunch time. Let's talk about it in more detail in a separate article.
Breaks when working in cold or hot conditions
The working day is shortened.
A break when working in heat or cold is, in some way, a technical break. But at the same time, they are provided for heating or rest of employees working in unfavorable working conditions.
First of all, workers who work in the open air have the right to such a break - janitors, construction workers, workers repairing and marking roads, plowmen and other workers in the agricultural industry.
Depending on working conditions and weather conditions, the duration of the break can range from 10 minutes to one hour. At the same time, reducing the duration of rest or heating below the minimum limit is unacceptable.
Additionally, when working in the cold season, employees are entitled to a hot meal, and at least 10 minutes must pass between taking it and going outside.
Separately, it should be said that the place for rest and heating must be equipped in the manner established by law, in particular, the temperature in the room must be at least 21 degrees, and the room must be closed - not blown by the wind and contain a roof in its structure, if we are talking about the summer version.
Separately, it should be noted that in extreme heat (above 30 degrees), as well as in severe frost, if the temperature in the office premises does not exceed 15 degrees, the working day is reduced to 5 hours, and when performing heavy physical work - to two and a half.
In addition, employees are given an additional break from work every one and a half to two hours for 10-15 minutes. The specified break time is usually included in working hours.
This recommendation is not mandatory, but when used in practice it gives fairly good results and significantly increases the performance of employees.
If the working day is part-time
Part-time work, if it lasts 4 hours or more, entitles you to lunch of the same duration as other employees. When asked whether lunch is included in working hours, the answer is the same - it is not included. Its duration may differ from lunch time for other employees, but remain within the Labor Code - from 30 minutes. up to 2 hours. Lunch can also be postponed. Employees who work less than 4 hours are not entitled to rest for meals, but may take meals when work permits.
Several servings
Legal status of lunch breaks
The lunch period does not count towards working time and, as a result, is not paid.
The need to introduce a lunch break on a daily basis is established by Art. 100 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Its provisions regulate the distribution of working hours and rest periods. At the same time, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates the total duration of the working week, acceptable norms for the duration of shifts and options for ensuring personnel rest.
The procedure for providing a lunch break under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is regulated by several articles:
| Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Content |
| Art. 107 | Lunch time is attributed to the period of release of officials from performing labor functions |
| Art. 108 | Time allocated for meals is allocated from the work schedule. Therefore, the answer to the question of whether lunch is included in working hours is always negative. |
Lunch time is a period of short rest. At these moments, the employer cannot force the employee to engage in his main work activity. The application of sanctions by management to an employee for behavior contrary to labor regulations and corporate ethics is possible only during working hours.
The distinction between periods of work and non-work plays a role in determining the duration of absence from work. As a general rule, an employee can be fired for leaving the workplace for more than 4 hours. But if this period includes lunch time, and the actual absence is less than 4 working hours, termination of the employment contract is unlawful (JSC Sverdlovsk Regional Court dated March 13, 2018 No. 33-4752/2018).
The position of legislators on the issue of whether a lunch break is included in working hours is clear:
- absence from the workplace during the hours allocated for meals cannot be regarded as absenteeism;
- Officials cannot be held accountable if they refuse to resolve production issues during lunch time.
The only exception, when lunch is included in working hours, is made in relation to persons whose specific work requires their constant presence at the workplace throughout the entire shift.
In this case, the employer is obliged to provide the employee with the opportunity to eat food on the territory of the enterprise. Lunch will be carried out without actual interruption from work functions, so it is counted towards the total duration of the working day. In the PVTR, the employer has the right to provide for types of work that cannot be interrupted.